这里写自定义目录标题
- P3838_线性表_线性表概述
- P3939_线性表_顺序表_基本实现
- P4040_线性表_顺序表_测试
- P4141_线性表_顺序表_遍历
- P4242_线性表_顺序表_容量可变
- P4343_线性表_顺序表_时间复杂度
- P4444_线性表_顺序表_ArrayList源码
- P4545_线性表_链表_概述
- P4646_线性表_链表_单向链表1
- P4747_线性表_链表_单向链表2
- P4848_线性表_链表_单向链表3
- P4949_线性表_链表_双向链表1
- P5454_线性表_链表_双向链表_LinkeList源码
- P5555_线性表_链表_时间复杂度分析
- P5656_线性表_链表_单链表反转1
- P5757_线性表_链表_单链表反转2
- P5858_线性表_链表_快慢指针_中间值问题
- P5959_线性表_链表_快慢指针_单链表是否有环问题
- P6060_线性表_链表_快慢指针_有环链表入口问题
- P6161_线性表_链表_循环链表
- P6262_线性表_链表_约瑟夫问题1
P3838_线性表_线性表概述



P3939_线性表_顺序表_基本实现

P4040_线性表_顺序表_测试
P4141_线性表_顺序表_遍历


P4242_线性表_顺序表_容量可变

package linear;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class SequenceList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
//存储元素的数组
private T[] eles;
//记录当前顺序表中的元素个数
private int N;
//构造方法
public SequenceList(int capacity){
//初始化数组
this.eles=(T[])new Object[capacity];//强制类型转换
//初始化长度
this.N=0;
}
//将一个线性表置为空表
public void clear(){
this.N=0;
}
//判断当前线性表是否为空表
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N==0;//判断元素个数是否为零
}
//获取线性表的长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//获取指定位置的元素
public T get(int i){
return eles[i];
}
//向线型表中添加元素t
public void insert(T t){
if (N==eles.length){
resize(2*eles.length);
}
eles[N++]=t;
}
//在i元素处插入元素t
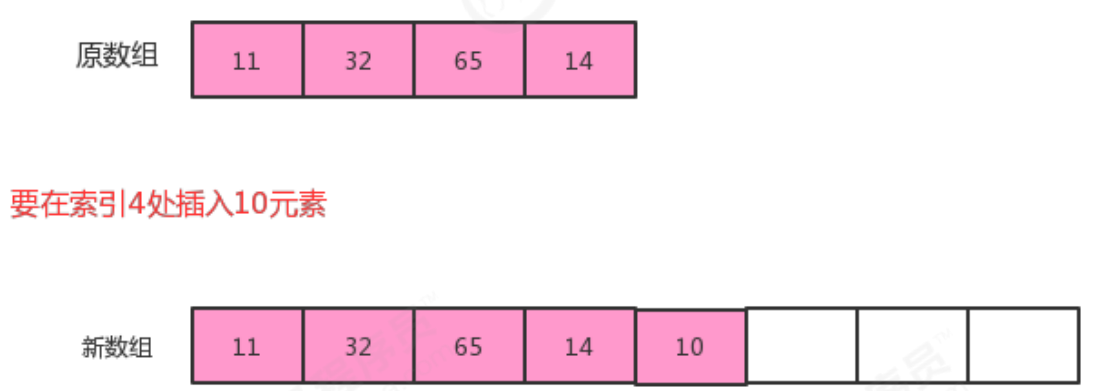
public void insert(int i,T t){
if (N==eles.length){
resize(2*eles.length);
}
//先把i索引处的元素及其后面的元素依次向后移动一位
for(int index=N;index>i;index--){
//为什么index=N,因为往后面移动,最后一个元素的索引是N-1,它也要往后移动,移动到N上。
eles[index]=eles[index-1];
}
//再把t元素放到i索引处即可
eles[i]=t;
//元素个数+1
N++;
}
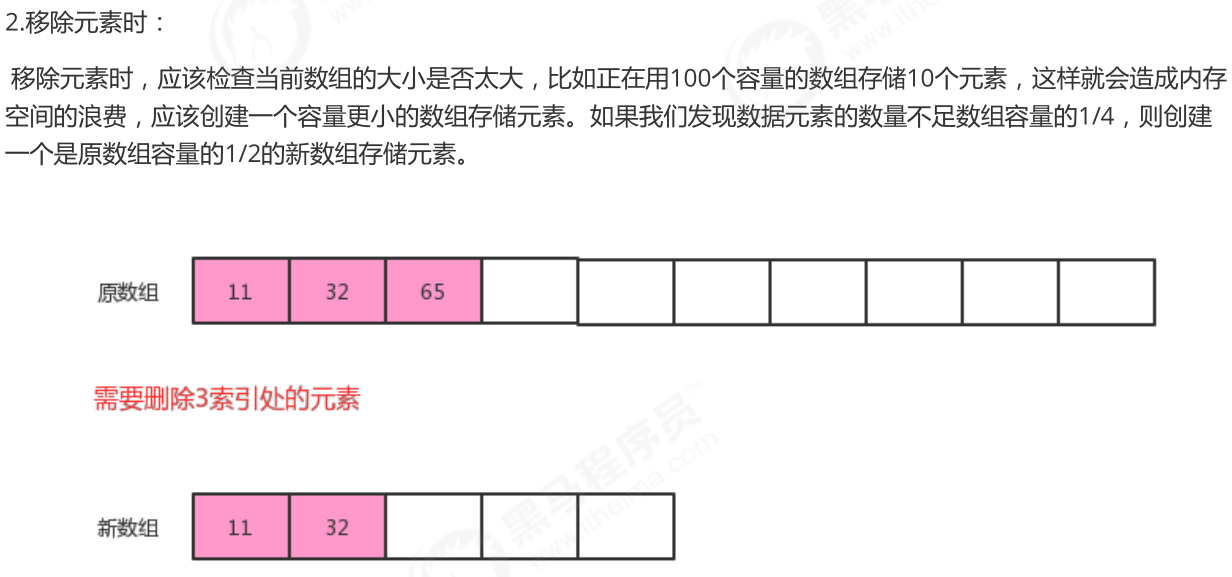
//删除指定位置i处的元素,并返回该元素
public T remove(int i){
//记录索引i处的值
T current = eles[i];
//索引i后面元素依次向前移动一位即可
for(int index=i;index<N-1;index++){
eles[index]=eles[index+1];
}
//元素个数-1
N--;
if (N<eles.length/4){
resize(eles.length/2);
}
return current;
}
//查找t元素第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
if (eles[i].equals(t)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;//没有找到,返回-1,习惯而已,没有原因
}
//根据参数newSize,重置eles的大小
public void resize(int newSize){
//定义一个临时数组,指向原数组
T[] temp=eles;
//创建新数组
eles=(T[])new Object[newSize];
//把原数组的数据拷贝到新数组即可
for(int i=0;i<N;i++){
eles[i]=temp[i];
}
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new SIterator();//想要直接new,发现是接口,无法直接new。所以去写一个内部类,去实现这个接口
}
//内部类
private class SIterator implements Iterator{
private int cusor;//指针
public SIterator(){
this.cusor=0;//初始化为0,因为需要从第一个开始遍历
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return cusor<N;//或者<=N-1,都是一个意思
}
@Override
public Object next() {
return eles[cusor++];//获取了[cusor]后,++,下移一位
}
}
}
package test;
import linear.SequenceList;
public class SequenceListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建顺序表对象
SequenceList<String> sl = new SequenceList<>(10);
//测试插入
sl.insert("姚明");
sl.insert("科比");
sl.insert("麦迪");
sl.insert(1,"詹姆斯");
//为什么要搞iterator?
//因为以前是集合,可以直接用,现在不是。
for (String s : sl) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
//测试获取
String getResult = sl.get(1);
System.out.println("获取索引1处的结果为:"+getResult);
//测试删除
String removeResult = sl.remove(0);
System.out.println("删除的元素是:"+removeResult);
//测试清空
sl.clear();
System.out.println("清空后的线性表中的元素个数为:"+sl.length());
}
}
import cn.itcast.algorithm.linear.SequenceList;
public class SequenceListTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SequenceList<String> sl = new SequenceList<>(3);
sl.insert("张三");
sl.insert("李四");
sl.insert("王五");
sl.insert("赵六");
}
}
P4343_线性表_顺序表_时间复杂度

P4444_线性表_顺序表_ArrayList源码

123、是
有了ArrayList为什么还要自己写顺序表?
ArrayList通用性好,特殊写法可能不合适。
ArrayList臃肿1500行代码,运行慢,自己写快。
P4545_线性表_链表_概述



P4646_线性表_链表_单向链表1

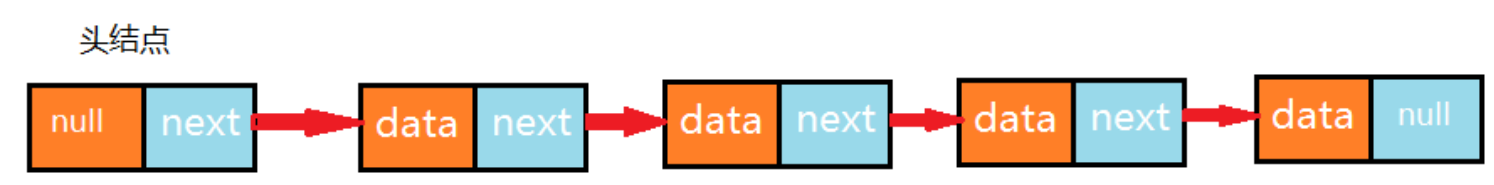

P4747_线性表_链表_单向链表2
P4848_线性表_链表_单向链表3
package linear;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class LinkList<T> implements Iterable{
//记录头结点
private Node head;
//记录链表的长度
private int N;
//结点类
private class Node{
//存储数据
T item;
//下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item,Node next){
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
public LinkList() {
//初始化头结点
this.head = new Node(null,null);
//初始化元素个数
this.N=0;
}
//清空链表
public void clear(){
//只要让头结点找不到,这个链表也就相当于清空了。
head.next = null;
head.item = null;
this.N=0;
}
//获取链表的长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty() {
return N==0;
}
//获取指定位置i处的元素
//比如1处的值,n = n.next;
public T get(int i) {
//通过循环,从头结点开始往后找,依次找i次,就可以找到对应的元素
Node n = head.next;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++){
n=n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
//向链表的末尾添加元素t
public void insert(T t){
//找到当前最后一个结点
Node n = head;
while(n.next!=null){//最后一个结点指针域为空
n=n.next;
}
//创建新结点,保存元素t
Node newNode = new Node(t,null);
//让当前最后一个结点指向新结点
n.next = newNode;
//元素的个数+1
N++;
}
//向指定位置i出,添加元素t
public void insert (int i,T t){
//找到i位置的前一个结点
Node pre = head;
for (int index=0;index<=i-1;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//创建新结点,并且新结点需要指向原来i位置的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, curr);
//原来i位置的前一个节点指向新结点即可
pre.next=newNode;
//元素的个数+1
N++;
}
public T remove(int i) {
//找到i位置的前一个节点
Node pre = head;
for(int index=0;index<=i-1;i++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//要找到i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//找到i位置的下一个结点
Node nextNode = curr.next;
//前一个结点指向下一个结点
pre.next=nextNode;
//元素个数-1
N--;
return curr.item;
}
//查找元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t) {
//从头结点开始,依次找到每一个结点,取出item,和t比较,如果相同,就找到了
Node n = head;
for(int i=0;n.next!=null;i++){//n.next!=null说明有下一个元素。
n=n.next;
if (n.item.equals(t)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {//Iterator是接口
return new LIterator();//返回:new一个实现类
}
// 为什么要搞这个?
// 我们以前用增强for循环,循环的集合已经写好了这些东西
// 现在我们自己写一个链表类,需要些循环,就需要重写这个东西
//创建一个内部类,外部类里面定义一个类,就是内部类
private class LIterator implements Iterator{
private Node n;
public LIterator(){
this.n=head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
// 为null说明,是最后一个结点
// 不为null,说明需要继续遍历
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n = n.next;//this.n=head;,头结点没有数据,我们往后走一位
return n.item;
}
}
}
package test;
import linear.LinkList;
import linear.SequenceList;
public class LinkListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建单向链表对象
LinkList<String> sl = new LinkList<>();
//测试插入
sl.insert("姚明");
sl.insert("科比");
sl.insert("麦迪");
sl.insert(1,"詹姆斯");
//为什么要搞iterator?
//因为以前是集合,可以直接用,现在不是。
for (Object o : sl) {
System.out.println(o);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
//测试获取
String getResult = sl.get(1);
System.out.println("获取索引1处的结果为:"+getResult);
//测试删除
String removeResult = sl.remove(0);
System.out.println("删除的元素是:"+removeResult);
//测试清空
sl.clear();
System.out.println("清空后的线性表中的元素个数为:"+sl.length());
}
}
/*
姚明
詹姆斯
科比
麦迪
------------------------------------------
获取索引1处的结果为:詹姆斯
删除的元素是:姚明
清空后的线性表中的元素个数为:0
*/
P4949_线性表_链表_双向链表1
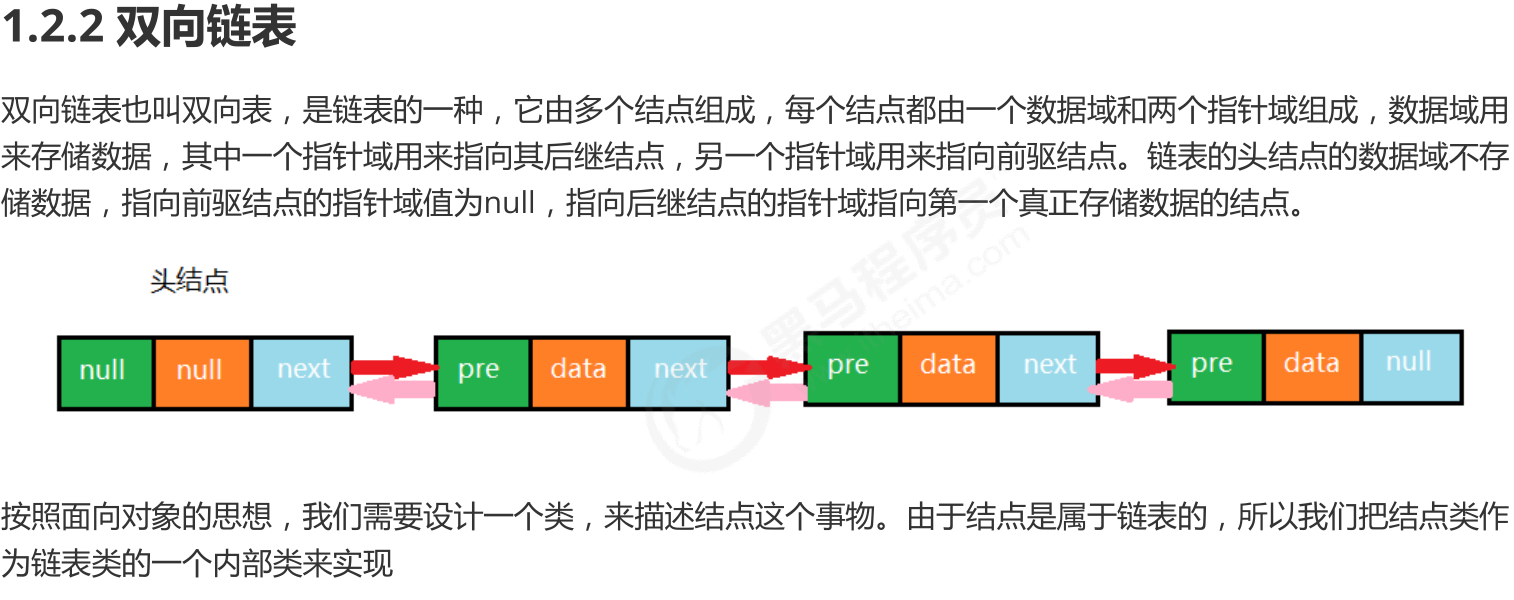

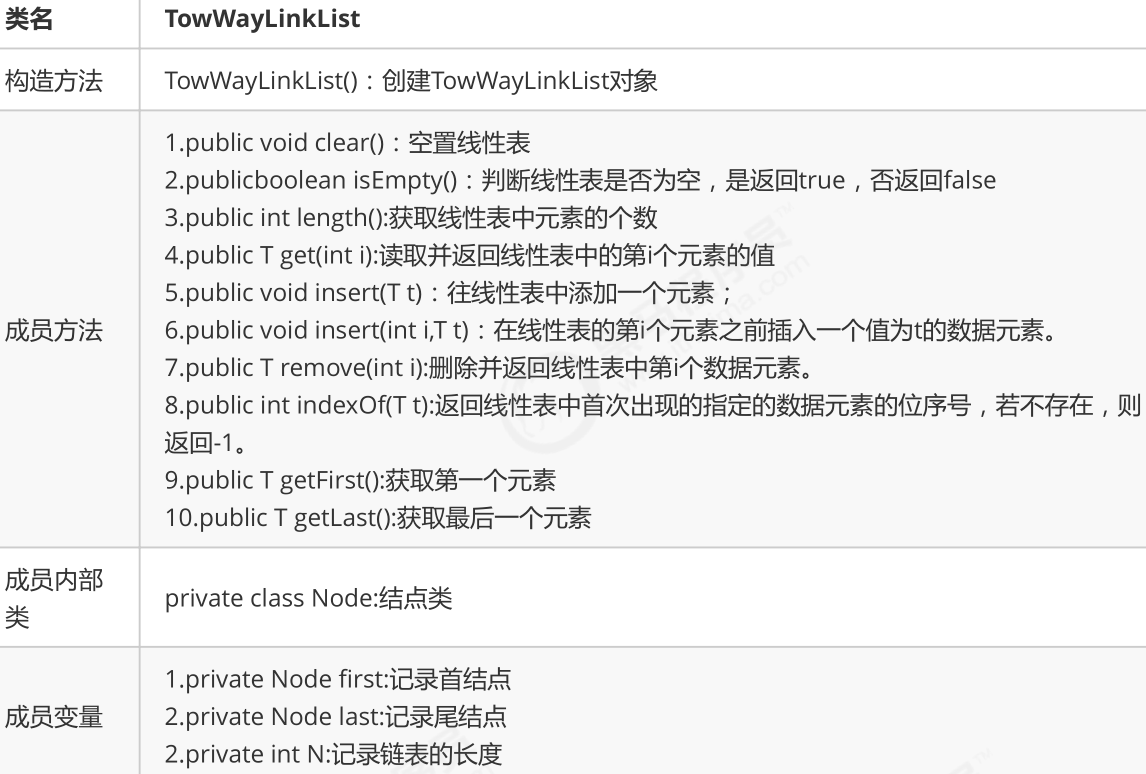
package linear;
import org.w3c.dom.Node;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class TowWayLinkList<T> implements Iterable<T>{
//首结点
private Node head;
//最后一个结点
private Node last;
//链表的长度
private int N;
//结点类
private class Node{
public Node(T item, Node pre, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.pre = pre;
this.next = next;
}
//存储数据
public T item;
//指向上一个结点
public Node pre;
//指向下一个结点
public Node next;
}
public TowWayLinkList(){
//初始化头结点和尾结点
this.head = new Node(null,null,null);
this.last=null;
//初始化元素个数
this.N=0;
}
//清空链表
public void clear(){
this.head.next=null;
this.head.pre=null;
this.head.item=null;
this.last=null;
this.N=0;
}
//获取链表长度
public int length(){
return N;
}
//判断链表是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return N==0;
}
//获取第一个元素
public T getFirst(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return head.next.item;
}
//获取最后一个元素
public T getLast(){
if (isEmpty()){
return null;
}
return last.item;
}
//插入元素t
public void insert(T t){
if (isEmpty()){
//如果链表为空:
//创建新的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t,head, null);
//让新结点称为尾结点
last=newNode;
//让头结点指向尾结点
head.next=last;
}else {
//如果链表不为空
Node oldLast = last;
//创建新的结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, oldLast, null);
//让当前的尾结点指向新结点
oldLast.next=newNode;
//让新结点称为尾结点
last = newNode;
}
//元素个数+1
N++;
}
//向指定位置i处插入元素t
public void insert(int i,T t){
//找到i位置的前一个结点
Node pre = head;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++){//index<i = index<=i-1
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//创建新结点
Node newNode = new Node(t, pre, curr);
//让i位置的前一个结点的下一个结点变为新结点
pre.next=newNode;
//让i位置的前一个结点变为新结点
curr.pre=newNode;
//元素个数+1
N++;
}
//获取指定位置i处的元素
public T get(int i){
Node n = head.next;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++){
n=n.next;
}
return n.item;
}
//找到元素t在链表中第一次出现的位置
public int indexOf(T t){
Node n = head;
for(int i=0;n.next!=null;i++){
n=n.next;
if (n.item.equals(t)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
//删除位置i处的元素,并返回该元素
public T remove(int i){
//找到i位置的前一个结点
Node pre = head;
for(int index=0;index<i;index++){
pre=pre.next;
}
//找到i位置的结点
Node curr = pre.next;
//找到i位置的下一个结点
Node nextNode= curr.next;
//让i位置的前一个结点的下一个结点变为i位置的下一个结点
pre.next=nextNode;
//让i位置的下一个结点的上一个结点变为i位置的前一个结点
nextNode.pre=pre;
//元素的个数-1
N--;
return curr.item;
}
@Override
public Iterator<T> iterator() {
return new TIterator();
}
private class TIterator implements Iterator{
private TowWayLinkList.Node n;
public TIterator(){
this.n=head;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return n.next!=null;
}
@Override
public Object next() {
n=n.next;
return n.item;
}
}
}
package test;
import linear.TowWayLinkList;
public class TowWayLinkListTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建双向链表对象
TowWayLinkList<String> sl = new TowWayLinkList<>();
//测试插入
sl.insert("姚明");
sl.insert("科比");
sl.insert("麦迪");
sl.insert(1,"詹姆斯");
//为什么要搞iterator?
//因为以前是集合,可以直接用,现在不是。
for (String s : sl) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
System.out.println("第一个元素是:"+sl.getFirst());
System.out.println("最后一个元素是:"+sl.getLast());
System.out.println("--------------------------------------");
//测试获取
String getResult = sl.get(1);
System.out.println("获取索引1处的结果为:"+getResult);
//测试删除
String removeResult = sl.remove(0);
System.out.println("删除的元素是:"+removeResult);
//测试清空
sl.clear();
System.out.println("清空后的线性表中的元素个数为:"+sl.length());
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
}
}
/*
姚明
詹姆斯
科比
麦迪
------------------------------------------
第一个元素是:姚明
最后一个元素是:麦迪
--------------------------------------
获取索引1处的结果为:詹姆斯
删除的元素是:姚明
清空后的线性表中的元素个数为:0
------------------------------------------
*/
P5454_线性表_链表_双向链表_LinkeList源码
P5555_线性表_链表_时间复杂度分析

1、对的
2、用三个域
顺序表有扩容,有可能是几何级别的增加。
链表没有扩容。
P5656_线性表_链表_单链表反转1

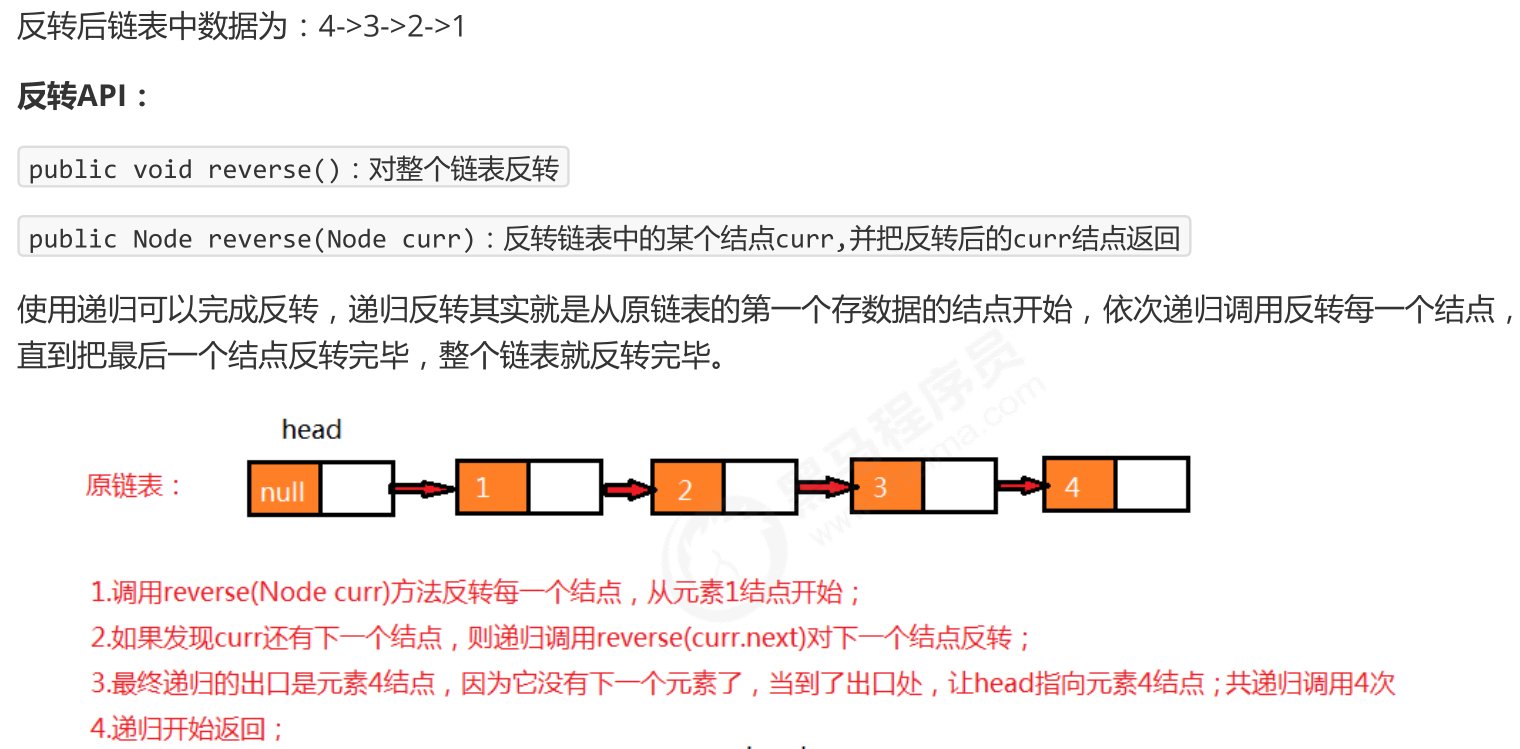
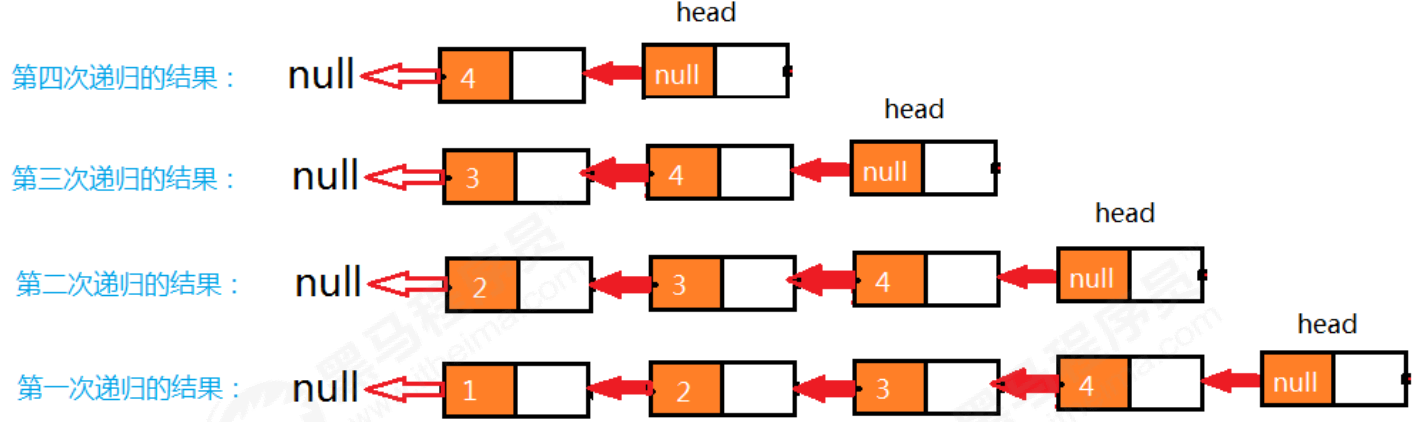
P5757_线性表_链表_单链表反转2
package ch05;
import ch04.Node;
/*
* 双端链表
*/
public class FirstLastLinkList {
//头结点
private Node first;
//尾结点
private Node last;
public FirstLastLinkList() {
first = null;
last = null;
}
/**
* 插入一个结点,在头结点后进行插入
*/
public void insertFirst(long value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
if(isEmpty()) {
last = node;
}
node.next = first;
first = node;
}
/**
* 插入一个结点,从尾结点进行插入
*/
public void insertLast(long value) {
Node node = new Node(value);
if(isEmpty()) {
first = node;
} else {
last.next = node;
}
last = node;
}
/**
* 删除一个结点,在头结点后进行删除
*/
public Node deleteFirst() {
Node tmp = first;
if(first.next == null) {
last = null;
}
first = tmp.next;
return tmp;
}
/**
* 显示方法
*/
public void display() {
Node current = first;
while(current != null) {
current.display();
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* 查找方法
*/
public Node find(long value) {
Node current = first;
while(current.data != value) {
if(current.next == null) {
return null;
}
current = current.next;
}
return current;
}
/**
* 删除方法,根据数据域来进行删除
*/
public Node delete(long value) {
Node current = first;
Node previous = first;
while(current.data != value) {
if(current.next == null) {
return null;
}
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
if(current == first) {
first = first.next;
} else {
previous.next = current.next;
}
return current;
}
/**
* 判断是否为空
*/
public boolean isEmpty() {
return (first == null);
}
}
package cn.itcast.algorithm.test;
import cn.itcast.algorithm.linear.LinkList;
public class LinkListTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建单向链表对象
LinkList<String> sl = new LinkList<>();
//测试插入
sl.insert("姚明");
sl.insert("科比");
sl.insert("麦迪");
sl.insert(1,"詹姆斯");
for (String s : sl) {
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("------------------------------------------");
sl.reverse();
for (String s : sl) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
}
P5858_线性表_链表_快慢指针_中间值问题

通过快慢指针,得到中间值。
package cn.itcast.algorithm.test;
public class FastSlowTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建结点
Node<String> first = new Node<String>("aa", null);
Node<String> second = new Node<String>("bb", null);
Node<String> third = new Node<String>("cc", null);
Node<String> fourth = new Node<String>("dd", null);
Node<String> fifth = new Node<String>("ee", null);
Node<String> six = new Node<String>("ff", null);
Node<String> seven = new Node<String>("gg", null);
//完成结点之间的指向
first.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
fourth.next = fifth;
fifth.next = six;
six.next = seven;
//查找中间值
String mid = getMid(first);
System.out.println("中间值为:"+mid);
}
/**
* @param first 链表的首结点
* @return 链表的中间结点的值
*/
public static String getMid(Node<String> first) {
//定义两个指针
Node<String> fast = first;
Node<String> slow = first;
//使用两个指针遍历链表,当快指针指向的结点没有下一个结点了,就可以结束了,结束之后,慢指针指向的结点就是中间值
while(fast!=null &&fast.next!=null){
//变化fast的值和slow的值
fast = fast.next.next;
slow=slow.next;
}
return slow.item;
}
//结点类
private static class Node<T> {
//存储数据
T item;
//下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
P5959_线性表_链表_快慢指针_单链表是否有环问题
通过快慢指针,看单链表是否有环。
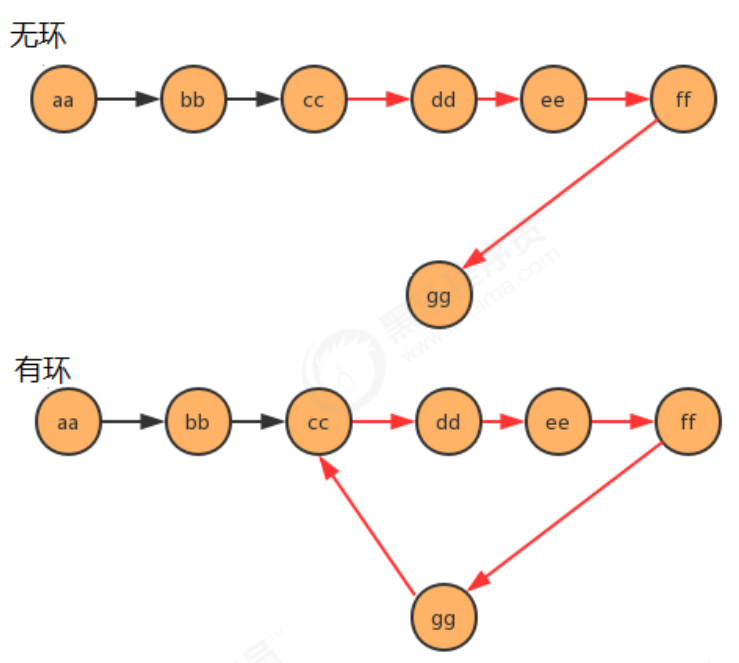
无环,快慢指针永远不可能相遇。
有环,快慢指针,有可能相遇。
package cn.itcast.algorithm.test;
public class CircleListCheckTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建结点
Node<String> first = new Node<String>("aa", null);
Node<String> second = new Node<String>("bb", null);
Node<String> third = new Node<String>("cc", null);
Node<String> fourth = new Node<String>("dd", null);
Node<String> fifth = new Node<String>("ee", null);
Node<String> six = new Node<String>("ff", null);
Node<String> seven = new Node<String>("gg", null);
//完成结点之间的指向
first.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
fourth.next = fifth;
fifth.next = six;
six.next = seven;
// //产生环
// seven.next = third;
//判断链表是否有环
boolean circle = isCircle(first);
System.out.println("first链表中是否有环:"+circle);
}
/**
* 判断链表中是否有环
* @param first 链表首结点
* @return ture为有环,false为无环
*/
public static boolean isCircle(Node<String> first) {
//定义快慢指针
Node<String> fast = first;
Node<String> slow = first;
//遍历链表,如果快慢指针指向了同一个结点,那么证明有环
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
//变换fast和slow
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
if (fast.equals(slow)){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
//结点类
private static class Node<T> {
//存储数据
T item;
//下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
P6060_线性表_链表_快慢指针_有环链表入口问题
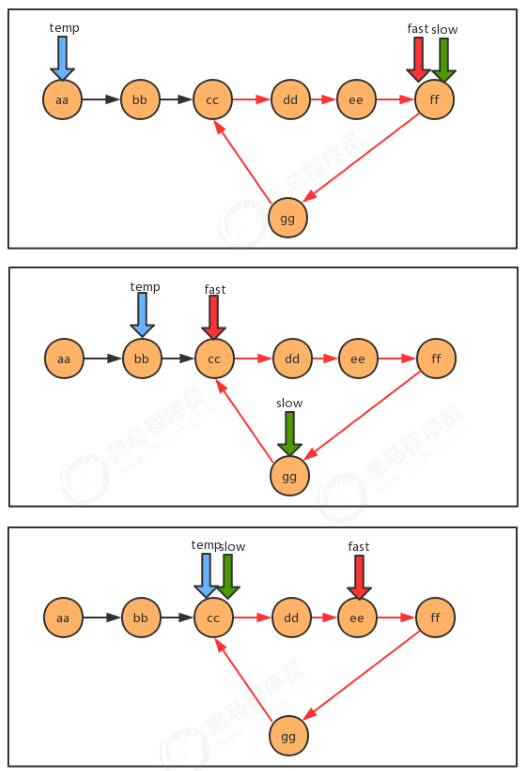
package cn.itcast.algorithm.test;
public class CircleListInTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Node<String> first = new Node<String>("aa", null);
Node<String> second = new Node<String>("bb", null);
Node<String> third = new Node<String>("cc", null);
Node<String> fourth = new Node<String>("dd", null);
Node<String> fifth = new Node<String>("ee", null);
Node<String> six = new Node<String>("ff", null);
Node<String> seven = new Node<String>("gg", null);
//完成结点之间的指向
first.next = second;
second.next = third;
third.next = fourth;
fourth.next = fifth;
fifth.next = six;
six.next = seven;
//产生环
seven.next = third;
//查找环的入口结点
Node<String> entrance = getEntrance(first);
System.out.println("first链表中环的入口结点元素为:"+entrance.item);
}
/**
* 查找有环链表中环的入口结点
* @param first 链表首结点
* @return 环的入口结点
*/
public static Node getEntrance(Node<String> first) {
//定义快慢指针
Node<String> fast = first;
Node<String> slow = first;
Node<String> temp = null;
//遍历链表,先找到环(快慢指针相遇),准备一个临时指针,指向链表的首结点,继续遍历,直到慢指针和临时指针相遇,那么相遇时所指向的结点就是环的入口
while(fast!=null && fast.next!=null){
//变换快慢指针
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
//判断快慢指针是否相遇
if (fast.equals(slow)){
temp = first;
continue;
}
//让临时结点变换
if (temp!=null){
temp = temp.next;
//判断临时指针是否和慢指针相遇
if (temp.equals(slow)){
break;
}
}
}
return temp;
}
//结点类
private static class Node<T> {
//存储数据
T item;
//下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
P6161_线性表_链表_循环链表
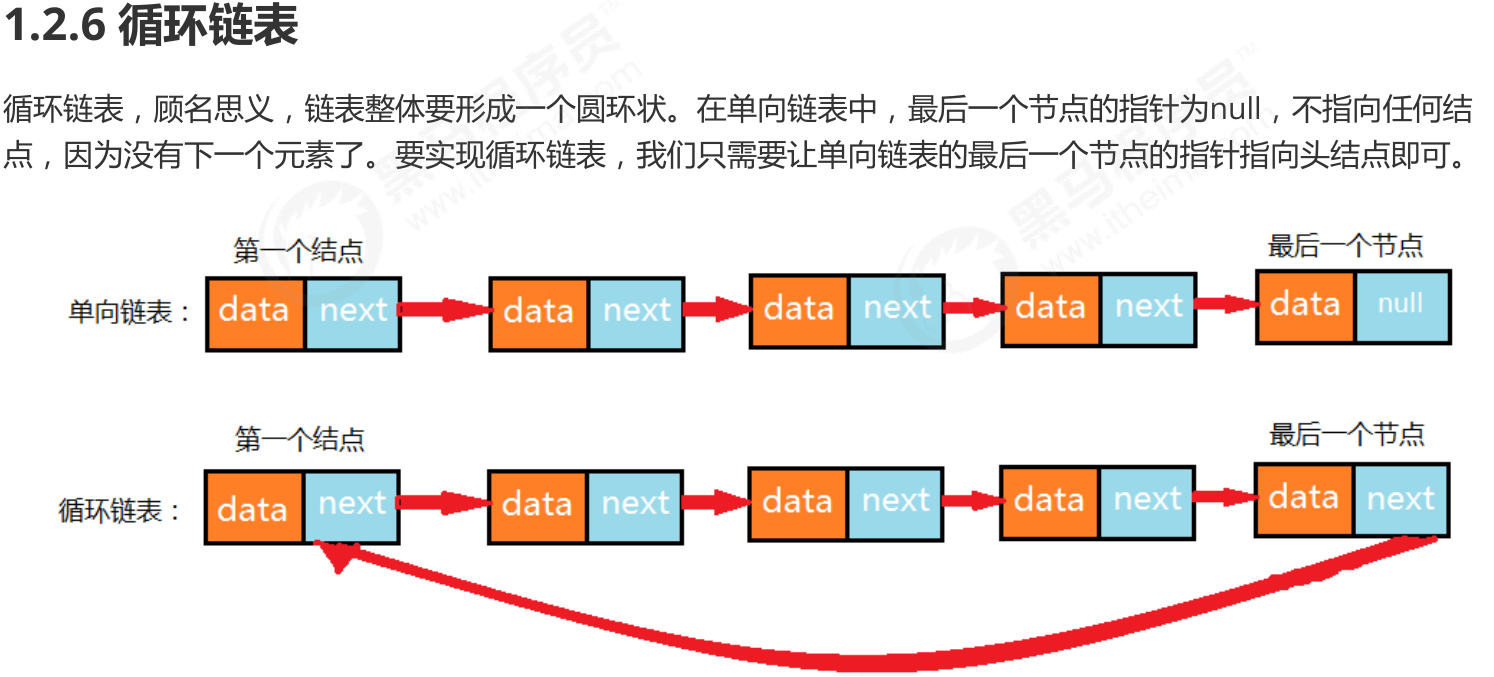

P6262_线性表_链表_约瑟夫问题1

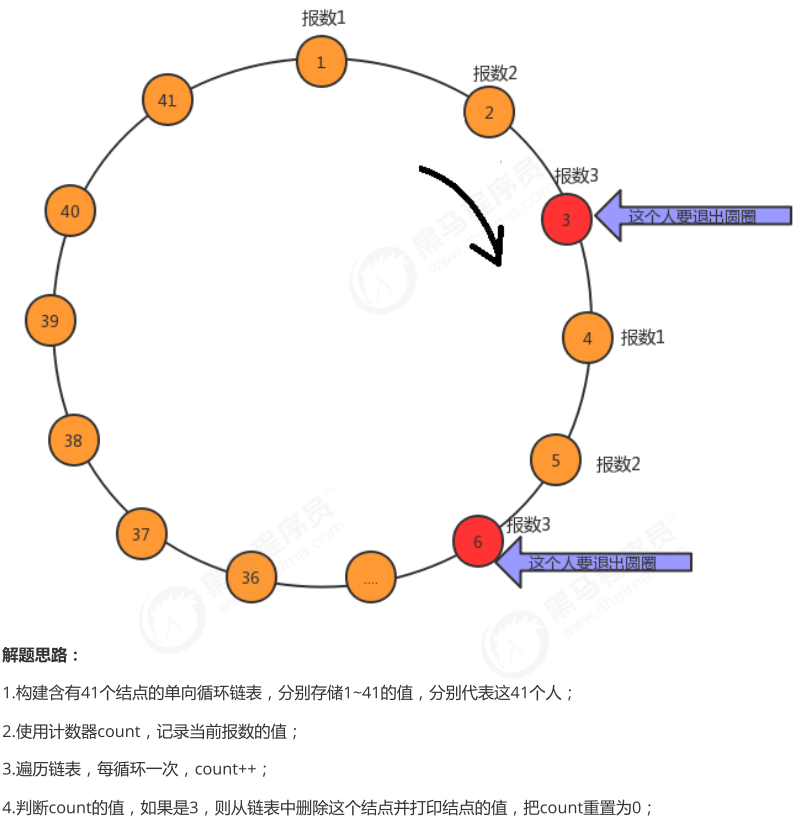
package cn.itcast.algorithm.test;
public class JosephTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//解决约瑟夫问题
//1.构建循环链表,包含41个结点,分别存储1~41之间的值
//用来就首结点
Node<Integer> first = null;
//用来记录前一个结点
Node<Integer> pre = null;
for(int i = 1;i<=41;i++){
//如果是第一个结点
if (i==1){
first = new Node<>(i,null);
pre = first;
continue;//创建完第一个节点后,直接进入下一个循环。
}
//如果不是第一个结点
Node<Integer> newNode = new Node<>(i, null);
pre.next=newNode;
pre=newNode;
//如果是最后一个结点,那么需要让最后一个结点的下一个结点变为first,变为循环链表了
if (i==41){
pre.next=first;
}
}
//2.需要count计数器,模拟报数
int count=0;
//3.遍历循环链表
//记录每次遍历拿到的结点,默认从首结点开始
Node<Integer> n = first;
//记录当前结点的上一个结点
Node<Integer> before = null;
while(n!=n.next){//n==n.next,自己自己的时候,就可以结束循环了,否则就停不下来了。
//模拟报数
count++;
//判断当前报数是不是为3
if (count==3){
//如果是3,则把当前结点删除调用,打印当前结点,重置count=0,让当前结点n后移
before.next=n.next;
System.out.print(n.item+",");
count=0;
n=n.next;
}else{
//如果不是3,让before变为当前结点,让当前结点后移;
before=n;
n=n.next;
}
}
//打印最后一个元素
System.out.println(n.item);
}
//结点类
private static class Node<T> {
//存储数据
T item;
//下一个结点
Node next;
public Node(T item, Node next) {
this.item = item;
this.next = next;
}
}
}
最后
以上就是乐观背包最近收集整理的关于8线性表P3838_线性表_线性表概述P3939_线性表_顺序表_基本实现P4040_线性表_顺序表_测试P4141_线性表_顺序表_遍历P4242_线性表_顺序表_容量可变P4343_线性表_顺序表_时间复杂度P4444_线性表_顺序表_ArrayList源码P4545_线性表_链表_概述P4646_线性表_链表_单向链表1P4747_线性表_链表_单向链表2P4848_线性表_链表_单向链表3P4949_线性表_链表_双向链表1P5454_线性表_链表_双向链表_LinkeList源码P55的全部内容,更多相关8线性表P3838_线性表_线性表概述P3939_线性表_顺序表_基本实现P4040_线性表_顺序表_测试P4141_线性表_顺序表_遍历P4242_线性表_顺序表_容量可变P4343_线性表_顺序表_时间复杂度P4444_线性表_顺序表_ArrayList源码P4545_线性表_链表_概述P4646_线性表_链表_单向链表1P4747_线性表_链表_单向链表2P4848_线性表_链表_单向链表3P4949_线性表_链表_双向链表1P5454_线性表_链表_双向链表_LinkeList源码P55内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复