通过labelme制作coco格式数据集,包含train,val,test三部分
- 第一步,建立文件夹,标注格式采用soft-1,soft-2
- 第二步,通过creat_txt.py生成val2019.txt,train2019.txt,test2019.txt
- 第三步,通过classify.py程序将json文件与图片分类
- 第五步,通过labelme2coco.py生成train2019.json,test2019.json,val2019.json
- 可视化
- 训练
代码地址:https://github.com/Xiu7/mask-r-cnn
第一步之前,你需要安装pycocotools等工具包。
第一步,建立文件夹,标注格式采用soft-1,soft-2
文件夹列表如下:
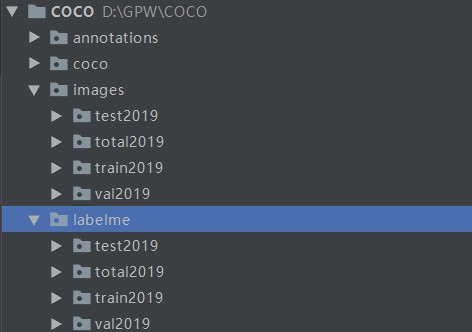
1. labelme/total2019下存放labelme生成的json文件,images/total2019下存放图片,其他文件夹先不用管
2. 下图时整体目录,后边建py文件参考
3. 注意一张图片里的多个同类目标采用soft-1,soft-2,soft-3,这类方式命名
第二步,通过creat_txt.py生成val2019.txt,train2019.txt,test2019.txt
程序如下,通过trainval_percent ,train_percent 参数设置train,test,val数据集的比例,程序直接运行
# !/usr/bin/python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import random
trainval_percent = 0.8 # 验证集+训练集占总比例多少
train_percent = 0.7 # 训练数据集占验证集+训练集比例多少
jsonfilepath = 'labelme/total2019'
txtsavepath = './'
total_xml = os.listdir(jsonfilepath)
num = len(total_xml)
list = range(num)
tv = int(num * trainval_percent)
tr = int(tv * train_percent)
trainval = random.sample(list, tv)
train = random.sample(trainval, tr)
ftrainval = open('./trainval2019.txt', 'w')
ftest = open('./test2019.txt', 'w')
ftrain = open('./train2019.txt', 'w')
fval = open('./val2019.txt', 'w')
for i in list:
name = total_xml[i][:-5] + 'n'
if i in trainval:
ftrainval.write(name)
if i in train:
ftrain.write(name)
else:
fval.write(name)
else:
ftest.write(name)
ftrainval.close()
ftrain.close()
fval.close()
ftest.close()
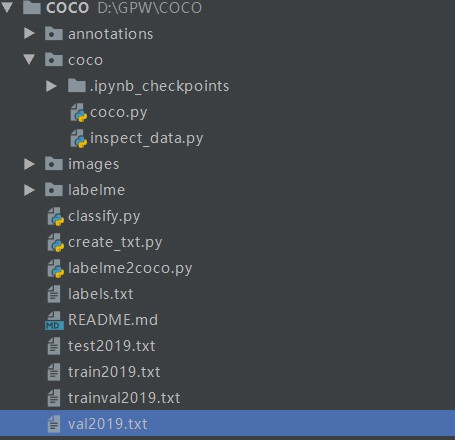
生成后txt文件后文件结构如下:
第三步,通过classify.py程序将json文件与图片分类
代码如下,程序直接运行
import shutil
import cv2 as cv
sets=['train2019', 'val2019', 'test2019']
for image_set in sets:
image_ids = open('./%s.txt'%(image_set)).read().strip().split()
for image_id in image_ids:
img = cv.imread('images/total2019/%s.jpg' % (image_id))
json='labelme/total2019/%s.json'% (image_id)
cv.imwrite('images/%s/%s.jpg' % (image_set,image_id), img)
cv.imwrite('labelme/%s/%s.jpg' % (image_set,image_id), img)
shutil.copy(json,'labelme/%s/%s.json' % (image_set,image_id))
print("完成")
第五步,通过labelme2coco.py生成train2019.json,test2019.json,val2019.json
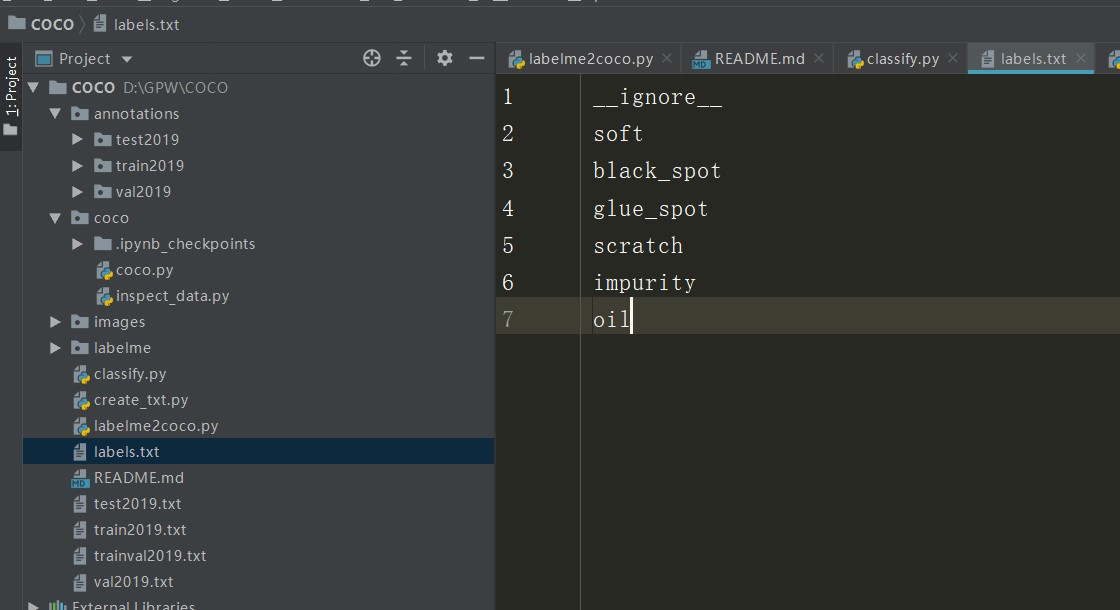
在根目录下建立labels.txt文件,内容首行为__ignore__,后续为你的分类标签。样例如下
建立labelme2coco.py文件,代码如下
#!/usr/bin/env python
import argparse
import collections
import datetime
import glob
import json
import os
import os.path as osp
import sys
import numpy as np
import PIL.Image
import labelme
try:
import pycocotools.mask
except ImportError:
print('Please install pycocotools:nn pip install pycocotoolsn')
sys.exit(1)
def main():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
formatter_class=argparse.ArgumentDefaultsHelpFormatter
)
parser.add_argument('--input_dir', help='input annotated directory')
parser.add_argument('--output_dir', help='output dataset directory')
parser.add_argument('--filename', help='output filename')
parser.add_argument('--labels', help='labels file', required=True)
args = parser.parse_args()
if osp.exists(args.output_dir):
print('Output directory already exists:', args.output_dir)
sys.exit(1)
os.makedirs(args.output_dir)
os.makedirs(osp.join(args.output_dir, 'JPEGImages'))
print('Creating dataset:', args.output_dir)
now = datetime.datetime.now()
data = dict(
info=dict(
description=None,
url=None,
version=None,
year=now.year,
contributor=None,
date_created=now.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S.%f'),
),
licenses=[dict(
url=None,
id=0,
name=None,
)],
images=[
# license, url, file_name, height, width, date_captured, id
],
type='instances',
annotations=[
# segmentation, area, iscrowd, image_id, bbox, category_id, id
],
categories=[
# supercategory, id, name
],
)
class_name_to_id = {}
for i, line in enumerate(open(args.labels).readlines()):
class_id = i - 1 # starts with -1
class_name = line.strip()
if class_id == -1:
assert class_name == '__ignore__'
continue
class_name_to_id[class_name] = class_id
data['categories'].append(dict(
supercategory=None,
id=class_id,
name=class_name,
))
out_ann_file = osp.join(args.output_dir, args.filename+'.json')
label_files = glob.glob(osp.join(args.input_dir, '*.json'))
for image_id, label_file in enumerate(label_files):
print('Generating dataset from:', label_file)
with open(label_file) as f:
label_data = json.load(f)
base = osp.splitext(osp.basename(label_file))[0]
out_img_file = osp.join(
args.output_dir, 'JPEGImages', base + '.jpg'
)
path=label_data['imagePath'].split("\")
img_file = osp.join(
osp.dirname(label_file), path[2]
)
img = np.asarray(PIL.Image.open(img_file))
PIL.Image.fromarray(img).save(out_img_file)
data['images'].append(dict(
license=0,
url=None,
file_name=osp.relpath(out_img_file, osp.dirname(out_ann_file)),
height=img.shape[0],
width=img.shape[1],
date_captured=None,
id=image_id,
))
masks = {} # for area
segmentations = collections.defaultdict(list) # for segmentation
for shape in label_data['shapes']:
points = shape['points']
label = shape['label']
shape_type = shape.get('shape_type', None)
mask = labelme.utils.shape_to_mask(
img.shape[:2], points, shape_type
)
if label in masks:
masks[label] = masks[label] | mask
else:
masks[label] = mask
points = np.asarray(points).flatten().tolist()
segmentations[label].append(points)
for label, mask in masks.items():
cls_name = label.split('-')[0]
if cls_name not in class_name_to_id:
continue
cls_id = class_name_to_id[cls_name]
mask = np.asfortranarray(mask.astype(np.uint8))
mask = pycocotools.mask.encode(mask)
area = float(pycocotools.mask.area(mask))
bbox = pycocotools.mask.toBbox(mask).flatten().tolist()
data['annotations'].append(dict(
id=len(data['annotations']),
image_id=image_id,
category_id=cls_id,
segmentation=segmentations[label],
area=area,
bbox=bbox,
iscrowd=0,
))
with open(out_ann_file, 'w') as f:
json.dump(data, f)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
运行三次labelme2coco.py文件,在annotations下生成coco格式的文件,指令如下
python ./labelme2coco.py --input_dir ./labelme/train2019 --output_dir ./annotations/train2019 --filename instances_train2019 --labels labels.txt
python ./labelme2coco.py --input_dir ./labelme/val2019 --output_dir ./annotations/val2019 --filename instances_val2019 --labels labels.txt
python ./labelme2coco.py --input_dir ./labelme/test2019 --output_dir ./annotations/test2019 --filename instances_test2019 --labels labels.txt
可视化
在coco文件夹下建立coco.py与inspect_data.py
coco.py代码如下
"""
Mask R-CNN
Configurations and data loading code for MS COCO.
Copyright (c) 2017 Matterport, Inc.
Licensed under the MIT License (see LICENSE for details)
Written by Waleed Abdulla
------------------------------------------------------------
Usage: import the module (see Jupyter notebooks for examples), or run from
the command line as such:
# Train a new model starting from pre-trained COCO weights
python3 coco.py train --dataset=/path/to/coco/ --model=coco
# Train a new model starting from ImageNet weights. Also auto download COCO dataset
python3 coco.py train --dataset=/path/to/coco/ --model=imagenet --download=True
# Continue training a model that you had trained earlier
python3 coco.py train --dataset=/path/to/coco/ --model=/path/to/weights.h5
# Continue training the last model you trained
python3 coco.py train --dataset=/path/to/coco/ --model=last
# Run COCO evaluatoin on the last model you trained
python3 coco.py evaluate --dataset=/path/to/coco/ --model=last
"""
import os
import sys
import time
import numpy as np
import imgaug # https://github.com/aleju/imgaug (pip3 install imgaug)
# Download and install the Python COCO tools from https://github.com/waleedka/coco
# That's a fork from the original https://github.com/pdollar/coco with a bug
# fix for Python 3.
# I submitted a pull request https://github.com/cocodataset/cocoapi/pull/50
# If the PR is merged then use the original repo.
# Note: Edit PythonAPI/Makefile and replace "python" with "python3".
from pycocotools.coco import COCO
from pycocotools.cocoeval import COCOeval
from pycocotools import mask as maskUtils
import zipfile
import urllib.request
import shutil
# Root directory of the project
ROOT_DIR = os.path.abspath("model")
# Import Mask RCNN
sys.path.append(ROOT_DIR) # To find local version of the library
from mrcnn.config import Config
from mrcnn import model as modellib, utils
# Path to trained weights file
COCO_MODEL_PATH = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "mask_rcnn_coco.h5")
# Directory to save logs and model checkpoints, if not provided
# through the command line argument --logs
DEFAULT_LOGS_DIR = os.path.join(ROOT_DIR, "logs")
DEFAULT_DATASET_YEAR = "2019"
############################################################
# Configurations
############################################################
class CocoConfig(Config):
"""Configuration for training on MS COCO.
Derives from the base Config class and overrides values specific
to the COCO dataset.
"""
# Give the configuration a recognizable name
NAME = "coco"
# We use a GPU with 12GB memory, which can fit two images.
# Adjust down if you use a smaller GPU.
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
# Uncomment to train on 8 GPUs (default is 1)
# GPU_COUNT = 8
# Number of classes (including background)
NUM_CLASSES = 1 + 6 # COCO has 80 classes
############################################################
# Dataset
############################################################
class CocoDataset(utils.Dataset):
def load_coco(self, dataset_dir, subset, year=DEFAULT_DATASET_YEAR, class_ids=None,
class_map=None, return_coco=False, auto_download=False):
"""Load a subset of the COCO dataset.
dataset_dir: The root directory of the COCO dataset.
subset: What to load (train, val, minival, valminusminival)
year: What dataset year to load (2014, 2017) as a string, not an integer
class_ids: If provided, only loads images that have the given classes.
class_map: TODO: Not implemented yet. Supports maping classes from
different datasets to the same class ID.
return_coco: If True, returns the COCO object.
auto_download: Automatically download and unzip MS-COCO images and train
"""
if auto_download is True:
self.auto_download(dataset_dir, subset, year)
coco = COCO("{}/train2019/instances_{}{}.json".format(dataset_dir, subset, year))
if subset == "minival" or subset == "valminusminival":
subset = "val"
image_dir = "{}/{}{}".format(dataset_dir, subset, year)
# Load all classes or a subset?
if not class_ids:
# All classes
class_ids = sorted(coco.getCatIds())
# All images or a subset?
if class_ids:
image_ids = []
for id in class_ids:
image_ids.extend(list(coco.getImgIds(catIds=[id])))
# Remove duplicates
image_ids = list(set(image_ids))
else:
# All images
image_ids = list(coco.imgs.keys())
# Add classes
for i in class_ids:
self.add_class("coco", i, coco.loadCats(i)[0]["name"])
# Add images
for i in image_ids:
self.add_image(
"coco", image_id=i,
path=os.path.join(image_dir, coco.imgs[i]['file_name']),
width=coco.imgs[i]["width"],
height=coco.imgs[i]["height"],
annotations=coco.loadAnns(coco.getAnnIds(
imgIds=[i], catIds=class_ids, iscrowd=None)))
if return_coco:
return coco
def auto_download(self, dataDir, dataType, dataYear):
"""Download the COCO dataset/train if requested.
dataDir: The root directory of the COCO dataset.
dataType: What to load (train, val, minival, valminusminival)
dataYear: What dataset year to load (2014, 2017) as a string, not an integer
Note:
For 2014, use "train", "val", "minival", or "valminusminival"
For 2017, only "train" and "val" train are available
"""
# Setup paths and file names
if dataType == "minival" or dataType == "valminusminival":
imgDir = "{}/{}{}".format(dataDir, "val", dataYear)
imgZipFile = "{}/{}{}.zip".format(dataDir, "val", dataYear)
imgURL = "http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/{}{}.zip".format("val", dataYear)
else:
imgDir = "{}/{}{}".format(dataDir, dataType, dataYear)
imgZipFile = "{}/{}{}.zip".format(dataDir, dataType, dataYear)
imgURL = "http://images.cocodataset.org/zips/{}{}.zip".format(dataType, dataYear)
# print("Image paths:"); print(imgDir); print(imgZipFile); print(imgURL)
# Create main folder if it doesn't exist yet
if not os.path.exists(dataDir):
os.makedirs(dataDir)
# Download images if not available locally
if not os.path.exists(imgDir):
os.makedirs(imgDir)
print("Downloading images to " + imgZipFile + " ...")
with urllib.request.urlopen(imgURL) as resp, open(imgZipFile, 'wb') as out:
shutil.copyfileobj(resp, out)
print("... done downloading.")
print("Unzipping " + imgZipFile)
with zipfile.ZipFile(imgZipFile, "r") as zip_ref:
zip_ref.extractall(dataDir)
print("... done unzipping")
print("Will use images in " + imgDir)
# Setup train data paths
annDir = "{}/train".format(dataDir)
if dataType == "minival":
annZipFile = "{}/instances_minival2014.json.zip".format(dataDir)
annFile = "{}/instances_minival2014.json".format(annDir)
annURL = "https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/o43o90bna78omob/instances_minival2014.json.zip?dl=0"
unZipDir = annDir
elif dataType == "valminusminival":
annZipFile = "{}/instances_valminusminival2014.json.zip".format(dataDir)
annFile = "{}/instances_valminusminival2014.json".format(annDir)
annURL = "https://dl.dropboxusercontent.com/s/s3tw5zcg7395368/instances_valminusminival2014.json.zip?dl=0"
unZipDir = annDir
else:
annZipFile = "{}/annotations_trainval{}.zip".format(dataDir, dataYear)
annFile = "{}/instances_{}{}.json".format(annDir, dataType, dataYear)
annURL = "http://images.cocodataset.org/annotations/annotations_trainval{}.zip".format(dataYear)
unZipDir = dataDir
# print("Annotations paths:"); print(annDir); print(annFile); print(annZipFile); print(annURL)
# Download train if not available locally
if not os.path.exists(annDir):
os.makedirs(annDir)
if not os.path.exists(annFile):
if not os.path.exists(annZipFile):
print("Downloading zipped train to " + annZipFile + " ...")
with urllib.request.urlopen(annURL) as resp, open(annZipFile, 'wb') as out:
shutil.copyfileobj(resp, out)
print("... done downloading.")
print("Unzipping " + annZipFile)
with zipfile.ZipFile(annZipFile, "r") as zip_ref:
zip_ref.extractall(unZipDir)
print("... done unzipping")
print("Will use train in " + annFile)
def load_mask(self, image_id):
"""Load instance masks for the given image.
Different datasets use different ways to store masks. This
function converts the different mask format to one format
in the form of a bitmap [height, width, instances].
Returns:
masks: A bool array of shape [height, width, instance count] with
one mask per instance.
class_ids: a 1D array of class IDs of the instance masks.
"""
# If not a COCO image, delegate to parent class.
image_info = self.image_info[image_id]
if image_info["source"] != "coco":
return super(CocoDataset, self).load_mask(image_id)
instance_masks = []
class_ids = []
annotations = self.image_info[image_id]["annotations"]
# Build mask of shape [height, width, instance_count] and list
# of class IDs that correspond to each channel of the mask.
for annotation in annotations:
class_id = self.map_source_class_id(
"coco.{}".format(annotation['category_id']))
if class_id:
m = self.annToMask(annotation, image_info["height"],
image_info["width"])
# Some objects are so small that they're less than 1 pixel area
# and end up rounded out. Skip those objects.
if m.max() < 1:
continue
# Is it a crowd? If so, use a negative class ID.
if annotation['iscrowd']:
# Use negative class ID for crowds
class_id *= -1
# For crowd masks, annToMask() sometimes returns a mask
# smaller than the given dimensions. If so, resize it.
if m.shape[0] != image_info["height"] or m.shape[1] != image_info["width"]:
m = np.ones([image_info["height"], image_info["width"]], dtype=bool)
instance_masks.append(m)
class_ids.append(class_id)
# Pack instance masks into an array
if class_ids:
mask = np.stack(instance_masks, axis=2).astype(np.bool)
class_ids = np.array(class_ids, dtype=np.int32)
return mask, class_ids
else:
# Call super class to return an empty mask
return super(CocoDataset, self).load_mask(image_id)
def image_reference(self, image_id):
"""Return a link to the image in the COCO Website."""
info = self.image_info[image_id]
if info["source"] == "coco":
return "http://cocodataset.org/#explore?id={}".format(info["id"])
else:
super(CocoDataset, self).image_reference(image_id)
# The following two functions are from pycocotools with a few changes.
def annToRLE(self, ann, height, width):
"""
Convert annotation which can be polygons, uncompressed RLE to RLE.
:return: binary mask (numpy 2D array)
"""
segm = ann['segmentation']
if isinstance(segm, list):
# polygon -- a single object might consist of multiple parts
# we merge all parts into one mask rle code
rles = maskUtils.frPyObjects(segm, height, width)
rle = maskUtils.merge(rles)
elif isinstance(segm['counts'], list):
# uncompressed RLE
rle = maskUtils.frPyObjects(segm, height, width)
else:
# rle
rle = ann['segmentation']
return rle
def annToMask(self, ann, height, width):
"""
Convert annotation which can be polygons, uncompressed RLE, or RLE to binary mask.
:return: binary mask (numpy 2D array)
"""
rle = self.annToRLE(ann, height, width)
m = maskUtils.decode(rle)
return m
############################################################
# COCO Evaluation
############################################################
def build_coco_results(dataset, image_ids, rois, class_ids, scores, masks):
"""Arrange resutls to match COCO specs in http://cocodataset.org/#format
"""
# If no results, return an empty list
if rois is None:
return []
results = []
for image_id in image_ids:
# Loop through detections
for i in range(rois.shape[0]):
class_id = class_ids[i]
score = scores[i]
bbox = np.around(rois[i], 1)
mask = masks[:, :, i]
result = {
"image_id": image_id,
"category_id": dataset.get_source_class_id(class_id, "coco"),
"bbox": [bbox[1], bbox[0], bbox[3] - bbox[1], bbox[2] - bbox[0]],
"score": score,
"segmentation": maskUtils.encode(np.asfortranarray(mask))
}
results.append(result)
return results
def evaluate_coco(model, dataset, coco, eval_type="bbox", limit=0, image_ids=None):
"""Runs official COCO evaluation.
dataset: A Dataset object with valiadtion data
eval_type: "bbox" or "segm" for bounding box or segmentation evaluation
limit: if not 0, it's the number of images to use for evaluation
"""
# Pick COCO images from the dataset
image_ids = image_ids or dataset.image_ids
# Limit to a subset
if limit:
image_ids = image_ids[:limit]
# Get corresponding COCO image IDs.
coco_image_ids = [dataset.image_info[id]["id"] for id in image_ids]
t_prediction = 0
t_start = time.time()
results = []
for i, image_id in enumerate(image_ids):
# Load image
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
# Run detection
t = time.time()
r = model.detect([image], verbose=0)[0]
t_prediction += (time.time() - t)
# Convert results to COCO format
# Cast masks to uint8 because COCO tools errors out on bool
image_results = build_coco_results(dataset, coco_image_ids[i:i + 1],
r["rois"], r["class_ids"],
r["scores"],
r["masks"].astype(np.uint8))
results.extend(image_results)
# Load results. This modifies results with additional attributes.
coco_results = coco.loadRes(results)
# Evaluate
cocoEval = COCOeval(coco, coco_results, eval_type)
cocoEval.params.imgIds = coco_image_ids
cocoEval.evaluate()
cocoEval.accumulate()
cocoEval.summarize()
print("Prediction time: {}. Average {}/image".format(
t_prediction, t_prediction / len(image_ids)))
print("Total time: ", time.time() - t_start)
############################################################
# Training
############################################################
if __name__ == '__main__':
import argparse
# Parse command line arguments
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(
description='Train Mask R-CNN on MS COCO.')
parser.add_argument("command",
metavar="<command>",
help="'train' or 'evaluate' on MS COCO")
parser.add_argument('--dataset', required=True,
metavar="/path/to/coco/",
help='Directory of the MS-COCO dataset')
parser.add_argument('--year', required=False,
default=DEFAULT_DATASET_YEAR,
metavar="<year>",
help='Year of the MS-COCO dataset (2014 or 2017) (default=2014)')
parser.add_argument('--model', required=True,
metavar="/path/to/weights.h5",
help="Path to weights .h5 file or 'coco'")
parser.add_argument('--logs', required=False,
default=DEFAULT_LOGS_DIR,
metavar="/path/to/logs/",
help='Logs and checkpoints directory (default=logs/)')
parser.add_argument('--limit', required=False,
default=500,
metavar="<image count>",
help='Images to use for evaluation (default=500)')
parser.add_argument('--download', required=False,
default=False,
metavar="<True|False>",
help='Automatically download and unzip MS-COCO files (default=False)',
type=bool)
args = parser.parse_args()
print("Command: ", args.command)
print("Model: ", args.model)
print("Dataset: ", args.dataset)
print("Year: ", args.year)
print("Logs: ", args.logs)
print("Auto Download: ", args.download)
# Configurations
if args.command == "train":
config = CocoConfig()
else:
class InferenceConfig(CocoConfig):
# Set batch size to 1 since we'll be running inference on
# one image at a time. Batch size = GPU_COUNT * IMAGES_PER_GPU
GPU_COUNT = 1
IMAGES_PER_GPU = 1
DETECTION_MIN_CONFIDENCE = 0
config = InferenceConfig()
config.display()
# Create model
if args.command == "train":
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="training", config=config,
model_dir=args.logs)
else:
model = modellib.MaskRCNN(mode="inference", config=config,
model_dir=args.logs)
# Select weights file to load
if args.model.lower() == "coco":
model_path = COCO_MODEL_PATH
elif args.model.lower() == "last":
# Find last trained weights
model_path = model.find_last()
elif args.model.lower() == "imagenet":
# Start from ImageNet trained weights
model_path = model.get_imagenet_weights()
else:
model_path = args.model
# Load weights
print("Loading weights ", model_path)
model.load_weights(model_path, by_name=True)
# Train or evaluate
if args.command == "train":
# Training dataset. Use the training set and 35K from the
# validation set, as as in the Mask RCNN paper.
dataset_train = CocoDataset()
dataset_train.load_coco(args.dataset, "train", year=args.year, auto_download=args.download)
if args.year in '2014':
dataset_train.load_coco(args.dataset, "valminusminival", year=args.year, auto_download=args.download)
dataset_train.prepare()
# Validation dataset
dataset_val = CocoDataset()
val_type = "val" if args.year in '2017' else "minival"
dataset_val.load_coco(args.dataset, val_type, year=args.year, auto_download=args.download)
dataset_val.prepare()
# Image Augmentation
# Right/Left flip 50% of the time
augmentation = imgaug.augmenters.Fliplr(0.5)
# *** This training schedule is an example. Update to your needs ***
# Training - Stage 1
print("Training network heads")
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE,
epochs=40,
layers='heads',
augmentation=augmentation)
# Training - Stage 2
# Finetune layers from ResNet stage 4 and up
print("Fine tune Resnet stage 4 and up")
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE,
epochs=120,
layers='4+',
augmentation=augmentation)
# Training - Stage 3
# Fine tune all layers
print("Fine tune all layers")
model.train(dataset_train, dataset_val,
learning_rate=config.LEARNING_RATE / 10,
epochs=160,
layers='all',
augmentation=augmentation)
elif args.command == "evaluate":
# Validation dataset
dataset_val = CocoDataset()
val_type = "val" if args.year in '2017' else "minival"
coco = dataset_val.load_coco(args.dataset, val_type, year=args.year, return_coco=True, auto_download=args.download)
dataset_val.prepare()
print("Running COCO evaluation on {} images.".format(args.limit))
evaluate_coco(model, dataset_val, coco, "bbox", limit=int(args.limit))
else:
print("'{}' is not recognized. "
"Use 'train' or 'evaluate'".format(args.command))
inspect_data.py代码如下
import os
import sys
import numpy as np
ROOT_DIR = os.path.abspath("../")
# Import Mask RCNN
sys.path.append(ROOT_DIR) # To find local version of the library
from mrcnn import utils
from mrcnn import visualize
# MS COCO Dataset
import coco
config = coco.CocoConfig()
COCO_DIR = "../annotations" # TODO: enter value here
# Load dataset
if config.NAME == 'shapes':
dataset = shapes.ShapesDataset()
dataset.load_shapes(500, config.IMAGE_SHAPE[0], config.IMAGE_SHAPE[1])
elif config.NAME == "coco":
dataset = coco.CocoDataset()
dataset.load_coco(COCO_DIR, "train")
# Must call before using the dataset
dataset.prepare()
print("Image Count: {}".format(len(dataset.image_ids)))
print("Class Count: {}".format(dataset.num_classes))
for i, info in enumerate(dataset.class_info):
print("{:3}. {:50}".format(i, info['name']))
# Load and display random samples
image_ids = np.random.choice(dataset.image_ids, 3)
print(image_ids)
for image_id in image_ids:
image = dataset.load_image(image_id)
mask, class_ids = dataset.load_mask(image_id)
visualize.display_top_masks(image, mask, class_ids, dataset.class_names)
运行inspect_data.py,即可可视化数据集
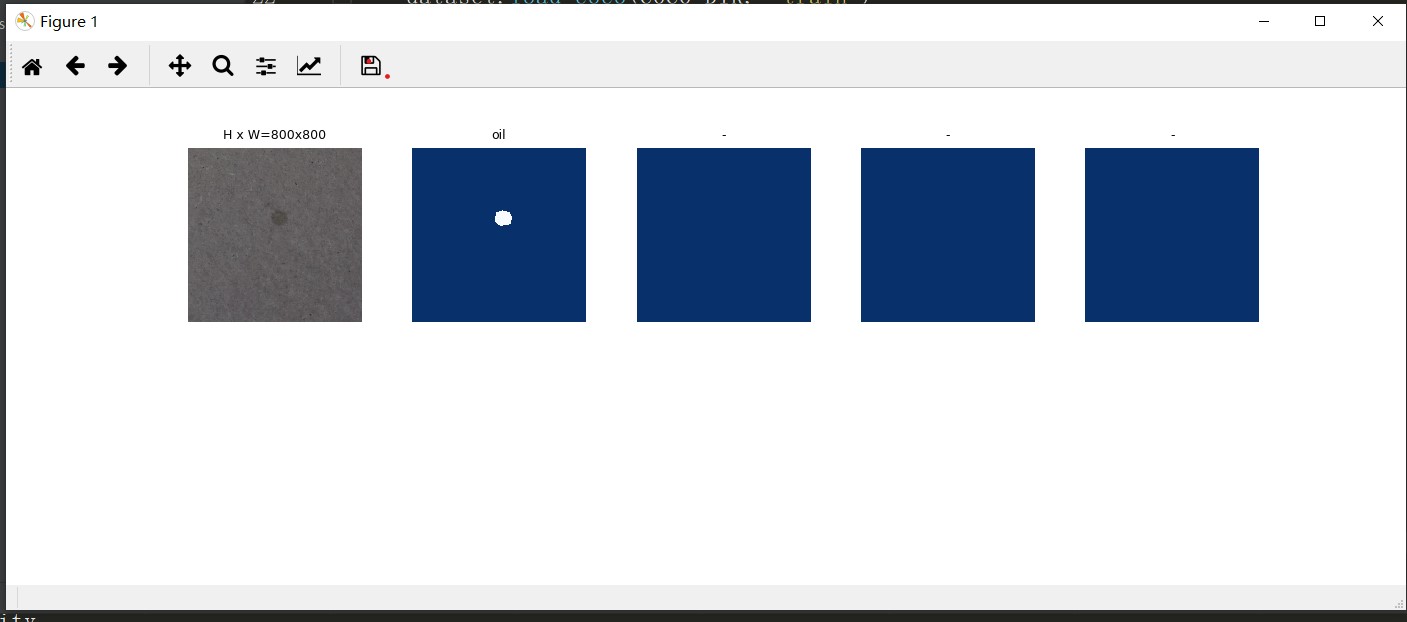
训练
第一步,在model中存放mask_rcnn_coco.h5模型
第二步,修改mdf.py参数,87行修改成自己的分类数(mdf.py 就是samples/coco中的coco.py,我重命名了一下)
最后一步,输入python mdf.py train --dataset=./coco_mdf --model=coco开始训练
最后
以上就是含糊蜡烛最近收集整理的关于通过labelme制作coco格式数据集,并使用mask r-cnn训练的全部内容,更多相关通过labelme制作coco格式数据集,并使用mask内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复