方式一:最小二乘法(正规方程)
公式推导
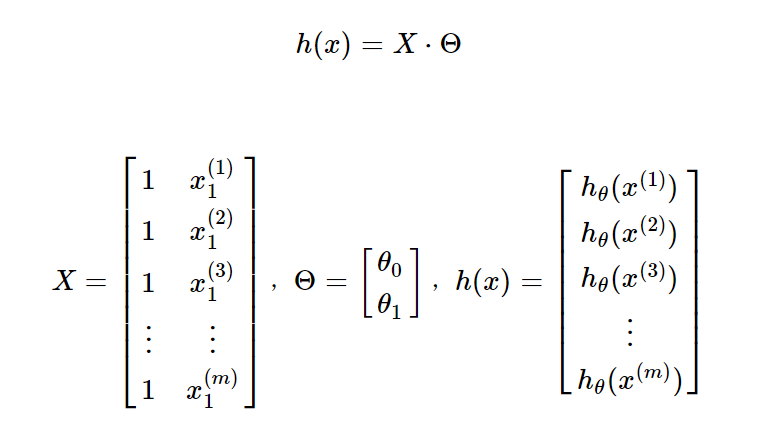
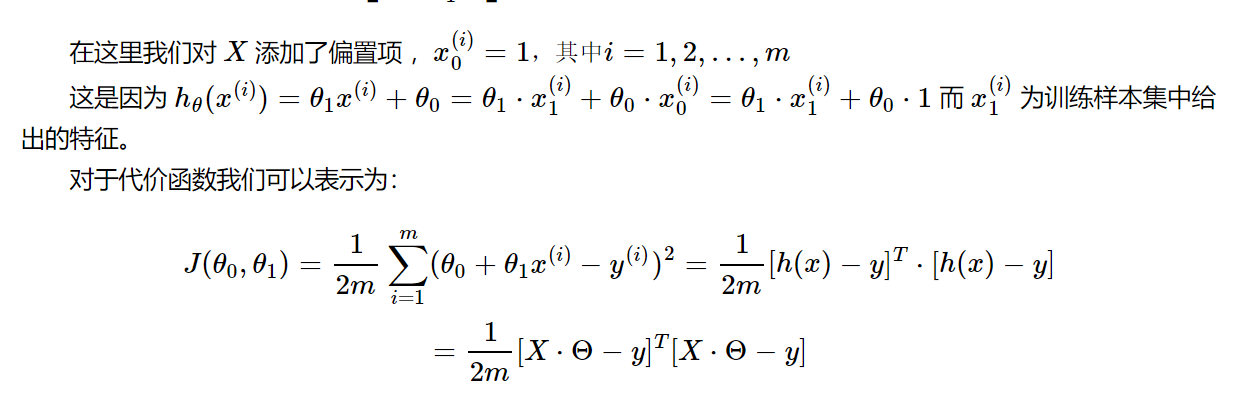
其中:
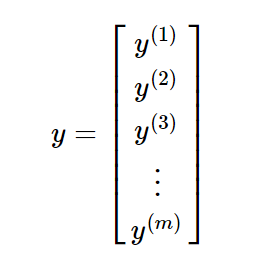
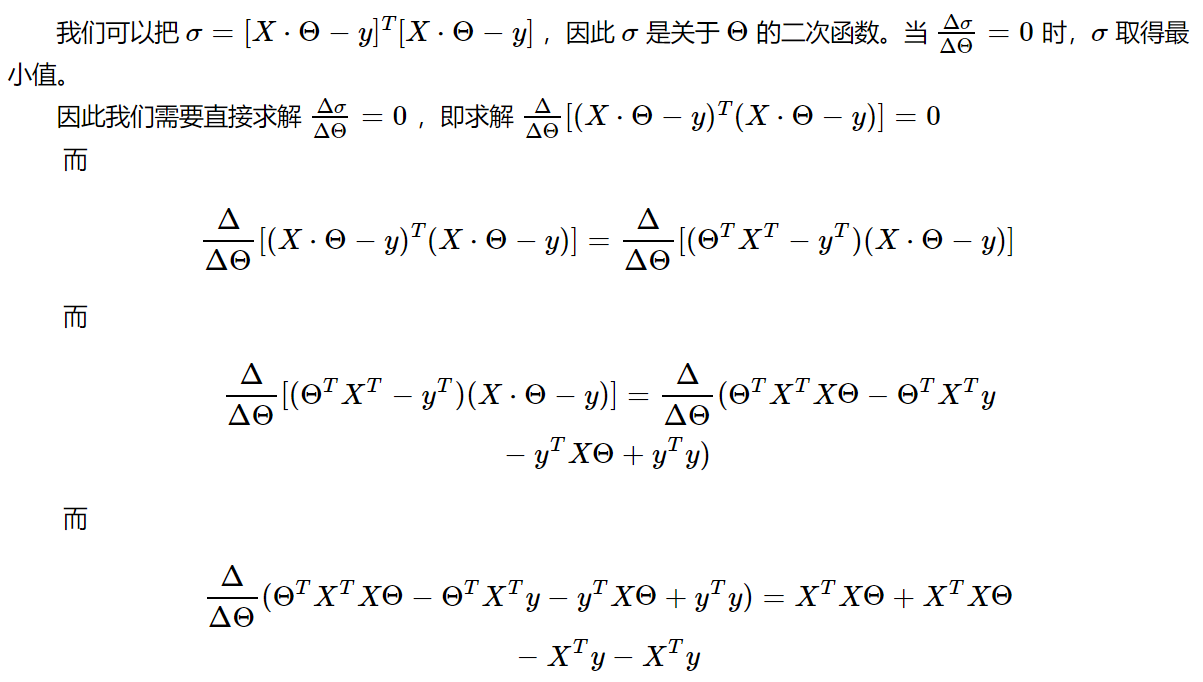

代码实现:
1.导入库
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_boston
boston = load_boston()
x = boston.data
y = boston.target
2.由于我们的特征中没有1,所以需要插入1
然后我们需要把1和特征放在一起
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x),1)),x]
3.用正规方程求解参数
theta = np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y)
4.获得截距(b)和系数(w)
intercept = theta[0]
coef = theta[1:]
5.预测
x_test = x[0].reshape(1,-1)
x_test = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x_test),1)),x_test])
x_test.dot(theta) #预测结果
6.封装代码
import numpy as np
class LinearRegression_2:
def __init__(self):
self._theta = None
self.intercept_ = None
self.coef_ = None
def fit(self,x_train,y_train):
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x_train),1)), x_train])
self._theta = np.linalg.inv(X_b.T.dot(X_b)).dot(X_b.T).dot(y_train)
self.intercept_ = self._theta[0]
self.coef_ = self._theta[1:]
return self
def predict(self,x_predict):
X_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x_predict),1)), x_predict])
return X_b.dot(self._theta)
def __repr__(self): #用作自我介绍
return "LinearRegression_2()"
此代码在矩阵不可逆时,容易报错
方式二:梯度下降
损失函数:
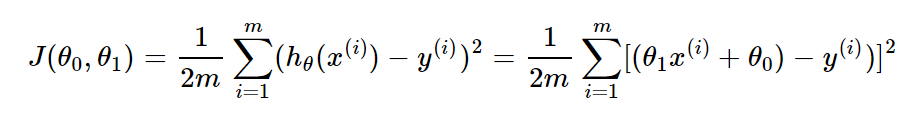
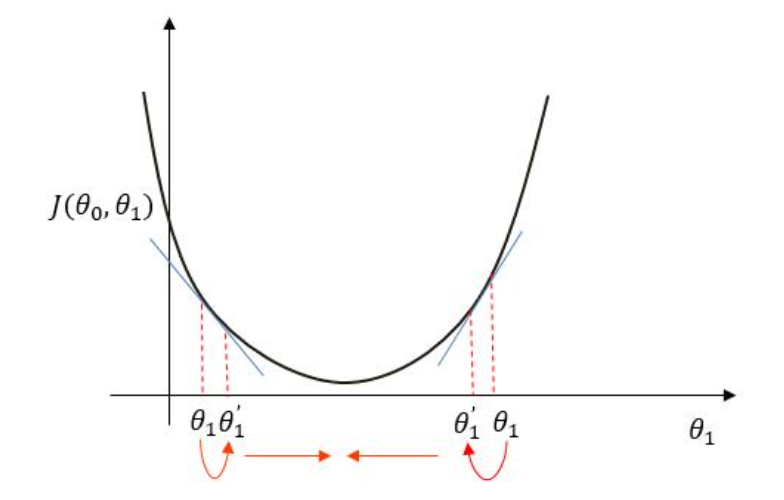
单元线性回归


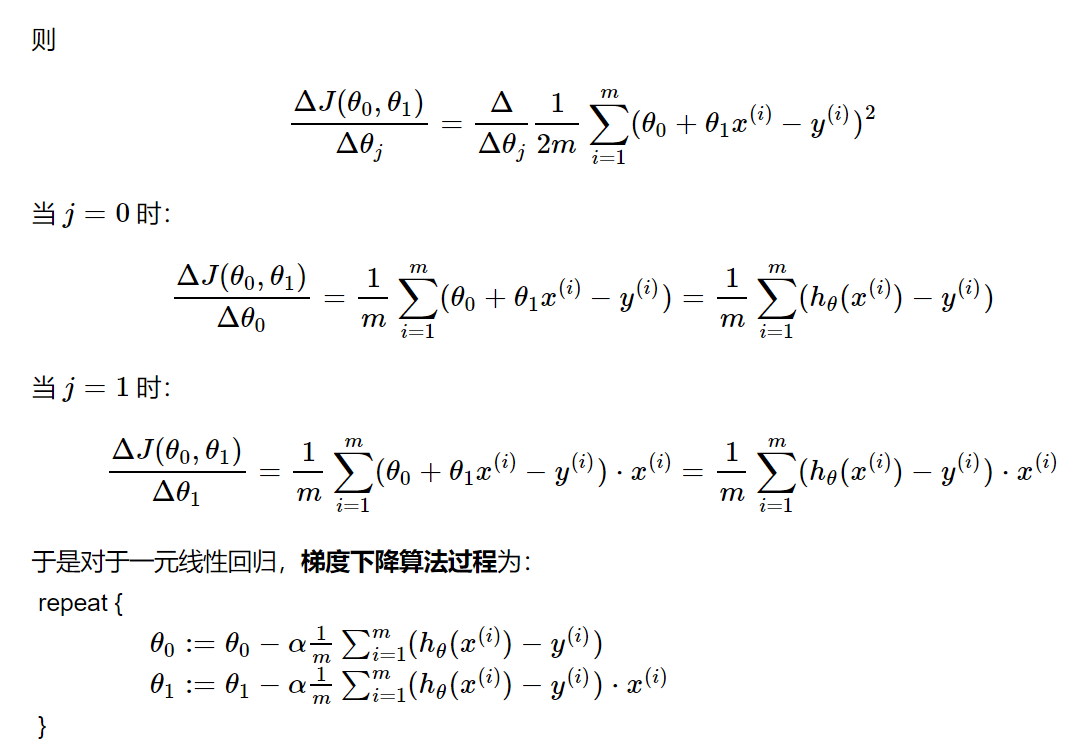

同理可得多元线性回归
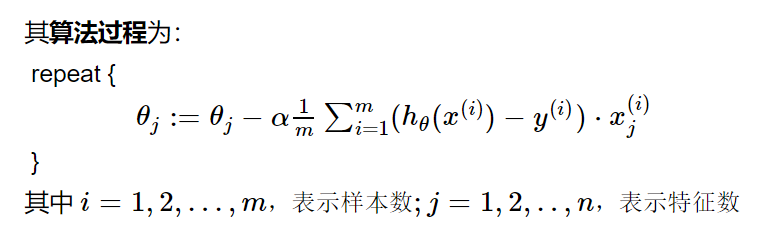
代码`
class LinerRegression2(object):
def __init__(self,learning_rate=0.01, max_iter=100, seed=None):
np.random.seed(seed)
self.lr = learning_rate #设置学习率
self.max_iter = max_iter
self.loss_arr = []
def fit(self,x,y):
self.x = x
self.x_b = np.hstack([np.ones((len(x), 1)), x])
self.x_b_dim = np.size(self.x_b,1)
self.x_sample = np.size(self.x_b, 0)
self.y = y
self.w = np.random.normal(1,0.001,(self.x_b_dim,1))
for i in range(self.max_iter):
self._train_step()
self.loss_arr.append(self.loss())
def _f(self,x,w):
return x.dot(w)
def predict(self,x=None):
if x is None:
x = self.x_b
y_pred = self._f(x,self.w)
return y_pred
def loss(self,y_true=None,y_pred=None):
if y_true is None or y_pred is None:
y_true = self.y
# y_pred = self.predict(self.x_b)
return np.sum(np.power(y_true-self.x_b.dot(self.w),2))/self.x_sample
def _calc_gradient(self):
d_w = np.empty(self.x_b_dim).reshape(-1,1)
d_w[0] = np.sum(self.x_b.dot(self.w)-self.y)
for i in range(1,self.x_b_dim):
print(self.x_b.shape)
print(self.w.shape)
print(self.y.shape)
print(self.x_b[:,i].T.shape)
d_w[i] = np.squeeze((self.x_b.dot(self.w)-self.y)).dot(self.x_b[:,i].T)
return d_w*2/self.x_sample
def _train_step(self):
d_w = self._calc_gradient()
self.w = self.w-self.lr*d_w
return self.w
注意:请将输入数据进行归一化,否则梯度下降的时候,可能数据可能会非常大,最终溢出
最后
以上就是忧郁翅膀最近收集整理的关于线性回归(两种方式代码实现)的全部内容,更多相关线性回归(两种方式代码实现)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复