第一部分 中断系统的总体逻辑
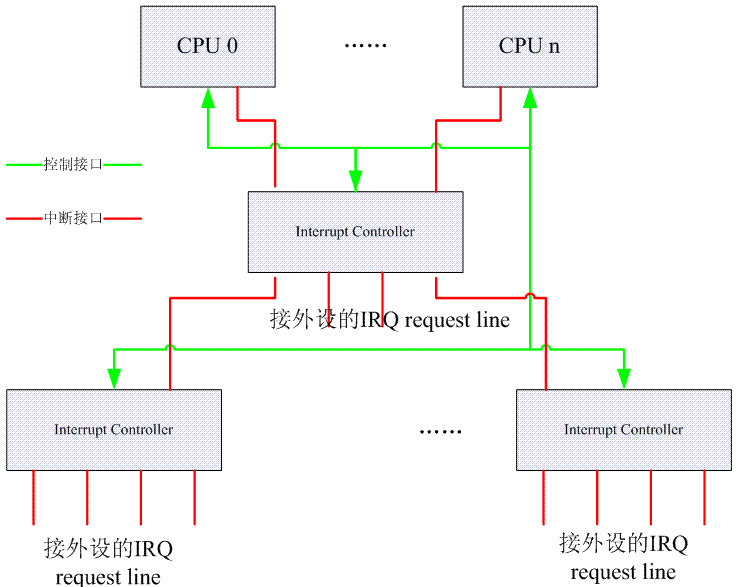
CPU的主要功能是运算,因此CPU并不处理中断优先级,那是Interrupt controller的事情。对于CPU而言,一般有两种中断请求,例如:对于ARM,是IRQ和FIQ信号线,分别让ARM进入IRQ mode和FIQ mode。对于X86,有可屏蔽中断和不可屏蔽中断。
CPU和Interrupt Controller之间主要有两类接口,第一种是中断接口。上面的红色线条可能是实际的PCB上的铜线(或者SOC内部的铜线),也可能是一个message而已。第二种是控制接口。Interrupt Controller会开放一些寄存器让CPU访问、控制, 图中的绿色接口即为控制接口。
特定中断由2个CPU轮流处理的算法?
为Interrupt Controller支持的每一个中断设定一个target cpu的控制接口(当然应该是以寄存器形式出现,对于GIC,这个寄存器就是Interrupt processor target register)。系统有多个cpu,这个控制接口就有多少个bit,每个bit代表一个CPU。如果该bit设定为1,那么该interrupt就上报给该CPU,如果为0,则不上报给该CPU。
例如如果系统有两个cpu core,某中断想轮流由两个CPU处理。那么当CPU0相应该中断进入interrupt handler的时候,可以将本CPU对应的bit设定为0,另外一个CPU设定为1。这样,在下次中断发生的时候,interupt controller就把中断送给了CPU1。对于CPU1而言,在执行该中断的handler的时候,将Interrupt processor target register中CPU0的bit为设置为1,disable本CPU的比特位,这样在下次中断发生的时候,interupt controller就把中断送给了CPU0。
以下为三星平台中断系统实例:
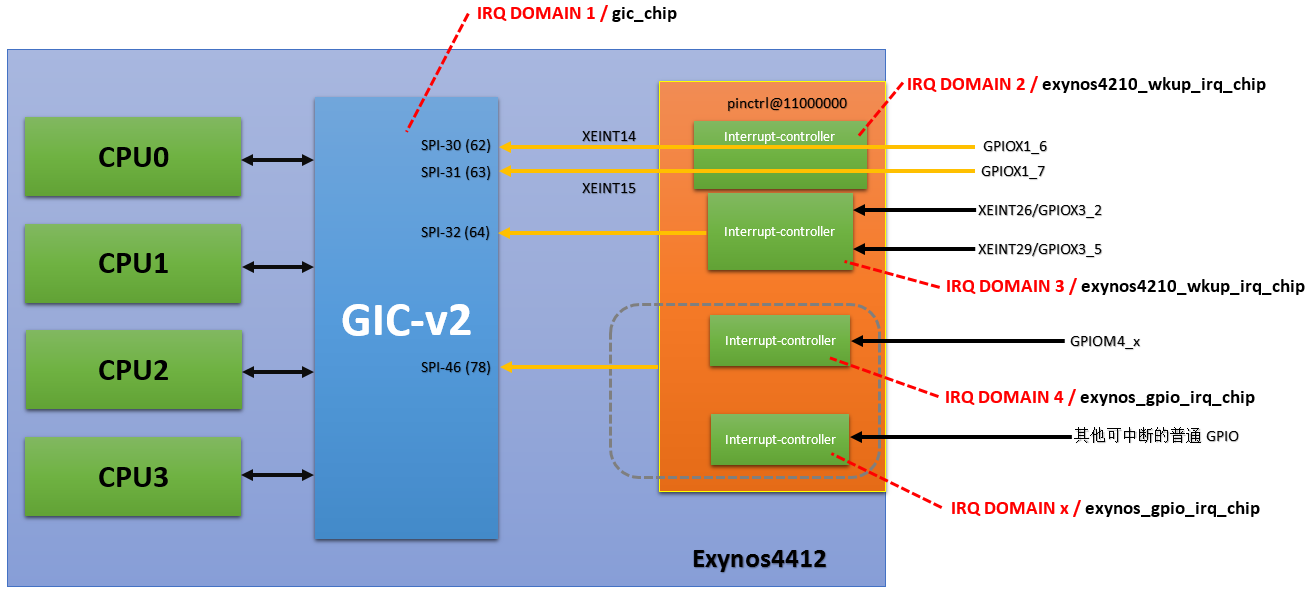
对于外部中断XEINT0-15,每一个都对应的SPI中断,但是XEINT16-31共享了同一个SPI中断。这里引脚上产生中断后,会直接通知GIC,然后GIC会通过irq或者firq触发某个CPU中断。
对于其他的pinctrl@11000000中的其他普通的GPIO来说,它们产生中断后,并没有直接通知GIC,而是先通知pinctrl@11000000,然后pinctrl@11000000再通过SPI-46通知GIC,然后GIC会通过irq或者firq触发某个CPU中断。
其中涉及到了多个irq domain, irq domain存放的的hwirq(来自硬件寄存器)到virq(逻辑中断号,全局唯一)的映射。每一个irq_domain都对应一个irq_chip,irq_chip是kernel对中断控制器的软件抽象。
第二部分 irq_domain
对于每个interrupt controller都可以连接若干个外设的中断请求(我们称之interrupt source),interrupt controller会对连接其上的interrupt source(根据其在Interrupt controller中物理特性)进行编号(也就是HW interrupt ID了)。但这个编号仅仅限制在本interrupt controller范围内。
struct irq_domain {
struct list_head link; ----用于将irq_domain连接到全局链表irq_domain_list中
const char *name; ----irq_domain的名称
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops; ----callback函数
void *host_data;
/* Optional data */
struct device_node *of_node; ----对应的interrupt controller的device node
struct irq_domain_chip_generic *gc; ---generic irq chip的概念,本文暂不描述
/* reverse map data. The linear map gets appended to the irq_domain */
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max; ----该domain中最大的那个HW interrupt ID
unsigned int revmap_direct_max_irq; ----
unsigned int revmap_size; ---线性映射的size,for Radix Tree map和no map,该值等于0
struct radix_tree_root revmap_tree; ----Radix Tree map使用到的radix tree root node
unsigned int linear_revmap[]; -----线性映射使用的lookup table
};
linux内核中,所有的irq domain被挂入一个全局链表,链表头定义如下:
static LIST_HEAD(irq_domain_list);
- 向系统注册irq domain
(1) 线性映射。其实就是一个lookup table,HW interrupt ID作为index,通过查表可以获取对应的IRQ number。
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_linear(struct device_node *of_node,
unsigned int size,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), size, size, 0, ops, host_data);
}
struct irq_domain *__irq_domain_add(struct fwnode_handle *fwnode, int size,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_max, int direct_max,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
struct device_node *of_node = to_of_node(fwnode);
struct irq_domain *domain;
// 分配1个irq_domain结构体,多了 (sizeof(unsigned int) * size)用于最后1个成员linear_revmap
domain = kzalloc_node(sizeof(*domain) + (sizeof(unsigned int) * size),
GFP_KERNEL, of_node_to_nid(of_node));
of_node_get(of_node);
// 填充 此 irq_domain结构体
INIT_RADIX_TREE(&domain->revmap_tree, GFP_KERNEL);
domain->ops = ops;
domain->host_data = host_data;
domain->fwnode = fwnode;
domain->hwirq_max = hwirq_max;
domain->revmap_size = size;
domain->revmap_direct_max_irq = direct_max;
irq_domain_check_hierarchy(domain);
mutex_lock(&irq_domain_mutex);
list_add(&domain->link, &irq_domain_list); // 将此domain结构体加入到irq_domain_list
mutex_unlock(&irq_domain_mutex);
return domain;
}
(2) Radix Tree map。建立一个Radix Tree来维护HW interrupt ID到IRQ number映射关系。HW interrupt ID作为lookup key,在Radix Tree检索到IRQ number。内核中使用Radix Tree map的只有powerPC和MIPS的硬件平台。
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_tree(struct device_node *of_node,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), 0, ~0, 0, ops, host_data);
}
(3) no map 。 不需映射,直接把IRQ number写入HW interrupt ID配置寄存器,生成的HW interrupt ID就是IRQ number,也就不需要进行mapping了
static inline struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_nomap(struct device_node *of_node,
unsigned int max_irq,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
return __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), 0, max_irq, max_irq, ops, host_data);
}
2、为irq domain创建映射
向系统注册一个irq domain后,具体HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的映射关系都是空的,因此,具体各个irq domain如何管理映射所需要的database还是需要建立的。
(1)irq_create_mapping:以irq domain和HW interrupt ID为参数,返回IRQ number(这个IRQ number是动态分配的)。
unsigned int irq_create_mapping(struct irq_domain *domain,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq) // 传入 domain 和 hwirq
{
struct device_node *of_node;
int virq;
/* Look for default domain if nececssary */
if (domain == NULL)
domain = irq_default_domain;
// 获得中断控制器的device node, 在注册irq domain的时候,domain的fwnode成员就指向了device node的fwnode,因此根据domain的fwnode成员也即device node 的fwnode 成员可以获得device node的地址
of_node = irq_domain_get_of_node(domain);
/* Check if mapping already exists */
virq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq);
// 动态分配1个虚拟中断号,从allocated_irqs位图中查找空闲的比特位,并分配1个或多个struct irq_desc结构体
/* Allocate a virtual interrupt number */
virq = irq_domain_alloc_descs(-1, 1, hwirq, of_node_to_nid(of_node), NULL);
// 建立映射关系
if (irq_domain_associate(domain, virq, hwirq)) {
irq_free_desc(virq);
return 0;
}
return virq;
}
驱动调用该函数的时候必须提供HW interrupt ID,而一般情况下,HW interrupt ID其实对具体的driver应该是不可见的,不过有些场景比较特殊,例如GPIO类型的中断,它的HW interrupt ID和GPIO有着特定的关系(如下图),driver知道自己使用那个GPIO,也就是知道使用哪一个HW interrupt ID了。
// 传入的viq为-1,cnt 为1 , hwirq 为 第三个参数
int irq_domain_alloc_descs(int virq, unsigned int cnt, irq_hw_number_t hwirq,
int node, const struct cpumask *affinity)
{
unsigned int hint;
if (virq >= 0) {
virq = __irq_alloc_descs(virq, virq, cnt, node, THIS_MODULE,
affinity);
} else {
hint = hwirq % nr_irqs;
if (hint == 0)
hint++;
virq = __irq_alloc_descs(-1, hint, cnt, node, THIS_MODULE,
affinity); // 分配虚拟中断号从hint 开始,说明是以hwirq开始寻找到第一个连续cnt为0的bit,返回其下标值即为virq
if (virq <= 0 && hint > 1) {
virq = __irq_alloc_descs(-1, 1, cnt, node, THIS_MODULE,
affinity);
}
}
return virq;
}
int __ref
__irq_alloc_descs(int irq, unsigned int from, unsigned int cnt, int node,
struct module *owner, const struct cpumask *affinity)
{
int start, ret;
if (irq >= 0) {
if (from > irq)
return -EINVAL;
from = irq;
} else {
/*
* For interrupts which are freely allocated the
* architecture can force a lower bound to the @from
* argument. x86 uses this to exclude the GSI space.
*/
from = arch_dynirq_lower_bound(from);
}
mutex_lock(&sparse_irq_lock);
start = bitmap_find_next_zero_area(allocated_irqs, IRQ_BITMAP_BITS,
from, cnt, 0);
ret = -EEXIST;
if (irq >=0 && start != irq)
goto unlock;
if (start + cnt > nr_irqs) {
ret = irq_expand_nr_irqs(start + cnt);
if (ret)
goto unlock;
}
ret = alloc_descs(start, cnt, node, affinity, owner); // return start,返回virq
unlock:
mutex_unlock(&sparse_irq_lock);
return ret;
}
int irq_domain_associate(struct irq_domain *domain, unsigned int virq,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq)
{
struct irq_data *irq_data = irq_get_irq_data(virq);
int ret;
mutex_lock(&irq_domain_mutex);
irq_data->hwirq = hwirq;
irq_data->domain = domain;
if (domain->ops->map) {
ret = domain->ops->map(domain, virq, hwirq); // 调用irq domain的map callback函数
/* If not already assigned, give the domain the chip's name */
if (!domain->name && irq_data->chip)
domain->name = irq_data->chip->name;
}
if (hwirq < domain->revmap_size) {
domain->linear_revmap[hwirq] = virq; // 填写线性映射lookup table的数据
} else {
mutex_lock(&revmap_trees_mutex);
radix_tree_insert(&domain->revmap_tree, hwirq, irq_data); // 向radix tree插入一个node
mutex_unlock(&revmap_trees_mutex);
}
mutex_unlock(&irq_domain_mutex);
irq_clear_status_flags(virq, IRQ_NOREQUEST); // 该IRQ已经可以申请了,因此clear相关flag
return 0;
}
(2)irq_create_strict_mappings。这个接口函数用来为一组HW interrupt ID建立映射。具体函数的原型定义如下:
int irq_create_strict_mappings(struct irq_domain *domain, unsigned int irq_base,
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_base, int count)
{
struct device_node *of_node;
int ret;
of_node = irq_domain_get_of_node(domain);
ret = irq_alloc_descs(irq_base, irq_base, count,
of_node_to_nid(of_node));
if (unlikely(ret < 0))
return ret;
irq_domain_associate_many(domain, irq_base, hwirq_base, count);
return 0;
}
(3)irq_of_parse_and_map。利用device tree进行映射关系的建立。具体函数的原型定义如下:
unsigned int irq_of_parse_and_map(struct device_node *dev, int index)
{
struct of_phandle_args oirq;
if (of_irq_parse_one(dev, index, &oirq)) // 获得interrupts的第index个中断参数,并封装到oirq中
return 0;
return irq_create_of_mapping(&oirq); // 创建映射
}
of_irq_parse_one的用法实例:
i2c0: i2c@5a800000
{
interrupts = <GIC_SPI 220 IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH>;
interrupt-parent = <&gic>;
};
解析的目的是初始化struct of_phandle_args结构体,该结构体定义如下:
struct of_phandle_args
{
struct device_node *np; // 指向了外设对应的interrupt controller的device node
int args_count; // interrupt-controller的#interrupt-cells的值
uint32_t args[MAX_PHANDLE_ARGS]; // 具体的interrupt相当属性的定义
};
解析的结果为:
out_irq->np = interrupt-parent = gic node
out_irq->args[0] = GIC_SPI;
out_irq->args[1] = 硬件中断号 = 220
out_irq->args[2] = 中断触发类型 = IRQ_TYPE_LEVEL_HIGH
unsigned int irq_create_of_mapping(struct of_phandle_args *irq_data)
{
struct irq_fwspec fwspec;
of_phandle_args_to_fwspec(irq_data, &fwspec); // 将解析到的 struct of_phandle_args *irq_data中的元素赋予fwspec
return irq_create_fwspec_mapping(&fwspec);
}
static void of_phandle_args_to_fwspec(struct of_phandle_args *irq_data,
struct irq_fwspec *fwspec)
{
int i;
fwspec->fwnode = irq_data->np ? &irq_data->np->fwnode : NULL;
fwspec->param_count = irq_data->args_count;
for (i = 0; i < irq_data->args_count; i++)
fwspec->param[i] = irq_data->args[i];
}
unsigned int irq_create_fwspec_mapping(struct irq_fwspec *fwspec)
{
struct irq_domain *domain;
struct irq_data *irq_data;
irq_hw_number_t hwirq;
unsigned int type = IRQ_TYPE_NONE;
int virq;
// 根据中断控制器的device_node找到所对应的irq domain,在GIC驱动注册irq domian的时候, 会将irq_domain的fwnode设置为中断控制器的device_node的fwnode成员
if (fwspec->fwnode) {
domain = irq_find_matching_fwspec(fwspec, DOMAIN_BUS_WIRED);
if (!domain)
domain = irq_find_matching_fwspec(fwspec, DOMAIN_BUS_ANY);
} else {
domain = irq_default_domain;
}
// 解释、解析出中断属性 :interrupt ID 和 interrupt type
if (irq_domain_translate(domain, fwspec, &hwirq, &type))
return 0;
/*
* If we've already configured this interrupt,
* don't do it again, or hell will break loose.
*/
// 从这个irq domain查询看该hwirq之前是否已经映射过,一般情况下都没有
virq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq);
if (irq_domain_is_hierarchy(domain)) {
// 对于GIC的irq domain这样定义了alloc的domain来说,走这个分支
virq = irq_domain_alloc_irqs(domain, 1, NUMA_NO_NODE, fwspec);
if (virq <= 0)
return 0;
} else {
/* Create mapping */
virq = irq_create_mapping(domain, hwirq); // 其他没有定义irq_domain->ops->alloc的domain,走这个分支, 建立映射
if (!virq)
return virq;
}
// struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(irq); return &desc->irq_data
irq_data = irq_get_irq_data(virq);
/* Store trigger type */
irqd_set_trigger_type(irq_data, type); // 如果有需要,调用irq_set_irq_type函数设定trigger type
return virq;
}
// 给定 fwspec,遍历irq_domain_list 链表找到对应的domain
struct irq_domain *irq_find_matching_fwspec(struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
enum irq_domain_bus_token bus_token)
{
struct irq_domain *h, *found = NULL;
struct fwnode_handle *fwnode = fwspec->fwnode;
int rc;
mutex_lock(&irq_domain_mutex);
list_for_each_entry(h, &irq_domain_list, link) { // 实 头 虚
if (h->ops->select && fwspec->param_count)
rc = h->ops->select(h, fwspec, bus_token); // 通过domain中的select 回调函数来找到对应的domian
else if (h->ops->match)
rc = h->ops->match(h, to_of_node(fwnode), bus_token); // 通过domain中的match回调函数来找到对应的domian
else
rc = ((fwnode != NULL) && (h->fwnode == fwnode) &&
((bus_token == DOMAIN_BUS_ANY) ||
(h->bus_token == bus_token)));
if (rc) {
found = h;
break;
}
}
mutex_unlock(&irq_domain_mutex);
return found; // 返回对应的irq_domain的指针
}
static int irq_domain_translate(struct irq_domain *d,
struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
irq_hw_number_t *hwirq, unsigned int *type)
{
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN_HIERARCHY
// 对于GIC的irq domain来说,会调用d->ops->translate(d, fwspec, hwirq, type)
// 也就是gic_irq_domain_translate
if (d->ops->translate)
return d->ops->translate(d, fwspec, hwirq, type); // 对于没有定义translate的irq_domain 会调用d->ops->xlate
#endif
if (d->ops->xlate)
return d->ops->xlate(d, to_of_node(fwspec->fwnode),
fwspec->param, fwspec->param_count,
hwirq, type);
/* If domain has no translation, then we assume interrupt line */
*hwirq = fwspec->param[0];
return 0;
}
static int gic_irq_domain_translate(struct irq_domain *d,
struct irq_fwspec *fwspec,
unsigned long *hwirq,
unsigned int *type)
{
if (is_of_node(fwspec->fwnode)) {
if (fwspec->param_count < 3) // 检查描述中断的参数个数是否合法
return -EINVAL;
/* Get the interrupt number and add 16 to skip over SGIs */
// 这里加16的目的是跳过SGI中断,因为SGI用于CPU之间通信,不归中断子系统管
// GIC支持的中断中从0-15号属于SGI,16-32属于PPI,32-1020属于SPI
*hwirq = fwspec->param[1] + 16;
/*
* For SPIs, we need to add 16 more to get the GIC irq
* ID number
*/
// 描述GIC中断的三个参数中第一个表示中断种类,0表示的是SPI,非0表示PPI
// 这里加16的意思是跳过PPI
// 第二个参数表示某种类型的中断(PPI or SPI)中的偏移量(从0开始)
if (!fwspec->param[0])
*hwirq += 16; // 如果是SPI类型的中断,再加16
// 第三个参数表示的中断的类型,如上升沿、下降沿或者高低电平触发
*type = fwspec->param[2] & IRQ_TYPE_SENSE_MASK;
return 0;
}
if (is_fwnode_irqchip(fwspec->fwnode)) {
if(fwspec->param_count != 2)
return -EINVAL;
// 返回硬件中断号和中断类型
*hwirq = fwspec->param[0];
*type = fwspec->param[1];
return 0;
}
return -EINVAL;
}
int __irq_domain_alloc_irqs(struct irq_domain *domain, int irq_base,
unsigned int nr_irqs, int node, void *arg,
bool realloc, const struct cpumask *affinity)
{
int i, ret, virq;
if (realloc && irq_base >= 0) {
virq = irq_base;
} else {
// 全局变量allocated_irqs从低位到高位第一个为0的位的位号
// 然后将allocated_irqs的第virq位置为1, 然后会为这个virq分配一个irq_desc, virq会存放到irq_desc的irq_data.irq中
// 最后将这个irq_desc存放到irq_desc_tree中,以virq为key,函数irq_to_desc就是以virq为key,查询irq_desc_tree 迅速定位到irq_desc
virq = irq_domain_alloc_descs(irq_base, nr_irqs, 0, node, affinity);
return virq;
}
}
if (irq_domain_alloc_irq_data(domain, virq, nr_irqs)) { // 会根据virq获得对应的irq_desc,然后将domain赋值给irq_desc->irq_data->domain
pr_debug("cannot allocate memory for IRQ%dn", virq);
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out_free_desc;
}
mutex_lock(&irq_domain_mutex);
ret = irq_domain_alloc_irqs_recursive(domain, virq, nr_irqs, arg); // 这个函数会调用gic irq domain的domain->ops->alloc,即gic_irq_domain_alloc
for (i = 0; i < nr_irqs; i++)
irq_domain_insert_irq(virq + i); // 将virq跟hwirq的映射关系存放到irq domain中,这样就可以通过hwirq在该irq_domain中快速找到virq
mutex_unlock(&irq_domain_mutex);
return virq;
out_free_irq_data:
irq_domain_free_irq_data(virq, nr_irqs);
out_free_desc:
irq_free_descs(virq, nr_irqs);
return ret;
}
int irq_domain_alloc_irqs_recursive(struct irq_domain *domain,
unsigned int irq_base,
unsigned int nr_irqs, void *arg)
{
int ret = 0;
struct irq_domain *parent = domain->parent;
bool recursive = irq_domain_is_auto_recursive(domain);
BUG_ON(recursive && !parent);
if (recursive)
ret = irq_domain_alloc_irqs_recursive(parent, irq_base,
nr_irqs, arg); // 递归调用和映射
if (ret < 0)
return ret;
ret = domain->ops->alloc(domain, irq_base, nr_irqs, arg); //进行硬件中断号和软件中断号的映射
if (ret < 0 && recursive)
irq_domain_free_irqs_recursive(parent, irq_base, nr_irqs);
return ret;
}
3、irq domain的low level 操作函数
以GIC irq domain 为例
// 此函数是 gic domain 的操作函数,随gic domain 注册进内核
static int gic_irq_domain_alloc(struct irq_domain *domain, unsigned int virq,
unsigned int nr_irqs, void *arg)
{
int i, ret;
irq_hw_number_t hwirq;
unsigned int type = IRQ_TYPE_NONE;
struct irq_fwspec *fwspec = arg;
ret = gic_irq_domain_translate(domain, fwspec, &hwirq, &type);
for (i = 0; i < nr_irqs; i++)
gic_irq_domain_map(domain, virq + i, hwirq + i);
return 0;
}
static int gic_irq_domain_map(struct irq_domain *d, unsigned int irq,
irq_hw_number_t hw)
{
struct gic_chip_data *gic = d->host_data;
if (hw < 32) { // PPI类型的中断(hwirq<32)
irq_set_percpu_devid(irq);
irq_domain_set_info(d, irq, hw, &gic->chip, d->host_data,
handle_percpu_devid_irq, NULL, NULL); // 将hwirq存放到irq_desc的irq_data.hwirq, 将irq chip存放到irq_desc的irq_data.chip, 将irq_desc的handle_irq设置为handle_percpu_devid_irq
irq_set_status_flags(irq, IRQ_NOAUTOEN);
} else { // SPI类型的中断
irq_domain_set_info(d, irq, hw, &gic->chip, d->host_data,
handle_fasteoi_irq, NULL, NULL); // 将hwirq存放到irq_desc的irq_data.hwirq, 将irq chip存放到irq_desc的irq_data.chip,将irq_desc的handle_irq设置为handle_fasteoi_irq
irq_set_probe(irq);
}
return 0;
}
- Mapping DB的建立
在machine driver初始化的时候会调用of_irq_init函数,在该函数中会扫描所有interrupt controller的节点,并调用适合的interrupt controller driver进行初始化,向系统增加irq domain。
首先初始化root,然后first level,second level,最后是leaf node。在各个driver初始化的过程中,创建映射。将使用以上介绍的irq_domain的mapping 函数。
(1)GIC的driver代码为例。
IRQCHIP_DECLARE(cortex_a9_gic, "arm,cortex-a9-gic", gic_of_init);
IRQCHIP_DECLARE宏会定义出一个存放于内核镜像__irqchip_of_table段的__of_table_cortex_a9_gic,gic_of_init被赋值给__of_table_cortex_a9_gic->data,在kernel启动时平台代码会遍历__irqchip_of_table,按照interrupt controller的连接关系从root开始,依次初始化每一个interrupt controller,此时gic_of_init会被调用。
int __init
gic_of_init(struct device_node *node, struct device_node *parent)
{
struct gic_chip_data *gic;
int irq, ret;
gic = &gic_data[gic_cnt];
ret = gic_of_setup(gic, node);
/*
* Disable split EOI/Deactivate if either HYP is not available
* or the CPU interface is too small.
*/
if (gic_cnt == 0 && !gic_check_eoimode(node, &gic->raw_cpu_base))
static_key_slow_dec(&supports_deactivate);
ret = __gic_init_bases(gic, -1, &node->fwnode);
if (!gic_cnt) {
gic_init_physaddr(node);
gic_of_setup_kvm_info(node);
}
if (parent) {
irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(node, 0);
gic_cascade_irq(gic_cnt, irq);
}
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_ARM_GIC_V2M))
gicv2m_init(&node->fwnode, gic_data[gic_cnt].domain);
gic_cnt++;
return 0;
}
static int __init __gic_init_bases(struct gic_chip_data *gic,
int irq_start,
struct fwnode_handle *handle)
{
char *name;
int i, ret;
if (gic == &gic_data[0]) {
/*
* Initialize the CPU interface map to all CPUs.
* It will be refined as each CPU probes its ID.
* This is only necessary for the primary GIC.
*/
for (i = 0; i < NR_GIC_CPU_IF; i++)
gic_cpu_map[i] = 0xff;
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
set_smp_cross_call(gic_raise_softirq); // 触发SGI中断,用于CPU之间通信
#endif
cpuhp_setup_state_nocalls(CPUHP_AP_IRQ_GIC_STARTING,
"AP_IRQ_GIC_STARTING",
gic_starting_cpu, NULL);
set_handle_irq(gic_handle_irq); //设置handle_arch_irq为gic_handle_irq。在kernel发生中断后,会跳转到汇编代码entry-armv.S中__irq_svc处,进而调用handle_arch_irq,从而进入GIC驱动,进行后续的中断处理
if (static_key_true(&supports_deactivate))
pr_info("GIC: Using split EOI/Deactivate moden");
}
if (static_key_true(&supports_deactivate) && gic == &gic_data[0]) {
name = kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "GICv2");
gic_init_chip(gic, NULL, name, true);
} else {
name = kasprintf(GFP_KERNEL, "GIC-%d", (int)(gic-&gic_data[0]));
gic_init_chip(gic, NULL, name, false);
}
ret = gic_init_bases(gic, irq_start, handle);
if (ret)
kfree(name);
return ret;
}
static int gic_init_bases(struct gic_chip_data *gic, int irq_start,
struct fwnode_handle *handle)
{
irq_hw_number_t hwirq_base;
int gic_irqs, irq_base, ret;
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GIC_NON_BANKED) && gic->percpu_offset) {
/* Frankein-GIC without banked registers... */
unsigned int cpu;
gic->dist_base.percpu_base = alloc_percpu(void __iomem *);
gic->cpu_base.percpu_base = alloc_percpu(void __iomem *);
for_each_possible_cpu(cpu) {
u32 mpidr = cpu_logical_map(cpu);
u32 core_id = MPIDR_AFFINITY_LEVEL(mpidr, 0);
unsigned long offset = gic->percpu_offset * core_id;
*per_cpu_ptr(gic->dist_base.percpu_base, cpu) =
gic->raw_dist_base + offset;
*per_cpu_ptr(gic->cpu_base.percpu_base, cpu) =
gic->raw_cpu_base + offset;
}
gic_set_base_accessor(gic, gic_get_percpu_base);
} else {
/* Normal, sane GIC... */
WARN(gic->percpu_offset,
"GIC_NON_BANKED not enabled, ignoring %08x offset!",
gic->percpu_offset);
gic->dist_base.common_base = gic->raw_dist_base;
gic->cpu_base.common_base = gic->raw_cpu_base;
gic_set_base_accessor(gic, gic_get_common_base);
}
/*
* Find out how many interrupts are supported.
* The GIC only supports up to 1020 interrupt sources.
*/
// 计算这个GIC模块所支持的中断个数gic_irqs,然后创建一个linear irq domain。此时尚未分配virq,也没有建立hwirq跟virq的映射
gic_irqs = readl_relaxed(gic_data_dist_base(gic) + GIC_DIST_CTR) & 0x1f;
gic_irqs = (gic_irqs + 1) * 32;
if (gic_irqs > 1020)
gic_irqs = 1020;
gic->gic_irqs = gic_irqs;
// 在初始化的时候既没有给hwirq分配对应的virq,也没有建立二者之间的映射,这部分工作会到后面有人引用GIC上的某个中断时再分配和建立。
if (handle) { /* DT/ACPI */
gic->domain = irq_domain_create_linear(handle, gic_irqs,
&gic_irq_domain_hierarchy_ops,
gic);
} else { /* Legacy support */
/*
* For primary GICs, skip over SGIs.
* For secondary GICs, skip over PPIs, too.
*/
if (gic == &gic_data[0] && (irq_start & 31) > 0) {
hwirq_base = 16;
if (irq_start != -1)
irq_start = (irq_start & ~31) + 16;
} else {
hwirq_base = 32;
}
gic_irqs -= hwirq_base; /* calculate # of irqs to allocate */
irq_base = irq_alloc_descs(irq_start, 16, gic_irqs,
numa_node_id());
if (irq_base < 0) {
WARN(1, "Cannot allocate irq_descs @ IRQ%d, assuming pre-allocatedn",
irq_start);
irq_base = irq_start;
}
gic->domain = irq_domain_add_legacy(NULL, gic_irqs, irq_base,
hwirq_base, &gic_irq_domain_ops, gic);
}
gic_dist_init(gic);
ret = gic_cpu_init(gic);
if (ret)
goto error;
ret = gic_pm_init(gic);
if (ret)
goto error;
return 0;
error:
if (IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_GIC_NON_BANKED) && gic->percpu_offset) {
free_percpu(gic->dist_base.percpu_base);
free_percpu(gic->cpu_base.percpu_base);
}
return ret;
}
许多嵌入式系统单板支持文件对中断号使用#define 定义,此时虚拟中断号不可被动态分配,应当使用legacy(遗产)映射。中断号可通过在hwirq上加固定offset来实现。缺点是需要中断控制器来管理中断分配,并且对于每个hwirq,即使未使用,也要求其irq_desc已分配。
在GIC的代码中没有调用标准的注册irq domain的接口函数。在旧的linux kernel中,在arch/arm目录充斥了很多board specific的代码,其中定义了各个device使用的资源,包括IRQ资源。HW interrupt ID和IRQ number的关系是固定的。一旦关系固定,我们就可以在interupt controller的代码中创建这些映射关系。
struct irq_domain *irq_domain_add_legacy(struct device_node *of_node,
unsigned int size,
unsigned int first_irq,
irq_hw_number_t first_hwirq,
const struct irq_domain_ops *ops,
void *host_data)
{
struct irq_domain *domain;
domain = __irq_domain_add(of_node_to_fwnode(of_node), first_hwirq + size,
first_hwirq + size, 0, ops, host_data); // 注册 irq_domain
if (domain)
irq_domain_associate_many(domain, first_irq, first_hwirq, size); // 创建映射
return domain;
}
(2) irq_domain 创建映射实例 (device node转化为platform_device)
of_platform_populate (drivers/of/platform.c)
---> of_platform_bus_create
---> of_platform_device_create_pdata
---> of_device_alloc
struct platform_device *of_device_alloc(struct device_node *np,
const char *bus_id,
struct device *parent)
{
struct platform_device *dev;
int rc, i, num_reg = 0, num_irq;
struct resource *res, temp_res;
dev = platform_device_alloc("", -1);
/* count the io and irq resources */
while (of_address_to_resource(np, num_reg, &temp_res) == 0)
num_reg++;
num_irq = of_irq_count(np); // 统计这个节点的interrupts属性中描述了几个中断
/* Populate the resource table */
if (num_irq || num_reg)
res = kzalloc(sizeof(*res) * (num_irq + num_reg), GFP_KERNEL);
dev->num_resources = num_reg + num_irq;
dev->resource = res;
for (i = 0; i < num_reg; i++, res++) {
// struct platform_device *op = of_find_device_by_node(node);
// memcpy(r, &op->archdata.resource[index], sizeof(*r));
// 由np节点对应的平台设备,并将其内部的resource赋予res结构体
rc = of_address_to_resource(np, i, res);
WARN_ON(rc);
}
// 知道interrupts中描述了几个中断后,这个函数开始将这些中断转换为resource
if (of_irq_to_resource_table(np, res, num_irq) != num_irq)
pr_debug("not all legacy IRQ resources mapped for %sn",
np->name);
}
dev->dev.of_node = of_node_get(np);
dev->dev.fwnode = &np->fwnode;
dev->dev.parent = parent ? : &platform_bus;
if (bus_id)
dev_set_name(&dev->dev, "%s", bus_id);
else
of_device_make_bus_id(&dev->dev);
return dev;
}
/**
* of_irq_count - Count the number of IRQs a node uses
* @dev: pointer to device tree node
*/
int of_irq_count(struct device_node *dev)
{
struct of_phandle_args irq;
int nr = 0;
// nr表示的是index,of_irq_parse_one每次成功返回,都表示成功从interrupts属性中解析到了第nr个中断,同时将关于这个中断的信息存放到struct of_phandle_args irq中
while (of_irq_parse_one(dev, nr, &irq) == 0) //解析第nr个中断
nr++;
return nr;
}
/**
* of_irq_to_resource_table - Fill in resource table with node's IRQ info
* @dev: pointer to device tree node
* @res: array of resources to fill in
* @nr_irqs: the number of IRQs (and upper bound for num of @res elements)
*
* Returns the size of the filled in table (up to @nr_irqs).
*/
int of_irq_to_resource_table(struct device_node *dev, struct resource *res,
int nr_irqs)
{
int i;
for (i = 0; i < nr_irqs; i++, res++)
if (!of_irq_to_resource(dev, i, res)) // 第二个参数i表示的是index,即interrupts属性中的第i个中断
break;
return i;
}
/**
* of_irq_to_resource - Decode a node's IRQ and return it as a resource
* @dev: pointer to device tree node
* @index: zero-based index of the irq
* @r: pointer to resource structure to return result into.
*/
int of_irq_to_resource(struct device_node *dev, int index, struct resource *r)
{
int irq = irq_of_parse_and_map(dev, index); // 返回interrupts中第index个hwirq中断映射到的virq,因此驱动从platform_get_resource获取到的中断信息是虚拟中断号,而寄存器信息则需ioremap
/* Only dereference the resource if both the
* resource and the irq are valid. */
if (r && irq) {
const char *name = NULL;
memset(r, 0, sizeof(*r));
/*
* Get optional "interrupt-names" property to add a name
* to the resource.
*/
of_property_read_string_index(dev, "interrupt-names", index,
&name);
r->start = r->end = irq;
r->flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ | irqd_get_trigger_type(irq_get_irq_data(irq)); // 这个中断的属性,如上升沿还是下降沿触发
r->name = name ? name : of_node_full_name(dev);
}
return irq;
}
第三部分 中断触发和处理
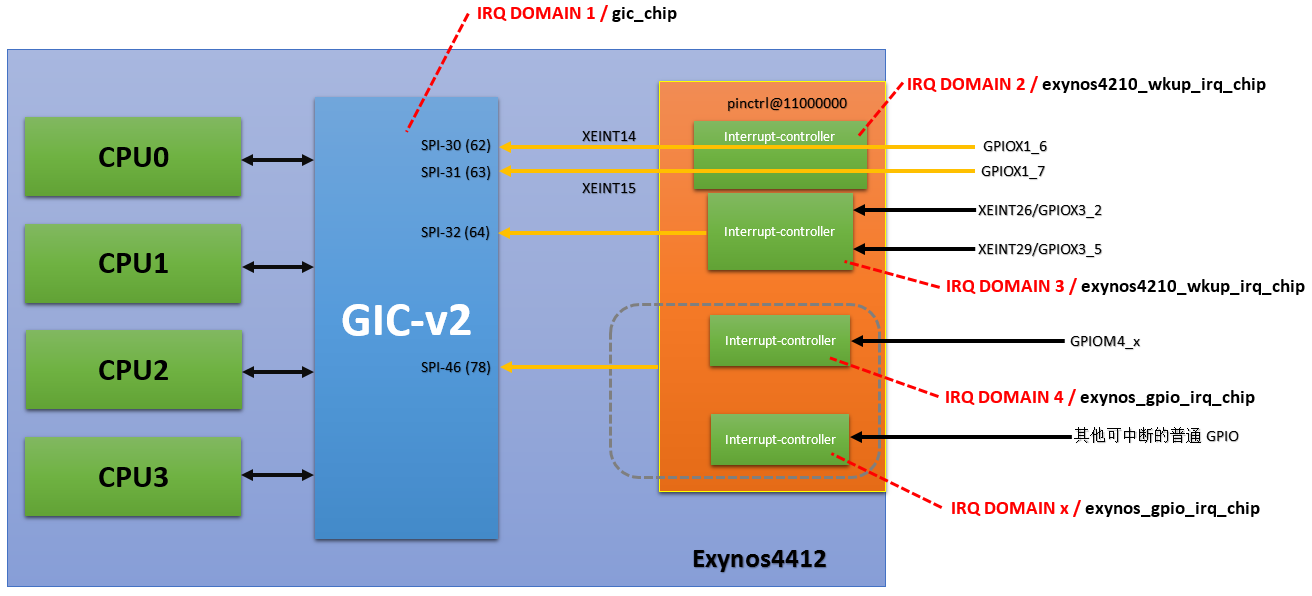
XEINT15: 这个中断直接对应到了GIC模块上面的SPI-31
XEINT26: XEINT24-XEINT31共用了GIC模块上面的SPI-32,在处理过程中会涉及到demux
GPM4-0:: 是个普通的可以产生中断的gpio,在上图中的pinctrl中具备这个功能的gpio共享的是pinctrl在GIC上面的中断SPI-46
Exynos4412中断控制器包括160个中断控制源,这些中断源来自软中断(SGI),私有外部中断(PPI),公共外部中断(SPI)。
Exynos4412采用GIC中断控制器,主要是因为Contex-A9 是多核处理器,GIC(Generic Interrupt Controller)通用中断控制器用来选择使用哪个CPU接口,具体主要有两个功能:
1)分配器:设置一个开关,是否接收外部中断源;为该中断源选择CPU接口;
2)CPU接口:设置一个开关,是否接受该中断源请求;
在irq中断发生后,PC指针会跳转到中断向量表(起始地址0xffff0000)中负责处理irq中断的位置:
在vector_irq中会跳转到irq_handler,irq_handler其实是个宏,它完成的操作是将PC赋值为handle_arch_irq的地址。
在GIC驱动中会将handle_arch_irq设置为gic_handle_irq,这样GIC就接管了剩下的工作。
static void __exception_irq_entry gic_handle_irq(struct pt_regs *regs)
{
u32 irqstat, irqnr;
struct gic_chip_data *gic = &gic_data[0];
void __iomem *cpu_base = gic_data_cpu_base(gic); // cpu interface的基地址
do {
// GIC_CPU_INTACK是0x0c,参考4412的datasheet的第9节可以知道, ICCIAR_CPUn的[9:0]存放的是发生中断的中断号 所以,irqnr中就是发生中断的那个中断号,当然这个获得的是hwirq,而不是virq。对于XEINT15,hwirq就是SPI-31,由于是跟PPI和SGI统一编号,就是63
irqstat = readl_relaxed_no_log(cpu_base + GIC_CPU_INTACK);
irqnr = irqstat & GICC_IAR_INT_ID_MASK; // 中断触发几个时钟周期之后,CPU interface 模块会更新GICC_IAR寄存器的值
if (likely(irqnr > 15 && irqnr < 1020)) { // PPI和SPI的范围是16到1020
if (static_key_true(&supports_deactivate))
writel_relaxed_no_log(irqstat,
cpu_base + GIC_CPU_EOI);
handle_domain_irq(gic->domain, irqnr, regs);
uncached_logk(LOGK_IRQ, (void *)(uintptr_t)irqnr);
continue;
}
// SGI中断号的范围是0到15, SGI用于CPU之间通讯用的,当然只有SMP才有可能
if (irqnr < 16) {
writel_relaxed_no_log(irqstat, cpu_base + GIC_CPU_EOI);
if (static_key_true(&supports_deactivate))
writel_relaxed_no_log(irqstat,
cpu_base + GIC_CPU_DEACTIVATE);
#ifdef CONFIG_SMP
/*
* Ensure any shared data written by the CPU sending
* the IPI is read after we've read the ACK register
* on the GIC.
*
* Pairs with the write barrier in gic_raise_softirq
*/
smp_rmb();
handle_IPI(irqnr, regs); // 处理SGI中断用的,不归kernel的中断子系统管理
#endif
uncached_logk(LOGK_IRQ, (void *)(uintptr_t)irqnr);
continue;
}
break;
} while (1);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_HANDLE_DOMAIN_IRQ
/**
* __handle_domain_irq - Invoke the handler for a HW irq belonging to a domain
* @domain: The domain where to perform the lookup
* @hwirq: The HW irq number to convert to a logical one
* @lookup: Whether to perform the domain lookup or not
* @regs: Register file coming from the low-level handling code
*
* Returns: 0 on success, or -EINVAL if conversion has failed
*/
int __handle_domain_irq(struct irq_domain *domain, unsigned int hwirq,
bool lookup, struct pt_regs *regs)
{
struct pt_regs *old_regs = set_irq_regs(regs);
unsigned int irq = hwirq;
int ret = 0;
irq_enter();
#ifdef CONFIG_IRQ_DOMAIN
if (lookup)
irq = irq_find_mapping(domain, hwirq); // 在gic的irq domain中利用从寄存器中得到的hwirq, 查询得到virq
#endif
/*
* Some hardware gives randomly wrong interrupts. Rather
* than crashing, do something sensible.
*/
if (unlikely(!irq || irq >= nr_irqs)) {
ack_bad_irq(irq);
ret = -EINVAL;
} else {
generic_handle_irq(irq);
}
irq_exit();
set_irq_regs(old_regs);
return ret;
}
#endif
/**
* generic_handle_irq - Invoke the handler for a particular irq
* @irq: The irq number to handle
*/
int generic_handle_irq(unsigned int irq)
{
struct irq_desc *desc = irq_to_desc(irq); // 根据virq,查询irq_desc_tree,就可以迅速定位到之前分配的irq_desc
generic_handle_irq_desc(desc);
return 0;
}
static inline void generic_handle_irq_desc(struct irq_desc *desc)
{
desc->handle_irq(desc);
}
XEINT26
有了分析XEINT15的基础,我们只需要注意不同点。
前面我们知道,XEINT16-31共享了GIC上面的SPI-32,按照分析XEINT15的逻辑:
vector_irq
—> irq_handler
—> gic_handle_irq
—> __handle_domain_irq
第四部分 中断线程化
正常流程下,handle_fasteoi_irq—>handle_irq_event—>irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS);—>handle_irq_event_percpu(desc, action);
—>硬中断—>线程化中断(需要的话)—>irqd_clear(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS);
/**
* request_threaded_irq - allocate an interrupt line
* @irq: Interrupt line to allocate
* @handler: Function to be called when the IRQ occurs.
* Primary handler for threaded interrupts
* If NULL and thread_fn != NULL the default
* primary handler is installed
* @thread_fn: Function called from the irq handler thread
* If NULL, no irq thread is created
* @irqflags: Interrupt type flags
* @devname: An ascii name for the claiming device
* @dev_id: A cookie passed back to the handler function
*
* This call allocates interrupt resources and enables the
* interrupt line and IRQ handling. From the point this
* call is made your handler function may be invoked. Since
* your handler function must clear any interrupt the board
* raises, you must take care both to initialise your hardware
* and to set up the interrupt handler in the right order.
*
* If you want to set up a threaded irq handler for your device
* then you need to supply @handler and @thread_fn. @handler is
* still called in hard interrupt context and has to check
* whether the interrupt originates from the device. If yes it
* needs to disable the interrupt on the device and return
* IRQ_WAKE_THREAD which will wake up the handler thread and run
* @thread_fn. This split handler design is necessary to support
* shared interrupts.
*
* Dev_id must be globally unique. Normally the address of the
* device data structure is used as the cookie. Since the handler
* receives this value it makes sense to use it.
*
* If your interrupt is shared you must pass a non NULL dev_id
* as this is required when freeing the interrupt.
*
* Flags:
*
* IRQF_SHARED Interrupt is shared
* IRQF_TRIGGER_* Specify active edge(s) or level
*
*/
int request_threaded_irq(unsigned int irq, irq_handler_t handler,
irq_handler_t thread_fn, unsigned long irqflags,
const char *devname, void *dev_id)
{
struct irqaction *action;
struct irq_desc *desc;
int retval;
if (irq == IRQ_NOTCONNECTED)
return -ENOTCONN;
/*
* Sanity-check: shared interrupts must pass in a real dev-ID,
* otherwise we'll have trouble later trying to figure out
* which interrupt is which (messes up the interrupt freeing
* logic etc).
*
* Also IRQF_COND_SUSPEND only makes sense for shared interrupts and
* it cannot be set along with IRQF_NO_SUSPEND.
*/
if (((irqflags & IRQF_SHARED) && !dev_id) || // 使用共享中断必须提供dev_id,通常根据dev_id查询设备寄存器来确定是哪个共享外设的中断。虽然只是一个外设产生的中断,linux kernel还是把所有共享的那些中断handler都逐个调用执行。为了让系统的performance不受影响,irqaction的callback函数必须在函数的最开始进行判断,是否是自己的硬件设备产生了中断(读取硬件的寄存器),如果不是,尽快的退出。
(!(irqflags & IRQF_SHARED) && (irqflags & IRQF_COND_SUSPEND)) ||
((irqflags & IRQF_NO_SUSPEND) && (irqflags & IRQF_COND_SUSPEND)))
return -EINVAL;
desc = irq_to_desc(irq); // 在过去,以IRQ number为index,从irq_desc这个全局数组中直接获取中断描述符。如果配置CONFIG_SPARSE_IRQ选项,则需要从radix tree中搜索。
if (!irq_settings_can_request(desc) || //判断中断描述符是否被标记为IRQ_NOREQUEST,它是系统预留的,外设不可以使用这些中断描述符。
WARN_ON(irq_settings_is_per_cpu_devid(desc))) // 设置了_IRQ_PER_CPU_DEVID标志位的中断描述符是预留给IRQF_PERCPU类型的中断,应该使用request_percpu_irq函数api注册
return -EINVAL;
if (!handler) {
if (!thread_fn) //如果handler 和 thread_fn 都没有则返回
return -EINVAL;
handler = irq_default_primary_handler; // 如果有 thread_fn 而无handler,则使用默认的irq_default_primary_handler,irq_default_primary_handler直接返回IRQ_WAKE_THREAD,表示要唤醒中断线程
}
如果有handler 而无 thread_fn,中断处理都是在primary handler中完成
action = kzalloc(sizeof(struct irqaction), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!action)
return -ENOMEM;
action->handler = handler;
action->thread_fn = thread_fn;
action->flags = irqflags;
action->name = devname;
action->dev_id = dev_id;
retval = irq_chip_pm_get(&desc->irq_data);
if (retval < 0) {
kfree(action);
return retval;
}
// 在内核中,有很多函数,有的是需要调用者自己加锁保护的,有些是不需要加锁保护的。对于这些场景,linux kernel采取了统一的策略:基本函数名字是一样的,只不过需要调用者自己加锁保护的那个函数需要增加__的前缀,例如内核有有下面两个函数:setup_irq和__setup_irq
chip_bus_lock(desc);
// desc->irq_data.chip->irq_bus_lock(&desc->irq_data);
// 大部分的interrupt controller并没有定义irq_bus_lock这个callback函数,因此chip_bus_lock这个函数对大多数的中断控制器而言是没有实际意义的。但是,有些interrupt controller是连接到慢速总线上的,例如一个i2c接口的IO expander芯片(这种芯片往往也提供若干有中断功能的GPIO,因此也是一个interrupt controller),在访问这种interrupt controller的时候需要lock住那个慢速bus(只能有一个client在使用I2C bus)。
retval = __setup_irq(irq, desc, action);
chip_bus_sync_unlock(desc);
if (retval) {
irq_chip_pm_put(&desc->irq_data);
kfree(action->secondary);
kfree(action);
}
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SHIRQ_FIXME
if (!retval && (irqflags & IRQF_SHARED)) {
/*
* It's a shared IRQ -- the driver ought to be prepared for it
* to happen immediately, so let's make sure....
* We disable the irq to make sure that a 'real' IRQ doesn't
* run in parallel with our fake.
*/
unsigned long flags;
disable_irq(irq);
local_irq_save(flags);
handler(irq, dev_id);
local_irq_restore(flags);
enable_irq(irq);
}
#endif
return retval;
}
/*
* Internal function to register an irqaction - typically used to
* allocate special interrupts that are part of the architecture.
*/
static int
__setup_irq(unsigned int irq, struct irq_desc *desc, struct irqaction *new)
{
struct irqaction *old, **old_ptr;
unsigned long flags, thread_mask = 0;
int ret, nested, shared = 0;
cpumask_var_t mask;
if (!desc)
return -EINVAL;
if (desc->irq_data.chip == &no_irq_chip) // 如果指向no_irq_chip,说明还未正确初始化中断控制器。对于GIC-V2中断控制器来说,它是在gic_irq_domain_alloc函数中就指定chip指针指向该中断控制器的struct irq_chip * gic_chip 数据结构
return -ENOSYS;
if (!try_module_get(desc->owner))
return -ENODEV;
new->irq = irq;
/*
* If the trigger type is not specified by the caller,
* then use the default for this interrupt.
*/
if (!(new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK))
new->flags |= irqd_get_trigger_type(&desc->irq_data);
/*
* Check whether the interrupt nests into another interrupt
* thread.
*/
nested = irq_settings_is_nested_thread(desc); // return desc->status_use_accessors & _IRQ_NESTED_THREAD;
if (nested) {
if (!new->thread_fn) {
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out_mput;
}
/*
* Replace the primary handler which was provided from
* the driver for non nested interrupt handling by the
* dummy function which warns when called.
*/
new->handler = irq_nested_primary_handler; // 替换primary handler,此handler只会打印一段日志
} else {
if (irq_settings_can_thread(desc)) { // return !(desc->status_use_accessors & _IRQ_NOTHREAD);
ret = irq_setup_forced_threading(new);
if (ret)
goto out_mput;
}
}
/*
* Create a handler thread when a thread function is supplied
* thread.
*/
if (new->thread_fn && !nested) {
ret = setup_irq_thread(new, irq, false); // 对没有嵌套的线程化中断创建1个内核线程,它是1个实时线程,调度策略为SCHED_FIFO,优先级是50. 使用get_task_struct(t)增加该线程的task_struct-->usage 计数,确保即使该内核线程异常退出了也不会释放task_struct,防止中断线程化的处理程序访问了空指针
if (ret)
goto out_mput;
if (new->secondary) {
ret = setup_irq_thread(new->secondary, irq, true);
if (ret)
goto out_thread;
}
}
if (!alloc_cpumask_var(&mask, GFP_KERNEL)) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto out_thread;
}
/*
* Drivers are often written to work w/o knowledge about the
* underlying irq chip implementation, so a request for a
* threaded irq without a primary hard irq context handler
* requires the ONESHOT flag to be set. Some irq chips like
* MSI based interrupts are per se one shot safe. Check the
* chip flags, so we can avoid the unmask dance at the end of
* the threaded handler for those.
*/
if (desc->irq_data.chip->flags & IRQCHIP_ONESHOT_SAFE)
new->flags &= ~IRQF_ONESHOT; // IRQCHIP_ONESHOT_SAFE表示该中断控制器不支持嵌套,即只支持 one shot,例如 MSI based interrupt ,因此 flag可以删掉驱动注册的IRQ_ONESHOT标志位。
/*
* The following block of code has to be executed atomically
*/
raw_spin_lock_irqsave(&desc->lock, flags);
old_ptr = &desc->action;
old = *old_ptr; // 指向desc-->action 指向的链表
if (old) {
/*
* Can't share interrupts unless both agree to and are
* the same type (level, edge, polarity). So both flag
* fields must have IRQF_SHARED set and the bits which
* set the trigger type must match. Also all must
* agree on ONESHOT.
*/
if (!((old->flags & new->flags) & IRQF_SHARED) ||
((old->flags ^ new->flags) & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK) ||
((old->flags ^ new->flags) & IRQF_ONESHOT))
goto mismatch;
/* All handlers must agree on per-cpuness */
if ((old->flags & IRQF_PERCPU) !=
(new->flags & IRQF_PERCPU))
goto mismatch;
/* add new interrupt at end of irq queue */
do {
/*
* Or all existing action->thread_mask bits,
* so we can find the next zero bit for this
* new action.
*/
thread_mask |= old->thread_mask; // struct irqaction 也有1个thread_mask位图成员,在共享中断中每个action有1个比特位来表示
old_ptr = &old->next;
old = *old_ptr;
} while (old); //循环遍历到这个链表尾
shared = 1; // old 不为空,说明之前已经有中断添加到中断描述符irq_desc中,即这是个共享的中断
}
/*
* Setup the thread mask for this irqaction for ONESHOT. For
* !ONESHOT irqs the thread mask is 0 so we can avoid a
* conditional in irq_wake_thread().
*/
if (new->flags & IRQF_ONESHOT) { //
/*
* Unlikely to have 32 resp 64 irqs sharing one line,
* but who knows.
*/
if (thread_mask == ~0UL) { // 如果thread_mask变量如果是全1,那么说明irqaction list上已经有了太多的irq action(大于32或者64,和具体系统和编译器相关)。如果没有满,那么通过ffz函数找到第一个为0的bit作为该irq action的thread bit mask。
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out_mask;
}
new->thread_mask = 1 << ffz(thread_mask);
} else if (new->handler == irq_default_primary_handler &&
!(desc->irq_data.chip->flags & IRQCHIP_ONESHOT_SAFE)) {
/*
如果是电平触发的中断,我们需要操作外设的寄存器才可以让那个asserted的电平信号消失,否则它会一直持续。一般,我们都是直接在primary中操作外设寄存器(slow bus类型的interrupt controller不行),尽早的clear interrupt,但是,对于irq_default_primary_handler,它仅仅是wakeup了threaded interrupt handler,并没有clear interrupt,这样,执行完了primary handler,外设中断仍然是asserted,一旦打开CPU中断,立刻触发下一次的中断,然后不断的循环。因此,如果注册中断的时候没有指定primary interrupt handler,并且没有设定IRQF_ONESHOT,那么系统是会报错的。当然,有一种情况可以豁免,当底层的irq chip是one shot safe的(IRQCHIP_ONESHOT_SAFE)
*/
pr_err("Threaded irq requested with handler=NULL and !ONESHOT for irq %dn",
irq);
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out_mask;
}
if (!shared) { // 非共享中断的情况
ret = irq_request_resources(desc);
init_waitqueue_head(&desc->wait_for_threads);
/* Setup the type (level, edge polarity) if configured: */
if (new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK) { // 设置中断类型
ret = __irq_set_trigger(desc,
new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK);
}
desc->istate &= ~(IRQS_AUTODETECT | IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED |
IRQS_ONESHOT | IRQS_WAITING);
irqd_clear(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS); // 清 IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS中断
if (new->flags & IRQF_PERCPU) {
irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_PER_CPU);
irq_settings_set_per_cpu(desc);
}
if (new->flags & IRQF_ONESHOT)
desc->istate |= IRQS_ONESHOT;
if (irq_settings_can_autoenable(desc))
irq_startup(desc, true);
else
/* Undo nested disables: */
desc->depth = 1;
/* Exclude IRQ from balancing if requested */
if (new->flags & IRQF_NOBALANCING) {
irq_settings_set_no_balancing(desc);
irqd_set(&desc->irq_data, IRQD_NO_BALANCING);
}
/* Set default affinity mask once everything is setup */
setup_affinity(desc, mask);
} else if (new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK) {
unsigned int nmsk = new->flags & IRQF_TRIGGER_MASK;
unsigned int omsk = irqd_get_trigger_type(&desc->irq_data);
if (nmsk != omsk)
/* hope the handler works with current trigger mode */
pr_warn("irq %d uses trigger mode %u; requested %un",
irq, omsk, nmsk);
}
*old_ptr = new; // 把新的中断action描述符new添加到中断描述符desc的链表中
irq_pm_install_action(desc, new);
/* Reset broken irq detection when installing new handler */
desc->irq_count = 0;
desc->irqs_unhandled = 0;
/*
* Check whether we disabled the irq via the spurious handler
* before. Reenable it and give it another chance.
*/
if (shared && (desc->istate & IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED)) {
desc->istate &= ~IRQS_SPURIOUS_DISABLED;
__enable_irq(desc);
}
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&desc->lock, flags);
/*
* Strictly no need to wake it up, but hung_task complains
* when no hard interrupt wakes the thread up.
*/
if (new->thread)
wake_up_process(new->thread); // new->thread = t,唤醒的传参是task_struct *类型,如果该中断被线程化,那么就唤醒该内核线程,每个中断1个线程而不是每个cpu 1个线程。
if (new->secondary)
wake_up_process(new->secondary->thread);
register_irq_proc(irq, desc);
new->dir = NULL;
register_handler_proc(irq, new);
free_cpumask_var(mask);
return 0;
mismatch:
if (!(new->flags & IRQF_PROBE_SHARED)) {
pr_err("Flags mismatch irq %d. %08x (%s) vs. %08x (%s)n",
irq, new->flags, new->name, old->flags, old->name);
#ifdef CONFIG_DEBUG_SHIRQ
dump_stack();
#endif
}
ret = -EBUSY;
out_mask:
raw_spin_unlock_irqrestore(&desc->lock, flags);
free_cpumask_var(mask);
out_thread:
if (new->thread) {
struct task_struct *t = new->thread;
new->thread = NULL;
kthread_stop(t);
put_task_struct(t);
}
if (new->secondary && new->secondary->thread) {
struct task_struct *t = new->secondary->thread;
new->secondary->thread = NULL;
kthread_stop(t);
put_task_struct(t);
}
out_mput:
module_put(desc->owner);
return ret;
}
static int irq_setup_forced_threading(struct irqaction *new)
{
if (!force_irqthreads) //系统配置了CONFIG_IRQ_FORCED_THREADING选项且内核启动参数包含"threadirqs"时,全局变量force_irqthreads会为true,表示系统支持强制中断线程化
return 0;
if (new->flags & (IRQF_NO_THREAD | IRQF_PERCPU | IRQF_ONESHOT))
return 0; // 如果注册的中断传入 new->flags & (IRQF_NO_THREAD | IRQF_PERCPU | IRQF_ONESHOT),也不符合中断线程化的要求; IRQF_PERCPU是一些特殊的中断,不是一般意义上的外设中断,不适合强制中断线程化
new->flags |= IRQF_ONESHOT; // 保证所有中断线程化的thread_fn都执行完成后才打开中断源
/*
* Handle the case where we have a real primary handler and a
* thread handler. We force thread them as well by creating a
* secondary action.
*/
if (new->handler != irq_default_primary_handler && new->thread_fn) {
/* Allocate the secondary action */
new->secondary = kzalloc(sizeof(struct irqaction), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!new->secondary)
return -ENOMEM;
new->secondary->handler = irq_forced_secondary_handler;
new->secondary->thread_fn = new->thread_fn;
new->secondary->dev_id = new->dev_id;
new->secondary->irq = new->irq;
new->secondary->name = new->name;
}
/* Deal with the primary handler */
set_bit(IRQTF_FORCED_THREAD, &new->thread_flags); // 设置thread_flags表明该中断已被强制中断线程化
new->thread_fn = new->handler; // 把原来primary handler 处理的函数弄到中断线程中运行
new->handler = irq_default_primary_handler; // return IRQ_WAKE_THREAD;
return 0;
}
*
* Oneshot interrupts keep the irq line masked until the threaded
* handler finished. unmask if the interrupt has not been disabled and
* is marked MASKED.
*/
static void irq_finalize_oneshot(struct irq_desc *desc,
struct irqaction *action)
{
if (!(desc->istate & IRQS_ONESHOT) ||
action->handler == irq_forced_secondary_handler)
return; // 非ONESHOT类型或action->handler不为空的直接退出
again:
chip_bus_lock(desc);
raw_spin_lock_irq(&desc->lock);
/*
* Implausible though it may be we need to protect us against
* the following scenario:
*
* The thread is faster done than the hard interrupt handler
* on the other CPU. If we unmask the irq line then the
* interrupt can come in again and masks the line, leaves due
* to IRQS_INPROGRESS and the irq line is masked forever.
*
* This also serializes the state of shared oneshot handlers
* versus "desc->threads_onehsot |= action->thread_mask;" in
* irq_wake_thread(). See the comment there which explains the
* serialization.
*/
// 有一种场景,硬中断唤醒中断线程后,它们分别在不同CPU上运行,线程运行的比硬中断还要快(这种情况比较少见)。这样的后果是,中断线程先
unmask了对应的中断线,而此时desc->irq_data仍然保持IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS置1,硬中断还在执行,而中断线已经reenable了。
所以这里做了一个额外的检查,如果此时还在IRQD_IRQ_INPROGRESS状态,那么cpu_relax等待。
if (unlikely(irqd_irq_inprogress(&desc->irq_data))) {
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&desc->lock);
chip_bus_sync_unlock(desc);
cpu_relax();
goto again;
}
/*
* Now check again, whether the thread should run. Otherwise
* we would clear the threads_oneshot bit of this thread which
* was just set.
*/
if (test_bit(IRQTF_RUNTHREAD, &action->thread_flags))
goto out_unlock;
desc->threads_oneshot &= ~action->thread_mask;
if (!desc->threads_oneshot && !irqd_irq_disabled(&desc->irq_data) &&
irqd_irq_masked(&desc->irq_data))
unmask_threaded_irq(desc);
out_unlock:
raw_spin_unlock_irq(&desc->lock);
chip_bus_sync_unlock(desc);
}
参考blog:
https://www.cnblogs.com/pengdonglin137/p/6349209.html
https://www.2cto.com/kf/201611/561848.html
最后
以上就是阳光耳机最近收集整理的关于Linux内核中断系统的全部内容,更多相关Linux内核中断系统内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复