一、最长公共字串与最长公共子序列
最长公共子串(Longest Common Substirng)
子串是串的一个连续的部分,子串中字符的位置必须连续。
例如:有两个字符串ABCBDAB 和 BDCABA,则它们的最长公共子串是:AB。
最长公共子序列(Longest Common Subsequence,LCS)
子序列是从串中去掉任意的元素而获得新的序列,子串中字符的位置不必连续。
例如:有两个字符串ABCBDAB 和 BDCABA,则它们的最长公共子序列是:BCAB。
二、LCS算法
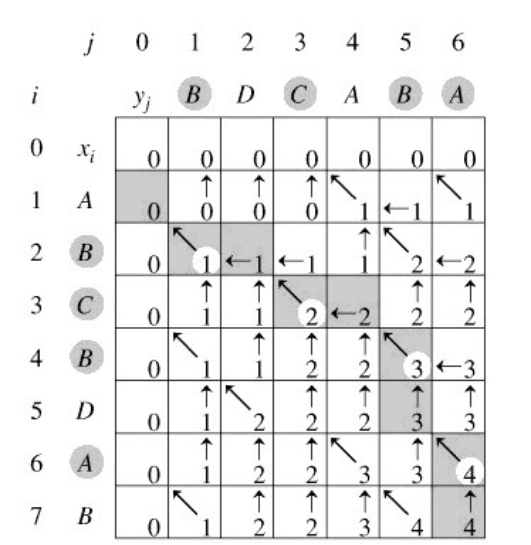
step1:生成矩阵
创建一个大小为str1_len×str2_len的矩阵,其中str1_len和str2_len分别为串str1和串str2的长度,初始化为0。
按照以下规则生成矩阵:
i和j分别从1开始,i++,j++循环:
如果
str1[i] == str2[j],则L[i,j] = L[i - 1, j -1] + 1;如果
str1[i] != str2[j],则L[i,j] = max{L[i,j - 1],L[i - 1, j]};
void init_array(char *str1, char *str2) {
int i,j;
for(i=1; i<=str1_len; i++)
for(j=1; j<=str2_len; j++) {
if(str1[i-1] == str2[j-1])
a[i][j] = a[i-1][j-1] + 1;
else {
if(a[i][j-1] >= a[i-1][j])
a[i][j] = a[i][j-1];
else
a[i][j] = a[i-1][j];
}
}
}step2:计算公共子序列
按照以下规则计算公共子序列:
i和j分别从str1_len,str2_len开始,递减循环直到i = 0,j = 0。
如果
str1[i-1] == str2[j-1],则将str[i]字符插入到子序列中,i--,j--;如果
str1[i-1] != str[j-1],则比较L[i,j-1]与L[i-1,j],L[i,j-1]大,则j--,否则i--;(如果相等,则任选一个)
void parser(char *str1, char *str2, char *res) {
int i,j,k = 0;
for(i = str1_len, j = str2_len; i >= 1 && j >= 1;) {
if(str1[i-1] == str2[j-1]) {
res[k++] = str1[i-1];
i--;
j--;
} else
if (a[i][j-1] > a[i-1][j])
j--;
else
i--;
}
}step3:逆序存放公共子序列
step2得到的公共子序列是从后往前获得的,需要逆序存放或输出。
char* reverse(char *str) {
int n = strlen(str) / 2;
int i = 0;
char tmp;
for(i=0; i<n; i++) {
tmp = str[i];
str[i] = str[strlen(str)-i-1];
str[strlen(str)-i-1] = tmp;
}
return str;
}三、完整代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#define MAX_LEN 256
int str1_len, str2_len;
int a[MAX_LEN][MAX_LEN];
void init_str(char *str1, char *str2) {
printf("please input str1: ");
scanf("%s", str1);
printf("please input str2: ");
scanf("%s", str2);
}
void init_array(char *str1, char *str2) {
int i,j;
for(i=1; i<=str1_len; i++)
for(j=1; j<=str2_len; j++) {
if(str1[i-1] == str2[j-1])
a[i][j] = a[i-1][j-1] + 1;
else {
if(a[i][j-1] >= a[i-1][j])
a[i][j] = a[i][j-1];
else
a[i][j] = a[i-1][j];
}
}
}
void parser(char *str1, char *str2, char *res) {
int i,j,k = 0;
for(i = str1_len, j = str2_len; i >= 1 && j >= 1;) {
if(str1[i-1] == str2[j-1]) {
res[k++] = str1[i-1];
i--;
j--;
} else
if (a[i][j-1] > a[i-1][j])
j--;
else
i--;
}
}
char* reverse(char *str) {
int n = strlen(str) / 2;
int i = 0;
char tmp;
for(i=0; i<n; i++) {
tmp = str[i];
str[i] = str[strlen(str)-i-1];
str[strlen(str)-i-1] = tmp;
}
return str;
}
int main(void) {
char str1[MAX_LEN], str2[MAX_LEN], *res;
init_str(str1, str2);
str1_len = strlen(str1);
str2_len = strlen(str2);
init_array(str1, str2);
res = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * (str1_len + str2_len));
parser(str1, str2, res);
printf("Result : %sn", reverse(res));
return 0;
}四、牛刀小试
POJ 1458 Common Subsequence
Description
A subsequence of a given sequence is the given sequence with some elements (possible none) left out. Given a sequence X = < x1, x2, …, xm > another sequence Z = < z1, z2, …, zk > is a subsequence of X if there exists a strictly increasing sequence < i1, i2, …, ik > of indices of X such that for all j = 1,2,…,k, xij = zj. For example, Z = < a, b, f, c > is a subsequence of X = < a, b, c, f, b, c > with index sequence < 1, 2, 4, 6 >. Given two sequences X and Y the problem is to find the length of the maximum-length common subsequence of X and Y.
Input
The program input is from the std input. Each data set in the input contains two strings representing the given sequences. The sequences are separated by any number of white spaces. The input data are correct.
Output
For each set of data the program prints on the standard output the length of the maximum-length common subsequence from the beginning of a separate line.
Sample Input
abcfbc abfcab
programming contest
abcd mnp
Sample Output
4
2
0
Code
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while (sc.hasNext()) {
String[] tmp = sc.nextLine().trim().split("\s+");
String str1 = tmp[0];
String str2 = tmp[1];
int[][] data = new int[str1.length() + 1][str2.length() + 1];
for (int i = 1; i < data.length; i++)
for (int j = 1; j < data[i].length; j++) {
if (str1.charAt(i - 1) == str2.charAt(j - 1)) {
data[i][j] = data[i - 1][j - 1] + 1;
} else {
data[i][j] = Math.max(data[i][j - 1], data[i - 1][j]);
}
}
System.out.println(data[str1.length()][str2.length()]);
}
}
}最后
以上就是潇洒毛巾最近收集整理的关于最长公共子序列(LCS)算法的全部内容,更多相关最长公共子序列(LCS)算法内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复