Queuing
Time Limit:5000MS Memory Limit:32768KB 64bit IO Format:%I64d & %I64u
Appoint description:
Description
Queues and Priority Queues are data structures which are known to most computer scientists. The Queue occurs often in our daily life. There are many people lined up at the lunch time.

Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2 L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue.
Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.

Now we define that ‘f’ is short for female and ‘m’ is short for male. If the queue’s length is L, then there are 2 L numbers of queues. For example, if L = 2, then they are ff, mm, fm, mf . If there exists a subqueue as fmf or fff, we call it O-queue else it is a E-queue.
Your task is to calculate the number of E-queues mod M with length L by writing a program.
Input
Input a length L (0 <= L <= 10
6) and M.
Output
Output K mod M(1 <= M <= 30) where K is the number of E-queues with length L.
Sample Input
3 8
4 7
4 8
Sample Output
6
2
1
题意:队伍里面有f和m, 对于长度为L的队伍,可组成这样的队伍:fm, mf, mm, ff。如果存在 fmf 或 fff 这样的子队伍,就称队伍为O-queues,否则为E-queues。问长度为L的队伍里E-queues的数目模M是多少。
思路:因为假设F(N)为已经是E队列的个数, 那么有3种情况
1,在F(N-1)后加一个M
2,在F(N-3)后加MMF
3,在F(N-4)后加MMFF
所以得到递推公式:f(n)=f(n-1)+f(n-3)+f(n-4);
数值较大,递推肯定会TLE,所以构造一个矩阵,用矩阵快速幂做。
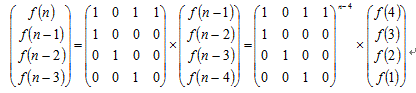
#include <stdio.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
const int inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
int mod;
int a[10];
struct node
{
int mp[5][5];
}init,res;
struct node Mult(struct node x,struct node y)
{
struct node tmp;
int i,j,k;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++){
tmp.mp[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<4;k++){
tmp.mp[i][j]=(tmp.mp[i][j]+x.mp[i][k]*y.mp[k][j])%mod;
}
}
return tmp;
};
struct node expo(struct node x,int k)
{
struct node tmp;
int i,j;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++){
if(i==j)
tmp.mp[i][j]=1;
else
tmp.mp[i][j]=0;
}
while(k){
if(k&1) tmp=Mult(tmp,x);
x=Mult(x,x);
k>>=1;
}
return tmp;
};
int main()
{
int i,j,k;
while(~scanf("%d %d",&k,&mod)){
memset(a,0,sizeof(a));
a[0]=0;a[1]=2;a[2]=4;a[3]=6;a[4]=9;
if(k<5){
printf("%dn",a[k]%mod);
continue;
}
init.mp[0][0]=1;
init.mp[0][1]=0;
init.mp[0][2]=1;
init.mp[0][3]=1;
for(i=1;i<4;i++)
for(j=0;j<4;j++){
if(i==j+1)
init.mp[i][j]=1;
else
init.mp[i][j]=0;
}
res=expo(init,k-4);
int ans=0;
for(i=0;i<4;i++)
ans=(ans+res.mp[0][i]*a[4-i])%mod;
printf("%dn",ans);
}
return 0;
}
最后
以上就是清秀缘分最近收集整理的关于HDU 2604-Queuing(递推+矩阵快速幂)的全部内容,更多相关HDU内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复