1、I2C通信协议
参考博客:《I2C通信协议详解和通信流程分析》;
2、通过KXTF9-2050芯片分析I2C协议
参考博客:《通过KXTF9-2050芯片分析I2C协议》;
3、I2C子系统框架
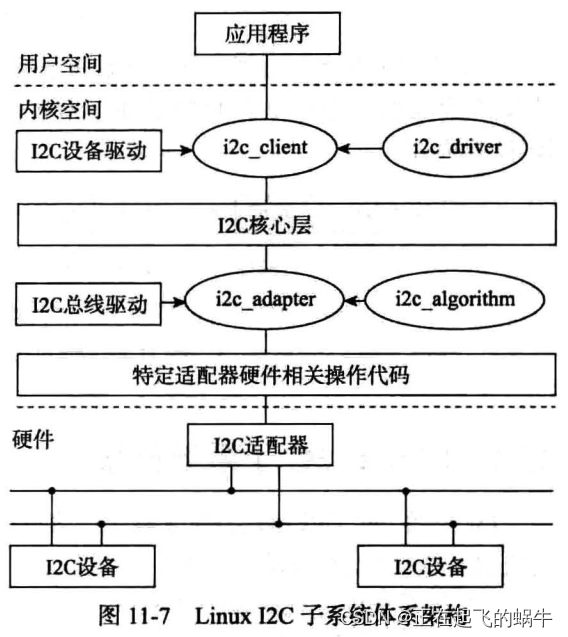
(1)I2C子系统分为三层:I2C核心层、I2C适配器驱动、I2C设备驱动;
(2)I2C核心层:管理I2C驱动和I2C设备的注册、匹配,实现I2C的通信方法,是对I2C通信的抽象框架,不和具体硬件相关;
(3)I2C适配器驱动:对应Soc的I2C控制器,把I2C控制器看做一个设备,实现I2C控制器的驱动代码,和具体的Soc相关;
(4)I2C设备驱动:和具体I2C接口的外设相关,每种外设都有自己的专属I2C驱动代码;
4、I2C子系统的初始化流程
(1)内核在启动过程中先注册I2C核心层,包括注册I2C总线,提供适配器驱动和设备驱动的注册、卸载接口;
(2)内核向I2C核心层注册I2C适配器驱动;
(3)内核向I2C核心层注册I2C设备驱动;
(4)I2C适配器驱动和I2C设备驱动在I2C总线上进行匹配,如果匹配上就调用I2C设备驱动probe方法;
(5)I2C适配器驱动和I2C设备驱动匹配上的效果:I2C设备驱动调用I2C适配器驱动在I2C总线上实现主控Soc和I2C接口外设的通信,I2C适配器驱动只提供最基础的数据传输功能,具体的通信协议由I2C设备驱动控制;
5、I2C驱动实现的两种思路
参考博客:《I2C驱动实现的两种思路(i2c-dev.c和i2c-core.c)》;
6、I2C子系统中重要的数据结构
6.1、i2c_adapter结构体
struct i2c_adapter {
struct module *owner;
unsigned int id;
unsigned int class; /* classes to allow probing for */
const struct i2c_algorithm *algo; /* the algorithm to access the bus */
void *algo_data;
/* data fields that are valid for all devices */
struct rt_mutex bus_lock;
int timeout; /* in jiffies */
int retries;
struct device dev; /* the adapter device */
int nr;
char name[48];
struct completion dev_released;
struct list_head userspace_clients;
};
| 变量名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| id | 适配器 ID,对于一些特定的适配器,内核在 include/linux/i2c-id.h 中定义了它们的 ID。该字段在一般的适配器驱动中并不常用 |
| class | 适配器的类类型,在一些口I2C设备驱动中会检查该成员,以判断设备能否被该适配器操作 |
| algo | 指向该造配器通信方法描述结构的指针,就是该适配器具体操作I2C控制器的函数 |
| algo_data | 指向通信方法数据的指针,该成员不会被I2C核心层修改,仅供具体的 i2c_algorithm使用 |
| timeout | 传输超时时间 |
| retries | 传输超时的重试次数 |
| name | 适配器名称,该名称可以通过sys/bus/i2c/devices/i2c-x/name (x=0,1,2 … )来访问 |
| nr | 总线编号(也是适配器编号),同时对应设备节点/dev/i2c-x (x=0,1,2 …)中的 x |
6.2、i2c_algorithm结构体
struct i2c_algorithm {
/* If an adapter algorithm can't do I2C-level access, set master_xfer
to NULL. If an adapter algorithm can do SMBus access, set
smbus_xfer. If set to NULL, the SMBus protocol is simulated
using common I2C messages */
/* master_xfer should return the number of messages successfully
processed, or a negative value on error */
int (*master_xfer)(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_msg *msgs,
int num);
int (*smbus_xfer) (struct i2c_adapter *adap, u16 addr,
unsigned short flags, char read_write,
u8 command, int size, union i2c_smbus_data *data);
/* To determine what the adapter supports */
u32 (*functionality) (struct i2c_adapter *);
};
| 适配器能力的宏定义 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| I2C_FUNC_I2C | 支持以I2C方式通信 |
| I2C_FUNC_SMBUS_EMUL | 支持SMBus协议模拟 |
| I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING | 支持I2C协议改编,即支持按非标准的时序访问设备 |
| I2C_FUNC_10BIT_ADDR | 支持传输数据10bit的模式,一般都是8bit的模式 |
| 变量名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| master_xfer | 指向具体I2C传输函数的指针,对应的传输一般会通过直接操作适配器硬件来发起。 函数的传参分别是:使用该传输方法的适配器adap、待传输的消息msgs、消息数量 返回值:成功就返回成功发送的消息数量,失败返回一个负值 |
| smbus_xfer | 指向具体 SMBus传输函数的指针 |
| functionality | 指向返回适配器支持功能的函数的指针,查看适配的能力。这些功能都是以宏定义的方式表示,定义在include/linux/i2c.h中,以I2C_FUNC开头 |
(1)SMBus协议大部分基于I2C总线规范,并在I2C基础上扩展,在访问时序上有一些差异;
(2)如果是支持I2C协议就实现master_xfer函数指针,支持SMBus协议就实现smbus_xfer函数指针;
6.3、i2c_msg结构体
struct i2c_msg {
__u16 addr; /* 从机在I2C总线上的地址*/
__u16 flags; /* 消息特征的标志 */
//下面的宏定义就是消息特征的标志
#define I2C_M_TEN 0x0010 /* this is a ten bit chip address */
#define I2C_M_RD 0x0001 /* read data, from slave to master */
#define I2C_M_NOSTART 0x4000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_REV_DIR_ADDR 0x2000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_IGNORE_NAK 0x1000 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_NO_RD_ACK 0x0800 /* if I2C_FUNC_PROTOCOL_MANGLING */
#define I2C_M_RECV_LEN 0x0400 /* length will be first received byte */
__u16 len; /* 消息数据长度,单位是字节 */
__u8 *buf; /* 指向存放消息数据的缓冲区 */
};
6.4、i2c_driver结构体
struct i2c_driver {
unsigned int class;
int (*attach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *);
int (*detach_adapter)(struct i2c_adapter *);
/* Standard driver model interfaces */
int (*probe)(struct i2c_client *, const struct i2c_device_id *);
int (*remove)(struct i2c_client *);
/* driver model interfaces that don't relate to enumeration */
void (*shutdown)(struct i2c_client *);
int (*suspend)(struct i2c_client *, pm_message_t mesg);
int (*resume)(struct i2c_client *);
void (*alert)(struct i2c_client *, unsigned int data);
int (*command)(struct i2c_client *client, unsigned int cmd, void *arg);
struct device_driver driver;
const struct i2c_device_id *id_table;
/* Device detection callback for automatic device creation */
int (*detect)(struct i2c_client *, struct i2c_board_info *);
const unsigned short *address_list;
struct list_head clients;
};
| 变量名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| attach_adapter | 依附i2c_adapter的函数指针:(1)在向系统添加i2c_driver时,驱动注册函数遍历适配器设备类i2c_adapter_class中的所有设备,并调用该驱动的attach_adapter方法进行依附。 (2)相应的,在添加i2c_adapter时,适配器注册函数遍历总线i2c_bus_type上的所有驱动,如果定义了attach_adapter方法,它也将得到调用 |
| detach_adapter | 脱离i2c_adapter的函数指针 |
| probe | 当总线 i2c_bus_type 上的设备与设备驱动匹配后被调用 |
| driver | 在注册i2c_driver对象时,i2c_driver->driver的总线类型被指定为i2c_bus_type |
| id_table | 存放该驱动支持的设备列表,驱动和设备匹配时会用到 |
| detect | 基于设备探测机制实现的 12C 设备驱动:设备探测的回调函数 |
| address_list | 设备探测的地址范围 |
| clients | 探测到的设备列表 |
6.5、i2c_client结构体
struct i2c_client {
unsigned short flags; /* div., see below */
unsigned short addr; /* chip address - NOTE: 7bit */
/* addresses are stored in the */
/* _LOWER_ 7 bits */
char name[I2C_NAME_SIZE];
struct i2c_adapter *adapter; /* the adapter we sit on */
struct i2c_driver *driver; /* and our access routines */
struct device dev; /* the device structure */
int irq; /* irq issued by device */
struct list_head detected;
};
| 变量名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| flags | I2C_CLIENT_TEN:设备使用10bit地址; I2C_CLIENT_PEC:设备使用SMBus包错误检查 |
| addr | 设备地址,7bit地址格式下,地址存放在该成员的低7位 |
| name | 设备的名称 |
| adapter | 依附的适配器 |
| driver | 设备绑定的驱动 |
| irq | 设备使用的中断号 |
| dev | 内嵌的device结构体,在注册i2c_client对象时,i2c_client->dev的总线类型被指定为i2c_bus_type,其type成员被指定为i2c_client_type |
6.6、i2c_board_info结构体
//适配器上要支持的I2C设备信息,将来要传给驱动程序
struct i2c_board_info {
char type[I2C_NAME_SIZE]; //用于和驱动匹配的名字
unsigned short flags;
unsigned short addr; //设备在I2C总线上的地址
void *platform_data; //要传给I2C总线上对应驱动的数据
struct dev_archdata *archdata;
#ifdef CONFIG_OF
struct device_node *of_node;
#endif
int irq; //将使用的中断号
};
6.7、结构体之间的关联
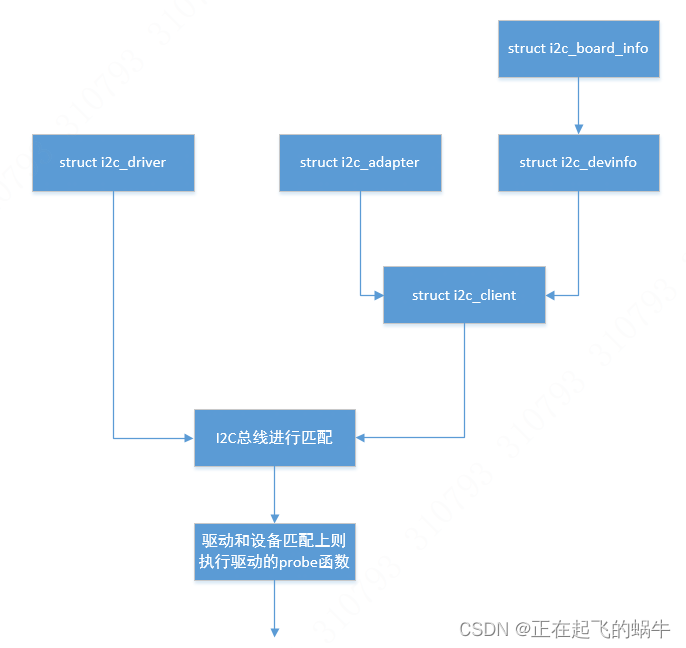
(1)struct i2c_adapter结构体:用于描述Soc的I2C控制器;
(2)struct i2c_algorithm结构体:描述具体I2C控制器的数据通信方法,和具体硬件相关;
(3)struct i2c_msg结构体:I2C子系统中传递数据的基本单位,通过I2C控制器发送数据都是以消息为基本单位,用我们要通信的数据按照struct i2c_msg结构体的方式进行填充;
(4)struct i2c_driver结构体:描述I2C驱动的结构体,I2C设备驱动就是构造一个struct i2c_driver结构体调用I2C核心层提供驱动注册接口进行注册;
(5)struct i2c_client结构体:描述I2C设备的结构体,当在I2C总线上和I2C驱动匹配上后,会把设备信息传给驱动,这里是驱动设计数据的操作方法分离的思想;
(6)i2c_board_info结构体:描述I2C适配器驱动支持的I2C设备的信息,包括支持的I2C设备的名字、I2C总线上的地址、中断数据、私有数据等;
7、I2C核心层
7.1、核心层的功能
(1)定义并注册I2C总线i2c_bus_type和适配器类i2c_adapter_class;
(2)提供i2c_driver、i2c_adapter和i2c_client的分配、创建、注册、注销等方法;
(3)实现I2C通信方法的上层代码;
(4)提供I2C设备的探测、添加以及地址检查等方法;
7.2、核心层的注册
//i2c-core.c
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = "i2c",
.match = i2c_device_match, //总线上驱动和设备的匹配函数
.probe = i2c_device_probe, //总线上设备和驱动匹配时调用
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
.pm = &i2c_device_pm_ops,
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_bus_type);
static const struct i2c_device_id dummy_id[] = {
{ "dummy", 0 },
{ },
};
static struct i2c_driver dummy_driver = {
.driver.name = "dummy",
.probe = dummy_probe,
.remove = dummy_remove,
.id_table = dummy_id,
};
static int __init i2c_init(void)
{
int retval;
//注册I2C总线
retval = bus_register(&i2c_bus_type);
if (retval)
return retval;
//向I2C总线注册一个名字为dummy的驱动,这个驱动没什么实际的功能,空实现的驱动
retval = i2c_add_driver(&dummy_driver);
if (retval)
goto class_err;
return 0;
class_err:
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
return retval;
}
static void __exit i2c_exit(void)
{
//删除dummy驱动
i2c_del_driver(&dummy_driver);
//卸载I2C总线
bus_unregister(&i2c_bus_type);
}
/* We must initialize early, because some subsystems register i2c drivers
* in subsys_initcall() code, but are linked (and initialized) before i2c.
*/
postcore_initcall(i2c_init);
module_exit(i2c_exit);
I2C核心层的注册接口功能很简单,就是注册了I2C总线和注册了I2C设备驱动dummy_driver;
7.3、I2C总线
7.3.1、I2C总线描述
(1)I2C总线上有两条链表,一条用于挂接驱动,一条用于挂接设备;
(2)其中I2C上挂接的设备有两类:i2c_client_type和i2c_adapter_type;
(3)i2c_adapter_type是代表适配器,i2c_client_type是adap注册时结合struct i2c_board_info结构体产生的;
(4)工作流程:当设备向I2C总线注册时,会遍历I2C总线上已经注册的驱动是否有匹配的,如果匹配则调用驱动的probe方法;驱动向I2C总线注册时,也会遍历I2C总线上的设备是否有匹配的,如果匹配则调用 驱动的probe方法;
7.3.2、I2C总线注册
struct bus_type i2c_bus_type = {
.name = "i2c",
.match = i2c_device_match, //总线上驱动和设备的匹配函数
.probe = i2c_device_probe, //总线上设备和驱动匹配时调用
.remove = i2c_device_remove,
.shutdown = i2c_device_shutdown,
.pm = &i2c_device_pm_ops,
};
EXPORT_SYMBOL_GPL(i2c_bus_type);
I2C总线是在I2C核心层的注册接口i2c_init()里注册的,在I2C核心层中负责I2C设备和I2C驱动的匹配;
7.3.3、I2C总线的匹配函数
static const struct i2c_device_id *i2c_match_id(const struct i2c_device_id *id,
const struct i2c_client *client)
{
while (id->name[0]) {
if (strcmp(client->name, id->name) == 0)
return id;
id++;
}
return NULL;
}
static int i2c_device_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv)
{
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
if (!client)
return 0;
//利用container_of宏获取到I2C驱动结构体
driver = to_i2c_driver(drv);
/* 比较驱动id_table中是否有名字能和client匹配上 */
if (driver->id_table)
return i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client) != NULL;
return 0;
}
向I2C总线注册I2C驱动或者I2C设备时,会逐一将I2C驱动的名字和I2C设备的名字进行匹配,如果匹配上则调用I2C总线的probe方法;
7.3.4、I2C总线的probe函数
static int i2c_device_probe(struct device *dev)
{
//利用container_of宏获取到I2C设备结构体
struct i2c_client *client = i2c_verify_client(dev);
struct i2c_driver *driver;
int status;
if (!client)
return 0;
//利用container_of宏获取到I2C驱动结构体
driver = to_i2c_driver(dev->driver);
if (!driver->probe || !driver->id_table)
return -ENODEV;
// 把I2C设备驱动和I2C设备绑定,将来可以互相查找到对方
client->driver = driver;
if (!device_can_wakeup(&client->dev))
device_init_wakeup(&client->dev,
client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_WAKE);
dev_dbg(dev, "proben");
//调用I2C驱动的probe函数
status = driver->probe(client, i2c_match_id(driver->id_table, client));
if (status) {
client->driver = NULL;
i2c_set_clientdata(client, NULL);
}
return status;
}
I2C总线的probe方法没有实际的功能,就是调用匹配上的I2C驱动的probe方法;
8、I2C适配器驱动
8.1、I2C适配器介绍
(1)I2C适配器在硬件上对应Soc的I2C控制器,在内核中把I2C控制器看做一个设备,既然是一个设备就有对应的驱动,也就是I2C设备驱动;
(2)I2C适配器驱动就是操作I2C控制器,向接在I2C控制器上的I2C设备提供在I2C总线上通信的基础方法;
(3)I2C适配器驱动主要就是通过操作Soc的I2C控制器相关的寄存器来实现数据的收发;
8.2、I2C适配器驱动注册
(1)先用平台总线注册I2C适配器驱动,将I2C适配器需要的数据都以platform device的方式传给I2C适配器驱动;
(2)在S5PV210芯片中,三个I2C适配器操作方法是一样的,只是操作的寄存器地址和中断号不同,而适配器之间的不同都已经放在platformdevice中传给适配器驱动了,因此适配器共用上i2c-s3c2410.c适配器 驱动文件;
(3)s3c24xx_i2c_probe会被调用三次,因为在platform总线上会被匹配上三次,用platform_device.dev.platform_data中的私有数据来区分不同的适配器;
8.3、i2c_board_info结构体注册
/*
* busnum:适配器的编号,就是struct i2c_board_info结构体注册到哪个适配器驱动上
* info:要注册的struct i2c_board_info结构体
* len:注册的struct i2c_board_info结构体个数
*/
int __init i2c_register_board_info(int busnum, struct i2c_board_info const *info, unsigned len)
{
int status;
down_write(&__i2c_board_lock);
/* 动态的总线编号必须在静态的总线编号之后,动态总线编号永远比静态总线编号大一 */
if (busnum >= __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num)
__i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num = busnum + 1;
//为每一个struct i2c_board_info构建一个对应的struct i2c-devinfo结构体
//并挂接到__i2c_board_list链表
for (status = 0; len; len--, info++) {
struct i2c_devinfo *devinfo;
devinfo = kzalloc(sizeof(*devinfo), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!devinfo) {
pr_debug("i2c-core: can't register boardinfo!n");
status = -ENOMEM;
break;
}
devinfo->busnum = busnum; //对应适配器的编号
devinfo->board_info = *info;
list_add_tail(&devinfo->list, &__i2c_board_list);
}
up_write(&__i2c_board_lock);
return status;
}
(1)为每一个struct i2c_board_info构建一个对应的struct i2c-devinfo结构体;
(2)生成的struct i2c-devinfo结构体都挂接在__i2c_board_list链表上;
8.4、适配器struct i2c_adapter注册
static int i2c_register_adapter(struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
······
//初始化锁和队列
rt_mutex_init(&adap->bus_lock);
INIT_LIST_HEAD(&adap->userspace_clients);
/* 设置默认超时时间为1s */
if (adap->timeout == 0)
adap->timeout = HZ;
//设置adap设备的名字
dev_set_name(&adap->dev, "i2c-%d", adap->nr);
adap->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type; //设备注册到I2C总线上
adap->dev.type = &i2c_adapter_type; //设备类型是i2c_adapter_type
//向内核注册adap
res = device_register(&adap->dev);
/* 和已经注册的struct i2c_board_info结构体通过适配器编号进行匹配,匹配上就产生struct client结构体 */
if (adap->nr < __i2c_first_dynamic_bus_num)
i2c_scan_static_board_info(adap);
/* 新注册了adap适配器,通知I2C总线上已经注册的I2C驱动 */
mutex_lock(&core_lock);
dummy = bus_for_each_drv(&i2c_bus_type, NULL, adap,
__process_new_adapter);
mutex_unlock(&core_lock);
······
}
(1)适配器adap在内核中被看做是一个设备,i2c_register_adapter()函数会首先对adap内置的内核设备结构体进行初始化;
(2)向内核注册adap时,因为adap内置的设备结构体的bus总线类型被设置为i2c_bus_type,其实就是向I2C总线注册设备,会由I2C总线的match函数去和已经向I2C总线注册的驱动进行匹配,如果匹配成功就调用I2C总线的prob函数;
(3)adap和已经注册的struct i2c_board_info结构体通过适配器编号进行匹配,匹配上就产生struct client结构体;
(4)adap和已经注册的I2C驱动进行逐一匹配,如果I2C驱动定义了driver->attach_adapter方法就调用;
8.5、产生struct i2c_client结构体
8.5.1、函数调用关系
i2c_register_adapter();
i2c_scan_static_board_info();
i2c_new_device();
device_register(&client->dev);
(1)struct i2c_client结构体是在注册适配器adap时,适配器adap和匹配上的struct i2c_board_info结构体共同构成的,是I2C总线上的设备;
(2)struct i2c_client结构体时描述I2C设备的,I2C总线上的设备类型是i2c_client_type;
8.5.2、i2c_scan_static_board_info()函数
static void i2c_scan_static_board_info(struct i2c_adapter *adapter)
{
struct i2c_devinfo *devinfo;
down_read(&__i2c_board_lock);
//__i2c_board_list是保存struct i2c-devinfo结构体的链表,在i2c_register_board_info()函数中提到
//遍历__i2c_board_list链表,当i2c-devinfo结构体的适配器编号和adapter的编号相等,就调用i2c_new_device()函数
list_for_each_entry(devinfo, &__i2c_board_list, list) {
if (devinfo->busnum == adapter->nr
&& !i2c_new_device(adapter,
&devinfo->board_info))
dev_err(&adapter->dev,
"Can't create device at 0x%02xn",
devinfo->board_info.addr);
}
up_read(&__i2c_board_lock);
}
(1)遍历__i2c_board_list链表上所有的struct i2c_devinfo结构体,逐一和刚注册的适配器adapter的编号进行匹配;
(2)如果匹配上则调用i2c_new_device()函数,该函数会根据struct i2c_devinfo结构体和adapter适配器产生一个struct client结构体;
8.5.3、i2c_new_device()函数
struct i2c_client * i2c_new_device(struct i2c_adapter *adap, struct i2c_board_info const *info)
{
struct i2c_client *client;
int status;
······
//分配struct i2c_client内存
client = kzalloc(sizeof *client, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!client)
return NULL;
//保存对应的适配器结构体
client->adapter = adap;
//struct i2c_board_info结构体要传给I2C总线上对应驱动的数据
client->dev.platform_data = info->platform_data;
if (info->archdata)
client->dev.archdata = *info->archdata;
//struct i2c_board_info结构体保存的信息赋值给struct client
client->flags = info->flags;
client->addr = info->addr;
client->irq = info->irq;
strlcpy(client->name, info->type, sizeof(client->name));
/* 检测i2c_board_info结构体传递的设备在I2C总线上的从地址是否符合要求 */
status = i2c_check_client_addr_validity(client);
if (status) {
dev_err(&adap->dev, "Invalid %d-bit I2C address 0x%02hxn",
client->flags & I2C_CLIENT_TEN ? 10 : 7, client->addr);
goto out_err_silent;
}
/* 检测i2c_board_info结构体传递的设备在I2C总线上的从地址是否已经被注册 */
status = i2c_check_addr_busy(adap, client->addr);
if (status)
goto out_err;
//client在内核中也是一个设备,初始化内置的设备结构体
client->dev.parent = &client->adapter->dev;
client->dev.bus = &i2c_bus_type; //设备类型
client->dev.type = &i2c_client_type; //设备所属的总线
//client的名字
dev_set_name(&client->dev, "%d-%04x", i2c_adapter_id(adap),
client->addr);
//向I2C总线注册client设备
status = device_register(&client->dev);
······
}
8.5.4、bus_for_each_drv()函数分析
int bus_for_each_drv(struct bus_type *bus, struct device_driver *start,
void *data, int (*fn)(struct device_driver *, void *))
{
struct klist_iter i;
struct device_driver *drv;
int error = 0;
if (!bus)
return -EINVAL;
//遍历bus总线上已经注册的驱动,调用fn匹配函数将驱动和data进行匹配
klist_iter_init_node(&bus->p->klist_drivers, &i,
start ? &start->p->knode_bus : NULL);
while ((drv = next_driver(&i)) && !error)
error = fn(drv, data);
klist_iter_exit(&i);
return error;
}
(1)bus_for_each_drv()函数是内核总线的驱动遍历函数,功能就是遍历bus总线上已经注册的驱动,调用fn匹配函数将驱动和data进行匹配;
(2)在i2c_register_adapter()注册函数中,bus传入的是I2C总线结构体,data是新注册的适配器struct i2c_adapter结构体,匹配函数是__process_new_adapter()函数;
(3)功能:将I2C总线上已经注册的驱动逐一和新注册的适配器adap进行匹配,匹配函数是__process_new_adapter()函数;
8.5.5、__process_new_adapter()函数
//I2C驱动和适配器adapter进行匹配
static int i2c_do_add_adapter(struct i2c_driver *driver,
struct i2c_adapter *adap)
{
/* Detect supported devices on that bus, and instantiate them */
i2c_detect(adap, driver);
/* 如果I2C驱动定义了attach_adapter方法,就调用 */
if (driver->attach_adapter) {
/* We ignore the return code; if it fails, too bad */
driver->attach_adapter(adap);
}
return 0;
}
//根据内核通用驱动,利用container_of宏得到struct i2c_driver驱动结构体
#define to_i2c_driver(d) container_of(d, struct i2c_driver, driver)
static int __process_new_adapter(struct device_driver *d, void *data)
{
return i2c_do_add_adapter(to_i2c_driver(d), data);
}
(1)__process_new_adapter()函数实际功能就是检查I2C总线上定义的I2C驱动是否定义了attach_adapter方法,如果定义了就调用驱动的attach_adapter方法,把刚注册的adapter适配器作为参数传进去;
(2)实际上一般驱动都是没有定义attach_adapter方法的,只有在i2cdev_driver驱动中定义了attach_adapter方法,i2cdev_driver驱动是在i2c-dev.c的i2c_dev_init()函数中定义的,在博客:《I2C子系统之适配器的设备接口分析(i2c-dev.c文件分析)》中有详细介绍;
(3)实际效果:每个新注册的adapter适配器,都会调用i2cdev_driver->attach_adapter方法,在sysfs中创建i2c-dev类"/sys/class/i2c-dev/i2c-n(n=0、1、······)“类,创建设备节点”/dev/i2c-n(n=0、1、······)"
8.6、I2C适配器的设备接口分析(i2c-dev.c文件分析)
(1)i2c-dev.c就是实现将I2C适配器暴露给上层应用的方法,表现为设备节点"/dev/i2c-n(n=0、1、2、······)",有多少个设备节点就代表Soc有多少个I2C控制器;
(2)应用可以直接通过设备节点去操作I2C适配器来与接在I2C适配器上的设备进行通信;
(2)参考博客:《I2C子系统之适配器的设备接口分析(i2c-dev.c文件分析)》;
8.7、I2C适配器驱动源码分析(i2c-s3c2410.c)
参考博客:《S5PV210芯片I2C适配器驱动分析(i2c-s3c2410.c)》;
9、I2设备驱动层
9.1、I2C设备驱动介绍
(1)I2C设备驱动是和具体硬件紧密相关的,指设备是I2C接口的,接在Soc的I2C控制器上,通过I2C总线和主控Soc进行通信;
(2)I2C设备驱动的会向I2C核心层注册I2C设备驱动,然后核心层会在I2C总线上和I2C设备进行匹配,会为I2C设备驱动匹配一个I2C适配器驱动;
(3)I2C设备驱动在I2C核心层匹配成功后,设备就可以直接调用I2C适配器进行数据通信;
9.2、触摸屏驱动源码码分析(gslX680.c)
参考博客:《gslx680触摸屏驱动源码码分析(gslX680.c)》;
最后
以上就是懦弱过客最近收集整理的关于linux内核I2C子系统详解——看这一篇就够了1、I2C通信协议2、通过KXTF9-2050芯片分析I2C协议3、I2C子系统框架4、I2C子系统的初始化流程5、I2C驱动实现的两种思路6、I2C子系统中重要的数据结构7、I2C核心层8、I2C适配器驱动9、I2设备驱动层的全部内容,更多相关linux内核I2C子系统详解——看这一篇就够了1、I2C通信协议2、通过KXTF9-2050芯片分析I2C协议3、I2C子系统框架4、I2C子系统内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复