背景
上一节介绍了蓝牙Android搜索BLE模块方法,搜索到蓝牙模块后,我们就可以进行蓝牙与手机间数据的通信,也就是Android手机端与BLE模块间实现数据的互相传输,本文将重点介绍手机端和蓝牙端程序的编写及其交互,从代码和现象入手,逐步了解BLE使用。
BLE模块代码分析
建立一个Service
此处修改了nordic官方代码。
这里我们将先贴出代码,明确代码所要实现的功能,后面会继续分析这些代码是如何与蓝牙协议所对应。
首先从main函数入手,其中有很多初始化代码,初始化协议栈和寄存器相关内容,我们并不需要过多关注,如图,我们先看这个服务初始化函数。
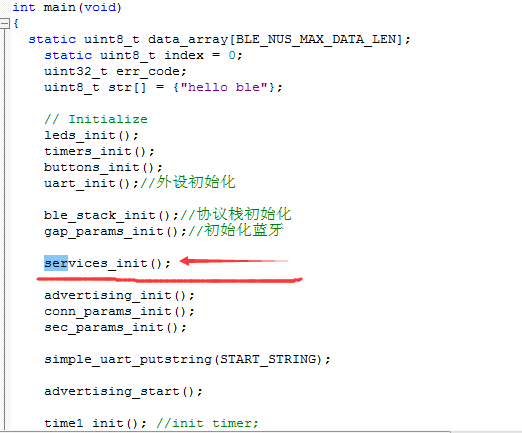
当我们需要为蓝牙模块添加一个功能时,我们需要在BLE模块中自定义一个自己的service,并按照一定的方式进行初始化,下面是我们为当前定义的service进行的初始化代码。
/**@brief Function for initializing services that will be used by the application.
*/
static void services_init(void)
{
uint32_t err_code;
ble_nus_init_t nus_init;
memset(&nus_init, 0, sizeof(nus_init));
nus_init.data_handler = nus_data_handler;
err_code = ble_nus_init(&m_nus, &nus_init);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
}- 1
其中的 ble_nus_init_t 是服务提供的一个接口,定义了这服务的基本功能要求,我们可以根据自己的需求进行不同的具体实现nus_data_handler函数即可。
typedef struct
{
ble_nus_data_handler_t data_handler; /**< Event handler to be called for handling received data. */
} ble_nus_init_t;- 1
下面我们实现一下自己的 nus_data_handler,这里我们将蓝牙接收到的数据直接原样通过BLE发送到手机端。
void nus_data_handler(ble_nus_t * p_nus, uint8_t * p_data, uint16_t length)
{
ble_nus_send_string(&m_nus, p_data, length);
}- 1
之后调用ble_nus_init函数来对我们的service进行注册。
uint32_t ble_nus_init(ble_nus_t * p_nus, const ble_nus_init_t * p_nus_init)
//参数:
// ble_nus_t * p_nus 自定义服务的结构体接口
// ble_nus_init_t * p_nus_init 我们在上面定义的回调接口,存储回调- 1
下面我们来看一下 ble_nus_t,这个接口中存储着我们服务中包含的属性和方法,是服务的核心。
typedef struct ble_nus_s
{
uint8_t uuid_type; //uuid类型
uint16_t service_handle; //服务回调
ble_gatts_char_handles_t tx_handles; //关联TX characteristic
ble_gatts_char_handles_t rx_handles; //关联 RX characteristic
uint16_t conn_handle; //连接
bool is_notification_enabled; //是否准备好 RX characteristic
ble_nus_data_handler_t data_handler; //处理接收到的数据回调
} ble_nus_t;- 1
ble_nus_init函数中,我们首先对这个结构体的变量进行初始化。初始化完毕后就可以使用nordic为我们提供的协议栈函数sd_ble_uuid_vs_add进行Service注册了。这里的参数总我们为服务指定一个uuid。
现在有了服务,我们就需要为服务添加功能了,我们要使用BLE与手机进行通信,所以最基本的功能就是数据的接收与发送。
所以接下来要做的就为Service是添加两个Characteristic,分别用作发送和接收。我们需要为这两个Characteristic也分别指定相应的UUid。
下面是初始化代码
uint32_t ble_nus_init(ble_nus_t * p_nus, const ble_nus_init_t * p_nus_init)
{
uint32_t err_code;
ble_uuid_t ble_uuid;
ble_uuid128_t nus_base_uuid = {0x9E, 0xCA, 0xDC, 0x24, 0x0E, 0xE5, 0xA9, 0xE0,
0x93, 0xF3, 0xA3, 0xB5, 0x00, 0x00, 0x40, 0x6E};
//6e400000-b5a3-f393-e0a9-e50e24dcca9e
if ((p_nus == NULL) || (p_nus_init == NULL))
{
return NRF_ERROR_NULL;
}
// Initialize service structure.
p_nus->conn_handle = BLE_CONN_HANDLE_INVALID;
p_nus->data_handler = p_nus_init->data_handler;
p_nus->is_notification_enabled = false;
/**@snippet [Adding proprietary Service to S110 SoftDevice] */
// Add custom base UUID.
err_code = sd_ble_uuid_vs_add(&nus_base_uuid, &p_nus->uuid_type);
if (err_code != NRF_SUCCESS)
{
return err_code;
}
ble_uuid.type = p_nus->uuid_type;
ble_uuid.uuid = BLE_UUID_NUS_SERVICE;
// Add service.
err_code = sd_ble_gatts_service_add(BLE_GATTS_SRVC_TYPE_PRIMARY,
&ble_uuid,
&p_nus->service_handle);
/**@snippet [Adding proprietary Service to S110 SoftDevice] */
if (err_code != NRF_SUCCESS)
{
return err_code;
}
// Add RX Characteristic.
err_code = rx_char_add(p_nus, p_nus_init);
if (err_code != NRF_SUCCESS)
{
return err_code;
}
// Add TX Characteristic.
err_code = tx_char_add(p_nus, p_nus_init);
if (err_code != NRF_SUCCESS)
{
return err_code;
}
return NRF_SUCCESS;
}- 1
这样就完成了蓝牙Service的初始化,下面我们就可以开启广播。
static void advertising_start(void)
{
uint32_t err_code;
ble_gap_adv_params_t adv_params;
// Start advertising
memset(&adv_params, 0, sizeof(adv_params));
// 设置广播数据包的信息
adv_params.type = BLE_GAP_ADV_TYPE_ADV_IND;
adv_params.p_peer_addr = NULL;
adv_params.fp = BLE_GAP_ADV_FP_ANY;
adv_params.interval = APP_ADV_INTERVAL;
adv_params.timeout = APP_ADV_TIMEOUT_IN_SECONDS;
err_code = sd_ble_gap_adv_start(&adv_params);
APP_ERROR_CHECK(err_code);
nrf_gpio_pin_set(ADVERTISING_LED_PIN_NO);
}- 1
这样,BLE模块端的基本功能就已经建立起来了。
通信过程简述
有了直观的代码,下面我们看看芯片内部做了些什么。
广播与连接
手机连接BLE模块时,BLE模块会有间隔地发送广播数据包,每次发送完数据包后模块会等待连接信息,当手机收到模块的数据包后,就会发出请求,请求更多数据包,称为扫描回应。
手机端会间隔地向BLE模块请求数据,而在这个请求的间隔,BLE模块就会像手机端发送数据包,数据包的大小是20字节。也就是说,我们在传输过程中,每次传输的buffer中的内容不应超过20字节。
上述过程在蓝牙的GAP中定义,也就是通用访问规范。
数据传输
当手机与BLE模块建立连接后,我们就可以开始数据传输,这些在蓝牙的GATT中定义,称为通用属性配置文件。
这里我们主要说说上文所建立的Service与Characteristic。
简单地说,我们可以认为Service中包含着一组Characteristic,而Characteristic就是为我们提供了数据,我们要发送的数据都要被组装到Characteristic中。
在此之上,一个profile中会包含一组Service,而每个Characteristic中又包含了一些属性。属性可以定义为属性或者描述符,描述符是一段信息,为了给人读的。
而这些GATT中的这些内容都有UUID,我们在用Android端读取的时候可以通过UUID一层一层地找出我们需要的内容。而在建立这些内容时,有的UUID需要我们根据情况自己定义,有的在协议栈中给出。
上面的代码所做的事情就是为我们自己定义一个Service,而在这个Service中我们又定义了两个Characteristic,一个用来读取接收到的数据,一个用于发送接收到的数据。当我们收到数据后触发回调函数,处理我们收到的数据,发送数据则是底层调用了协议栈的sd_ble_gatts_hvx函数。
手机端发送数据时会先找到Service,再由此通过UUID拿到Characteristic,向Characteristic中写入数据,这样BLE模块就可以接收到数据了。
Android端代码设计与分析
总体结构
通过上述对BLE模块实现原理的分析,我们可以大概了解到Android端具体要做的一些工作,主要如下。
1.发送连接请求,连接BLE模块
2.寻找相应的 Service和 Characteristic
3.从 Characteristic中根据UUID进行读取和写入
上一节中我们已经了解了Android与BLE搜索,下面我们开始进行后面功能的设计。
我们为BLE连接建立一个Service(注意,这个是Android四大组件中的Service),这个服务用于在后台维护与BLE模块的连接及其数据传输和一些相关的监控,同时在需要操作BLE的Activity中建立一个广播接受者。Service中监听到BLE状态改变时会通过广播的方式传送给我们的广播接收者,用来改变前端页面的状态。
下图为程序的基本结构
BLEActivityBLEActivityBLEServiceBLEService调用Service中方法通过内部维护的BluetoothGatt的对象完成与BLE模块的交互发送广播,改变前端状态
下面先介绍几个蓝牙使用的通用类
BluetoothManager
官网解释
High level manager used to obtain an instance of an BluetoothAdapter and to conduct overall Bluetooth Management.
Use getSystemService(java.lang.String) with BLUETOOTH_SERVICE to create an BluetoothManager, then call getAdapter() to obtain the BluetoothAdapter.
Alternately, you can just call the static helper getDefaultAdapter().
大概是说用来获取BluetoothAdapter用的。下面我们看一下BluetoothAdapter。
BluetoothAdapter
看着眼熟,这不是上一张的主角吗?具体作用看如下链接:
http://blog.csdn.net/lidec/article/details/50631742
通过如下方法我们可以获取到BluetoothGatt
final BluetoothDevice device = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(address);
if (device == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Device not found. Unable to connect.");
return false;
}
// We want to directly connect to the device, so we are setting the autoConnect
// parameter to false.
mBluetoothGatt = device.connectGatt(this, false, mGattCallback);- 1
BluetoothGatt
从名字上看,这个类包含Gatt,也就是前面我们提到的BLE数据传输的协议。咱们在BLE模块中建立的Service和Characteristic都属于GATT的内容。
下面是官网的介绍
Public API for the Bluetooth GATT Profile.
This class provides Bluetooth GATT functionality to enable communication with Bluetooth Smart or Smart Ready devices.
To connect to a remote peripheral device, create a BluetoothGattCallback and call connectGatt(Context, boolean, BluetoothGattCallback) to get a instance of this class. GATT capable devices can be discovered using the Bluetooth device discovery or BLE scan process.
我们与BLE进行GATT所定义的协议就可以直接使用这个类封装的方法。下面我们看看其中主要功能的实现。
/**
* Connects to the GATT server hosted on the Bluetooth LE device.
*
* @param address The device address of the destination device.
*
* @return Return true if the connection is initiated successfully. The connection result
* is reported asynchronously through the
* {@code BluetoothGattCallback#onConnectionStateChange(android.bluetooth.BluetoothGatt, int, int)}
* callback.
*/
public boolean connect(final String address) {
if (mBluetoothAdapter == null || address == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "BluetoothAdapter not initialized or unspecified address.");
return false;
}
// Previously connected device. Try to reconnect.
if (mBluetoothDeviceAddress != null && address.equals(mBluetoothDeviceAddress)
&& mBluetoothGatt != null) {
Log.d(TAG, "Trying to use an existing mBluetoothGatt for connection.");
if (mBluetoothGatt.connect()) {
mConnectionState = STATE_CONNECTING;
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
final BluetoothDevice device = mBluetoothAdapter.getRemoteDevice(address);
if (device == null) {
Log.w(TAG, "Device not found. Unable to connect.");
return false;
}
// We want to directly connect to the device, so we are setting the autoConnect
// parameter to false.
mBluetoothGatt = device.connectGatt(this, false, mGattCallback);
Log.d(TAG, "Trying to create a new connection.");
mBluetoothDeviceAddress = address;
mConnectionState = STATE_CONNECTING;
return true;
}- 1
这个方法用来连接蓝牙设备,通过Mac地址从BluetoothAdapter中获取BluetoothGatt对象,而我们定义的Android应用的Service主要功能就是维护这个对象,并使用其提供的方法与BLE模块进行数据通信。
public void writeRXCharacteristic(byte[] value)
{
BluetoothGattService RxService = mBluetoothGatt.getService(RX_SERVICE_UUID);
showMessage("mBluetoothGatt null"+ mBluetoothGatt);
if (RxService == null) {
showMessage("Rx service not found!");
broadcastUpdate(DEVICE_DOES_NOT_SUPPORT_UART);
return;
}
BluetoothGattCharacteristic RxChar = RxService.getCharacteristic(RX_CHAR_UUID);
if (RxChar == null) {
showMessage("Rx charateristic not found!");
broadcastUpdate(DEVICE_DOES_NOT_SUPPORT_UART);
return;
}
RxChar.setValue(value);
boolean status = mBluetoothGatt.writeCharacteristic(RxChar);
Log.d(TAG, "write TXchar - status=" + status);
}- 1
上述方法提供了操作GATT协议的基本方法,通过UUID获取BLE的Service,再从BLE的Service中获取用于写的Characteristic,然后调用setValue方法,将值写入,如果写入成功,那么我们的BLE模块此时就接收到数据了。
有了写入的方法,那么我们如何读取数据呢?
我们在获取BluetoothGatt时给它传入一个GattCallback对象,当收到数据时会触发回调函数onCharacteristicChanged。
public void onCharacteristicChanged(BluetoothGatt gatt, BluetoothGattCharacteristic characteristic)- 1
参数的characteristic就是变化的Characteristic,我们可以取出它的UUID,对比一下,如果这个UUID和我们在BLE模块中定义的发送数据的UUID一致,则说明收到了数据,我们就可以取这个值。示例代码如下:
if (TX_CHAR_UUID.equals(characteristic.getUuid())) {
byte[] value = characteristic.getValue();
} - 1
其他的功能以此类推。
下面提供一下APP的源码,实现其他BLE相关的功能都可以在这个APP的基础上修改。
http://download.csdn.net/detail/lidec/9434509
总结
本文主要梳理了51822BLE开发板与Android手机通信的方式,简要介绍了一些实用的蓝牙协议知识以,分析了协议在开发板控制程序和APP程序中的体现。
最后
以上就是细心白昼最近收集整理的关于Android与51822蓝牙模块通信流程的实现与分析的全部内容,更多相关Android与51822蓝牙模块通信流程内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复