全面了解SVG的特性
SVG概念
1:SVG定义
SVG的全称是Scalable Vector Graphics,叫可缩放矢量图形
ps:擎,是借用机器工业的同名术语,表明在整个系统中的核心地位。也可以称之为“支持应用的底层函数库”或者说是对特定应用的一种抽象。三维引擎需要解决场景构造、对象处理、场景渲染、事件处理、碰撞检测等问题
三维图像引擎:OpenGL或DirectX
2:SVG特性

3:SVG在Android中能做什么?
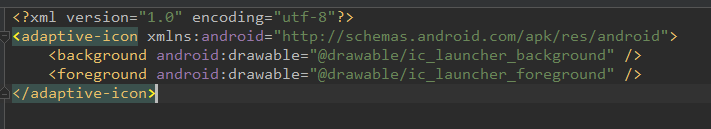
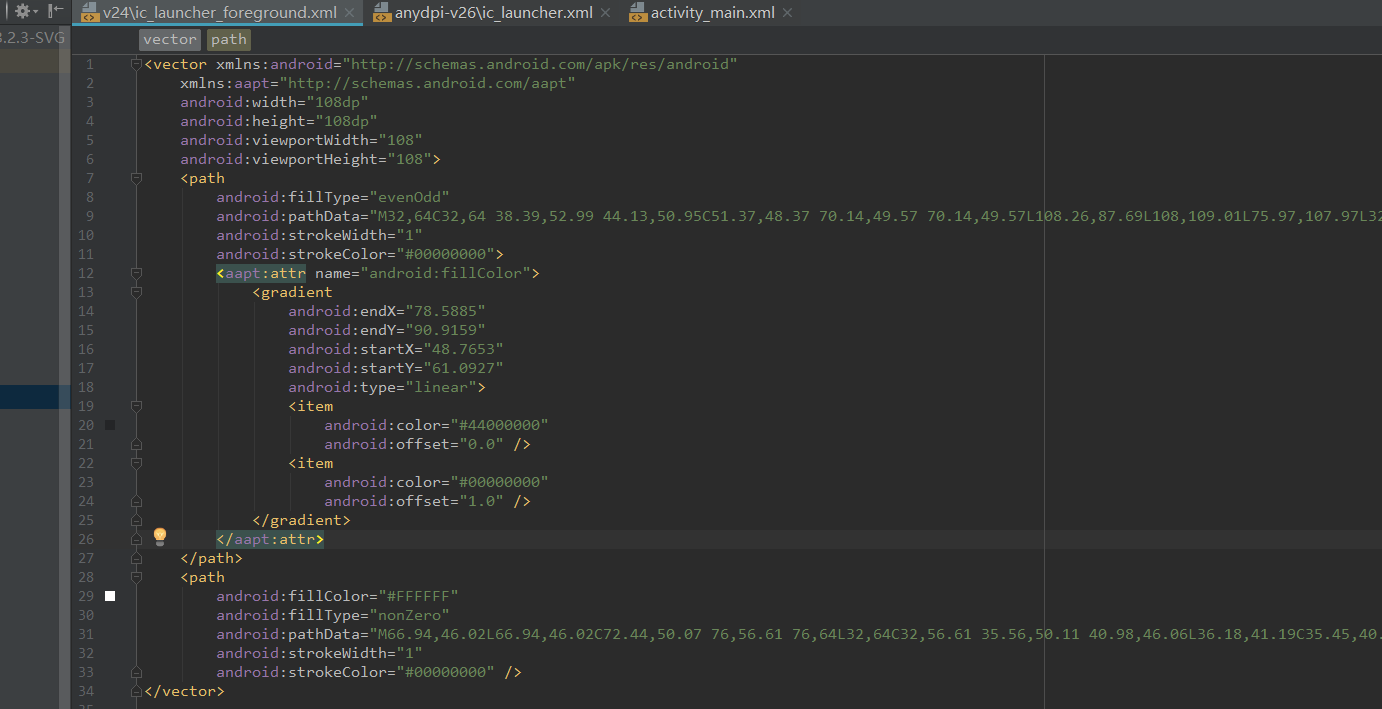
1,APP图标:能在SDK23后,APP的图标由SVG来表示
2,自定义控件:不规则的控件,复杂的交互,子空间重叠判断,图表等都可以用SVG来做
3,负责动画:如根据用户滑动动态显示动画,路径动画
4:Android 例子
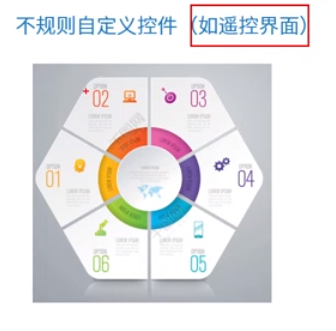
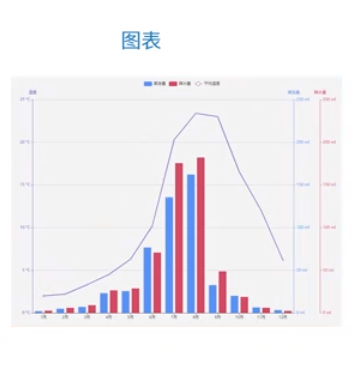
还有美团的下拉刷新,下拉幅度越大,小人动作也越快
5:标准SVG预览

类似与html,xml。
既然是表示图形,我们需要自己设计svg吗,其实是不需要的,需要设计设计师去做。
我们来学习一下简单的,百度搜索svg在线编辑
类似于这样
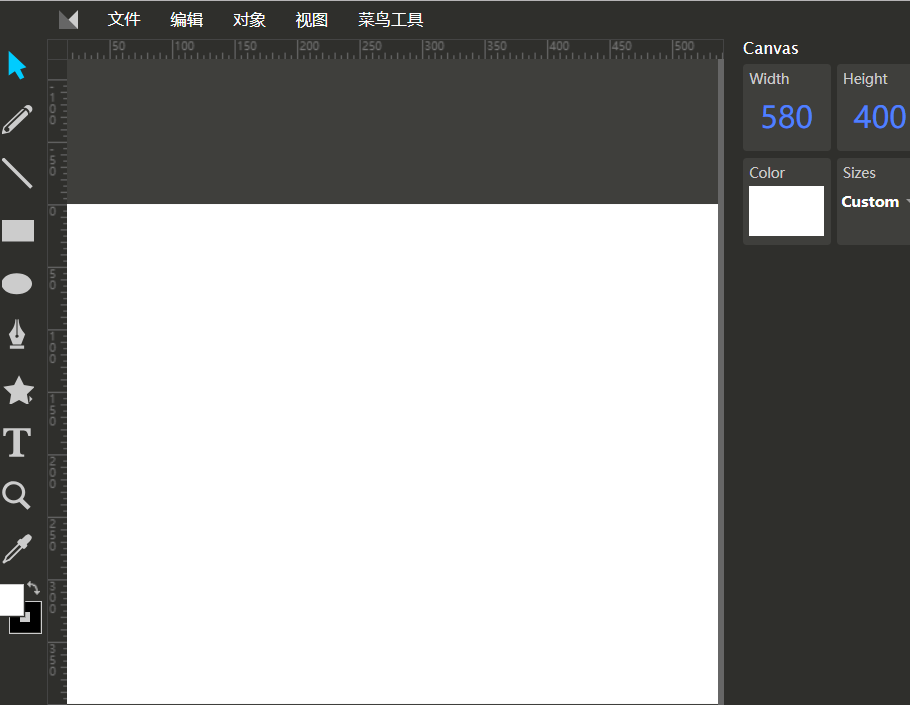
画一个直线,然后保存:

![]()
打开这个svg
<svg width="580" height="400" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg">
<!-- Created with Method Draw - http://github.com/duopixel/Method-Draw/ -->
<g>
<title>background</title>
<rect fill="#fff" id="canvas_background" height="402" width="582" y="-1" x="-1"/>
<g display="none" overflow="visible" y="0" x="0" height="100%" width="100%" id="canvasGrid">
<rect fill="url(#gridpattern)" stroke-width="0" y="0" x="0" height="100%" width="100%"/>
</g>
</g>
<g>
<title>Layer 1</title>
<line stroke-linecap="undefined" stroke-linejoin="undefined" id="svg_8" y2="140.4375" x2="373" y1="140.4375" x1="121" stroke-width="1.5" stroke="#000" fill="none"/>
</g>
</svg>line标签里面是画的东西 :line语法
还有其他语法:
5:svg语法:
svg特性:

二 :代码练习 实现中国地图的绘制,并且能正常点击省份
SVG下载地址:https://www.amcharts.com/download/
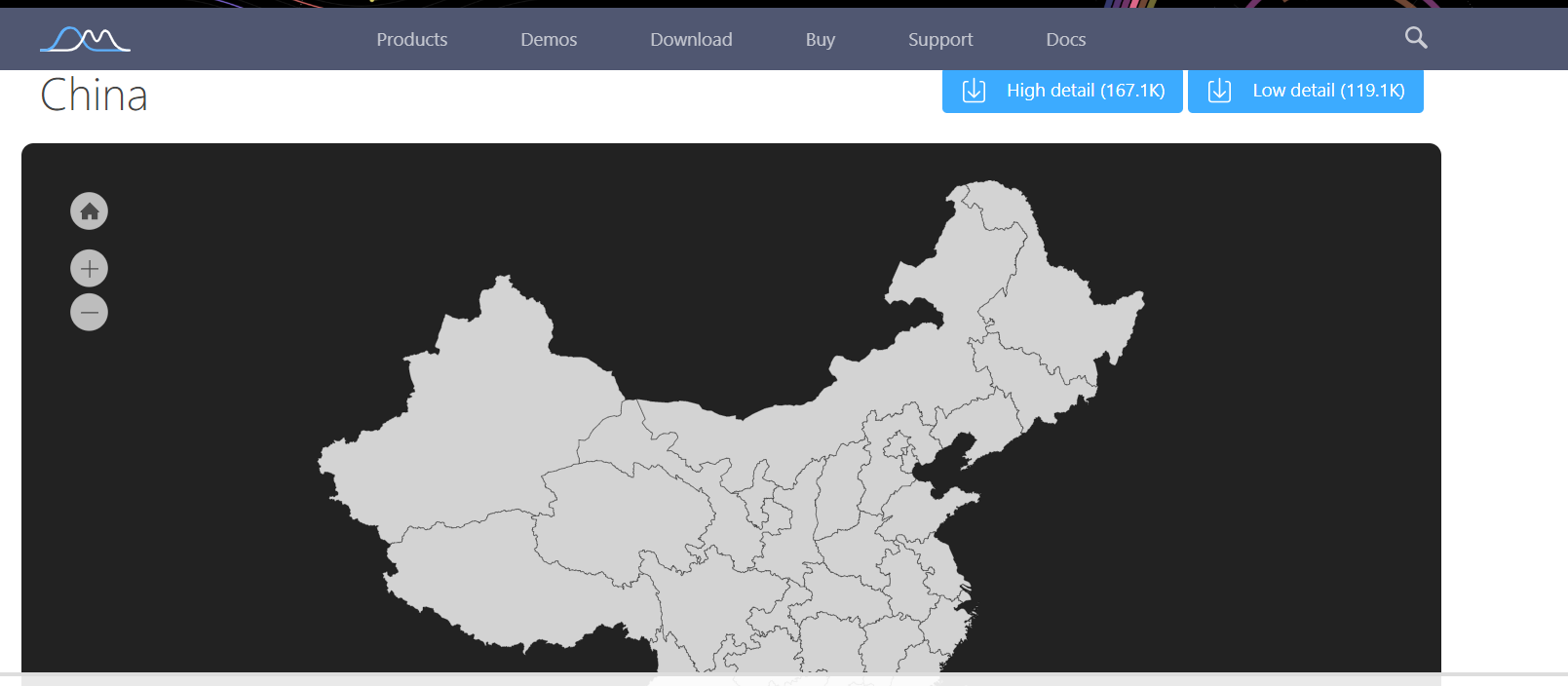
![]()
将下载好的文件放到
接下来我们需要实现一个自定义view实现给地图的各个省份着色并且实现点击效果:---z对画布进行操作
实现构造方法,然后通过 DocumentBuilderFactory 去解析xml,拿到不同省份的地址;
private Thread loadThread = new Thread() {
@Override
public void run() {
final InputStream inputStream = context.getResources().openRawResource(R.raw.china);
DocumentBuilderFactory factory = DocumentBuilderFactory.newInstance(); //取得DocumentBuilderFactory实例
DocumentBuilder builder = null; //从factory获取DocumentBuilder实例
try {
builder = factory.newDocumentBuilder();
Document doc = builder.parse(inputStream); //解析输入流 得到Document实例
Element rootElement = doc.getDocumentElement();
NodeList items = rootElement.getElementsByTagName("path");
float left = -1;
float right = -1;
float top = -1;
float bottom = -1;
List<ProviceItem> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < items.getLength(); i++) {
Element element = (Element) items.item(i);
String pathData = element.getAttribute("android:pathData");
@SuppressLint("RestrictedApi") Path path = PathParser.createPathFromPathData(pathData);
ProviceItem proviceItem = new ProviceItem(path);
proviceItem.setDrawColor(colorArray[i % 4]);
RectF rect = new RectF();
path.computeBounds(rect, true);
left = left == -1 ? rect.left : Math.min(left, rect.left);
right = right == -1 ? rect.right : Math.max(right, rect.right);
top = top == -1 ? rect.top : Math.min(top, rect.top);
bottom = bottom == -1 ? rect.bottom : Math.max(bottom, rect.bottom);
list.add(proviceItem);
}
itemList = list;
totalRect = new RectF(left, top, right, bottom);
// 刷新界面
Handler handler = new Handler(Looper.getMainLooper());
handler.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
requestLayout();
invalidate();
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
};将不同省份封装成一个对象:
public class ProviceItem {
private Path path;
/**
* 绘制颜色
*/
private int drawColor;
public ProviceItem(Path path) {
this.path = path;
}
public void setDrawColor(int drawColor) {
this.drawColor = drawColor;
}
void drawItem(Canvas canvas, Paint paint, boolean isSelect) {
if(isSelect){
// 绘制内部的颜色
paint.clearShadowLayer();
paint.setStrokeWidth(1);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setColor(drawColor);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
// 绘制边界
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE);
int strokeColor = 0xFFD0E8F4;
paint.setColor(strokeColor);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}else {
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
paint.setColor(Color.BLACK);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setShadowLayer(8,0,0,0xffffff);
canvas.drawPath(path,paint);
// 绘制边界
paint.clearShadowLayer();
paint.setColor(drawColor);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
paint.setStrokeWidth(2);
canvas.drawPath(path, paint);
}
}
public boolean isTouch(float x, float y) {
RectF rectF = new RectF();
path.computeBounds(rectF, true);
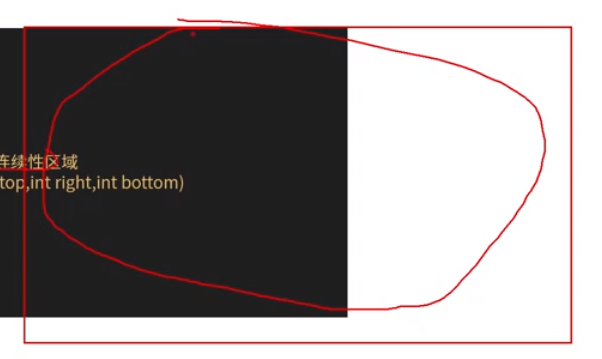
//android de API 如果有一个连续的范围 我们需要求出
Region region = new Region();
region.setPath(path, new Region((int) rectF.left, (int) rectF.top, (int) rectF.right, (int) rectF.bottom));
return region.contains((int)x, (int)y);
}
}
这里面的Region :

一个path与矩形的相交区域
然后在onDraw去绘制
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if (itemList != null) {
//保存画布
canvas.save();
canvas.scale(scale,scale);
//然后对每一个画布进行绘制
for (ProviceItem proviceItem : itemList) {
if (proviceItem != select) {
proviceItem.drawItem(canvas, paint, false);
}else {
select.drawItem(canvas, paint, true);
}
}
}
}然后处理点击事件
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
handleTouch(event.getX()/scale, event.getY()/scale);
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
private void handleTouch(float x, float y) {
if (itemList == null) {
return;
}
ProviceItem selectItem = null;
for (ProviceItem proviceItem : itemList) {
if (proviceItem.isTouch(x, y)) {
selectItem = proviceItem;
}
}
if (selectItem != null) {
select = selectItem;
postInvalidate();
}
}效果图
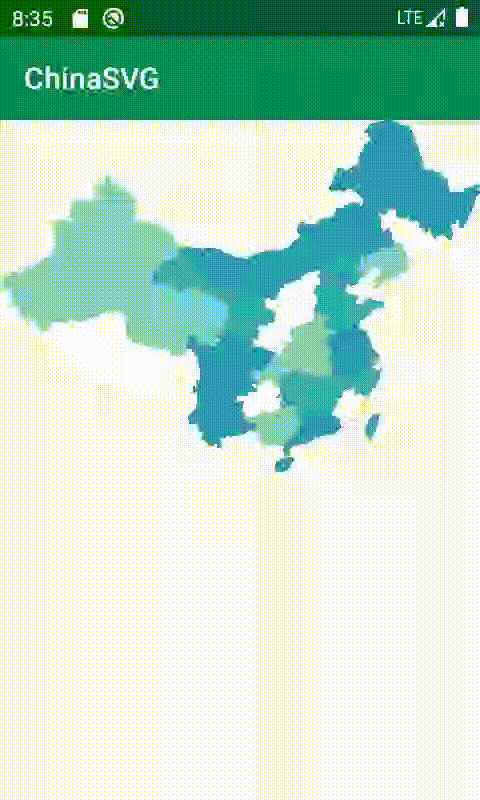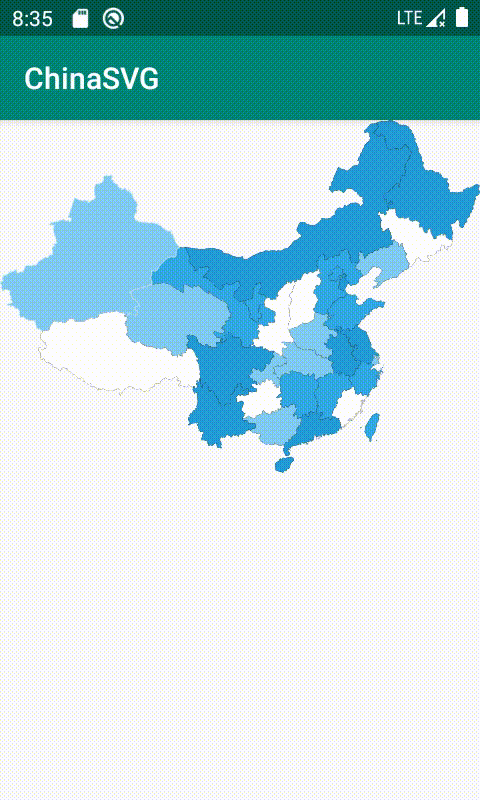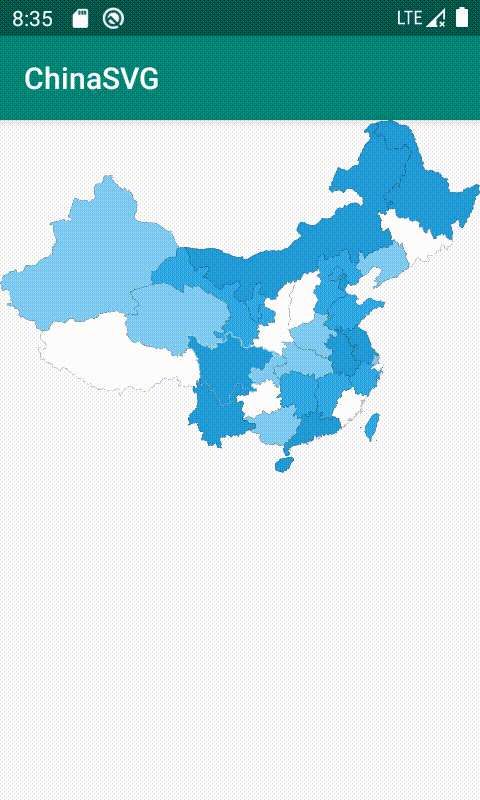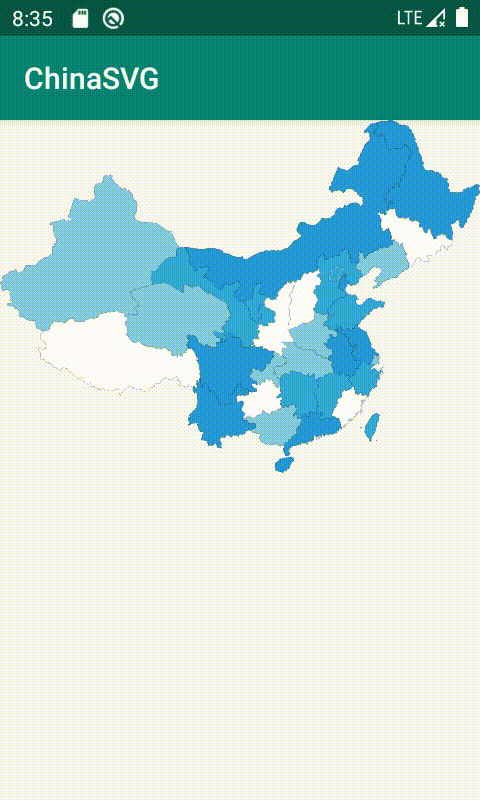
SVG缺点:他是基于像素开展的,他里面的坐标都是基于像素的
所以需要适配,对不同的图片进行缩放。
求出最左边,最上边,最下面,最右面,然后我们根据宽度进行缩放
我们拿到这个这个图片的最上,下,左,右的值与原始值进行比较。
最后
以上就是无奈小蜜蜂最近收集整理的关于Android高级-SVG矢量图形打造不规则的自定义控件的全部内容,更多相关Android高级-SVG矢量图形打造不规则内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复