一,直接指定GPU:
tf.ConfigProto一般用在创建session的时候。用来对session进行参数配置
with tf.Session(config = tf.ConfigProto(...),...)#tf.ConfigProto()的参数
log_device_placement=True : 是否打印设备分配日志
allow_soft_placement=True : 如果你指定的设备不存在,允许TF自动分配设备#coding:utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
a=tf.constant([1.0,2.0,3.0],shape=[3],name='a')
b=tf.constant([1.0,2.0,3.0],shape=[3],name='b')
c=a+b
#log_device_placement=True 输出运行每一个运算的设备
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
print(sess.run(c))可看出每个运算的设备是GPU:0
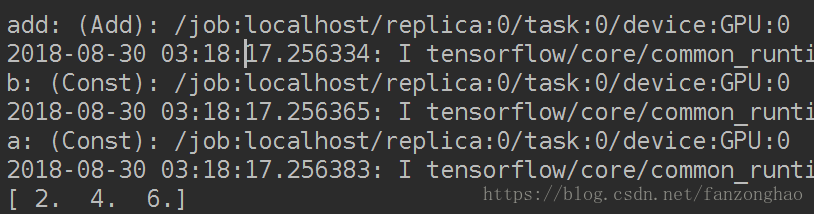
可以把运算放在不同的device上
#coding:utf-8
import tensorflow as tf
with tf.device('/cpu:0'):
a=tf.constant([1.0,2.0,3.0],shape=[3],name='a')
b=tf.constant([1.0,2.0,3.0],shape=[3],name='b')
with tf.device('/gpu:0'):
c=a+b
#log_device_placement=True 输出运行每一个运算的设备
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
print(sess.run(c))
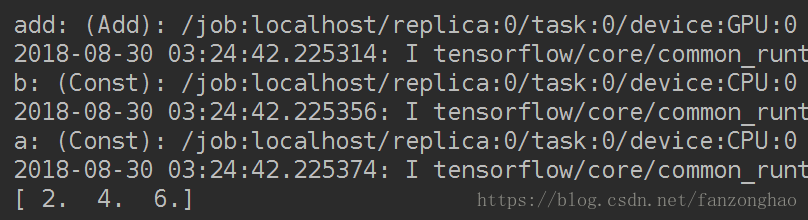
直接指定的缺点是,降低程序的可移植性,同时有些运算不能在GPU上执行,bi比如tf.Variable操作只支持实数型(float16,float32,和double的参数),对于整数不支持,故可用allow_soft_placement参数
报错:
a_cpu=tf.Variable(0,name='a_cpu')
with tf.device('/gpu:0'):
a_gpu=tf.Variable(0,name='a_gpu')
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
print(sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()))![]()
a_cpu=tf.Variable(0,name='a_cpu')
with tf.device('/gpu:0'):
a_gpu=tf.Variable(0,name='a_gpu')
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(allow_soft_placement=True,log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
print(sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer()))打印信息:
2018-08-30 03:40:26.905925: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:874] a_gpu: (VariableV2)/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
a_gpu/read: (Identity): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
2018-08-30 03:40:26.905952: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:874] a_gpu/read: (Identity)/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
a_gpu/Assign: (Assign): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:CPU:0
import tensorflow as tf
a=tf.constant([1.0,2.0,3.0],shape=[3],name='a')
b=tf.constant([1.0,2.0,3.0],shape=[3],name='b')
c=a+b
#log_device_placement=True 输出运行每一个运算的设备
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
print(sess.run(c))
二,命令行用gpu
![]()
打印信息
2018-08-30 03:46:25.130842: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:874] add: (Add)/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
b: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
2018-08-30 03:46:25.130872: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:874] b: (Const)/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
a: (Const): /job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
2018-08-30 03:46:25.130892: I tensorflow/core/common_runtime/placer.cc:874] a: (Const)/job:localhost/replica:0/task:0/device:GPU:0
运算在第二块gpu
![]()
或者直接在程序里
import tensorflow as tf
import os
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES']='1'
a=tf.constant([1.0,2.0,3.0],shape=[3],name='a')
b=tf.constant([1.0,2.0,3.0],shape=[3],name='b')
c=a+b
#log_device_placement=True 输出运行每一个运算的设备
with tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(log_device_placement=True)) as sess:
print(sess.run(c))三,动态分配GPU
上面的方式会占用整个GPU,可以在一块GPU上同时运行多个任务
import tensorflow as tf
import os
def set_config():
# 控制使用率
os.environ['CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES'] = '1'
# 假如有16GB的显存并使用其中的8GB:
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.5)
config = tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options)
# session = tf.Session(config=config)
return config
if __name__ == '__main__':
a = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], shape=[3], name='a')
b = tf.constant([1.0, 2.0, 3.0], shape=[3], name='b')
c = a + b
cfg=set_config()
with tf.Session(config=cfg) as sess:
print(sess.run(c))
最后
以上就是野性山水最近收集整理的关于tensorflow(GPU)使用的全部内容,更多相关tensorflow(GPU)使用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复