C - Catch That Cow
Farmer John has been informed of the location of a fugitive cow and wants to catch her immediately. He starts at a point N (0 ≤ N ≤ 100,000) on a number line and the cow is at a point K (0 ≤ K ≤ 100,000) on the same number line. Farmer John has two modes of transportation: walking and teleporting.
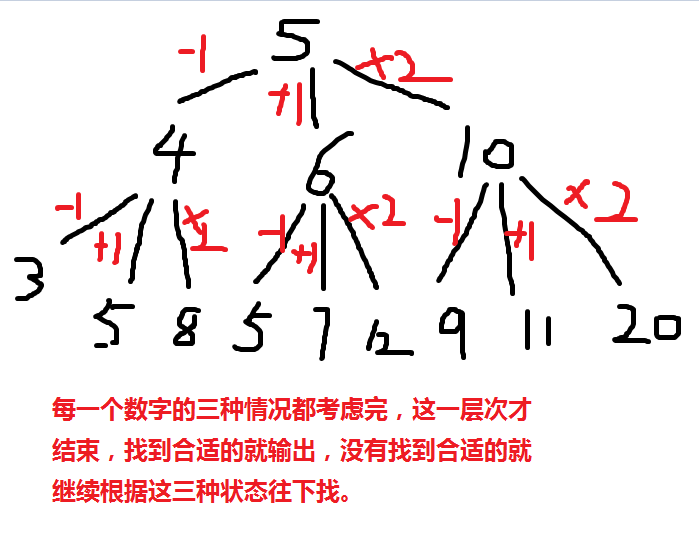
* Walking: FJ can move from any point X to the points X - 1 or X + 1 in a single minute
* Teleporting: FJ can move from any point X to the point 2 × X in a single minute.
If the cow, unaware of its pursuit, does not move at all, how long does it take for Farmer John to retrieve it?
5 17Sample Output
4Hint
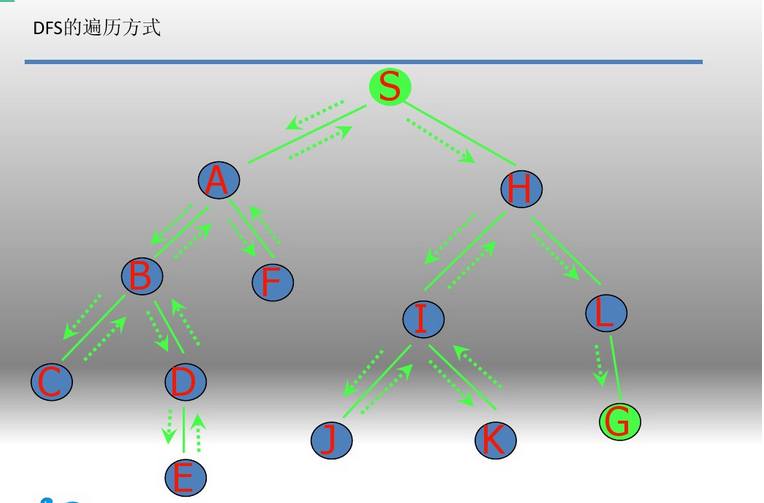
注:本题之所以用广度优先搜索,是因为超找的是最短路径,走哪一条路最短,所以采用广度优先搜索,广度优先搜索采用队列的形式来实现,那么现在就来总结一下DFS和BFS的区别和常用规格。
BFS算法:
思想:一直往深处走,直到找到解或者走不下去为止
大体框架:
DFS(dep,.......)
{
if(找到解 || 走不下去)
{
.........
return ;
}
枚举下一种情况,DFS(dep+1,........)
}
BFS算法:
思路:
1.从初始状态S开始,利用规则,生成下一层的状态。
2.顺序检查下一层的所有状态,看是否出现目标状态G。
否则就对该层所有状态节点,分别利用规则。生成再下一层的所有状态节点。
3.继续按照上面思想生成下一层的所有状态节点,这样一层一层往下展开。
直到出现目标状态为止
先遍历离起点近的,再到远的,网上有一个很形象的例子:你的眼镜掉在地上以后,你趴在地板上找。你总是先摸离你最近的地方,如果没有,再摸距离较远的地方。
通常用队列来实现
初始化队列Q
Q={起点s};
标记s为已访问;
while(Q非空)
{
取Q队首元素u;
u出队;
if(u==目标状态)
{.............}
所有与u相邻且未被访问的点进入队列;
标记u为已访问;
}
这个网址有BFS例子具体的实现过程:
https://wenku.baidu.com/view/97c9220452ea551810a687e4.html
参考文献::
http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_130976afd0102v4le.html
AC代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200100;
int n, k;
struct node
{
int x, step;
};
queue<node> Q;
int vis[N];
void BFS()
{
int X, STEP;
while(!Q.empty())
{
node w2= Q.front();
Q.pop();
X = w2.x;
STEP = w2.step;
if(X == k)
{
printf("%dn",STEP);
return ;
}
if(X >= 1 && vis[X - 1]==0)
{
node w3;
vis[X - 1] = 1;
w3.x = X - 1;
w3.step = STEP + 1;
Q.push(w3);
}
if(X <= k && vis[X + 1]==0)
{
node w3;
vis[X + 1] = 1;
w3.x = X + 1;
w3.step = STEP + 1;
Q.push(w3);
}
if(X <= k && vis[X * 2]==0)
{
node w3;
vis[X * 2] = 1;
w3.x = 2 * X;
w3.step = STEP + 1;
Q.push(w3);
}
}
}
int main()
{
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&k)!=EOF)
{
while(!Q.empty())
Q.pop();
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
vis[n] = 1;
node w1;
w1.x = n;
w1.step = 0;
Q.push(w1);
BFS();
}
return 0;
}最后
以上就是受伤大米最近收集整理的关于C - Catch That Cow 广度优先搜索的全部内容,更多相关C内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。






![Catch That Cow POJ - 3278 [bfs][最短路]Catch That CowInputOutputSample InputSample OutputHint](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg12.png)

发表评论 取消回复