前言
这是大一写过的一个小项目,现在大三,重新实现了一下。这是原来的链接,可以看一下效果,思路和现在的一样。
扩展性、健壮性比原来更好,思路也更清晰了。当时只想花里胡哨,这次重心放在质量、功能上。
后续会不断改进它,直到它贴近实际。
项目分析
项目围绕实现压缩、解压缩。
模块划分
-
压缩/解压缩均通过哈夫曼编码算法来实现,所以我们的第一个模块为算法模块。
-
实际的任务流程需要一个模块来控制,负责流程的控制,提供简单可用的接口,划分为接口模块。
-
在进行编码时,我们需要进行字节和位串的转换,这就需要位的操作,C语言没有提供这样的函数,需要自己实现,所以划分为位操作模块。
-
对于任一个模块,我们希望给它一个输入,产生一个结果,而不用它考虑输入来自哪里、输出到了哪里。所以我们需要一个流处理模块来集中解决这个问题,这样也可以降低各模块的耦合程度。
-
为了方便, 我们需要一个打印错误信息的模块,就把它作为错误处理模块。
-
为了出现错误时更方便排查,我们增加一个测试模块, 实际上是将各个模块节点的IO进行记录,方便对比排查。
将项目划分为以下几个模块:
- 算法模块
- 接口模块
- 流处理模块
- 错误处理模块
- 位操作模块
- 测试模块
实测中需要频繁地使用缓冲区,包括字符串缓冲区、字节缓冲区、位缓冲区 ,每次都要实现一遍非常不方便,好在数量不多,后续会增加缓冲区模块。
模块功能分析
1.算法模块
算法模块的任务是通过哈夫曼编码得到编码表,输入和输出进行功能分析。这个模块聚合程度很高,我们尽可能不去动它。
- 统计字节频率
- 编码需要构造哈夫曼树, 而构造树需要有weight(权值),而权值需要扫描输入流来进行统计,显然这一工作与编码独立,所以我们将它作为单独功能。
- 构造哈夫曼树
- 不用说,为编码做准备。
- 哈夫曼编码
- 得到哈夫曼编码表。
- 这里的表是抽象类型,实际上用二级指针数组存储编码字符串指针。
- 编码的结果写入输出流,流均由流处理模块指定。
2.接口模块
这个模块负责将各个模块连接,提供压缩、解压缩的接口。
3.流处理模块
这个模块负责压缩文件写入的格式、解析压缩文件、错误打印格式等。
4.错误处理模块
较为简单,但注意打印的消息要写入标准错误流(STDERR)而非标准输出流(STDOUT)。
5. 位操作模块
提供位操作。
6.测试模块
这个模块虽然名义上为模块,但实际上却渗透到各个模块中,我们通过宏定义开关来降低它与其他模块的耦合度。
流程图
这里主要描述压缩、解压、压缩文件格式。
压缩逻辑流程图
解压逻辑流程图
名词/行为解释
- 压缩
- 实际上是将原字节替换为哈夫曼编码。
- 解压
- 压缩的逆操作,即将哈夫曼编码替换为原字节码。
- 余码
- 由于编码总长度不是8的整数倍而多余出来的码。
压缩文件格式
压缩文件包括:
- 文件头
- 余码
- 原文件大小
- 编码表
- 压缩数据
例子
假设有个压缩文件1.hfm,那么在文件中的数据是这样的:
10000
1824
00 11111111011010110000
01 11111111011010110001
02 11111111011010110010
03 11111111011010110011
04 11111111011010110100
05 11111111011010110101
......
FE 1111111101101010110
FF 1111111101101010111
�fn�ղ�R_p�[/�n��`_�����]W�CI{z��<���P����kK��O������!&��,t䛮���p������
��a`nP
......
第一行是余码;第二行是原文件字节数;接下来的256行([0, 255])是编码表;最后的N行是压缩后的数据,没错,它是乱七八糟的。
代码解读
实际实现时,我们按照由易到难、由具体到抽象的顺序来实现。
很明显,错误处理模块、位操作模块、算法就很具体,而流格式化的模块就相对抽象。
错误处理模块
用到了变参函数。
err.c
#include "err.h"
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void errPrint(const char *format, va_list arg_list)
{
char buf[ERR_BUF_SIZE];
vsnprintf(buf, sizeof(buf), format, arg_list);
fprintf(stderr, "%s", buf);
}
void errExit(const char *format, va_list arg_list)
{
errPrint(format, arg_list);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
void errCaller(void (*errFunc)(const char *, va_list), const char *format, ...)
{
va_list arg_list;
va_start(arg_list, format);
errFunc(format, arg_list);
va_end(arg_list);
}
err.h
#ifndef ERR_H
#define ERR_H
#define ERR_BUF_SIZE 4096
#include <stdarg.h>
void errPrint(const char *format, va_list arg_list);
void errExit(const char *format, va_list arg_list);
void errCaller(void (*errFunc)(const char *, va_list), const char *format, ...);
#endif
位操作模块
bit.c
#include "bit.h"
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "err.h"
void setbit(Byte *pbyte, size_t ordinal, bool value)
{
// ordinal is [0,7], oridinal is from RIGHT to LEFT.
// bit&1 或者 bit|0,不改变值。bit&0 = 0, bit|1 = 1
Byte mask_AND_to_0[8] = {
0xFE, // 0b11111110,
0xFD, // 0b11111101,
0xFB, // 0b11111011,
0xF7, // 0b11110111,
0xEF, // 0b11101111,
0xDF, // 0b11011111,
0xBF, // 0b10111111,
0x7F // 0b01111111
};
Byte mask_OR_to_1[8] = {
0x01, // 0b00000001,
0x02, // 0b00000010,
0x04, // 0b00000100,
0x08, // 0b00001000,
0x10, // 0b00010000,
0x20, // 0b00100000,
0x40, // 0b01000000,
0x80 // 0b10000000
};
if (value == 0) // set to 0
(*pbyte) &= mask_AND_to_0[ordinal];
else if (value == 1)
(*pbyte) |= mask_OR_to_1[ordinal];
}
int getbit(Byte byte, size_t oridinal)
{
return (byte >> oridinal) & 0x00000001;
}
static size_t rest_bit_quantity(Byte *bytebit_buf, size_t buf_size, size_t byte_end, size_t bit_end)
{ //辅助函数,return the rest quantity of bits of bytebit_buf.
return (buf_size - byte_end) * 8 - bit_end;
}
// byte_end is the index of the last byte not full to 8 bits
// bit_end is the index of the end of bytebit_buf[byte_end], not saving data, just like '�' for string.
// bitcat() will trans _01_str to bit and join it to bytebit_buf.
bool bitcat(Byte *bytebit_buf, size_t buf_size, size_t *byte_end, size_t *bit_end, const char *_01_str)
{
size_t i;
if (strlen(_01_str) > rest_bit_quantity(bytebit_buf, buf_size, *byte_end, *bit_end))
return false; //缓冲区已满,无法存入整个01字符串,不存入缓冲区,返回false
for (i = 0; _01_str[i] != '�'; ++i) {
setbit(&(bytebit_buf[*byte_end]), 7 - *bit_end, _01_str[i] - '0');
++(*bit_end); // bit_end加1
if (*bit_end > 7) { // bit满8,byte_end+1,bit_end归零
(*bit_end) %= 8;
++(*byte_end);
}
}
return true;
}
bit.h
#ifndef BIT_H
#define BIT_H
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stddef.h>
typedef unsigned char Byte;
#define BYTE_NUM 256 //[0,255],2^8个
#define BYTE_MIN 0
#define BYTE_MAX 255
void setbit(Byte *pbyte, size_t ordinal, bool value);
int getbit(Byte byte, size_t oridinal);
bool bitcat(Byte *bytebit_buf, size_t buf_size, size_t *byte_end, size_t *bit_end, const char *_01_str);
#endif
包裹函数
在实现剩下的模块之前,我们将一些函数封装成包裹函数,这样不用频繁验证返回值,减少分散我们的注意力。
除了包裹函数还有以下两个自定义函数:
mFclose(),即many Fclose,可以一次性关闭多个文件(注意最后一个参数必须是NULL,否则会运行时错误而中止程序)。itoa_(),由于linux下没有itoa()函数,便自己实现了一下,并且扩展了它的功能,可选补齐前导0 (通过min_length参数)。在字节转位串的时候非常方便。加一条_是为了在其他系统编译时不与标准库的itoa()冲突。
由于FILE*无法得知打开的文件名,在报错误处理时很不方便,为了保留文件名我们将FILE封装为File,并为它适配了相关的包裹函数。
pkg.c
#include "pkg.h"
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "err.h"
File *Fopen(const char *filename, const char *mode)
{
File *file = (File *)malloc(sizeof(File));
file->pfile = fopen(filename, mode);
if (file->pfile == NULL) errCaller(errExit, ERR_MSG_FOPEN(file));
snprintf(file->filename, sizeof(file->filename), "%s", filename);
snprintf(file->mode, sizeof(file->mode), "%s", mode);
return file;
}
int Feof(File *stream) { return feof(stream->pfile); }
void Rewind(File *stream) { rewind(stream->pfile); }
void Fclose(File *stream)
{
if (stream == NULL) return;
if (fclose(stream->pfile) != 0) errCaller(errExit, ERR_MSG_FCLOSE(stream));
free(stream);
}
void mFclose(File *stream, ...) // File* stream_1, File* stream_2 ...,NULL
{
va_list arg_list;
va_start(arg_list, stream);
Fclose(stream);
for (;;) {
stream = va_arg(arg_list, File *);
if (stream == NULL) break;
Fclose(stream);
}
va_end(arg_list);
}
ssize_t Fread(void *mem, size_t elem_size, size_t elem_count, File *istream)
{
return fread(mem, elem_size, elem_count, istream->pfile);
}
ssize_t Fwrite(void *mem, size_t elem_size, size_t elem_count, File *ostream)
{
ssize_t count = fwrite(mem, elem_size, elem_count, ostream->pfile);
if (count < elem_count) errCaller(errExit, ERR_MSG_FWRITE(ostream));
return count;
}
int Fscanf(File *istream, const char *format, ...)
{
va_list arg_list;
va_start(arg_list, format);
int ret = vfscanf(istream->pfile, format, arg_list);
va_end(arg_list);
return ret;
}
int Fprintf(File *ostream, const char *format, ...)
{
va_list arg_list;
va_start(arg_list, format);
int ret = vfprintf(ostream->pfile, format, arg_list);
va_end(arg_list);
return ret;
}
char *itoa_(size_t value, char *result, size_t radix, size_t min_length)
{
const char digits[] = "0123456789abcdef";
char buf[66]; // 65 is the binary length of 2^64;
const size_t end = sizeof(buf) - 1;
const size_t prefix_0_beg = end - min_length;
size_t beg = end;
buf[end] = '�';
size_t digit, i;
for (; value > 0;) {
digit = value % radix;
buf[--beg] = digits[digit];
value /= radix;
}
for (i = prefix_0_beg; i < beg; ++i) //不到最小长度的补前缀0至最小长度,这对不满8位的转换相当重要。
buf[i] = '0';
if (beg > prefix_0_beg) beg = prefix_0_beg;
strcpy(result, &buf[beg]);
strcat(result, "�");
return result;
}
pkg.h
#ifndef PKG_H
#define PKG_H
#include <stdio.h>
#define countof(array) (sizeof(array) / sizeof(array[0]))
#define FILENAME_SIZE 512
#define MODE_SIZE 4
typedef struct File {
FILE *pfile;
char filename[FILENAME_SIZE];
char mode[MODE_SIZE];
} File;
// the type of pfile is File*.
#define ERR_MSG_FOPEN(pfile) "Failed to open file %s.", pfile->filename
#define ERR_MSG_FCLOSE(pfile) "Failed to close file %s.", pfile->filename
#define ERR_MSG_FWRITE(pfile) "Failed to write the whole memory to file %s.", pfile->filename
int Feof(File *stream);
void Rewind(File *stream);
File *Fopen(const char *file, const char *mode);
void Fclose(File *stream);
int Fscanf(File *istream, const char *format, ...);
int Fprintf(File *ostream, const char *format, ...);
void mFclose(File *stream, ...); // File* stream_1, File* stream_2 ...,NULL
ssize_t Fread(void *mem, size_t elem_size, size_t elem_count, File *istream);
ssize_t Fwrite(void *mem, size_t elem_size, size_t elem_count, File *ostream);
char *itoa_(size_t value, char *result, size_t radix, size_t min_length);
#endif
算法模块
到这里有两问题一直很纠结,
- 变量名是越长越好,还是越短越好?太长读代码就像阅读题,太短则像文言文,我宁愿它长一点。
- 用驼峰还是下划线?考虑到变量名长,下划线法单词辨识度应该更高。
huffman.c
#include "huffman.h"
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "bit.h"
#include "err.h"
#include "huffman.h"
static void select_min(huffman_tree tree, const size_t curr_node_index, size_t *min_1, size_t *min_2)
{
size_t i, min_weight = SIZE_MAX;
for (i = 0; i < curr_node_index; ++i)
if (tree[i].parent == HAVE_NO_PARENT && tree[i].weight < min_weight) {
min_weight = tree[i].weight;
*min_1 = i;
}
for (i = 0, min_weight = SIZE_MAX; i < curr_node_index; ++i)
if (tree[i].parent == HAVE_NO_PARENT && tree[i].weight < min_weight && i != *min_1) {
min_weight = tree[i].weight;
*min_2 = i;
}
}
//这里pTree是树的指针,因为要在外部保存树
void create_huffman_tree(huffman_tree *pTree, const size_t *weight, size_t weight_elem_num)
{
size_t i, min_1, min_2;
const size_t num_leafNode = weight_elem_num; //叶子结点数为权值数
const size_t num_allNode = 2 * num_leafNode - 1;
*pTree = (huffman_tree)malloc(num_allNode * sizeof(huffman_tree_node)); // huffman tree 结点数组
huffman_tree tree = *pTree;
for (i = 0; i < num_allNode; ++i) tree[i].parent = HAVE_NO_PARENT; //初始时没有父结点,设为-1
for (i = 0; i < num_leafNode; ++i) tree[i].weight = weight[i]; // leaf node 权值载入
//[0, n-1]是n个叶子结点,[n,2n-1)([n,2n-2]、[n, m))是n-1个双分支结点.
for (i = num_leafNode; i < num_allNode; ++i) { // i是当前结点,min_1、min_2是权值最小的两个结点
select_min(tree, i, &min_1, &min_2);
tree[min_1].parent = i;
tree[min_2].parent = i;
tree[i].lchild = min_1;
tree[i].rchild = min_2;
tree[i].weight = tree[min_1].weight + tree[min_2].weight;
}
}
char **huffman_encode(const huffman_tree tree, size_t num_leafNode)
{
size_t parent, curr, i, start;
const size_t n = num_leafNode;
char **encode_result = (char **)malloc(n * sizeof(char *));
char *one_code = (char *)alloca(n * sizeof(char)); //分配编码工作空间
one_code[n - 1] = '�';
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i) { //遍历tree中所有结点
curr = i;
start = n - 1;
parent = tree[curr].parent;
while (parent != HAVE_NO_PARENT) { //遍历该节点的父结点,一直找到根结点,即没有父结点的结点
if (tree[parent].lchild == curr) //当前结点位于左分支
one_code[--start] = '0';
else
one_code[--start] = '1';
curr = parent; //继续上行找父节点
parent = tree[parent].parent;
}
encode_result[i] = (char *)malloc((n - start) * sizeof(char)); //动态分配编码长度
strcpy(encode_result[i], &one_code[start]);
}
return encode_result; // static variable encode_result shold be free outside.
}
void huffman_decode(char *_01_str, size_t *_01_str_end, const char **encode_result, Byte *result,
size_t *result_end)
{ // result_end is the first byte not saving data, like '�'.
size_t beg, i;
*result_end = 0;
bool find;
for (beg = 0; _01_str[beg] != '�';) {
for (i = 0, find = false; i < BYTE_NUM; ++i) {
size_t len = strlen(encode_result[i]);
if (strncmp(encode_result[i], &_01_str[beg], len) == 0) { //匹配成功
result[*result_end] = i;
++(*result_end);
beg += len;
find = true;
break;
}
}
if (!find) break; //说明一个都没匹配到,结束
}
char tmp_str[9];
strcpy(tmp_str, &_01_str[beg]); //剩下的复位到首部
strcpy(_01_str, tmp_str);
*_01_str_end = strlen(_01_str);
}
huffman.h
#ifndef HUFFMAN_H
#define HUFFMAN_H
#define HAVE_NO_PARENT -1
#include "bit.h"
typedef struct huffman_node_data_type {
Byte data;
} huffman_node_data_type;
typedef struct huffman_tree_node {
huffman_node_data_type data;
size_t weight;
int lchild, rchild, parent;
} huffman_tree_node, *huffman_tree;
void create_huffman_tree(huffman_tree *pTree, const size_t *weight, size_t weight_elem_num);
char **huffman_encode(const huffman_tree tree, size_t num_leafNode);
void huffman_decode(char *_01_str, size_t *_01_str_end, const char **encode_result, Byte *result,
size_t *result_end);
#endif
接口模块
interface.c
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "bit.h"
#include "huffman.h"
#include "pkg.h"
#include "stream_manager.h"
void compress(File *istream, File *ostream, const char **encode_result)
{
Byte read_buf[IO_BUF_SIZE]; // 此处要保证IO_BUF_SIZE不小于strlen(one_code),否则永远存不下,永远失败.
Byte bytebit_buf[BYTE_BIT_BUF_SIZE];
ssize_t count;
size_t i, byte_end, bit_end, origin_size;
reserve_header(ostream);
output_huffmanCode(ostream, encode_result);
origin_size = 0;
for (byte_end = bit_end = 0; !Feof(istream);) {
count = Fread(read_buf, sizeof(read_buf[0]), countof(read_buf), istream);
if (count <= 0) continue;
origin_size += count * sizeof(read_buf[0]); //统计原来大小
for (i = 0; i < count; ++i) {
const char *one_code = encode_result[read_buf[i]];
if (bitcat(bytebit_buf, sizeof(bytebit_buf), &byte_end, &bit_end, one_code))
continue;
else { //连接失败,说明缓冲区已满
fflush_bytebit_buffer(bytebit_buf, &byte_end, ostream); //刷新缓冲区
--i; //抵消++i,使得one_code被重写
}
}
}
fflush_bytebit_buffer(bytebit_buf, &byte_end, ostream); //所有字符转换完了,再刷新一次.
char surplus[9];
itoa_(bytebit_buf[byte_end], surplus, 2, 0);
surplus[bit_end] = '�'; //截断非有效bit
fill_header(ostream, surplus, origin_size);
}
void decompress(File *istream, File *ostream)
{
char surplus[9];
size_t origin_size;
const char **encode_result = (const char **)parse_compress_header(istream, surplus, &origin_size);
Byte read_buf[IO_BUF_SIZE], decode_buf[IO_BUF_SIZE];
char _01_str[_01_STR_BUF_SIZE];
size_t i, _01_str_end, decode_buf_end;
ssize_t count;
for (decode_buf_end = _01_str_end = 0; !Feof(istream);) {
count = Fread(read_buf, sizeof(read_buf[0]), countof(read_buf), istream);
if (count <= 0) continue;
for (i = 0; i < count;) {
if (sizeof(_01_str) - 1 - _01_str_end >= 8) { //足8位
itoa_(read_buf[i], &_01_str[_01_str_end], 2, 8); //连接成01字符串
_01_str_end += 8;
++i;
} else { // 01_str缓冲区已满,刷新缓冲区
huffman_decode(_01_str, &_01_str_end, encode_result, decode_buf, &decode_buf_end);
Fwrite(decode_buf, sizeof(decode_buf[0]), decode_buf_end, ostream);
}
}
}
strcat(_01_str, surplus);
huffman_decode(_01_str, &_01_str_end, encode_result, decode_buf, &decode_buf_end);
Fwrite(decode_buf, sizeof(decode_buf[0]), decode_buf_end, ostream);
}
interface.h
#ifndef INTERFACE_H
#define INTERFACE_H
#include "pkg.h"
void compress(File *istream, File *ostream, const char **encode_result);
void decompress(File *istream, File *ostream);
#endif
流处理模块
stream_manager.c
#include "stream_manager.h"
#include <stddef.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "bit.h"
#include "err.h"
#include "pkg.h"
void count_byte_weight(File *istream, size_t *byte_times, size_t byte_times_size)
{
size_t i;
memset(byte_times, 0, byte_times_size); //字节集归零
Byte bytes[IO_BUF_SIZE]; // save the bytes read.
ssize_t count;
for (; !Feof(istream);) {
count = Fread(bytes, sizeof(bytes[0]), countof(bytes), istream);
if (count <= 0) continue;
for (i = 0; i < count; ++i) { // tarverse all the bytes read, 将对应字节值计数加一
++byte_times[bytes[i]];
}
}
}
void output_huffmanCode(File *ostream, const char **encode_result)
{
size_t i;
const size_t num_leafNode = BYTE_NUM;
for (i = 0; i < num_leafNode; ++i) {
Fprintf(ostream, O_FORMAT_BODY_HUFFMAN_CODE, i, encode_result[i]);
}
}
char **parse_compress_header(File *istream, char *surplus, size_t *origin_size)
{
Fscanf(istream, I_FORMAT_HEADER_SURPLUS, surplus);
Fscanf(istream, I_FORMAT_HEADER_ORIGIN_SIZE, origin_size);
char **encode_result = (char **)malloc(sizeof(char *) * BYTE_MAX);
char one_code[HUFFMAN_CODE_MAX_LEN];
size_t i, unused;
for (i = 0; i <= BYTE_MAX; ++i) {
Fscanf(istream, I_FORMAT_BODY_HUFFMAN_CODE, &unused, one_code);
encode_result[i] = (char *)malloc(strlen(one_code) * sizeof(char));
strcpy(encode_result[i], one_code);
}
return encode_result; // should be free outside.
}
ssize_t fflush_bytebit_buffer(Byte *bytebit_buf, size_t *byte_end, File *ostream)
{ // bytebit_buf[byte_end]是未填充满的字节,此处只写入填充满的字节,即byte_end-1个字节
ssize_t count = Fwrite(bytebit_buf, sizeof(bytebit_buf[0]), *byte_end, ostream);
bytebit_buf[0] = bytebit_buf[*byte_end]; //把结尾未满8位的bit复制到开头
*byte_end = 0; //缓冲区归零
return count;
}
void reserve_header(File *ostream)
{
Fprintf(ostream, O_FORMAT_HEADER_SURPLUS, ""); // surplus
Fprintf(ostream, O_FORMAT_HEADER_ORIGIN_SIZE, (long)0); // origin_size
}
static void rewind_header(File *ostream) { rewind(ostream->pfile); }
void fill_header(File *ostream, const char *surplus, size_t origin_size)
{
rewind_header(ostream);
Fprintf(ostream, O_FORMAT_HEADER_SURPLUS, surplus);
Fprintf(ostream, O_FORMAT_HEADER_ORIGIN_SIZE, origin_size);
}
stream_manager.h
#ifndef STREAM_MANAGER_H
#define STREAM_MANAGER_H
#include "bit.h"
#include "pkg.h"
#define HUFFMAN_CODE_MAX_LEN BYTE_NUM
#define IO_BUF_SIZE 4096
#define BYTE_BIT_BUF_SIZE 4096
#define _01_STR_BUF_SIZE 4096
#define I_FORMAT_HEADER_SURPLUS "%8sn" // surplus
#define O_FORMAT_HEADER_SURPLUS "%-8sn" // surplus
#define I_FORMAT_HEADER_ORIGIN_SIZE "%20ldn" // origin_size
#define O_FORMAT_HEADER_ORIGIN_SIZE "%-20ldn" // origin_size
#define I_FORMAT_BODY_HUFFMAN_CODE "%02lXt%sn" // byte, huffman_code
#define O_FORMAT_BODY_HUFFMAN_CODE "%02lXt%sn" // byte, huffman_code
void count_byte_weight(File *istream, size_t *byte_times, size_t byte_times_size);
void output_huffmanCode(File *ostream, const char **encode_result);
char **parse_compress_header(File *istream, char *surplus, size_t *origin_size);
ssize_t fflush_bytebit_buffer(Byte *bytebit_buf, size_t *byte_end, File *ostream);
void reserve_header(File *ostream);
void fill_header(File *ostream, const char *surplus, size_t origin_size);
#endif
main函数
main函数给了一个使用的例子。
main.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "bit.h"
#include "err.h"
#include "huffman.h"
#include "interface.h"
#include "pkg.h"
#include "stream_manager.h"
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
File *istream, *ostream;
const char *src_file = argv[1], *dest_file = argv[2];
//统计字节数
istream = Fopen(src_file, "r");
size_t byte_times[BYTE_NUM];
count_byte_weight(istream, byte_times, sizeof(byte_times));
//压缩
huffman_tree tree;
create_huffman_tree(&tree, byte_times, countof(byte_times));
const char **encode_result_1 = (const char **)huffman_encode(tree, BYTE_NUM);
Rewind(istream);
ostream = Fopen(dest_file, "w");
compress(istream, ostream, encode_result_1);
free(encode_result_1);
mFclose(istream, ostream, NULL);
//解压
const char new_file[] = "decompress.txt";
istream = Fopen(dest_file, "r");
ostream = Fopen(new_file, "w");
decompress(istream, ostream);
mFclose(istream, ostream, NULL);
return 0;
}
makefile
CC = gcc
BIN = main
OBJ = bit.o err.o huffman.o interface.o main.o pkg.o stream_manager.o
LIB =
INC =
FLAGS = $(INC) -Wall
main: $(OBJ)
@$(CC) $(OBJ) -o $(BIN) $(LIB)
bit.o: bit.c bit.h err.h
@$(CC) -c bit.c -o bit.o $(FLAGS)
err.o: err.c err.h
@$(CC) -c err.c -o err.o $(FLAGS)
huffman.o: huffman.c huffman.h bit.h err.h
@$(CC) -c huffman.c -o huffman.o $(FLAGS)
interface.o: interface.c bit.h pkg.h stream_manager.h
@$(CC) -c interface.c -o interface.o $(FLAGS)
main.o: main.c bit.h huffman.h interface.h pkg.h stream_manager.h
@$(CC) -c main.c -o main.o $(FLAGS)
pkg.o: pkg.c pkg.h err.h
@$(CC) -c pkg.c -o pkg.o $(FLAGS)
stream_manager.o: stream_manager.c stream_manager.h pkg.h bit.h err.h
@$(CC) -c stream_manager.c -o stream_manager.o $(FLAGS)
.PHONY: clean
clean:
@rm $(OBJ) $(BIN)
测试模块
这个部分我还没有实现,但是测试了一个618M的mkv视频文件。
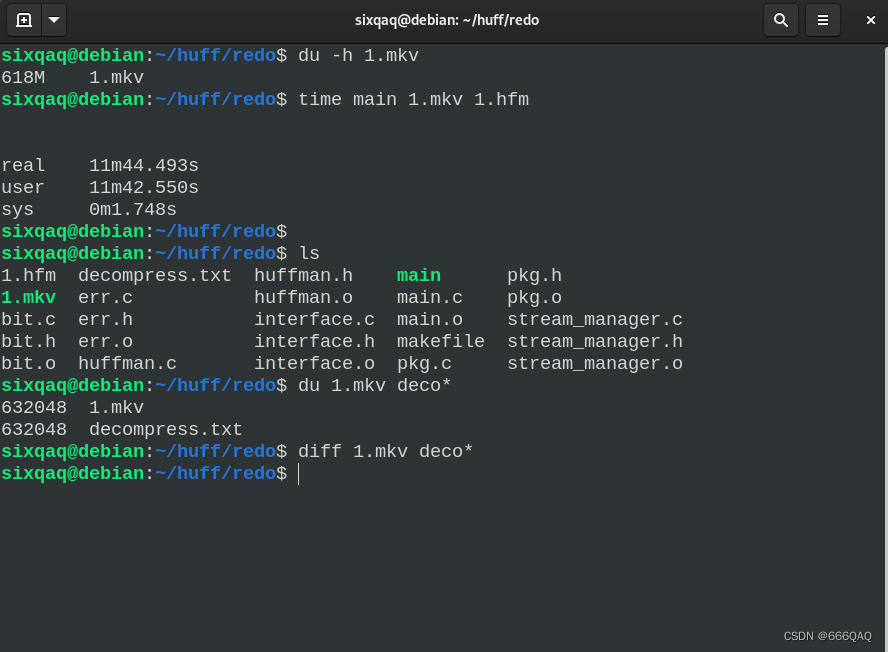
可以看到,100%地还原了。但是压缩后的文件更大了
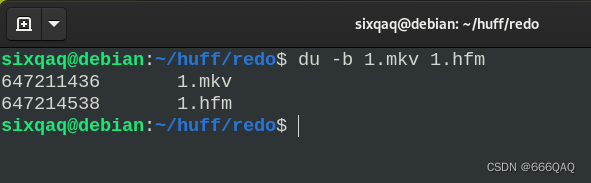
这是因为视频文件本身就是压缩格式的,再压缩它也没有效果。
上次做的压缩率在70%~75%,这次的理论上要高一点,因为为了赶工减少了一些优化步骤,后面会再改进。
后续
上面的代码在我的64位 debian11上编译0报错0警告,gcc版本为10.2.1。
windows上没有再测试了,应该也能通过。
同样也能看到,压缩+解压速度慢得惊人,23min,这是我们不可能接受的。
后续会进行效率提升……
改进 (2023.3.15)
- 位和串的转换
缓冲区那里写的太恶心了,需要把它整的干净利索一点。 - 解码匹配
另一个是解压时的字符串匹配,我们用的遍历暴力匹配,时间复杂度是 O(n2)。
有两种思路改进,-
用哈希表来暴力匹配。
- 单个字符用hash来查找复杂度是O(1)。n个字符,那么时间复杂度应该是O(n);
-
把编码重新构建成树,通过遍历树来匹配。
- 单个字符只需用
if判断一下即可,显然时间复杂度是O(1),n个字符,那么时间复杂度应该是O(n)。
- 单个字符只需用
-
后面有空就改进它。
1. 错误处理
有小的改动,不过用法是差不多的。
err.h
#ifndef ERR_H
#define ERR_H
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stddef.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <errno.h>
#ifdef __cplusplus
extern "C" {
#endif
/**
* @details 打印错误信息
*/
#define errPrint(format,...)
do{
__errPrint__(format, ##__VA_ARGS__);
}while(0)
/**
* @details 打印错误信息,附带调试信息
*/
#define errPrint_debug(format,...)
do{
__errPrint__("Error occurs at file <%s>, line <%d>.n",__FILE__,__LINE__);
__errPrint__("Errno value:<%d>, reasen:<%s>.n",errno,strerror(errno));
__errPrint__ (format, ##__VA_ARGS__);
} while (0)
/**
* @details 打印错误信息并终止线程
*/
#define errExit(format, ...)
do{
errPrint (format, ##__VA_ARGS__);
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
} while (0)
/**
* @details 打印错误并终止线程,附带调试信息
*/
#define errExit_debug(format, ...)
do{
errPrint_debug (format, ##__VA_ARGS__);
exit (EXIT_FAILURE);
} while (0)
void __errPrint__ (const char *format, ...);
#ifdef __cplusplus
}
#endif
#endif
err.c
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void __errPrint__ (const char *format, ...)
{
va_list argList;
va_start (argList, format);
vfprintf (stderr, format, argList);
va_end (argList);
}
memory.h
#ifndef MEMORY_H
#define MEMORY_h
#include <stdlib.h>
void *Malloc (size_t size);
//free mem and set it to NULL to avoid double free error, also easy to debug
#define Free(mem)
do{
free(mem);
mem = NULL;
} while (0)
#endif
memory.c
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "err.h"
void *Malloc (size_t size)
{
void *mem = malloc (size);
if (mem == NULL)
errExit_debug ("malloc() failed.n");
return mem;
}
2. 位串转换
这个部分比较重要,经过一番思考,之前用缓冲区的想法来设计,代码耦合度很高。因为我们需要的转换比较复杂琐碎。
带来的后果就是,代码不够清晰、不够健壮。
所以这里引入另一个数据结构:队列。
将缓冲区的一部分功能由队列实现,尽可能屏蔽掉底层细节,让代码抽象化。
实现上区别于一般的队列,我们需要增设一个变量来指示有效长度,因为总bit数不一定是8的整数倍。
bit_queue.h
#ifndef BIT_QUEUE_H
#define BIT_QUEUE_h
#include "bit.h"
#include "memory.h"
#include <stdio.h>
typedef struct BitQueue {
Byte *memory;
int front;//头元素
int rear;//尾元素的下一个位置
int effect_bits_count_of_last_byte;
const size_t size;
} BitQueue;
/**
* @warning 能否再弹出/压入,指的均是有效位数,不包含无效位数。
*
*/
//构造一个bit队列
BitQueue *construct_bit_queue (size_t byte_num);
//销毁一个bit队列
void destruct_bit_queue (BitQueue *queue);
//复制一个完全一样的bit队列
BitQueue *clone_bit_queue (const BitQueue *queue);
//清空队列
void clear_queue (BitQueue *queue);
//压入一个bit
void push_one_bit (BitQueue *queue, Bit bit);
//弹出一个bit
Bit pop_one_bit (BitQueue *queue);
//压入一个字节
void push_one_byte (BitQueue *queue, Byte byte);
//弹出一个字节
Byte pop_one_byte (BitQueue *queue);
//能否再压入一个bit
bool one_bit_pushable (const BitQueue *queue);
//能否再装下多个bit
bool many_bits_pushable (const BitQueue *queue, int count);
//能否再弹一个bit
bool one_bit_popable (const BitQueue *queue);
//能否再弹出多个bit
bool many_bits_popable (const BitQueue *queue, int count);
//能否再压入一个字节
bool one_byte_pushable (const BitQueue *queue);
//能否再压入多个字节
bool many_byte_pushable (const BitQueue *queue, int count);
//能否再弹出一个字节
bool one_byte_popable (const BitQueue *queue);
//能否再弹出多个字节
bool many_bytes_popable (const BitQueue *queue, int count);
//将一个BitQueue中的数据全部弹出,并压入另一个中
void push_bits (BitQueue *queue, BitQueue *bits);
//从一个BitQueue中弹出指定数量的bit,并压入到目标队列中
void pop_bits (BitQueue *queue, int bits_count, BitQueue *dest);
//当前bit数量
size_t current_bits_count (const BitQueue *queue);
//是否为空
bool is_empty (const BitQueue *queue);
//是否已满
bool is_full (const BitQueue *queue);
//最大可存bit数
size_t max_bits_count (const BitQueue *queue);
//剩余可存bit数
size_t empty_bits_count (const BitQueue *queue);
#endif
bit_queue.c
#include "bit_queue.h"
#include <string.h>
BitQueue *construct_bit_queue (size_t byte_num)
{
BitQueue *queue = malloc (sizeof (BitQueue));
* (size_t *) &queue->size = byte_num;
queue->front = queue->front = 0;
queue->memory = (Byte *) Malloc (byte_num);
return queue;
}
void destruct_bit_queue (BitQueue *queue)
{
Free (queue->memory);
Free (queue);
}
static size_t current_bytes_count (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return (queue->rear - queue->front) % queue->size;
}
size_t current_bits_count (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return (current_bytes_count (queue) - 1) * 8 + queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte;
}
bool is_empty (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return (queue->front == queue->rear) && queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte == 0;
}
bool is_full (const BitQueue *queue)
{
if ( (queue->rear % queue->size == queue->front) && queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte == 8)
return true;
return false;
}
size_t max_bits_count (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return (queue->size - 1) * 8;
}
size_t empty_bits_count (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return max_bits_count (queue) - current_bits_count (queue);
}
void push_one_bit (BitQueue *queue, Bit bit)
{
if (queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte == 8) {//如果最后一个字节已经装不下
queue->rear++;//瞄准下一个字节
queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte = 0;
}
Byte *last_byte = &queue->memory[queue->rear - 1];
set_bit (last_byte, queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte, bit);
queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte++;//有效比特数+1
}
Bit pop_one_bit (BitQueue *queue)
{
if (queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte == 0) { //最后一个字节已经空了
queue->rear--;//瞄准前一个字节
queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte = 8;
}
Byte last_byte = queue->memory[queue->rear - 1];
Bit bit = get_bit (last_byte, queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte);
queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte--;//有效比特-1;
return bit;
}
void clear_queue (BitQueue *queue)
{
queue->effect_bits_count_of_last_byte = 0;
queue->front = queue->rear = 0;
}
bool one_bit_pushable (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return many_bits_pushable (queue, 1);
}
bool one_bit_popable (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return many_bits_popable (queue, 1);
}
void push_bits (BitQueue *queue, BitQueue *bits)
{
for (; one_bit_popable (bits) ;) {
push_one_bit (queue, pop_one_bit (bits));
}
}
BitQueue *clone_bit_queue (const BitQueue *queue)
{
BitQueue *copy = construct_bit_queue (queue->size);
memcpy (copy->memory, queue->memory, queue->size);
copy->front = queue->front;
copy->rear = queue->rear;
return copy;
}
void pop_bits (BitQueue *queue, int bits_count, BitQueue *dest)
{
for (int i = 0; i < bits_count ; ++i) {
push_one_bit (dest, pop_one_bit (queue));
}
}
void push_one_byte (BitQueue *queue, Byte byte)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 8 ; ++i) {
push_one_bit (queue, get_bit (byte, i));
}
}
Byte pop_one_byte (BitQueue *queue)
{
Byte byte;
for (int i = 0; i < 8 ; ++i) {
set_bit (&byte, i, pop_one_bit (queue));
}
return byte;
}
bool one_byte_popable (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return current_bits_count (queue) >= 8;
}
bool one_byte_pushable (const BitQueue *queue)
{
return empty_bits_count (queue) >= 8;
}
bool many_bits_pushable (const BitQueue *queue, int count)
{
return empty_bits_count (queue) >= count;
}
bool many_bits_popable (const BitQueue *queue, int count)
{
return current_bits_count (queue) >= count;
}
bool many_bytes_pushable (const BitQueue *queue, int count)
{
return many_bits_pushable (queue, count * 8);
}
bool many_bytes_popable (const BitQueue *queue, int count)
{
return many_bits_popable (queue, count * 8);
}
- 待办
备战考研去了……
最后
以上就是凶狠蜜蜂最近收集整理的关于[小项目]手把手教你C语言哈夫曼压缩/解压缩的全部内容,更多相关[小项目]手把手教你C语言哈夫曼压缩/解压缩内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。




![[小项目]手把手教你C语言哈夫曼压缩/解压缩](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg1.png)



发表评论 取消回复