一、简介
Lzlib 压缩库提供了在内存中的 LZMA 压缩和解压算法功能,包括对数据进行完整性检查。压缩格式是 lzip
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/damenhanter/article/details/30757685
二、安装
http://www.educity.cn/linux/1577732.html
三、实例
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/turingo/article/details/8148264
示例1:compression.c
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <zlib.h> int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { FILE* file; uLong flen; unsigned char* fbuf = NULL; uLong clen; unsigned char* cbuf = NULL; /* 通过命令行参数将srcfile文件的数据压缩后存放到dstfile文件中 */ if(argc < 3) { printf("Usage: zcdemo srcfile dstfilen"); return -1; } if((file = fopen(argv[1], "rb")) == NULL) { printf("Can't open %s!n", argv[1]); return -1; } /* 装载源文件数据到缓冲区 */ fseek(file, 0L, SEEK_END); /* 跳到文件末尾 */ flen = ftell(file); /* 获取文件长度 */ fseek(file, 0L, SEEK_SET); if((fbuf = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * flen)) == NULL) { printf("No enough memory!n"); fclose(file); return -1; } fread(fbuf, sizeof(unsigned char), flen, file); /* 压缩数据 */ clen = compressBound(flen); if((cbuf = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * clen)) == NULL) { printf("No enough memory!n"); fclose(file); return -1; } if(compress(cbuf, &clen, fbuf, flen) != Z_OK) { printf("Compress %s failed!n", argv[1]); return -1; } fclose(file); if((file = fopen(argv[2], "wb")) == NULL) { printf("Can't create %s!n", argv[2]); return -1; } /* 保存压缩后的数据到目标文件 */ fwrite(&flen, sizeof(uLong), 1, file); /* 写入源文件长度 */ fwrite(&clen, sizeof(uLong), 1, file); /* 写入目标数据长度 */ fwrite(cbuf, sizeof(unsigned char), clen, file); fclose(file); free(fbuf); free(cbuf); return 0; }
decompression.c
#include <stdlib.h> #include <stdio.h> #include <zlib.h> int main(int argc, char* argv[]) { FILE* file; uLong flen; unsigned char* fbuf = NULL; uLong ulen; unsigned char* ubuf = NULL; /* 通过命令行参数将srcfile文件的数据解压缩后存放到dstfile文件中 */ if(argc < 3) { printf("Usage: zudemo srcfile dstfilen"); return -1; } if((file = fopen(argv[1], "rb")) == NULL) { printf("Can't open %s!n", argv[1]); return -1; } /* 装载源文件数据到缓冲区 */ fread(&ulen, sizeof(uLong), 1, file); /* 获取缓冲区大小 */ fread(&flen, sizeof(uLong), 1, file); /* 获取数据流大小 */ if((fbuf = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * flen)) == NULL) { printf("No enough memory!n"); fclose(file); return -1; } fread(fbuf, sizeof(unsigned char), flen, file); /* 解压缩数据 */ if((ubuf = (unsigned char*)malloc(sizeof(unsigned char) * ulen)) == NULL) { printf("No enough memory!n"); fclose(file); return -1; } if(uncompress(ubuf, &ulen, fbuf, flen) != Z_OK) { printf("Uncompress %s failed!n", argv[1]); return -1; } fclose(file); if((file = fopen(argv[2], "wb")) == NULL) { printf("Can't create %s!n", argv[2]); return -1; } /* 保存解压缩后的数据到目标文件 */ fwrite(ubuf, sizeof(unsigned char), ulen, file); fclose(file); free(fbuf); free(ubuf); return 0; }
编译
gcc -g -o compression compression.c -lz gcc -g -o decompression decompression.c -lz
运行
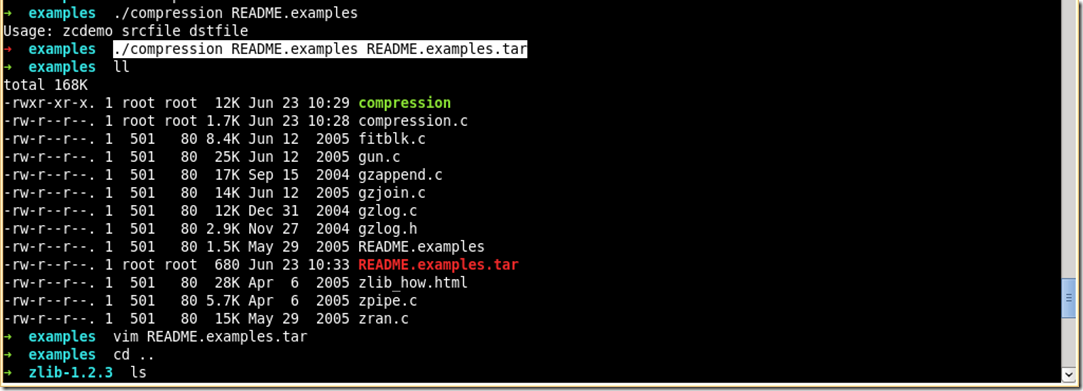
示例2:
参考:
http://blog.csdn.net/yoki2009/article/details/4291215 http://www.cppblog.com/woaidongmao/archive/2009/09/07/95495.html
/* zpipe.c: example of proper use of zlib's inflate() and deflate() Not copyrighted -- provided to the public domain Version 1.2 9 November 2004 Mark Adler */ /* Version history: 1.0 30 Oct 2004 First version 1.1 8 Nov 2004 Add void casting for unused return values Use switch statement for inflate() return values 1.2 9 Nov 2004 Add assertions to document zlib guarantees 1.3 6 Apr 2005 Remove incorrect assertion in inf() */ #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> #include <assert.h> #include "zlib.h" #define CHUNK 16384 /* Compress from file source to file dest until EOF on source. def() returns Z_OK on success, Z_MEM_ERROR if memory could not be allocated for processing, Z_STREAM_ERROR if an invalid compression level is supplied, Z_VERSION_ERROR if the version of zlib.h and the version of the library linked do not match, or Z_ERRNO if there is an error reading or writing the files. */ int def(FILE *source, FILE *dest, int level) { int ret, flush; unsigned have; z_stream strm; char in[CHUNK]; char out[CHUNK]; /* allocate deflate state */ strm.zalloc = Z_NULL; strm.zfree = Z_NULL; strm.opaque = Z_NULL; ret = deflateInit(&strm, level); if (ret != Z_OK) return ret; /* compress until end of file */ do { strm.avail_in = fread(in, 1, CHUNK, source); if (ferror(source)) { (void)deflateEnd(&strm); return Z_ERRNO; } flush = feof(source) ? Z_FINISH : Z_NO_FLUSH; strm.next_in = in; /* run deflate() on input until output buffer not full, finish compression if all of source has been read in */ do { strm.avail_out = CHUNK; strm.next_out = out; ret = deflate(&strm, flush); /* no bad return value */ assert(ret != Z_STREAM_ERROR); /* state not clobbered */ have = CHUNK - strm.avail_out; if (fwrite(out, 1, have, dest) != have || ferror(dest)) { (void)deflateEnd(&strm); return Z_ERRNO; } } while (strm.avail_out == 0); assert(strm.avail_in == 0); /* all input will be used */ /* done when last data in file processed */ } while (flush != Z_FINISH); assert(ret == Z_STREAM_END); /* stream will be complete */ /* clean up and return */ (void)deflateEnd(&strm); return Z_OK; } /* Decompress from file source to file dest until stream ends or EOF. inf() returns Z_OK on success, Z_MEM_ERROR if memory could not be allocated for processing, Z_DATA_ERROR if the deflate data is invalid or incomplete, Z_VERSION_ERROR if the version of zlib.h and the version of the library linked do not match, or Z_ERRNO if there is an error reading or writing the files. */ int inf(FILE *source, FILE *dest) { int ret; unsigned have; z_stream strm; char in[CHUNK]; char out[CHUNK]; /* allocate inflate state */ strm.zalloc = Z_NULL; strm.zfree = Z_NULL; strm.opaque = Z_NULL; strm.avail_in = 0; strm.next_in = Z_NULL; ret = inflateInit(&strm); if (ret != Z_OK) return ret; /* decompress until deflate stream ends or end of file */ do { strm.avail_in = fread(in, 1, CHUNK, source); if (ferror(source)) { (void)inflateEnd(&strm); return Z_ERRNO; } if (strm.avail_in == 0) break; strm.next_in = in; /* run inflate() on input until output buffer not full */ do { strm.avail_out = CHUNK; strm.next_out = out; ret = inflate(&strm, Z_NO_FLUSH); assert(ret != Z_STREAM_ERROR); /* state not clobbered */ switch (ret) { case Z_NEED_DICT: ret = Z_DATA_ERROR; /* and fall through */ case Z_DATA_ERROR: case Z_MEM_ERROR: (void)inflateEnd(&strm); return ret; } have = CHUNK - strm.avail_out; if (fwrite(out, 1, have, dest) != have || ferror(dest)) { (void)inflateEnd(&strm); return Z_ERRNO; } } while (strm.avail_out == 0); /* done when inflate() says it's done */ } while (ret != Z_STREAM_END); /* clean up and return */ (void)inflateEnd(&strm); return ret == Z_STREAM_END ? Z_OK : Z_DATA_ERROR; } /* report a zlib or i/o error */ void zerr(int ret) { fputs("zpipe: ", stderr); switch (ret) { case Z_ERRNO: if (ferror(stdin)) fputs("error reading stdinn", stderr); if (ferror(stdout)) fputs("error writing stdoutn", stderr); break; case Z_STREAM_ERROR: fputs("invalid compression leveln", stderr); break; case Z_DATA_ERROR: fputs("invalid or incomplete deflate datan", stderr); break; case Z_MEM_ERROR: fputs("out of memoryn", stderr); break; case Z_VERSION_ERROR: fputs("zlib version mismatch!n", stderr); } } /* compress or decompress from stdin to stdout */ int main(int argc, char **argv) { int ret; FILE *filein, *fileout; if((filein = fopen(argv[1], "rb")) == NULL) { printf("Can't open %s!n", argv[1]); return -1; } if((fileout = fopen(argv[2], "wb")) == NULL) { printf("Can't open %s!n", argv[1]); return -1; } /* do compression if no arguments */ if (argc == 3) { ret = def(filein, fileout, Z_DEFAULT_COMPRESSION); if (ret != Z_OK) zerr(ret); return ret; } /* do decompression if -d specified */ else if (argc == 4 && strcmp(argv[3], "-d") == 0) { ret = inf(filein, fileout); if (ret != Z_OK) zerr(ret); return ret; } /* otherwise, report usage */ else { fputs("zpipe usage: zpipe (source) (dest) [-d] n", stderr); return 1; } }
编译
gcc -g -o zpipe zpipe.c -lz
运行
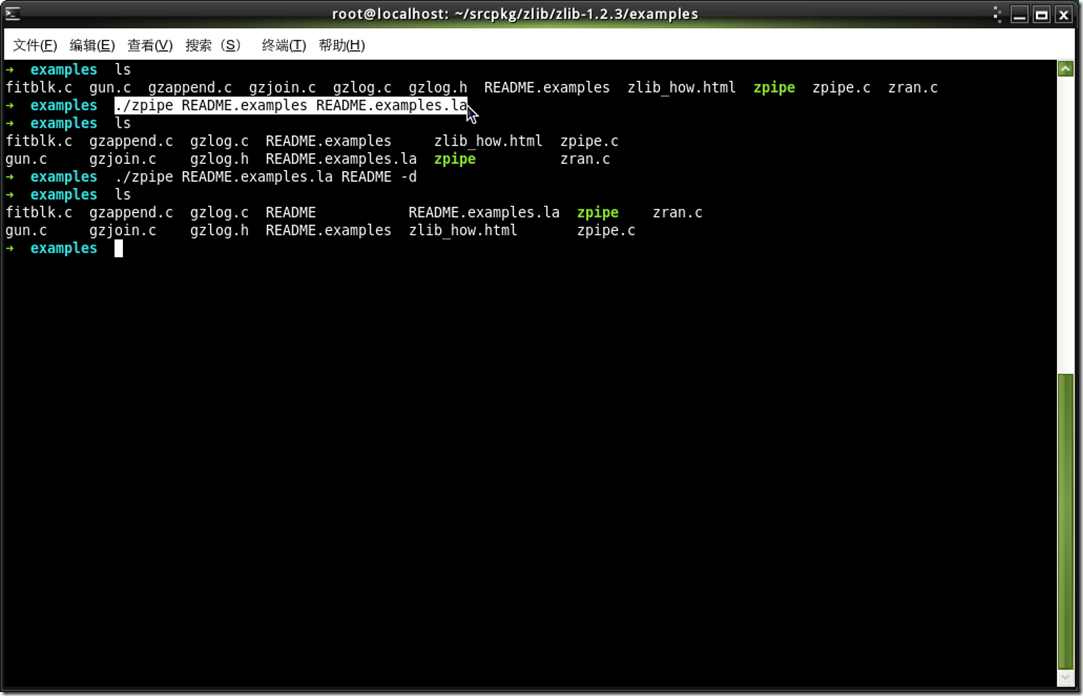
最后
以上就是温柔鲜花最近收集整理的关于C语言压缩/解压缩的全部内容,更多相关C语言压缩/解压缩内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复