目录
1. 简介
2. 整体流程
3. Sampler和BatchSampler
3.1 Sampler
3.2 BatchSampler
4. DataLoader
4.1 DataLoader
4.2 _DataLoaderIter
1. 简介
本文将简介pytorch采样器Sampler和数据加载器DataLoader,并解释在读取数据时每个batch形成的过程,附上部分源码解读。
了解这些能帮助我们更好地研究采样(sample)方法和模型训练。希望阅读后能让各位对数据批次产生的过程更加清晰。
让我们开始吧。
2. 整体流程
简要来说在pytorch中,Sampler负责决定读取数据时的先后顺序,DataLoader负责装载数据并根据Sampler提供的顺序安排数据,具体过程绘图和描述如下。
初始化DataLoader的时候需指定数据集Dataset(包括数据和标签),Sampler可选,没有Sampler时会根据是否打乱数据顺序(shuffle)分别采用顺序采样器(sequential sampler)和随机采样器(random sampler)。
第①步,Sampler首先根据Dataset的大小n形成一个可迭代的序号列表[0~n-1]。
第②步,BatchSampler根据DataLoader的batch_size参数将Sampler提供的序列划分成多个batch大小的可迭代序列组,drop_last参数决定是否保留最后一组。
第③步,兵分两路的Sampler(BatchSampler)和Dataset合二为一,在迭代读取DataLoader时,用BatchSampler中一个batch的编号查找Dataset中对应的数据和标签,读出一个batch数据。
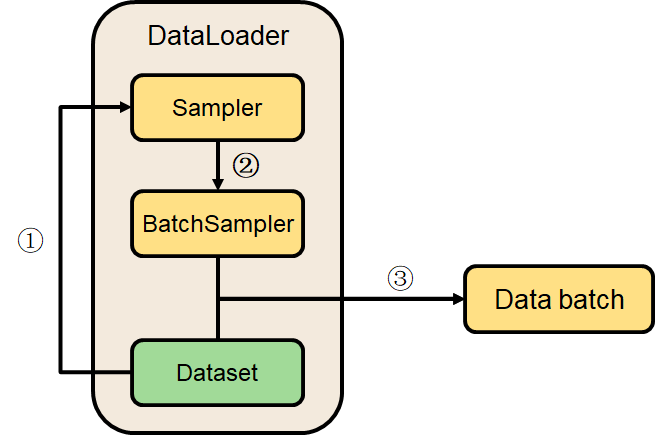
举个例子。
假如数据集D={X,Y},其中数据X为[野兔在野外.png,野猫在野外.png,野猫在家.png,野狗在家.png,野狗在野外.png],标签Y为[0,1,1,2,2]
第①步,初始的序号列表为[0, 1, 2, 3, 4],使用RandomSampler采样,不重复(replacement==FALSE),得到了采样后的序号列表[3, 2, 1, 0, 4]
第②步:输入batch_size为2,drop_last为FALSE,所以用BatchSampler批次采样,形成列表[[3, 2], [1, 0], [4]];若drop_last为TRUE,则列表变为[[3, 2], [1, 0]]
第③步:迭代读取数据,根据序号从Dataset里找到相应数据和标签,如第一个batch为:
[[野狗在家.png, 野猫在家.png], [2, 1]]
以上就是形成一个batch数据的整个流程,下文将从代码角度深入介绍各个Class中的重要参数和函数。我是用较旧的pytorch版本(0.4.1.post2),也自己对照了一下1.7.0版本的代码。其中BatchSampler类基本一致,Sampler类去掉了__len__()方法,总的来说采样改动不大;DataLoader类主要是针对多线程做了很多优化,具体代码中也补充了大量注释,整体基础仍然是本文提到的几个方法。
3. Sampler和BatchSampler
3.1 Sampler
知乎上一篇文章对pytorch Sampler进行了很详细的讲解:一文弄懂Pytorch的DataLoader, DataSet, Sampler之间的关系
 简要来说,Sampler类__init__()方法用于初始化采样算法,__iter__()方法用torch的random、multinomial方法实现随机和基于权重的采样并返回可迭代对象,__len__()是返回采样长度。
简要来说,Sampler类__init__()方法用于初始化采样算法,__iter__()方法用torch的random、multinomial方法实现随机和基于权重的采样并返回可迭代对象,__len__()是返回采样长度。
3.2 BatchSampler
参数:
sampler(Sampler类):输入的sampler
batch_size(int类):设定的批次大小
drop_last(bool类):是否弃掉不足batch_size大小的最后一个批次
重要函数:
__init__初始化各项参数
def __init__(self, sampler, batch_size, drop_last):
# ...
self.sampler = sampler
self.batch_size = batch_size
self.drop_last = drop_last__iter__循环读取sampler生成的序号列表,采样够batch_size大小后,返回batch,下一次清空batch继续采集。
def __iter__(self):
batch = []
for idx in self.sampler:
batch.append(idx)
if len(batch) == self.batch_size:
# 通过yield返回,下一个iter时清空batch继续采集
yield batch
batch = []
# 如果不需drop最后一组返回最后一组
if len(batch) > 0 and not self.drop_last:
yield batch__len__返回batch数量,如果drop最后一个,则序列长度对batch_size取整,否则加上一
def __len__(self):
if self.drop_last:
return len(self.sampler) // self.batch_size
else:
return (len(self.sampler) + self.batch_size - 1) // self.batch_size4. DataLoader
4.1 DataLoader
重要参数:
dataset(Dataset类):Dataset类型的输入数据,由数据和标签组成
batch_size(int类):同BatchSampler
shuffle(bool类):是否打乱数据顺序
sampler(Sampler类):同BatchSampler
batch_sampler(BatchSampler类)
drop_last(bool类):同BatchSampler
重要函数:
__init__中对参数关系中的互斥情况进行了排除,指定sampler并通过batch_sampler分出batch,
def __init__(self, dataset, batch_size=1, shuffle=False, sampler=None, batch_sampler=None,
num_workers=0, collate_fn=default_collate, pin_memory=False, drop_last=False,
timeout=0, worker_init_fn=None):
# ...
# 互斥关系,指定了batch_sampler时,batch_size,shuffle,sampler和drop_last无效
if batch_sampler is not None:
if batch_size > 1 or shuffle or sampler is not None or drop_last:
raise ValueError('batch_sampler option is mutually exclusive '
'with batch_size, shuffle, sampler, and '
'drop_last')
self.batch_size = None
self.drop_last = None
# 互斥关系,指定了sampler时,shuffle无效
if sampler is not None and shuffle:
raise ValueError('sampler option is mutually exclusive with '
'shuffle')
if self.num_workers < 0:
raise ValueError('num_workers option cannot be negative; '
'use num_workers=0 to disable multiprocessing.')
# 此处可以看出,shuffle与否其实还是靠sampler类型实现的
# 当不指定sampler时,不shuffle就是顺序采样,shuffle就是随机采样
if batch_sampler is None:
if sampler is None:
if shuffle:
sampler = RandomSampler(dataset)
else:
sampler = SequentialSampler(dataset)
# 用batch_sampler对sampler产生的序列划分batch
batch_sampler = BatchSampler(sampler, batch_size, drop_last)
self.sampler = sampler
self.batch_sampler = batch_sampler
self.__initialized = TrueDataLoader的__iter__是在_DataLoaderIter类中实现的,该类也是整个迭代方法的核心
def __iter__(self):
return _DataLoaderIter(self)4.2 _DataLoaderIter
__init__初始化并指定了sampler_iter,即batch_sampler
def __init__(self, loader):
self.dataset = loader.dataset
self.collate_fn = loader.collate_fn
self.batch_sampler = loader.batch_sampler
self.num_workers = loader.num_workers
self.pin_memory = loader.pin_memory and torch.cuda.is_available()
self.timeout = loader.timeout
self.done_event = threading.Event()
self.sample_iter = iter(self.batch_sampler)
# ...
_get_batch读取数据,加入了连接超时的判断
def _get_batch(self):
# 连接超时
if self.timeout > 0:
try:
return self.data_queue.get(timeout=self.timeout)
except queue.Empty:
raise RuntimeError('DataLoader timed out after {} seconds'.format(self.timeout))
else:
return self.data_queue.get()_DataLoaderIter在每次调用时会执行__next__方法返回下一个batch
def __next__(self):
if self.num_workers == 0: # same-process loading
indices = next(self.sample_iter) # may raise StopIteration
batch = self.collate_fn([self.dataset[i] for i in indices])
if self.pin_memory:
batch = pin_memory_batch(batch)
return batch
# check if the next sample has already been generated
if self.rcvd_idx in self.reorder_dict:
batch = self.reorder_dict.pop(self.rcvd_idx)
return self._process_next_batch(batch)
if self.batches_outstanding == 0:
self._shutdown_workers()
raise StopIteration
while True:
assert (not self.shutdown and self.batches_outstanding > 0)
idx, batch = self._get_batch()
self.batches_outstanding -= 1
if idx != self.rcvd_idx:
# store out-of-order samples
self.reorder_dict[idx] = batch
continue
return self._process_next_batch(batch)
# 调用时执行__next__
next = __next__ # Python 2 compatibility
欢迎交流和指正。
最后
以上就是沉默金针菇最近收集整理的关于[Pytorch] Sampler, DataLoader和数据batch的形成1. 简介2. 整体流程3. Sampler和BatchSampler4. DataLoader的全部内容,更多相关[Pytorch]内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。




![[Pytorch] Sampler, DataLoader和数据batch的形成1. 简介2. 整体流程3. Sampler和BatchSampler4. DataLoader](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg4.png)



发表评论 取消回复