进制转换(栈)
void DuiZhan(int num)
{
SqStack st;
InitStack(st); char x;
char sixteen[] = { '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F' };
int j;
cout << "要将num转为哪种进制" << endl;
cin >> j;
switch (j)
{
case 2:case 8:
while (num)
{
push(st, sixteen[num%j]);
num = num / j;
}
while (!StackEmpty(st))
{
pop(st, x);
cout << x;
}
cout << endl;
break;
case 16:
while (num)
{
push(st, sixteen[num % 16]);
num = num / 16;
}
while (!StackEmpty(st))
{
pop(st, x);
cout << x;
}
cout << endl;
break;
}
}
进制转换(递归)
void Digui(int num)
{
if (num == 0)
return;
else {
Digui(num/16);
if (num % 16 >= 10)
switch (num % 16)
{
case 10:
cout << "A";
break;
case 11:
cout << "B";
break;
case 12:
cout << "C";
break;
case 13:
cout << "D";
break;
case 14:
cout << "E";
break;
case 15:
cout << "F";
break;
default:break;
}
else
cout << num % 16;
}
}
总代码:
//进制转换
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
//五、分别用栈和递归来实现十进制转换为16进制。
#define maxsize 10
typedef struct
{
char data[maxsize];
int top;
}SqStack;
void InitStack(SqStack &st)
{
st.top = -1;
}
void DestroyStack(SqStack st)
{}
int push(SqStack &st, char x)//进栈
{
if (st.top == maxsize)
return 0;
else
{
st.top++;
st.data[st.top] = x;
return 1;
}
}
int pop(SqStack &st, char &x)//出栈
{
if (st.top == -1)
return 0;
else {
x = st.data[st.top];
st.top--;
return 1;
}
}
int StackEmpty(SqStack &st)//判断是否栈空 ,是:1;否:0.
{
if (st.top == -1)
return 1;
else
return 0;
}
int GetTop(SqStack &st, char &x)
{
if (st.top == -1)
return 0;
else {
x = st.data[st.top];
return 1;
}
}
void OutputStack(SqStack st)
{
SqStack sts = st;
while (sts.top != -1)
{
cout<< sts.data[sts.top] << " ";
sts.top--;
}
cout << endl;
}
void DuiZhan(int num)
{
SqStack st;
InitStack(st); char x;
char sixteen[] = { '0', '1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F' };
int j;
cout << "要将num转为哪种进制" << endl;
cin >> j;
switch (j)
{
case 2:case 8:
while (num)
{
push(st, sixteen[num%j]);
num = num / j;
}
while (!StackEmpty(st))
{
pop(st, x);
cout << x;
}
cout << endl;
break;
case 16:
while (num)
{
push(st, sixteen[num % 16]);
num = num / 16;
}
while (!StackEmpty(st))
{
pop(st, x);
cout << x;
}
cout << endl;
break;
}
}
void Digui(int num)
{
if (num == 0)
return;
else {
Digui(num/16);
if (num % 16 >= 10)
switch (num % 16)
{
case 10:
cout << "A";
break;
case 11:
cout << "B";
break;
case 12:
cout << "C";
break;
case 13:
cout << "D";
break;
case 14:
cout << "E";
break;
case 15:
cout << "F";
break;
default:break;
}
else
cout << num % 16;
}
}
void main()
{
int m;
cout << "请输入num" << endl;
cin >> m;
DuiZhan(m);
Digui(m);
}
后缀表达式
int fuhaocal(char fuhao, int x, int y)
{
switch (fuhao)
{
case'+':
return x + y;
case '-':
return x - y;
case '*':
return x * y;
case '/':
return x / y;
default:
cout << "false" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
int calculate(char *str, int *result)
{
char ch;
SqStack *st = new SqStack;
InitStack(*st);
int i = 0;
int c,x,y;
while (str[i] != '=')
{
ch = str[i];
if (ch >= '0'&&ch <= '9')
{
c = ch - '0';
if (push(*st, c) != 1)
{
cout << "超出界限" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
else if (ch == '+' || ch == '-' || ch == '*' || ch == '/')
{
pop(*st, x);
pop(*st, y);
int item = fuhaocal(ch,y, x);
push(*st, item);
}
i++;
}
*result = st->data[st->top];
return 0;
}
中缀表达式
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include"head.h"
using namespace std;
int priority(char a)
{
int i = 1;
switch (a)
{
case '#':
i = 0;
break;
case '+':
case '-':
i = 1;
break;
case '*':
case '/':
i = 2;
break;
case '(':
i = 3;
break;
default:
break;
}
return i;
}
string caculate(char a, string a1, string a2)
{
double re=0;
double b1, b2;
string result;
b1 = atof(a1.c_str());
b2 = atof(a2.c_str());
switch (a)
{
case '+':
re = b2 + b1;
break;
case '-':
re = b2 - b1;
break;
case '*':
re = b2 * b1;
break;
case '/':
re = b2 / b1;
break;
default:
break;
}
result = to_string(re);
return result;
}
void main()
{
stackNode *data,*symbol;
initNode(&data);
initNode(&symbol);
string question;
double result;
cin >> question;
question = '#' + question + '#';
for (int i = 0; i < question.length(); i++)
{
if (isdigit(question[i]))
{
string d;
d.push_back(question[i]);
data = push(data, d);
}
else
{
if (judge(symbol))
{
string s;
s.push_back(question[i]);
symbol = push(symbol, s);
continue;
}
if (question[i] == '(')
{
string s;
s.push_back(question[i]);
symbol = push(symbol, s);
continue;
}
if (question[i] == ')')
{
while (getTop(symbol)[0] != '(')
{
string s, d1, d2;
symbol = pop(symbol, s);
data = pop(data, d1);
data = pop(data, d2);
d1 = caculate(s[0], d1, d2);
data = push(data, d1);
}
string s1;
symbol = pop(symbol, s1);
continue;
}
else
{
if (getTop(symbol)[0] == '(')
{
string s;
s.push_back(question[i]);
symbol = push(symbol, s);
continue;
}
int iThis, iBefore;
iThis = priority(question[i]);
iBefore = priority(getTop(symbol)[0]);
if (iThis > iBefore)
{
string s;
s.push_back(question[i]);
symbol = push(symbol, s);
}
if (iThis <= iBefore)
{
if (question[i] == '#'&&getTop(symbol)[0] == '#')
continue;
while (getTop(symbol)[0] != '#'&& getTop(symbol)[0] != '(')
{
string s, d1,d2;
symbol = pop(symbol, s);
data = pop(data, d1);
data = pop(data, d2);
d1 = caculate(s[0],d1,d2);
data = push(data, d1);
}
string s;
s.push_back(question[i]);
symbol = push(symbol, s);
}
}
}
}
cout << getTop(data) << endl;
}
附:递归算法
斐波那契数列
该问题可以用递归形式来表示,即有递归公式:
fibo=fibonacci(n-1)+fibonacci(n-2)
递归结束条件为:当n=1或n=2,fibo=1
可以构建一个递归子函数int fibonacci(int n)来实现求第n项的值,主函数中调用该递归子函数。
int fibos(int n)
{
int fibo;
if (n == 1 || n == 2)
{
fibo=1;
}
else {
fibo = fibos(n - 1) + fibos(n - 2);//递归调用
}
return fibo;
}
当函数是void
void shunxu(int m)
{
if (m == 0)
{
return;
}
else {
mix(m - 1);
cout << m << " ";
}
}
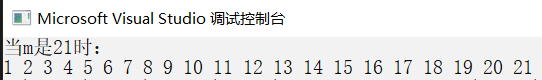
由于递归是内存自动建立栈,所以可以这样理解。递归函数先找到出口,从出口反向运算到初始条件。这就与栈表现相似。
最后
以上就是飘逸心锁最近收集整理的关于数据结构入门系列——用栈解决实际问题(2)的全部内容,更多相关数据结构入门系列——用栈解决实际问题(2)内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。





![Mybatis[4] - 配置文件 - plugins](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg2.png)


发表评论 取消回复