以下的全部内容都是yolo-v3-spp的预测模块
项目全部代码已上传至GitHub: yolov3-spp-annotations.
目录标题
- 一、predict.py
- 二、几个重要函数
- 2.1、letterbox函数
- 2.2、non_max_suppression函数
- 2.3、scale_coords函数
- 2.4、draw_box函数
- Reference
一、predict.py
1、整体流程
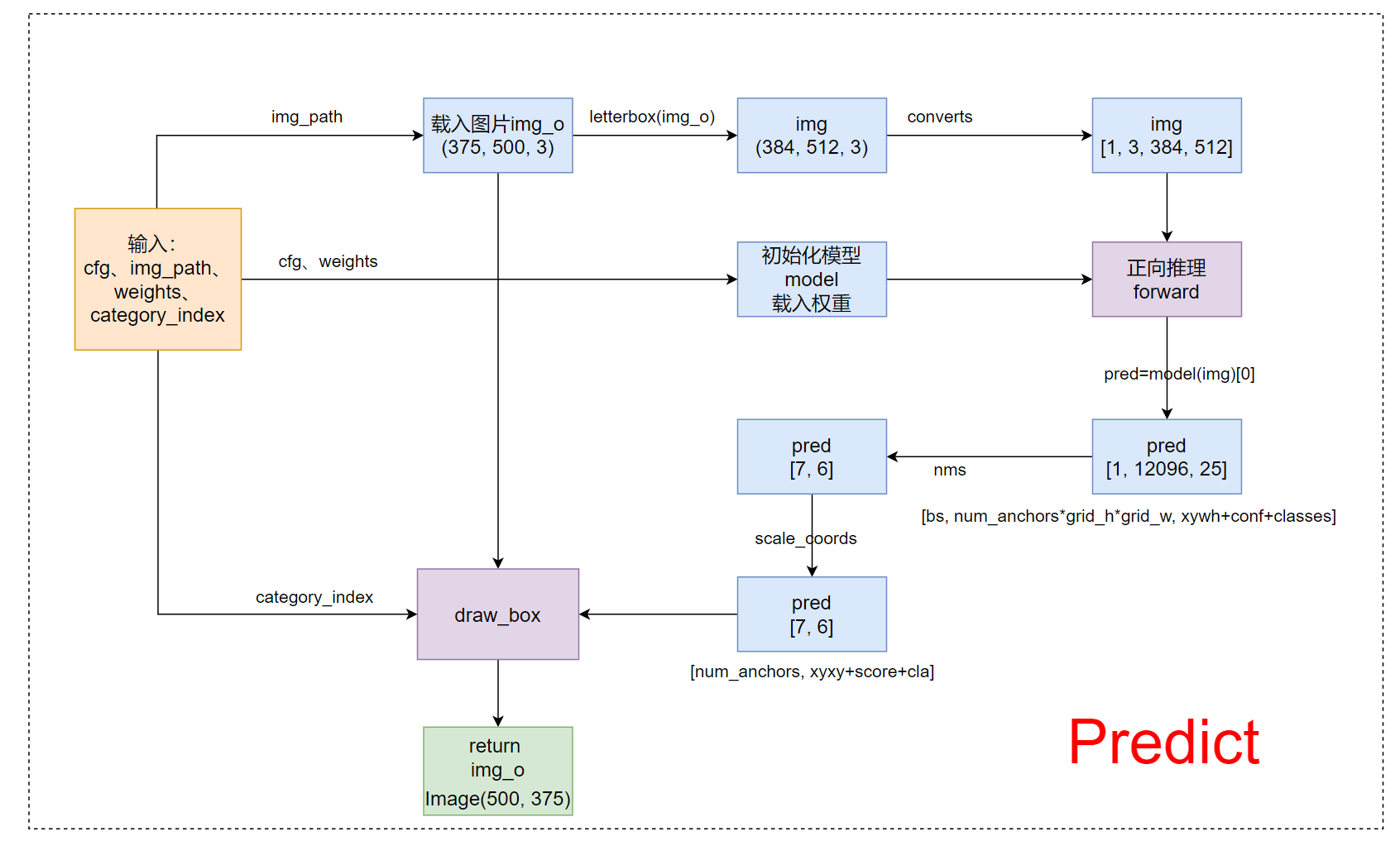
2、代码
import os
import json
import time
import torch
import cv2
import argparse
import numpy as np
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from build_utils import datasets
from modules.model import DarkNet
from train_val_utils.draw_box_utils import draw_box
from train_val_utils.other_utils import time_synchronized, check_file
from train_val_utils.post_processing_utils import non_max_suppression, scale_coords
def main(opt):
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print("Using {} device training.".format(device.type))
# 1、载入opt参数
cfg = opt.cfg # yolo网络配置文件path
weights = opt.weights # 训练权重path
json_path = opt.json_path # voc classes json path
img_path = opt.img_path # 预测图片地址
img_size = opt.img_size # 预测图像大小(letterbox后)
# 2、载入json文件 得到所有class
json_file = open(json_path, 'r')
class_dict = json.load(json_file)
category_index = {v: k for k, v in class_dict.items()}
# 3、初始化模型 模型载入权重
model = DarkNet(cfg)
model.load_state_dict(torch.load(weights, map_location=device)["model"], strict=False)
model.to(device)
# eval测试模式
model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# 载入原图 img_o (375, 500, 3) H W C
img_o = cv2.imread(img_path) # BGR numpy格式
assert img_o is not None, "Image Not Found " + img_path
# letterbox numpy格式(array) img:(384, 512, 3) H W C
# 将原图最长边缩放到指定大小,再将原图较短边按原图比例缩放,最后将较短边两边pad操作缩放到最长边大小(不会失真)
img = datasets.letterbox(img_o, new_shape=img_size, auto=True, color=(0, 0, 0))[0]
# Convert (384, 512, 3) => (384, 512, 3) => (3, 384, 512)
# img[:, :, ::-1] BGR to RGB => transpose(2, 0, 1) HWC(384, 512, 3) to CHW(3, 384, 512)
img = img[:, :, ::-1].transpose(2, 0, 1)
img = np.ascontiguousarray(img) # 使内存是连续的
# numpy(3, 384, 512) CHW => torch.tensor [3, 384, 512] CHW
img = torch.from_numpy(img).to(device).float()
img /= 255.0 # 归一化scale (0, 255) to (0, 1)
# [3, 384, 512] CHW => [1, 3, 384, 512] BCHW
img = img.unsqueeze(0) # add batch dimension
# start inference
t1 = time_synchronized() # 获取当前时间 其实可以用time.time()
# 推理阶段实际上会有两个返回值 x(相对原图的), p
# x: predictor数据处理后的输出(数值是相对原图的,这里是img)
# [batch_size, anchor_num * grid * grid, xywh + obj + classes]
# 这里pred[1,12096,25] (实际上是等于x)表示这张图片总共生成了12096个anchor(一个grid中三个anchor)
# p: predictor原始输出即数据是相对feature map的
# [batch_size, anchor_num, grid, grid, xywh + obj + classes]
pred = model(img)[0] # only get inference result
t2 = time_synchronized()
print("model inference time:", t2 - t1)
# nms pred=[7,6]=[obj_num, xyxy+score+cls] 这里的xyxy是相对img的
# pred: 按score从大到小排列; output[0]=第一张图片的预测结果 不一定一次只传入一张图片的
pred = non_max_suppression(pred)[0]
t3 = time.time()
print("nms time:", t3 - t2)
if pred is None:
print("No target detected.")
exit(0)
# 将nms后的预测结果pred tensor格式(是相对img上的)img.shape=[B,C,H,W]
# 映射到原图img_o上 img_o.shape=[H, W, C] pred=(anchor_nums, xyxy+score+class)
pred[:, :4] = scale_coords(img.shape[2:], pred[:, :4], img_o.shape).round()
print("pred shape:", pred.shape)
# tensor.detach()截断tensor变量反向传播的梯度流,因为是预测所以不需要计算梯度信息
# bboxes、scores、classes: 按score从大到小排列 tensor=>numpy
bboxes = pred[:, :4].detach().cpu().numpy() # xyxys
scores = pred[:, 4].detach().cpu().numpy() # scores
classes = pred[:, 5].detach().cpu().numpy().astype(int) + 1 # classes
# 到这一步,我们就得到了最终的相对原图的所有预测信息bboxes(位置信息)(7,4); scores(7); classes(类别)(7)
# 画出每个预测结果
img_o = draw_box(img_o[:, :, ::-1], bboxes, classes, scores, category_index)
# 显示预测图片
plt.imshow(img_o)
plt.show()
# 保存预测后的图片
img_o.save("outputs/predict_result.jpg")
if __name__ == "__main__":
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--cfg', type=str, default='cfg/yolov3-spp.cfg', help="cfg/*.cfg path")
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='weights/yolov3spp-voc-512.pt',
help='pretrain weights path')
parser.add_argument('--json-path', type=str, default='data/pascal_voc_classes.json',
help="voc_classes_json_path")
parser.add_argument('--img-path', type=str, default='imgs/2008_000011.jpg',
help="predict img path")
parser.add_argument('--img-size', type=int, default=512,
help="predict img path [416, 512, 608] 32的倍数")
opt = parser.parse_args()
# 检查文件是否存在
opt.cfg = check_file(opt.cfg)
opt.data = check_file(opt.weights)
opt.hyp = check_file(opt.json_path)
opt.hyp = check_file(opt.img_path)
print(opt)
main(opt)
3、执行效果
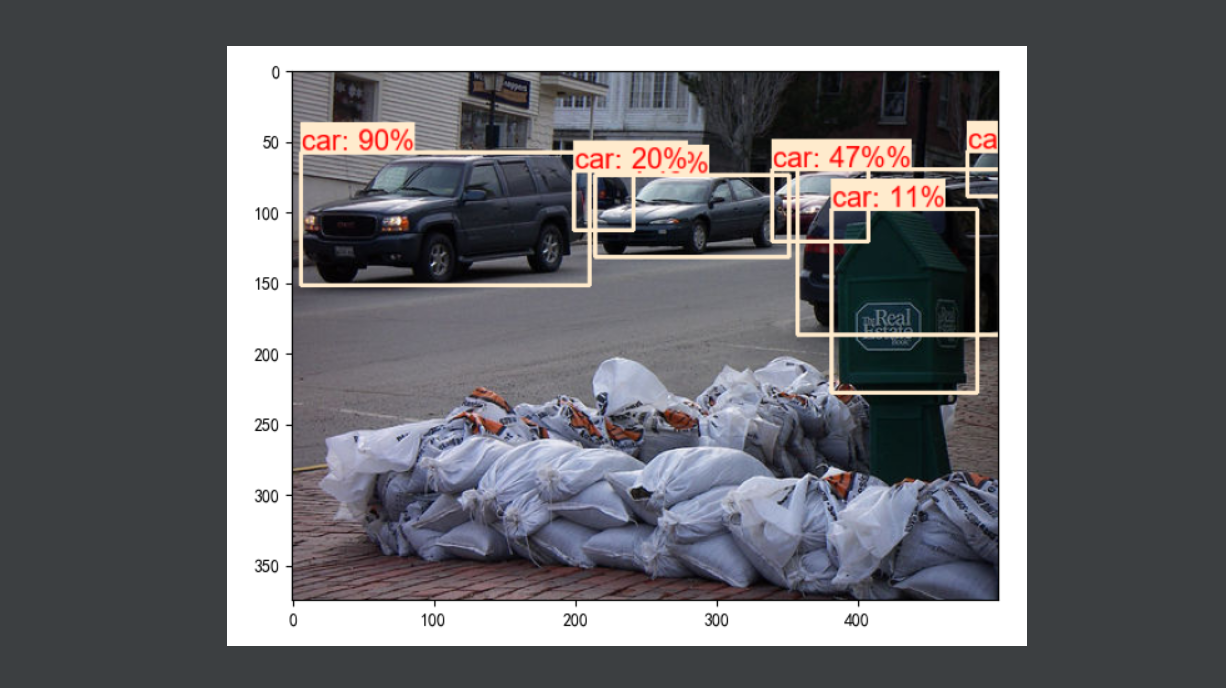

二、几个重要函数
上面的predict.py就是预测模块的执行脚本,代码还是比较简单的,主要难点就是集中在几下的几个函数,这里详细分析一下。
2.1、letterbox函数
以下代码我作了详细的注解,如果还是看不懂,可以看下图的函数流程
1、函数流程
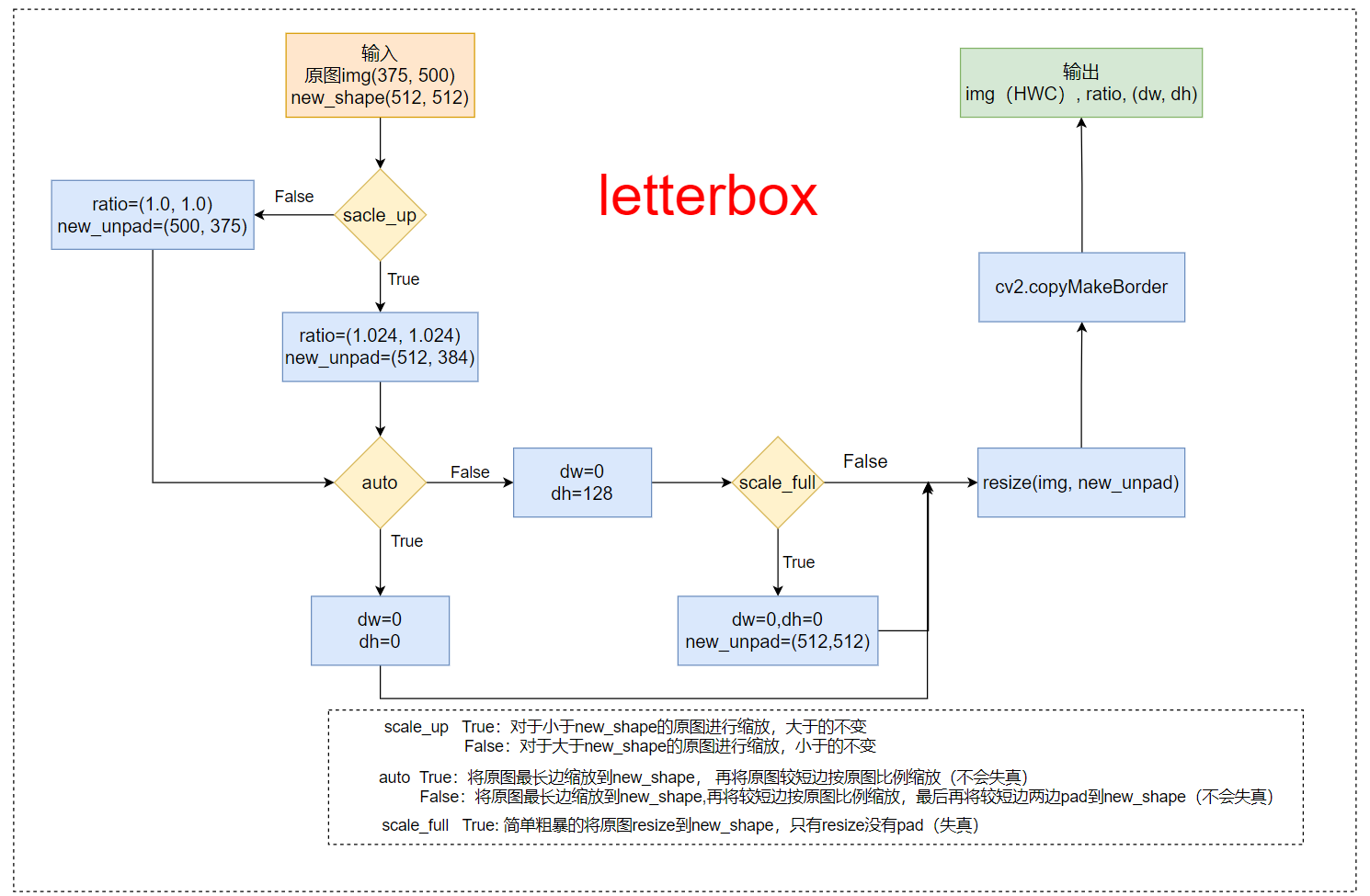
2、函数代码
datasets.py
import cv2
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = ['SimHei'] # 显示中文标签
plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False # 这两行需要手动设置
def letterbox(img: np.ndarray, new_shape=(416, 416), color=(114, 114, 114),
auto=True, scale_fill=False, scale_up=True):
"""
将图片缩放调整到指定大小
:param img: 原图 hwc=(375,500,3)
:param new_shape: 缩放后的最长边大小
:param color: pad的颜色
:param auto: True 保证缩放后的图片保持原图的比例 即 将原图最长边缩放到指定大小,再将原图较短边按原图比例缩放(不会失真)
False 将原图最长边缩放到指定大小,再将原图较短边按原图比例缩放,最后将较短边两边pad操作缩放到最长边大小(不会失真)
:param scale_fill: True 简单粗暴的将原图resize到指定的大小 相当于就是resize 没有pad操作(失真)
:param scale_up: True 对于小于new_shape的原图进行缩放,大于的不变
False 对于大于new_shape的原图进行缩放,小于的不变
:return: img: letterbox后的图片 HWC
ratio: wh ratios
(dw, dh): w和h的pad
"""
shape = img.shape[:2] # 原图大小[h, w] = [375, 500]
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape) # (512, 512)
# scale ratio (new / old) 1.024
r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scale_up: # (for better test mAP) scale_up = False 对于大于new_shape(r<1)的原图进行缩放,小于new_shape(r>1)的不变
r = min(r, 1.0)
# compute padding
ratio = r, r # width, height ratios (1.024, 1.024)
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * r)), int(round(shape[0] * r)) # wh(512, 384) 保证缩放后图像比例不变
dw, dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding dw=0 dh=128
if auto: # minimun rectangle 保证原图比例不变,将图像最大边缩放到指定大小
# 这里的取余操作可以保证padding后的图片是32的整数倍(416x416),如果是(512x512)可以保证是64的整数倍
dw, dh = np.mod(dw, 64), np.mod(dh, 64) # wh padding dw=0 dh=0
elif scale_fill: # stretch 简单粗暴的将图片缩放到指定尺寸
dw, dh = 0, 0
new_unpad = new_shape
ratio = new_shape[0] / shape[1], new_shape[1] / shape[0] # wh ratios
dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides 将padding分到上下,左右两侧
dh /= 2
# shape:[h, w] new_unpad:[w, h]
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # 将原图resize到new_unpad(长边相同,比例相同的新图)
img = cv2.resize(img, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(dh - 0.1)), int(round(dh + 0.1)) # 计算上下两侧的padding
left, right = int(round(dw - 0.1)), int(round(dw + 0.1)) # 计算左右两侧的padding
img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border/pad
return img, ratio, (dw, dh)
# 下面代码是做个测试,可以删除
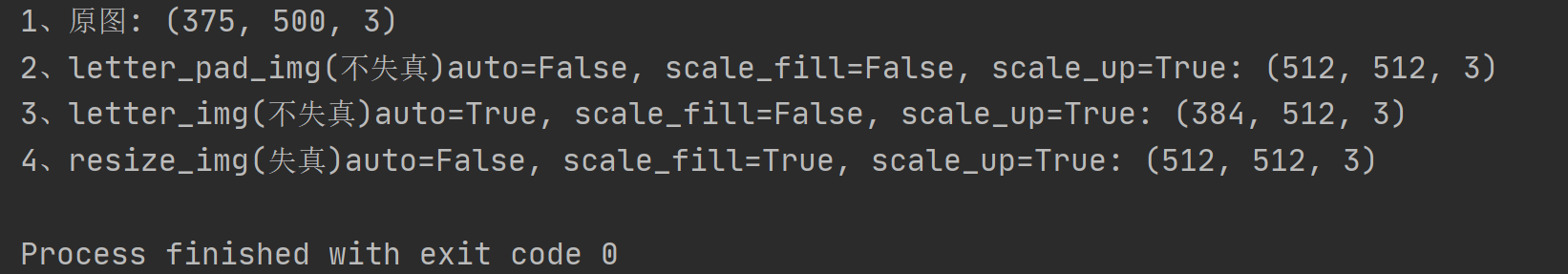
if __name__ == '__main__':
img_o = cv2.imread("../imgs/2008_000011.jpg") # BGR HWC
img_o = img_o[:, :, ::-1] # BGR => RGB
print("1、原图:", img_o.shape)
letter_pad_img = letterbox(img_o, new_shape=512, auto=False, color=(255, 255, 255))[0]
print("2、letter_pad_img(不失真)auto=False, scale_fill=False, scale_up=True:", letter_pad_img.shape)
letter_img = letterbox(img_o, new_shape=512, auto=True, color=(255, 255, 255))[0]
print("3、letter_img(不失真)auto=True, scale_fill=False, scale_up=True:", letter_img.shape)
resize_img = letterbox(img_o, new_shape=512, auto=False, scale_fill=True, color=(0, 0, 0))[0]
print("4、resize_img(失真)auto=False, scale_fill=True, scale_up=True:", resize_img.shape)
plt.figure(figsize=(20, 10))
plt.subplot(1, 4, 1)
plt.imshow(img_o)
plt.title('原图: (375, 500, 3)', fontsize=15)
plt.subplot(1, 4, 2)
plt.imshow(letter_pad_img)
plt.title('letter_pad_img(不失真): (512, 512, 3)', fontsize=15)
plt.subplot(1, 4, 3)
plt.imshow(letter_img)
plt.title('letter_img(不失真): (384, 512, 3)', fontsize=15)
plt.subplot(1, 4, 4)
plt.imshow(resize_img)
plt.title('暴力resize_img(失真): (512, 512, 3)', fontsize=15)
plt.show()
3、执行效果
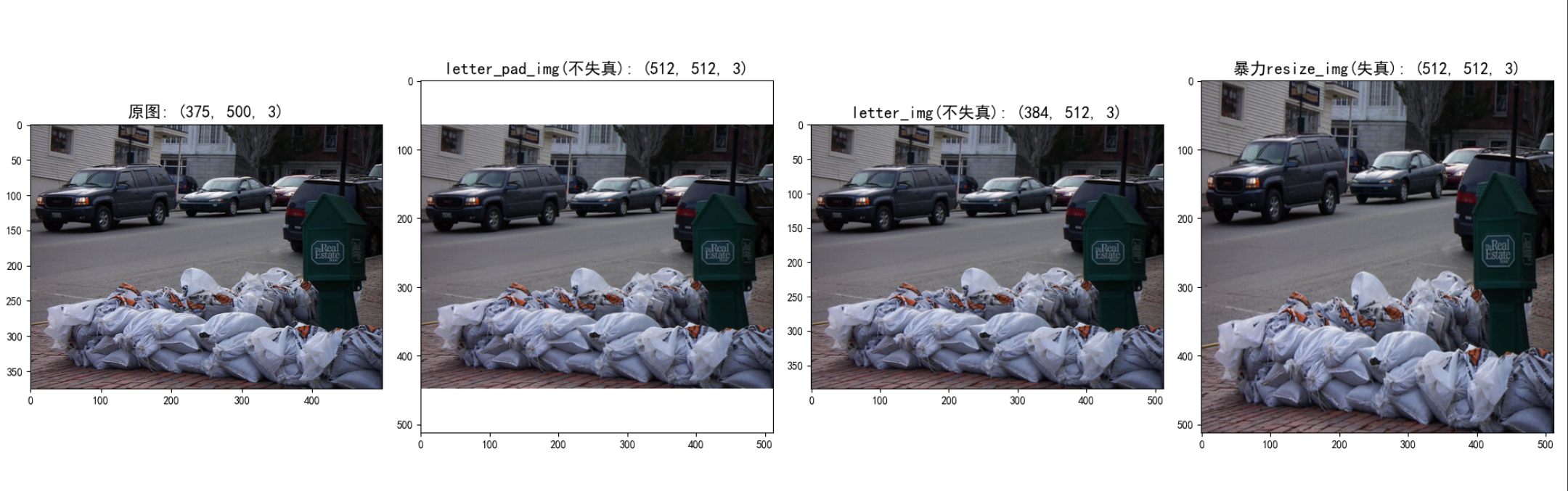
在推理阶段我们一般用第三种方式就可以了;而在训练阶段要使用letterbox的话一般是使用第二种方式(一般训练的时候输入的是一张正方形的图片)。
2.2、non_max_suppression函数
关于nms的算法步骤和原理部分不懂的朋友可以看我的另一篇博文: 常见的非极大值抑制方法:(Hard) NMS、Soft NMS、DIoU NMS.里面很详细的介绍了各种的nms算法原理及其区别。
1、函数流程
以 hard_nms_myself (自己实现的单输出hard_nms)为例:
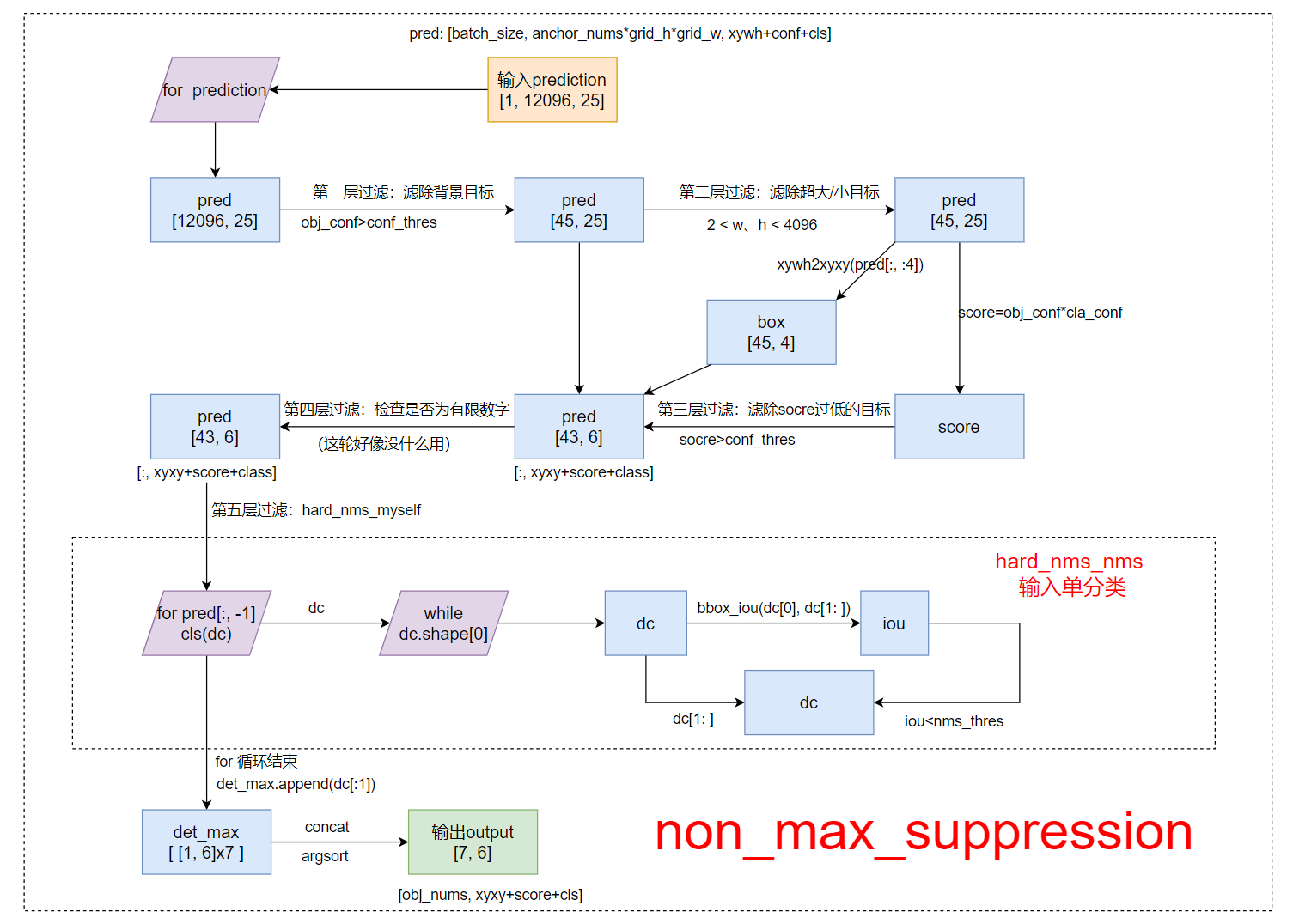
2、函数代码
以下代码我作了详细的注解,如果还是看不懂,可以看上面的函数流程
def non_max_suppression(prediction, conf_thres=0.1,
nms_thres=0.6, multi_cls=True, method='hard_nms_myself'):
"""
Removes detections with lower object confidence score than 'conf_thres'
Non-Maximum Suppression to further filter detections.
param:
prediction: [batch, num_anchors(3个yolo预测层), (x+y+w+h+1+num_classes)] 3个anchor的预测结果总和
conf_thres: 先进行一轮筛选,将分数过低的预测框(<conf_thres)删除(分数置0)
nms_thres: iou阈值, 如果其余预测框与target的iou>iou_thres, 就将那个预测框置0
multi_label: 是否是多标签
method: nms方法 (https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/679)
(https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/pull/795)
-hard_nms: 普通的 (hard) nms 官方实现(c函数库),可支持gpu,只支持单类别输入
-hard_nms_batch: 普通的 (hard) nms 官方实现(c函数库),可支持gpu,支持多类别输入
-hard_nms_myself: 普通的 (hard) nms 自己实现的,只支持单类别输入
-and: 在hard-nms的逻辑基础上,增加是否为单独框的限制,删除没有重叠框的框(减少误检)。
-merge: 在hard-nms的基础上,增加保留框位置平滑策略(重叠框位置信息求解平均值),使框的位置更加精确。
-soft_nms: soft nms 用一个衰减函数作用在score上来代替原来的置0
-diou_nms: 普通的 (hard) nms 的基础上引入DIoU(普通的nms用的是iou)
Returns detections with shape:
(x1, y1, x2, y2, object_conf, class)
"""
# Box constraints
min_wh, max_wh = 2, 4096 # (pixels) 宽度和高度的大小范围 [min_wh, max_wh]
output = [None] * len(prediction) # batch_size个output 存放最终筛选后的预测框结果
for image_i, pred in enumerate(prediction):
# 开始 pred = [12096, 25]
# 第一层过滤 根据conf_thres虑除背景目标(obj_conf<conf_thres 0.1的目标 置信度极低的目标)
pred = pred[pred[:, 4] > conf_thres] # pred = [45, 25]
# 第二层过滤 虑除超小anchor标和超大anchor x=[45, 25]
pred = pred[(pred[:, 2:4] > min_wh).all(1) & (pred[:, 2:4] < max_wh).all(1)]
# 经过前两层过滤后如果该feature map没有目标框了,就结束这轮直接进行下一张图
if len(pred) == 0:
continue
# 计算 score
pred[..., 5:] *= pred[..., 4:5] # score = cls_conf * obj_conf
# Box (center x, center y, width, height) to (x1, y1, x2, y2)
box = xywh2xyxy(pred[:, :4])
# Detections matrix nx6 (xyxy, conf, cls)
if multi_cls or conf_thres < 0.01:
# 第三轮过滤:针对每个类别score(obj_conf * cls_conf) > conf_thres [43, 6]
# 这里一个框是有可能有多个物体的,所以要筛选
# nonzero: 获得矩阵中的非0(True)数据的下标 a.t(): 将a矩阵拆开
# i: 下标 [43] j: 类别index [43] 过滤了两个score太低的
i, j = (pred[:, 5:] > conf_thres).nonzero(as_tuple=False).t()
# pred = [43, xyxy+score+class] [43, 6]
# unsqueeze(1): [43] => [43, 1] add batch dimension
# box[i]: [43,4] xyxy
# pred[i, j + 5].unsqueeze(1): [43,1] score 对每个i,取第(j+5)个位置的值(第j个class的值cla_conf)
# j.float().unsqueeze(1): [43,1] class
pred = torch.cat((box[i], pred[i, j + 5].unsqueeze(1), j.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)
else: # best class only
conf, j = pred[:, 5:].max(1) # 一个类别直接取分数最大类的即可
pred = torch.cat((box, conf.unsqueeze(1), j.float().unsqueeze(1)), 1)[conf > conf_thres]
# 第三轮过滤后如果该feature map没有目标框了,就结束这轮直接进行下一个feature map
if len(pred) == 0:
continue
# 第四轮过滤 这轮可有可无,一般没什么用 [43, 6] 检测数据是否为有限数
pred = pred[torch.isfinite(pred).all(1)]
# 降序排列 为NMS做准备 [43, 6]
pred = pred[pred[:, 4].argsort(descending=True)]
# Batched NMS
# Batched NMS推理时间:0.054
if method == 'hard_nms_batch': # 普通的(hard)nms: 官方实现(c函数库),可支持gpu,但支持多类别输入
# batched_nms:参数1 [43, xyxy] 参数2 [43, score] 参数3 [43, class] 参数4 [43, nms_thres]
output[image_i] = pred[torchvision.ops.boxes.batched_nms(pred[:, :4], pred[:, 4], pred[:, 5], nms_thres)]
# print("hard_nms_batch")
continue
# All other NMS methods 都是单类别输入
det_max = [] # 存放分数最高的框 即target
cls = pred[:, -1]
for c in cls.unique(): # 对所有的种类(不重复)
dc = pred[cls == c] # dc: 选出pred中所有类别是c的结果
n = len(dc) # 有多少个类别是c的预测框
if n == 1:
# No NMS required if only 1 prediction
det_max.append(dc)
continue
elif n > 500:
# limit to first 500 boxes: https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov3/issues/117
# 密集性 主要考虑到NMS是一个速度慢的算法(O(n^2)),预测框太多,算法的效率太慢 所以这里筛选一下(最多500个预测框)
dc = dc[:500]
# 推理时间:0.001
if method == 'hard_nms': # 普通的(hard)nms: 只支持单类别输入
det_max.append(dc[torchvision.ops.boxes.nms(dc[:, :4], dc[:, 4], nms_thres)])
# 推理时间:0.00299 是官方写的3倍
elif method == 'hard_nms_myself': # Hard NMS 自己写的 只支持单类别输入
while dc.shape[0]: # dc.shape[0]: 当前class的预测框数量
det_max.append(dc[:1]) # 让score最大的一个预测框(排序后的第一个)为target
if len(dc) == 1: # 出口 dc中只剩下一个框时,break
break
# dc[0] :target dc[1:] :其他预测框
iou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:]) # 计算 普通iou
dc = dc[1:][iou < nms_thres] # remove target and iou > threshold
# 在hard-nms的逻辑基础上,增加是否为单独框的限制,删除没有重叠框的框(减少误检)。
elif method == 'and': # requires overlap, single boxes erased
while len(dc) > 1:
iou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:]) # iou with other boxes
if iou.max() > 0.5: # 删除没有重叠框的框/iou小于0.5的框(减少误检)
det_max.append(dc[:1])
dc = dc[1:][iou < nms_thres] # remove ious > threshold
# 在hard-nms的基础上,增加保留框位置平滑策略(重叠框位置信息求解平均值),使框的位置更加精确。
elif method == 'merge': # weighted mixture box
while len(dc):
if len(dc) == 1:
det_max.append(dc)
break
i = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc) > nms_thres # i = True/False的集合
weights = dc[i, 4:5] # 根据i,保留所有True
dc[0, :4] = (weights * dc[i, :4]).sum(0) / weights.sum() # 重叠框位置信息求解平均值
det_max.append(dc[:1])
dc = dc[i == 0]
# 推理时间:0.0030s
elif method == 'soft_nms': # soft-NMS https://arxiv.org/abs/1704.04503
sigma = 0.5 # soft-nms sigma parameter
while len(dc):
# if len(dc) == 1: 这是U版的源码 我做了个小改动
# det_max.append(dc)
# break
# det_max.append(dc[:1])
det_max.append(dc[:1]) # append dc的第一行 即target
if len(dc) == 1:
break
iou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:]) # 计算target与其他框的iou
# 这里和上面的直接置0不同,置0不需要管维度
dc = dc[1:] # dc=target往后的所有预测框
# dc必须不包括target及其前的预测框,因为还要和值相乘, 维度上必须相同
dc[:, 4] *= torch.exp(-iou ** 2 / sigma) # 得分衰减
dc = dc[dc[:, 4] > conf_thres]
# 推理时间:0.00299
elif method == 'diou_nms': # DIoU NMS https://arxiv.org/pdf/1911.08287.pdf
while dc.shape[0]: # dc.shape[0]: 当前class的预测框数量
det_max.append(dc[:1]) # 让score最大的一个预测框(排序后的第一个)为target
if len(dc) == 1: # 出口 dc中只剩下一个框时,break
break
# dc[0] :target dc[1:] :其他预测框
diou = bbox_iou(dc[0], dc[1:], DIoU=True) # 计算 diou
dc = dc[1:][diou < nms_thres] # remove dious > threshold 保留True 删去False
if len(det_max):
det_max = torch.cat(det_max) # concatenate 因为之前是append进det_max的
output[image_i] = det_max[(-det_max[:, 4]).argsort()] # 排序
# output tensor [7, 6]
return output
2.3、scale_coords函数
这个部分的代码比较简单,这里我就不画流程图了,自己看代码理解。
核心思想:将预测的坐标信息coords(相对img1_shape)转换回相对原图尺度(img0_shape)
def scale_coords(img1_shape, coords, img0_shape, ratio_pad=None):
"""
将预测的坐标信息coords(相对img1_shape)转换回相对原图尺度(img0_shape)
:param img1_shape: 缩放后的图像大小 [H, W]=[384, 512]
:param coords: 预测的box信息 [7,4] [anchor_nums, x1y1x2y2] 这个预测信息是相对缩放后的图像尺寸(img1_shape)的
:param img0_shape: 原图的大小 [H, W, C]=[375, 500, 3]
:param ratio_pad: 缩放过程中的缩放比例以及pad 一般不传入
:return: coords: 相对原图尺寸(img0_shape)的预测信息
"""
# Rescale coords (xyxy) from img1_shape to img0_shape
if ratio_pad is None: # calculate from img0_shape
# gain = old/new = 1.024 max(img1_shape): 求img1的较长边 这一步对应的是之前的letterbox步骤
gain = max(img1_shape) / max(img0_shape)
# wh padding 这一步起不起作用,完全取决于letterbox的方式
# 当letterbox为letter_pad_img时,pad=(0.0, 64.0); 当letterbox为leeter_img时,pad=(0.0, 0.0)
pad = (img1_shape[1] - img0_shape[1] * gain) / 2, (img1_shape[0] - img0_shape[0] * gain) / 2
else:
gain = ratio_pad[0][0]
pad = ratio_pad[1]
# 将相对img1的预测信息缩放得到相对原图img0的预测信息
coords[:, [0, 2]] -= pad[0] # x padding
coords[:, [1, 3]] -= pad[1] # y padding
coords[:, :4] /= gain # 缩放
# 缩放到原图的预测结果,并对预测值进行了一定的约束,防止预测结果超出图像的尺寸
clip_coords(coords, img0_shape)
return coords
def clip_coords(boxes, img_shape):
"""
Clip bounding xyxy bounding boxes to image shape (height, width)
c.clamp_(a, b): 将矩阵c中所有的元素约束在[a, b]中间
如果某个元素小于a,就将这个元素变为a;如果元素大于b,就将这个元素变为b
这里将预测得到的xyxy做个约束,是因为当物体处于图片边缘的时候,预测值是有可能超过图片大小的
:param boxes: 函数开始=>缩放到原图的预测结果[7, 4]
函数结束=>缩放到原图的预测结果,并对预测值进行了一定的约束,防止预测结果超出图像的尺寸
:param img_shape: 原图的shape [H, W, C]=[375, 500, 3]
"""
boxes[:, 0].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x1
boxes[:, 1].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y1
boxes[:, 2].clamp_(0, img_shape[1]) # x2
boxes[:, 3].clamp_(0, img_shape[0]) # y2
2.4、draw_box函数
最后一步:将所有最终预测框画出来
import collections
from PIL import Image
import PIL.ImageDraw as ImageDraw
import PIL.ImageFont as ImageFont
import numpy as np
STANDARD_COLORS = [
'AliceBlue', 'Chartreuse', 'Aqua', 'Aquamarine', 'Azure', 'Beige', 'Bisque',
'BlanchedAlmond', 'BlueViolet', 'BurlyWood', 'CadetBlue', 'AntiqueWhite',
'Chocolate', 'Coral', 'CornflowerBlue', 'Cornsilk', 'Crimson', 'Cyan',
'DarkCyan', 'DarkGoldenRod', 'DarkGrey', 'DarkKhaki', 'DarkOrange',
'DarkOrchid', 'DarkSalmon', 'DarkSeaGreen', 'DarkTurquoise', 'DarkViolet',
'DeepPink', 'DeepSkyBlue', 'DodgerBlue', 'FireBrick', 'FloralWhite',
'ForestGreen', 'Fuchsia', 'Gainsboro', 'GhostWhite', 'Gold', 'GoldenRod',
'Salmon', 'Tan', 'HoneyDew', 'HotPink', 'IndianRed', 'Ivory', 'Khaki',
'Lavender', 'LavenderBlush', 'LawnGreen', 'LemonChiffon', 'LightBlue',
'LightCoral', 'LightCyan', 'LightGoldenRodYellow', 'LightGray', 'LightGrey',
'LightGreen', 'LightPink', 'LightSalmon', 'LightSeaGreen', 'LightSkyBlue',
'LightSlateGray', 'LightSlateGrey', 'LightSteelBlue', 'LightYellow', 'Lime',
'LimeGreen', 'Linen', 'Magenta', 'MediumAquaMarine', 'MediumOrchid',
'MediumPurple', 'MediumSeaGreen', 'MediumSlateBlue', 'MediumSpringGreen',
'MediumTurquoise', 'MediumVioletRed', 'MintCream', 'MistyRose', 'Moccasin',
'NavajoWhite', 'OldLace', 'Olive', 'OliveDrab', 'Orange', 'OrangeRed',
'Orchid', 'PaleGoldenRod', 'PaleGreen', 'PaleTurquoise', 'PaleVioletRed',
'PapayaWhip', 'PeachPuff', 'Peru', 'Pink', 'Plum', 'PowderBlue', 'Purple',
'Red', 'RosyBrown', 'RoyalBlue', 'SaddleBrown', 'Green', 'SandyBrown',
'SeaGreen', 'SeaShell', 'Sienna', 'Silver', 'SkyBlue', 'SlateBlue',
'SlateGray', 'SlateGrey', 'Snow', 'SpringGreen', 'SteelBlue', 'GreenYellow',
'Teal', 'Thistle', 'Tomato', 'Turquoise', 'Violet', 'Wheat', 'White',
'WhiteSmoke', 'Yellow', 'YellowGreen'
]
def filter_low_thresh(boxes, scores, classes, category_index, thresh,
box_to_display_str_map, box_to_color_map):
"""
1、过滤掉scores低于thresh的anchor;
2、为每个anchor生成显示信息和框框颜色并分别保存在box_to_display_str_map和box_to_color_map中
:param boxes: 最终预测结果 (anchor_nums, x1+y1+x2+y2)=(7, 4) (相对原图的预测结果) 分类别且按score从大到小排列
:param scores: 所有预测anchors的得分 (7) 分类别且按score从大到小排列
:param classes: 所有预测anchors的类别 (7) 分类别且按score从大到小排列
:param category_index: 所有类别的信息(从data/pascal_voc_classes.json中读出)
:param thresh: 设置阈值(默认0.1),过滤掉score太低的anchor
:param box_to_display_str_map: 拿来存放每个anchor的显示信息(list) 每个anchor: tuple(box) = list[显示信息]
:param box_to_color_map: 拿来存放每个anchor的框框颜色
"""
for i in range(boxes.shape[0]): # for anchors
# 过滤掉score太低的anchor
if scores[i] > thresh:
box = tuple(boxes[i].tolist()) # numpy -> list -> tuple
if classes[i] in category_index.keys():
class_name = category_index[classes[i]] # 得到每个anchor的class名
else:
class_name = 'N/A'
display_str = str(class_name)
display_str = '{}: {}%'.format(display_str, int(100 * scores[i])) # 显示信息如 car: 90%
# 将当前anchor的显示信息display_str加入到box_to_display_str_map中 每个anchor: tuple(box) = list[显示信息]
box_to_display_str_map[box].append(display_str)
# 为每个anchor对应的目标类别选择一个框框颜色 每个anchor: tuple(box) = list[颜色信息]
box_to_color_map[box] = STANDARD_COLORS[classes[i] % len(STANDARD_COLORS)]
else:
break # 网络输出概率已经排序过,当遇到一个不满足后面的肯定不满足
def draw_text(draw, box_to_display_str_map, box, left, right, top, bottom, color):
"""
:param draw: 一个可以在给定图像(image)上绘图的对象
:param box_to_display_str_map: 每个anchor的显示信息
:param box: 当前anchor的预测信息 (xyxy)
:param left: anchor的left
:param right: anchor的right
:param top: anchor的top
:param bottom: anchor的bottom
:param color: 当前anchor的信息颜色/anchor框框颜色
:return:
"""
try:
# 从指定的文件('arial.ttf')中加载了一个字体对象,并且为指定大小(20)的字体创建了字体对象。
font = ImageFont.truetype('arial.ttf', 20)
except IOError:
font = ImageFont.load_default() # 加载一个默认的字体
# 扫描ds(当前anchor的显示信息box_to_display_str_map[box])自动找到当前anchor显示信息的最大的字体大小(高)
display_str_heights = [font.getsize(ds)[1] for ds in box_to_display_str_map[box]]
# Each display_str has a top and bottom margin of 0.05x.
total_display_str_height = (1 + 2 * 0.05) * sum(display_str_heights)
# 如果添加到边界框顶部的显示字符串的总高度不超过图像顶部,就将字符串堆叠在边界框上方
# text_bottom: 盛装显示字符的矩形框的top
if top > total_display_str_height:
text_bottom = top
else:
# 如果添加到边界框顶部的显示字符串的总高度超过图像顶部,就将字符串堆叠在边界框下方
text_bottom = bottom + total_display_str_height
# Reverse list and print from bottom to top.
for display_str in box_to_display_str_map[box][::-1]:
# 得到当前anchor的显示字符的最佳w和h
text_width, text_height = font.getsize(display_str)
# 得到当前anchor的显示字符的margin
margin = np.ceil(0.05 * text_height)
# 画盛装显示字符的矩形 传入左下角坐标+右上角坐标
draw.rectangle([(left, text_bottom - text_height - 2 * margin),
(left + text_width, text_bottom)], fill=color)
# 写入显示字符 传入显示字符的左上角坐标
draw.text((left + margin, text_bottom - text_height - margin),
display_str, # 显示字符
fill='red', # 字体颜色
font=font) # 加载字体
text_bottom -= text_height - 2 * margin # ?
def draw_box(image, boxes, classes, scores, category_index, thresh=0.1, line_thickness=3):
"""
:param image: 原图 RGB (375, 500, 3) HWC numpy格式(array) img_o[:, :, ::-1]:BGR=>RGB
:param boxes: 最终预测结果 (anchor_nums, x1+y1+x2+y2)=(7, 4) (相对原图的预测结果)
按score从大到小排列 numpy格式(array)
:param classes: 所有预测anchors的类别 (7) 分类别且按score从大到小排列 numpy格式(array)
:param scores: 所有预测anchors的得分 (7) 分类别且按score从大到小排列 numpy格式(array)
:param category_index: 所有类别的信息(从data/pascal_voc_classes.json中读出)
:param thresh: 设置阈值(默认0.1),过滤掉score太低的anchor
:param line_thickness: 框框直线厚度
:return:
"""
box_to_display_str_map = collections.defaultdict(list) # 拿来存放每个anchor的显示信息
box_to_color_map = collections.defaultdict(str) # 拿来存放每个anchor的框框颜色
# 1、过滤掉scores低于thresh的anchor
# 2、为每个anchor生成显示信息和框框颜色并分别保存在box_to_display_str_map和box_to_color_map中
filter_low_thresh(boxes, scores, classes, category_index, thresh, box_to_display_str_map, box_to_color_map)
# Draw all boxes onto image.
if isinstance(image, np.ndarray):
image = Image.fromarray(image) # array(numpy) 转为Image格式
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image) # 创建一个可以在给定图像(image)上绘图的对象
for box, color in box_to_color_map.items():
xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax = box
(left, right, top, bottom) = (xmin * 1, xmax * 1, ymin * 1, ymax * 1)
# 为每个anchor画框 顺序:左上->左下->右下->右上->左上
draw.line([(left, top), (left, bottom), (right, bottom),
(right, top), (left, top)], width=line_thickness, fill=color)
# 在每个框框上写上显示信息
draw_text(draw, box_to_display_str_map, box, left, right, top, bottom, color)
return image
Reference
b站大佬1 霹雳吧啦Wz: YOLOv3 SPP源码解析(Pytorch版)
b站大佬2 比飞鸟贵重的多_HKL: 基于深度学习的目标检测算法
最后
以上就是轻松方盒最近收集整理的关于【YOLO-V3-SPP 源码解读】五、预测模块一、predict.py二、几个重要函数Reference的全部内容,更多相关【YOLO-V3-SPP内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复