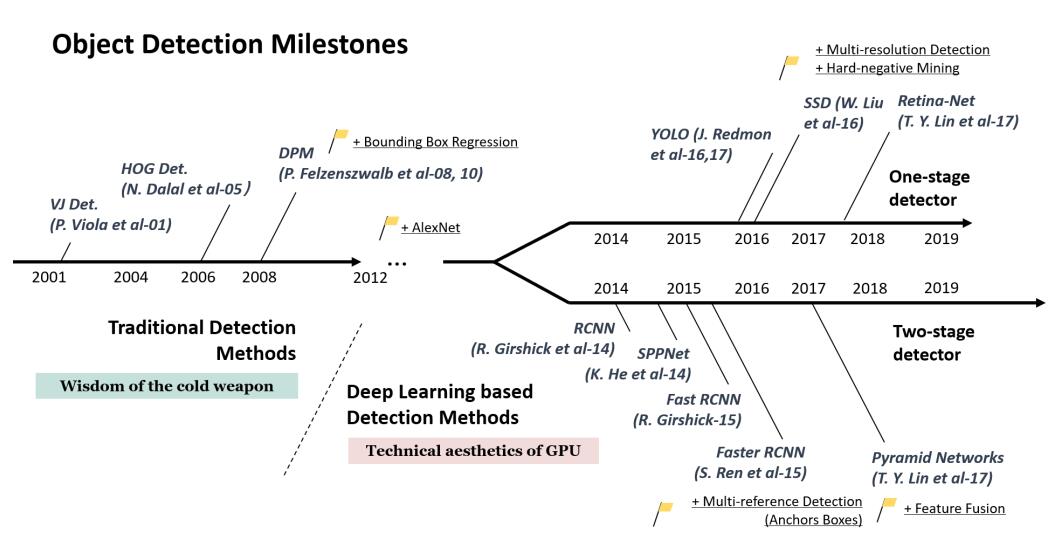
 自2014年
自2014年RCNN论文发表之后,机器学习在目标检测领域得到了飞速发展,本系列文章将介绍一些目标检测发展的里程碑著作的代码实现。
FasterRCNN
FasterRCNN框架图如下图所示,实际上就是RPN与Fast RCNN的结合
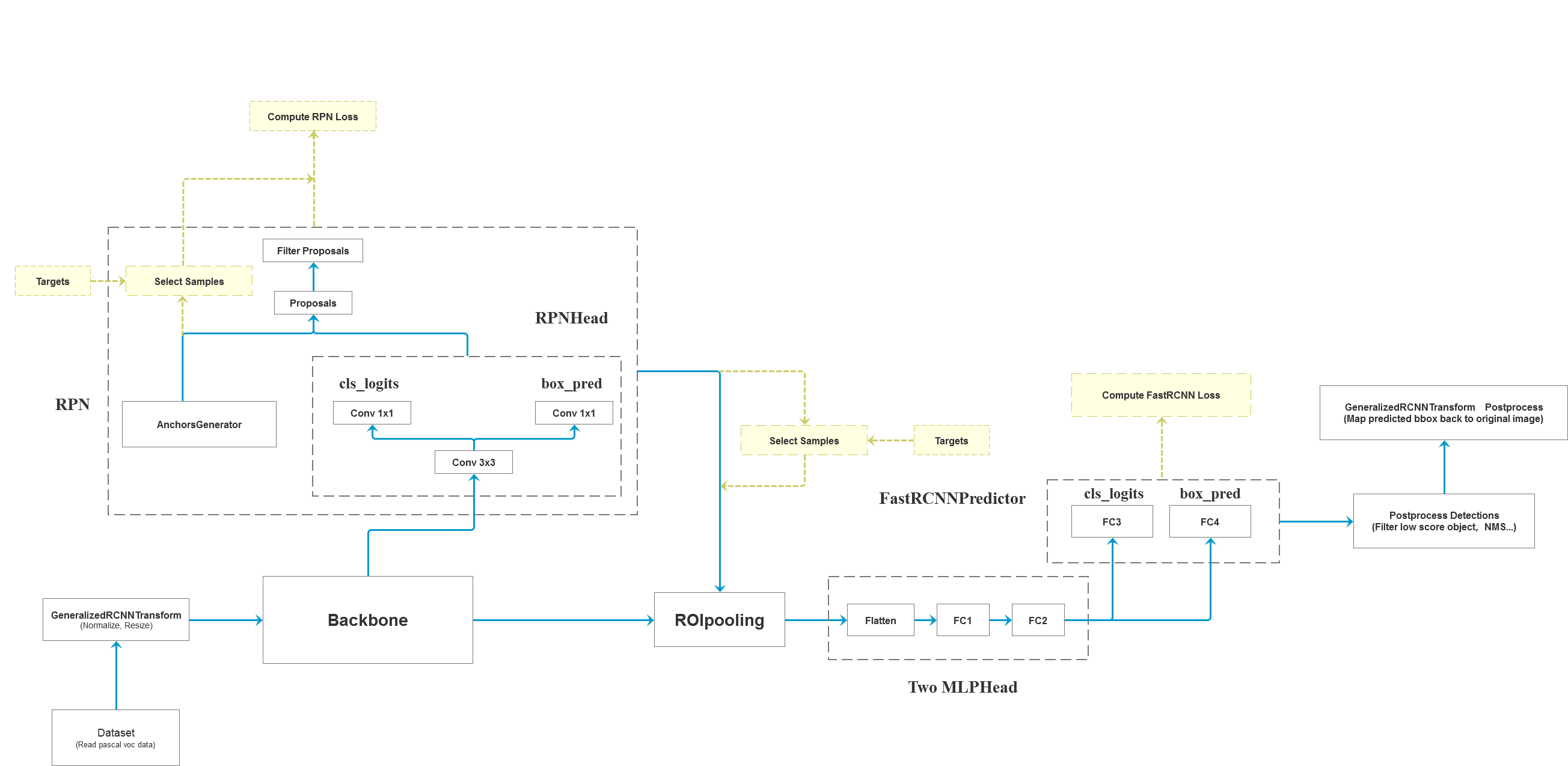
大致框架可以分为以下几步:
- 对图像进行预处理
- 将图像输入
backbone得到特征图 - 将特征层以及标注
target信息传入rpn中得到proposals和proposals loss - 将
rpn生成的数据以及标注target信息通过ROIPooling和MLPHead - 所得结果传入
fast rcnn后半部分,得到detections和detector loss - 对网络的预测结果进行后处理,主要将
bboxes还原到原图像尺度上
在本文中,我们只关注FasterRCNN的关键部分结构,包含RPN,ROIHead和Fast RCNN Predictor三个部分:
- FasterRCNN
- 一、RPN
- 1. 计算预测目标分数和bbox回归参数
- 2. 生成Anchors
- 3. 得到预测bbox的坐标
- 4. 对预测的bbox进行筛选
- 5. anchors分类
- 6. 计算regression参数
- 7. 计算损失
- 二、ROIHead
- 1. ROIpooling
- 2. Two MLPHead
- 三、FastRCNNPredictor
- 1. 预测目标分数和目标bbox回归参数
- 2. 损失计算
一、RPN
RPN中完成的任务有:
- 计算每个预测特征层上的预测目标概率和
bboxes回归参数 - 生成一个
batch的图像的所有anchors信息 - 将预测的
bbox regression参数应用到anchors上得到最终预测bbox坐标 - 筛除小
boxes框,nms处理,根据预测概率获取前post_nms_top_n个目标 - 计算每个
anchors最匹配的gt,并将anchors进分类为前景,背景以及废弃的anchors - 结合
anchors以及对应的gt,计算regression参数 - 结合
anchors以及对应的gt,计算损失
1. 计算预测目标分数和bbox回归参数
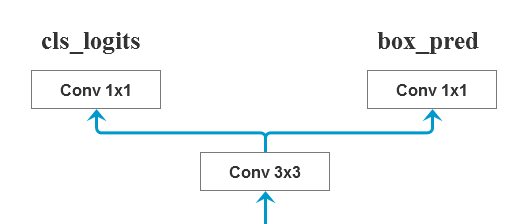
首先经过一个3x3的卷积层,然后分别使用一个1x1的卷积层预测目标分数和目标bbox regression参数:
class RPNHead(nn.Module):
"""
add a RPN head with classification and regression
通过滑动窗口计算预测目标概率与bbox regression参数
Arguments:
in_channels: number of channels of the input feature
num_anchors: number of anchors to be predicted
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_anchors):
super(RPNHead, self).__init__()
self.conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, in_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1)
self.cls_logits = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, num_anchors, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
self.bbox_pred = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, num_anchors * 4, kernel_size=1, stride=1)
for layer in self.children():
if isinstance(layer, nn.Conv2d):
torch.nn.init.normal_(layer.weight, std=0.01)
torch.nn.init.constant_(layer.bias, 0)
def forward(self, x):
# type: (List[Tensor]) -> Tuple[List[Tensor], List[Tensor]]
logits = []
bbox_reg = []
for i, feature in enumerate(x):
t = F.relu(self.conv(feature)) # 首先经过一个3x3的卷积层
logits.append(self.cls_logits(t)) # 使用一个1x1的卷积层预测目标分数
bbox_reg.append(self.bbox_pred(t)) # 使用一个1x1的卷积层预测目标bbox regression
return logits, bbox_reg
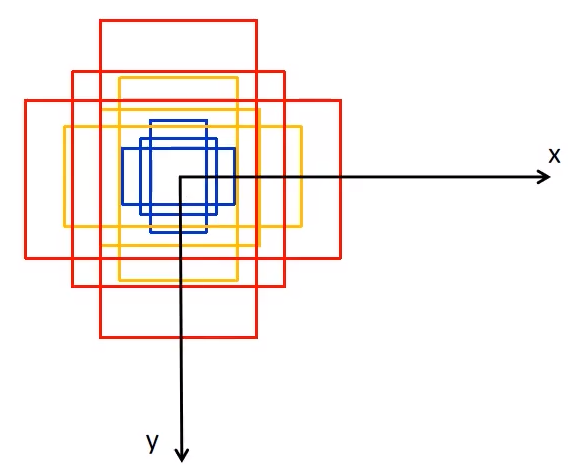
2. 生成Anchors
generate_anchors函数用于生成Anchors,该函数会生成大小分别为32, 64, 128, 256, 512,长宽比分别为0.5, 1.0, 2.0的共15个anchors,这些anchors是以(0, 0)为中心的,形状为[N, 4]的tensor,如下图所示。
def generate_anchors(self, scales, aspect_ratios, dtype=torch.float32, device=torch.device("cpu")):
# type: (List[int], List[float], torch.dtype, torch.device) -> Tensor
"""
compute anchor sizes
Arguments:
scales: sqrt(anchor_area)
aspect_ratios: h/w ratios
dtype: float32
device: cpu/gpu
"""
scales = torch.as_tensor(scales, dtype=dtype, device=device)
aspect_ratios = torch.as_tensor(aspect_ratios, dtype=dtype, device=device)
h_ratios = torch.sqrt(aspect_ratios)
w_ratios = 1.0 / h_ratios
# [r1, r2, r3]' * [s1, s2, s3, s4, s5]
# number of elements is len(ratios)*len(scales)
# 其中sizes=((32, 64, 128, 256, 512),)
# aspect_ratios=((0.5, 1.0, 2.0),))
ws = (w_ratios[:, None] * scales[None, :]).view(-1)
hs = (h_ratios[:, None] * scales[None, :]).view(-1)
# left-top, right-bottom coordinate relative to anchor center(0, 0)
# 生成的anchors模板都是以(0, 0)为中心的, shape [len(ratios)*len(scales), 4]
base_anchors = torch.stack([-ws, -hs, ws, hs], dim=1) / 2
return base_anchors.round() # round 四舍五入
grid_anchors函数用于计算预测特征图对应原始图像上的所有anchors的坐标,如下图所示
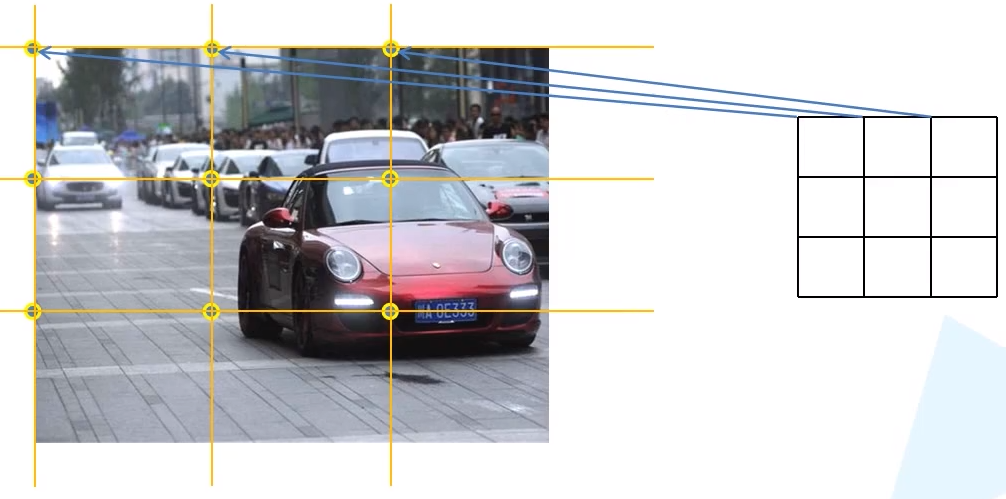
def grid_anchors(self, grid_sizes, strides):
# type: (List[List[int]], List[List[Tensor]]) -> List[Tensor]
"""
anchors position in grid coordinate axis map into origin image
计算预测特征图对应原始图像上的所有anchors的坐标
Args:
grid_sizes: 预测特征矩阵的height和width
strides: 预测特征矩阵上一步对应原始图像上的步距
"""
anchors = []
cell_anchors = self.cell_anchors
assert cell_anchors is not None
# 遍历每个预测特征层的grid_size,strides和cell_anchors
for size, stride, base_anchors in zip(grid_sizes, strides, cell_anchors):
grid_height, grid_width = size
stride_height, stride_width = stride
device = base_anchors.device
# For output anchor, compute [x_center, y_center, x_center, y_center]
# shape: [grid_width] 对应原图上的x坐标(列)
shifts_x = torch.arange(0, grid_width, dtype=torch.float32, device=device) * stride_width
# shape: [grid_height] 对应原图上的y坐标(行)
shifts_y = torch.arange(0, grid_height, dtype=torch.float32, device=device) * stride_height
# 计算预测特征矩阵上每个点对应原图上的坐标(anchors模板的坐标偏移量)
# torch.meshgrid函数分别传入行坐标和列坐标,生成网格行坐标矩阵和网格列坐标矩阵
# shape: [grid_height, grid_width]
shift_y, shift_x = torch.meshgrid(shifts_y, shifts_x)
shift_x = shift_x.reshape(-1)
shift_y = shift_y.reshape(-1)
# 计算anchors坐标(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)在原图上的坐标偏移量
# shape: [grid_width*grid_height, 4]
shifts = torch.stack([shift_x, shift_y, shift_x, shift_y], dim=1)
# 将anchors模板与原图上的坐标偏移量相加得到原图上所有anchors的坐标信息(shape不同时会使用广播机制)
shifts_anchor = shifts.view(-1, 1, 4) + base_anchors.view(1, -1, 4)
anchors.append(shifts_anchor.reshape(-1, 4))
return anchors # List[Tensor(all_num_anchors, 4)]
3. 得到预测bbox的坐标
这一步骤是对(1)和(2)所得结果的结合,将bbox回归参数应用到anchors上得到预测bbox的坐标。利用如下公式,利用预测得到的bbox回归参数,得到预测bbox的坐标
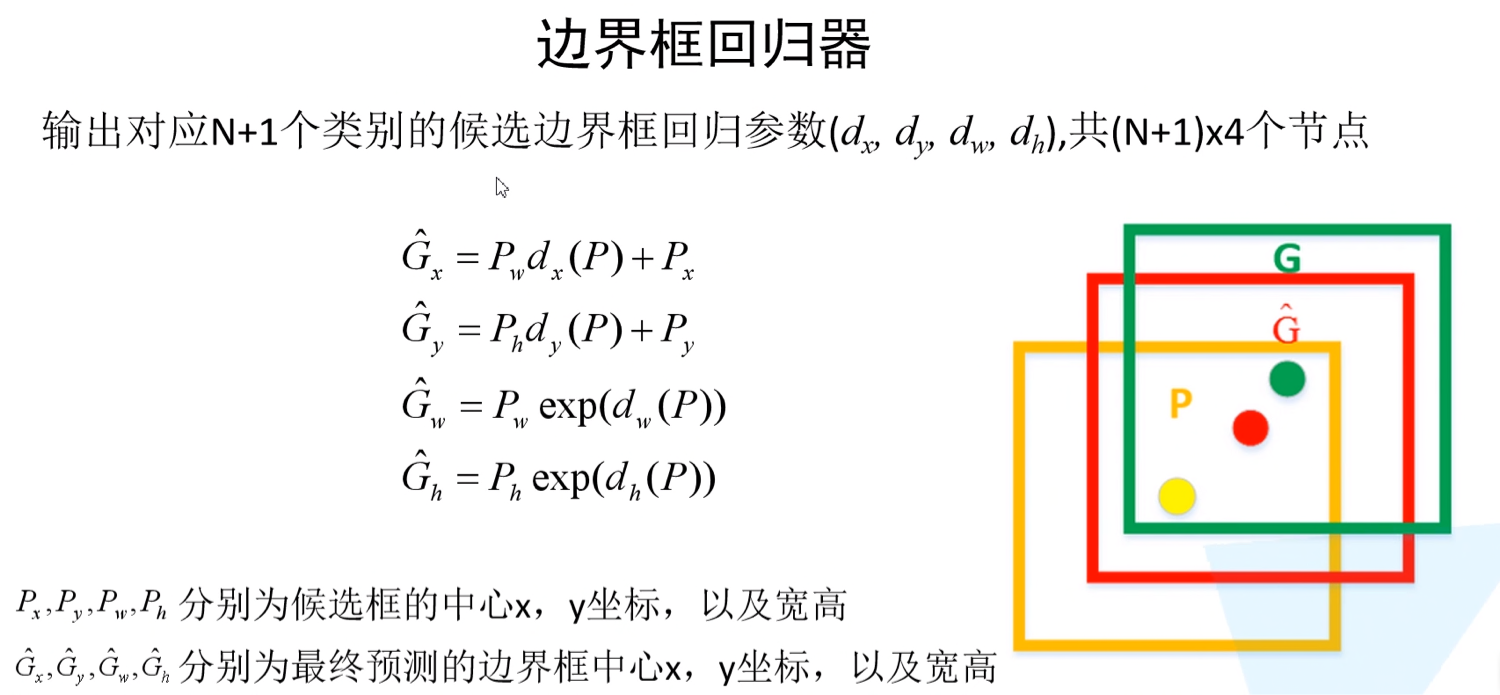
def decode_single(self, rel_codes, boxes):
"""
From a set of original boxes and encoded relative box offsets,
get the decoded boxes.
Arguments:
rel_codes (Tensor): encoded boxes (bbox regression parameters)
boxes (Tensor): reference boxes (anchors/proposals)
"""
boxes = boxes.to(rel_codes.dtype)
# xyxy -> xywh
widths = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0] # anchor/proposal宽度
heights = boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] # anchor/proposal高度
ctr_x = boxes[:, 0] + 0.5 * widths # anchor/proposal中心x坐标
ctr_y = boxes[:, 1] + 0.5 * heights # anchor/proposal中心y坐标
wx, wy, ww, wh = self.weights # RPN中为[1,1,1,1], fastrcnn中为[10,10,5,5]
dx = rel_codes[:, 0::4] / wx # 预测anchors/proposals的中心坐标x回归参数
dy = rel_codes[:, 1::4] / wy # 预测anchors/proposals的中心坐标y回归参数
dw = rel_codes[:, 2::4] / ww # 预测anchors/proposals的宽度回归参数
dh = rel_codes[:, 3::4] / wh # 预测anchors/proposals的高度回归参数
# limit max value, prevent sending too large values into torch.exp()
# self.bbox_xform_clip=math.log(1000. / 16) 4.135
dw = torch.clamp(dw, max=self.bbox_xform_clip)
dh = torch.clamp(dh, max=self.bbox_xform_clip)
pred_ctr_x = dx * widths[:, None] + ctr_x[:, None]
pred_ctr_y = dy * heights[:, None] + ctr_y[:, None]
pred_w = torch.exp(dw) * widths[:, None]
pred_h = torch.exp(dh) * heights[:, None]
# xywh -> xyxy
pred_boxes1 = pred_ctr_x - torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=pred_ctr_x.dtype, device=pred_w.device) * pred_w
pred_boxes2 = pred_ctr_y - torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=pred_ctr_y.dtype, device=pred_h.device) * pred_h
pred_boxes3 = pred_ctr_x + torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=pred_ctr_x.dtype, device=pred_w.device) * pred_w
pred_boxes4 = pred_ctr_y + torch.tensor(0.5, dtype=pred_ctr_y.dtype, device=pred_h.device) * pred_h
pred_boxes = torch.stack((pred_boxes1, pred_boxes2, pred_boxes3, pred_boxes4), dim=2).flatten(1)
return pred_boxes
4. 对预测的bbox进行筛选
筛选bboxes的过程包含
- 只取预测概率位于前
post_nms_top_n个目标 - 调整预测的
boxes坐标,将越界的坐标调整到图片边界上 - 移除宽或高小于
min_size的bbox nms处理
① 只取预测概率位于前post_nms_top_n个目标
主要利用ob.topk函数,作用:取最大的前k个目标
def _get_top_n_idx(self, objectness, num_anchors_per_level):
# type: (Tensor, List[int]) -> Tensor
"""
获取每张预测特征图上预测概率排前pre_nms_top_n的anchors索引值
Args:
objectness: Tensor(每张图像的预测目标概率信息 )
num_anchors_per_level: List(每个预测特征层上的预测的anchors个数)
Returns:
"""
r = [] # 记录每个预测特征层上预测目标概率前pre_nms_top_n的索引信息
offset = 0
# 遍历每个预测特征层上的预测目标概率信息
for ob in objectness.split(num_anchors_per_level, 1):
if torchvision._is_tracing():
num_anchors, pre_nms_top_n = _onnx_get_num_anchors_and_pre_nms_top_n(ob, self.pre_nms_top_n())
else:
num_anchors = ob.shape[1] # 预测特征层上的预测的anchors个数
pre_nms_top_n = min(self.pre_nms_top_n(), num_anchors)
# 取最大的前k个目标
_, top_n_idx = ob.topk(pre_nms_top_n, dim=1)
r.append(top_n_idx + offset)
offset += num_anchors
return torch.cat(r, dim=1)
② 调整预测的boxes坐标,将越界的坐标调整到图片边界上
主要利用最大最小值函数,把范围限制在 [0,图片尺寸] 之间
def clip_boxes_to_image(boxes, size):
# type: (Tensor, Tuple[int, int]) -> Tensor
"""
Clip boxes so that they lie inside an image of size `size`.
裁剪预测的boxes信息,将越界的坐标调整到图片边界上
Arguments:
boxes (Tensor[N, 4]): boxes in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format
size (Tuple[height, width]): size of the image
Returns:
clipped_boxes (Tensor[N, 4])
"""
dim = boxes.dim()
boxes_x = boxes[..., 0::2] # x1, x2
boxes_y = boxes[..., 1::2] # y1, y2
height, width = size
if torchvision._is_tracing():
boxes_x = torch.max(boxes_x, torch.tensor(0, dtype=boxes.dtype, device=boxes.device))
boxes_x = torch.min(boxes_x, torch.tensor(width, dtype=boxes.dtype, device=boxes.device))
boxes_y = torch.max(boxes_y, torch.tensor(0, dtype=boxes.dtype, device=boxes.device))
boxes_y = torch.min(boxes_y, torch.tensor(height, dtype=boxes.dtype, device=boxes.device))
else:
boxes_x = boxes_x.clamp(min=0, max=width) # 限制x坐标范围在[0,width]之间
boxes_y = boxes_y.clamp(min=0, max=height) # 限制y坐标范围在[0,height]之间
clipped_boxes = torch.stack((boxes_x, boxes_y), dim=dim)
return clipped_boxes.reshape(boxes.shape)
③ 移除宽或高小于min_size的bbox
主要利用最大最小值函数,把范围限制在 [0,图片尺寸] 之间
def remove_small_boxes(boxes, min_size):
# type: (Tensor, float) -> Tensor
"""
Remove boxes which contains at least one side smaller than min_size.
移除宽高小于指定阈值的索引
Arguments:
boxes (Tensor[N, 4]): boxes in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format
min_size (float): minimum size
Returns:
keep (Tensor[K]): indices of the boxes that have both sides
larger than min_size
"""
ws, hs = boxes[:, 2] - boxes[:, 0], boxes[:, 3] - boxes[:, 1] # 预测boxes的宽和高
# keep = (ws >= min_size) & (hs >= min_size) # 当满足宽,高都大于给定阈值时为True
keep = torch.logical_and(torch.ge(ws, min_size), torch.ge(hs, min_size))
# nonzero(): Returns a tensor containing the indices of all non-zero elements of input
# keep = keep.nonzero().squeeze(1)
keep = torch.where(keep)[0]
return keep
④ nms处理
如果直接利用官方nms函数的话,需要对每一个类别进行nms处理,在这里采取了一个巧妙的方法,就是将不同类别的bbox的坐标位置加上一个较大的偏移量,使得不同类别的bbox没有重合,就可以对所有类别的bbox只进行一次nms处理。例如:
原本的bbox位置如下:
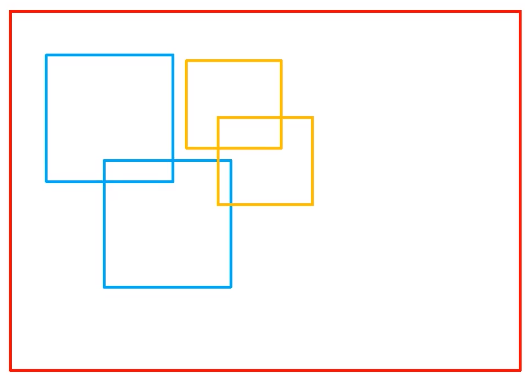
坐标加上偏移量之后的bbox位置如下:
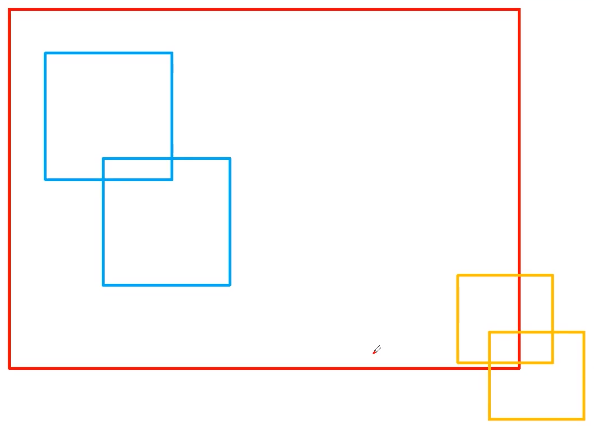
这样,不同类别的bbox没有重合,可以对所有类别的bbox只进行一次nms处理。
def batched_nms(boxes, scores, idxs, iou_threshold):
# type: (Tensor, Tensor, Tensor, float) -> Tensor
"""
Performs non-maximum suppression in a batched fashion.
Each index value correspond to a category, and NMS
will not be applied between elements of different categories.
Parameters:
boxes : Tensor[N, 4], boxes where NMS will be performed. They are expected to be in (x1, y1, x2, y2) format
scores : Tensor[N], scores for each one of the boxes
idxs : Tensor[N] indices of the categories for each one of the boxes.
iou_threshold : float, discards all overlapping boxes with IoU < iou_threshold
Returns:
keep : Tensor, int64 tensor with the indices of the elements that have been kept by NMS, sorted in decreasing order of scores
"""
if boxes.numel() == 0:
return torch.empty((0,), dtype=torch.int64, device=boxes.device)
# 获取所有boxes中最大的坐标值(xmin, ymin, xmax, ymax)
max_coordinate = boxes.max()
# 为每一个类别/每一层生成一个很大的偏移量
# 这里的to只是让生成tensor的dytpe和device与boxes保持一致
offsets = idxs.to(boxes) * (max_coordinate + 1)
# boxes加上对应层的偏移量后,保证不同类别/层之间boxes不会有重合的现象
boxes_for_nms = boxes + offsets[:, None]
keep = nms(boxes_for_nms, scores, iou_threshold)
return keep
5. anchors分类
交并比iou的计算方法如下:
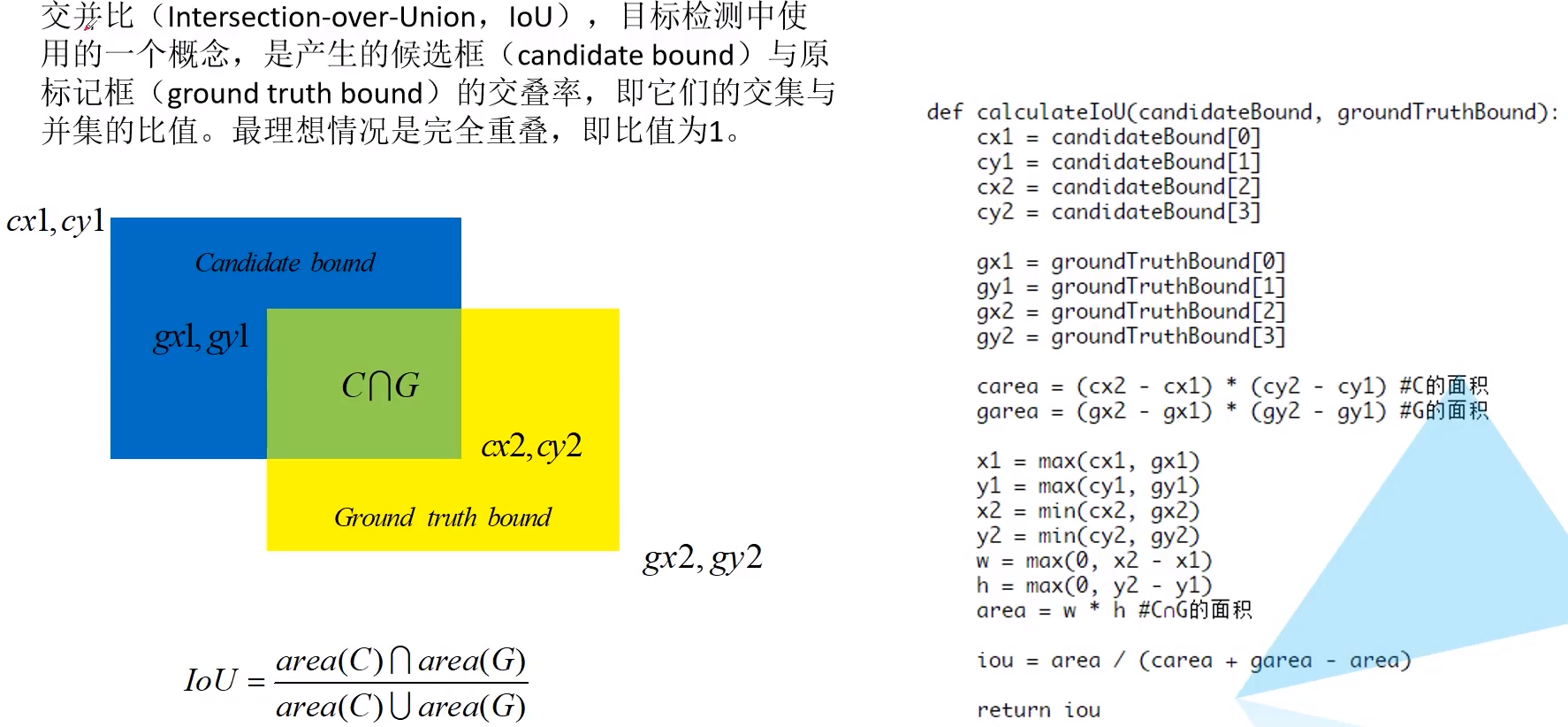
实现该功能的类为Matcher,传入参数match_quality_matrix的例子如下:
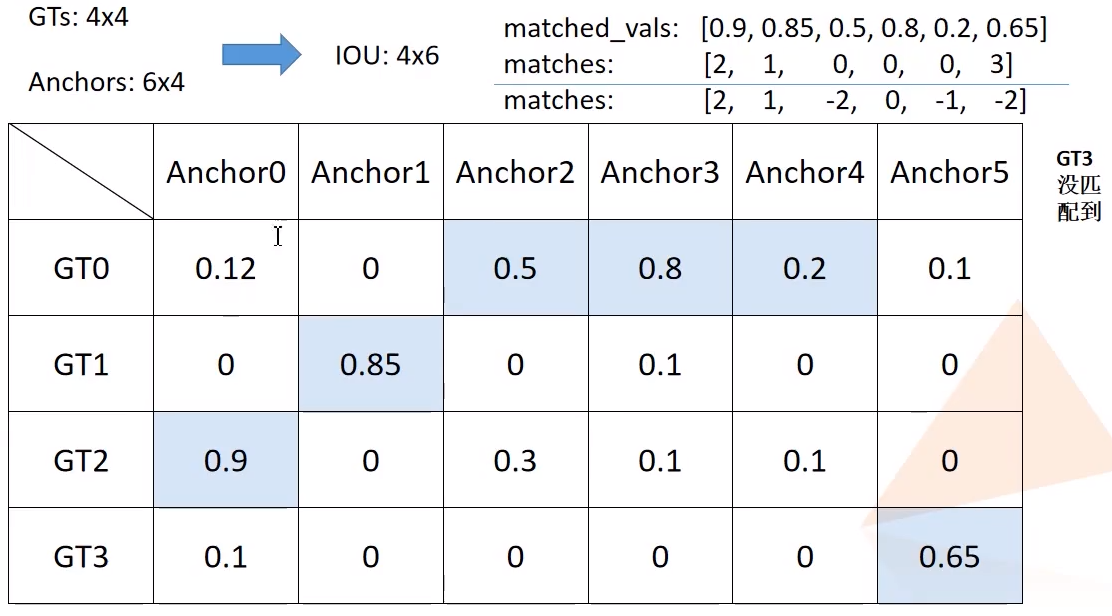
match_quality_matrix矩阵其中的元素为对应行gtbox与对应列anchor的交并比,算法步骤如下:
matched_vals和matches取得每一列最大元素的值和最大元素的位置iou<low_threshold的matches索引置为-1iou在[low_threshold, high_threshold]之间的matches索引置为-2
class Matcher(object):
BELOW_LOW_THRESHOLD = -1
BETWEEN_THRESHOLDS = -2
def __call__(self, match_quality_matrix):
"""
计算anchors与每个gtboxes匹配的iou最大值,并记录索引,
iou<low_threshold索引值为-1, low_threshold<=iou<high_threshold索引值为-2
Args:
match_quality_matrix (Tensor[float]): an MxN tensor, containing the
pairwise quality between M ground-truth elements and N predicted elements.
Returns:
matches (Tensor[int64]): an N tensor where N[i] is a matched gt in
[0, M - 1] or a negative value indicating that prediction i could not
be matched.
"""
# M x N 的每一列代表一个anchors与所有gt的匹配iou值
# matched_vals代表每列的最大值,即每个anchors与所有gt匹配的最大iou值
# matches对应最大值所在的索引
matched_vals, matches = match_quality_matrix.max(dim=0) # the dimension to reduce.
if self.allow_low_quality_matches:
all_matches = matches.clone()
else:
all_matches = None
# 计算iou小于low_threshold的索引
below_low_threshold = matched_vals < self.low_threshold
# 计算iou在low_threshold与high_threshold之间的索引值
between_thresholds = (matched_vals >= self.low_threshold) & (
matched_vals < self.high_threshold
)
# iou小于low_threshold的matches索引置为-1
matches[below_low_threshold] = self.BELOW_LOW_THRESHOLD # -1
# iou在[low_threshold, high_threshold]之间的matches索引置为-2
matches[between_thresholds] = self.BETWEEN_THRESHOLDS # -2
# 是否将gtbox对应所有anchors中iou最大的保留(仅对于maxiou<low_threshold时有效)
if self.allow_low_quality_matches:
assert all_matches is not None
self.set_low_quality_matches_(matches, all_matches, match_quality_matrix)
return matches
- 将每个
gtbox对应所有anchors中iou最大的matches保留(可选)
还是以之前的match_quality_matrix为例, highest_quality_foreach_gt为每个gt boxes对应iou的最大值,
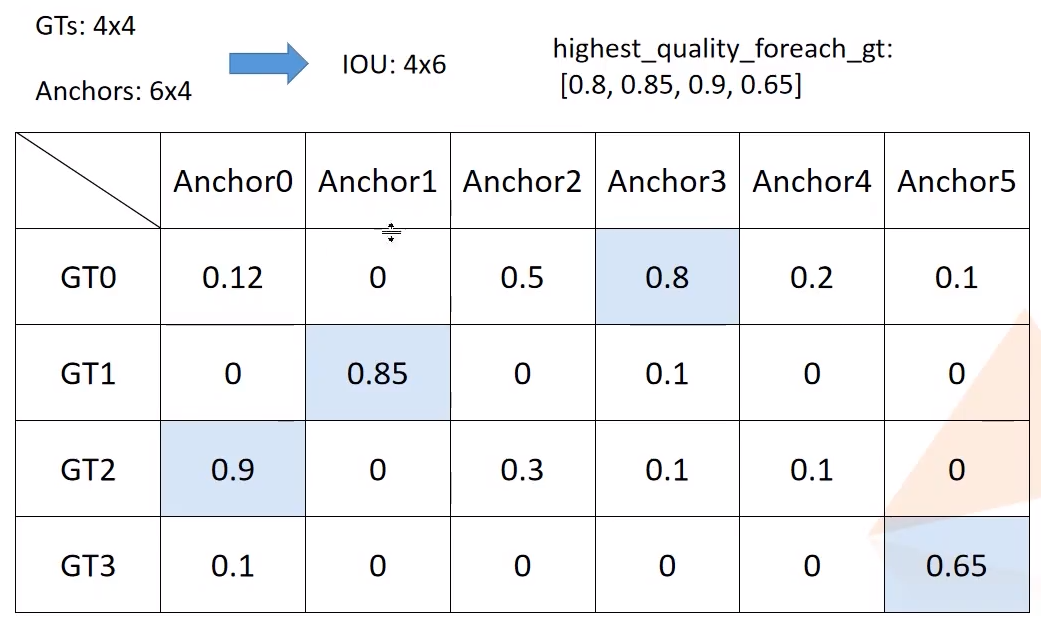
gt_pred_pairs_of_highest_quality为每个gt boxes对应最大iou的坐标,
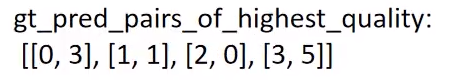
pre_inds_to_update代表是对应的anchor index

def set_low_quality_matches_(self, matches, all_matches, match_quality_matrix):
"""
将gtbox对应所有anchors中iou最大的保留(仅对于maxiou<low_threshold时有效)
"""
# 对于每个gt boxes寻找与其iou最大的anchor,
# highest_quality_foreach_gt为匹配到的最大iou值
highest_quality_foreach_gt, _ = match_quality_matrix.max(dim=1) # the dimension to reduce.
# 寻找每个gt boxes与其iou最大的anchor索引,一个gt匹配到的最大iou可能有多个anchor
# gt_pred_pairs_of_highest_quality = torch.nonzero(
# match_quality_matrix == highest_quality_foreach_gt[:, None]
# )
gt_pred_pairs_of_highest_quality = torch.where(
torch.eq(match_quality_matrix, highest_quality_foreach_gt[:, None])
)
# gt_pred_pairs_of_highest_quality[:, 0]代表是对应的gt index(不需要)
# pre_inds_to_update = gt_pred_pairs_of_highest_quality[:, 1]
pre_inds_to_update = gt_pred_pairs_of_highest_quality[1]
# 保留该anchor匹配gt最大iou的索引,即使iou低于设定的阈值
matches[pre_inds_to_update] = all_matches[pre_inds_to_update]
综上所述,我们计算了每个anchors最匹配的gt,并将anchors分类,将负样本的索引置为-1,丢弃样本的索引置为-2,所以通过获取索引为正数的样本就可以得到正样本。
6. 计算regression参数
利用如下公式,利用预测的anchors坐标以及对应的gt,得到预测的bbox回归参数
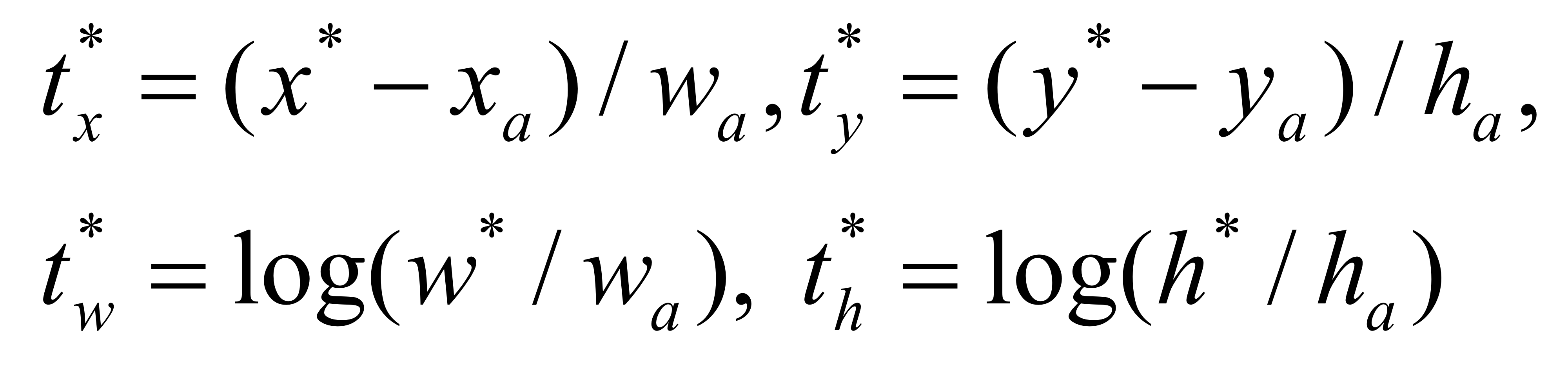
def encode_boxes(reference_boxes, proposals, weights):
# type: (torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor, torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor
"""
Encode a set of proposals with respect to some
reference boxes
Arguments:
reference_boxes (Tensor): reference boxes(gt)
proposals (Tensor): boxes to be encoded(anchors)
weights:
"""
# perform some unpacking to make it JIT-fusion friendly
wx = weights[0]
wy = weights[1]
ww = weights[2]
wh = weights[3]
# unsqueeze()
# Returns a new tensor with a dimension of size one inserted at the specified position.
proposals_x1 = proposals[:, 0].unsqueeze(1)
proposals_y1 = proposals[:, 1].unsqueeze(1)
proposals_x2 = proposals[:, 2].unsqueeze(1)
proposals_y2 = proposals[:, 3].unsqueeze(1)
reference_boxes_x1 = reference_boxes[:, 0].unsqueeze(1)
reference_boxes_y1 = reference_boxes[:, 1].unsqueeze(1)
reference_boxes_x2 = reference_boxes[:, 2].unsqueeze(1)
reference_boxes_y2 = reference_boxes[:, 3].unsqueeze(1)
# implementation starts here
# parse widths and heights
ex_widths = proposals_x2 - proposals_x1
ex_heights = proposals_y2 - proposals_y1
# parse coordinate of center point
ex_ctr_x = proposals_x1 + 0.5 * ex_widths
ex_ctr_y = proposals_y1 + 0.5 * ex_heights
gt_widths = reference_boxes_x2 - reference_boxes_x1
gt_heights = reference_boxes_y2 - reference_boxes_y1
gt_ctr_x = reference_boxes_x1 + 0.5 * gt_widths
gt_ctr_y = reference_boxes_y1 + 0.5 * gt_heights
targets_dx = wx * (gt_ctr_x - ex_ctr_x) / ex_widths
targets_dy = wy * (gt_ctr_y - ex_ctr_y) / ex_heights
targets_dw = ww * torch.log(gt_widths / ex_widths)
targets_dh = wh * torch.log(gt_heights / ex_heights)
targets = torch.cat((targets_dx, targets_dy, targets_dw, targets_dh), dim=1)
return targets
7. 计算损失
损失的计算包含:
- 边界框回归损失,使用
torch.smooth_l1_loss
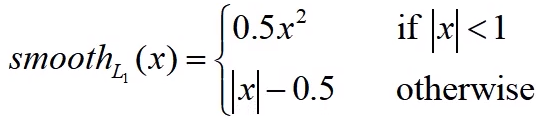
- 目标预测概率损失,使用
F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits

def compute_loss(self, objectness, pred_bbox_deltas, labels, regression_targets):
# type: (Tensor, Tensor, List[Tensor], List[Tensor]) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]
"""
计算RPN损失,包括类别损失(前景与背景),bbox regression损失
Arguments:
objectness (Tensor):预测的前景概率
pred_bbox_deltas (Tensor):预测的bbox regression
labels (List[Tensor]):真实的标签 1, 0, -1(batch中每一张图片的labels对应List的一个元素中)
regression_targets (List[Tensor]):真实的bbox regression
Returns:
objectness_loss (Tensor) : 类别损失
box_loss (Tensor):边界框回归损失
"""
# 按照给定的batch_size_per_image, positive_fraction选择正负样本
sampled_pos_inds, sampled_neg_inds = self.fg_bg_sampler(labels)
# 将一个batch中的所有正负样本List(Tensor)分别拼接在一起,并获取非零位置的索引
# sampled_pos_inds = torch.nonzero(torch.cat(sampled_pos_inds, dim=0)).squeeze(1)
sampled_pos_inds = torch.where(torch.cat(sampled_pos_inds, dim=0))[0]
# sampled_neg_inds = torch.nonzero(torch.cat(sampled_neg_inds, dim=0)).squeeze(1)
sampled_neg_inds = torch.where(torch.cat(sampled_neg_inds, dim=0))[0]
# 将所有正负样本索引拼接在一起
sampled_inds = torch.cat([sampled_pos_inds, sampled_neg_inds], dim=0)
objectness = objectness.flatten()
labels = torch.cat(labels, dim=0)
regression_targets = torch.cat(regression_targets, dim=0)
# 计算边界框回归损失
box_loss = det_utils.smooth_l1_loss(
pred_bbox_deltas[sampled_pos_inds],
regression_targets[sampled_pos_inds],
beta=1 / 9,
size_average=False,
) / (sampled_inds.numel())
# 计算目标预测概率损失
objectness_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy_with_logits(
objectness[sampled_inds], labels[sampled_inds]
)
return objectness_loss, box_loss
二、ROIHead
包含ROIpooling和Two MLPHead两个部分
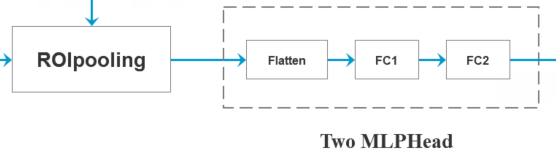
1. ROIpooling
使用pytorch自带的函数MultiScaleRoIAlign
box_roi_pool = MultiScaleRoIAlign(
featmap_names=['0', '1', '2', '3'], # 在哪些特征层进行roi pooling
output_size=[7, 7],
sampling_ratio=2)
2. Two MLPHead
是一个Flatten层和两个FC层组成的网络
class TwoMLPHead(nn.Module):
"""
Standard heads for FPN-based models
Arguments:
in_channels (int): number of input channels
representation_size (int): size of the intermediate representation
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, representation_size):
super(TwoMLPHead, self).__init__()
self.fc6 = nn.Linear(in_channels, representation_size)
self.fc7 = nn.Linear(representation_size, representation_size)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.flatten(start_dim=1)
x = F.relu(self.fc6(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc7(x))
return x
三、FastRCNNPredictor
1. 预测目标分数和目标bbox回归参数
分别使用一个全连接层预测目标分数和目标bbox回归参数
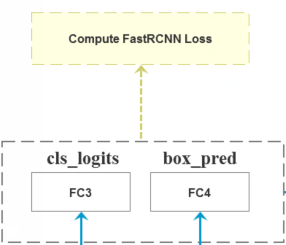
class FastRCNNPredictor(nn.Module):
"""
Standard classification + bounding box regression layers
for Fast R-CNN.
Arguments:
in_channels (int): number of input channels
num_classes (int): number of output classes (including background)
"""
def __init__(self, in_channels, num_classes):
super(FastRCNNPredictor, self).__init__()
self.cls_score = nn.Linear(in_channels, num_classes)
self.bbox_pred = nn.Linear(in_channels, num_classes * 4)
def forward(self, x):
x = x.flatten(start_dim=1)
scores = self.cls_score(x)
bbox_deltas = self.bbox_pred(x)
return scores, bbox_deltas
2. 损失计算
训练时需要计算损失函数,在计算损失之前也需要进行和之前RPN部分类似的步骤,如下:
- 划分正负样本,统计对应
gt的标签以及边界框回归信息 - 按给定数量和比例采样正负样本
- 根据
gt和proposal计算边框回归参数 - 计算损失函数
这里的损失函数同样也是包含了两个部分:
- 边界框回归损失,使用
torch.smooth_l1_loss
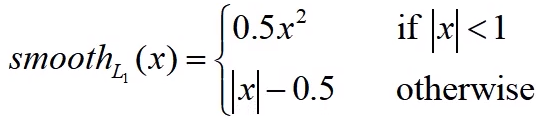
- 类别损失函数。使用
F.cross_entropy

def fastrcnn_loss(class_logits, box_regression, labels, regression_targets):
# type: (Tensor, Tensor, List[Tensor], List[Tensor]) -> Tuple[Tensor, Tensor]
"""
Computes the loss for Faster R-CNN.
Arguments:
class_logits : 预测类别概率信息,shape=[num_anchors, num_classes]
box_regression : 预测边目标界框回归信息
labels : 真实类别信息
regression_targets : 真实目标边界框信息
Returns:
classification_loss (Tensor)
box_loss (Tensor)
"""
labels = torch.cat(labels, dim=0)
regression_targets = torch.cat(regression_targets, dim=0)
# 计算类别损失信息
classification_loss = F.cross_entropy(class_logits, labels)
# get indices that correspond to the regression targets for
# the corresponding ground truth labels, to be used with
# advanced indexing
# 返回标签类别大于0的索引
# sampled_pos_inds_subset = torch.nonzero(torch.gt(labels, 0)).squeeze(1)
sampled_pos_inds_subset = torch.where(torch.gt(labels, 0))[0]
# 返回标签类别大于0位置的类别信息
labels_pos = labels[sampled_pos_inds_subset]
# shape=[num_proposal, num_classes]
N, num_classes = class_logits.shape
box_regression = box_regression.reshape(N, -1, 4)
# 计算边界框损失信息
box_loss = det_utils.smooth_l1_loss(
# 获取指定索引proposal的指定类别box信息
box_regression[sampled_pos_inds_subset, labels_pos],
regression_targets[sampled_pos_inds_subset],
beta=1 / 9,
size_average=False,
) / labels.numel()
return classification_loss, box_loss
源代码
最后
以上就是阔达鸡翅最近收集整理的关于目标检测代码解读一(FasterRCNN)FasterRCNN一、RPN二、ROIHead三、FastRCNNPredictor的全部内容,更多相关目标检测代码解读一(FasterRCNN)FasterRCNN一、RPN二、ROIHead三、FastRCNNPredictor内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复