目录
- 26.删除排序数组中的重复项
- 27.移除元素
- 53.最大子序和
- 66.加一
- 88.合并两个有序数组
- 118.杨辉三角形
- 119.杨辉三角形II
- 717.1比特与2比特字符
- 989.数组形式的整数加法
- 561.数组拆分I
- 1491.去掉最低工资和最高工资后的工资平均值
- 121.买卖股票的最佳时机
- 122.买卖股票的最佳时机II
- 1018.可被5整除的二进制前缀(没懂)
- 1502.判断能否形成等差数列
- 605.种花问题
- 1351.统计有序矩阵中的负数
- ———————8.8————————
- 509.斐波那契数
- 905.按奇偶排序数组
- 922.按奇偶排序数组 II
- 977.有序数组的平方
- -------------------8.9--------------------
- 1051.高度检查器
- 169.多数元素
- 1002.查找常用字符(没懂)
- --------------------8.15-----------------
- 189.旋转元素
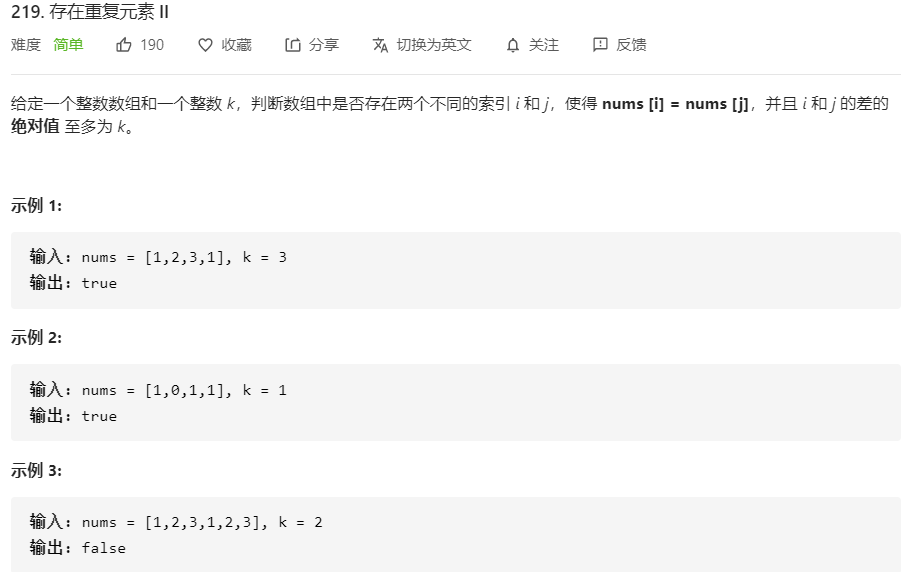
- 217.存在重复元素
- 219.存在重复元素II(哈希表)
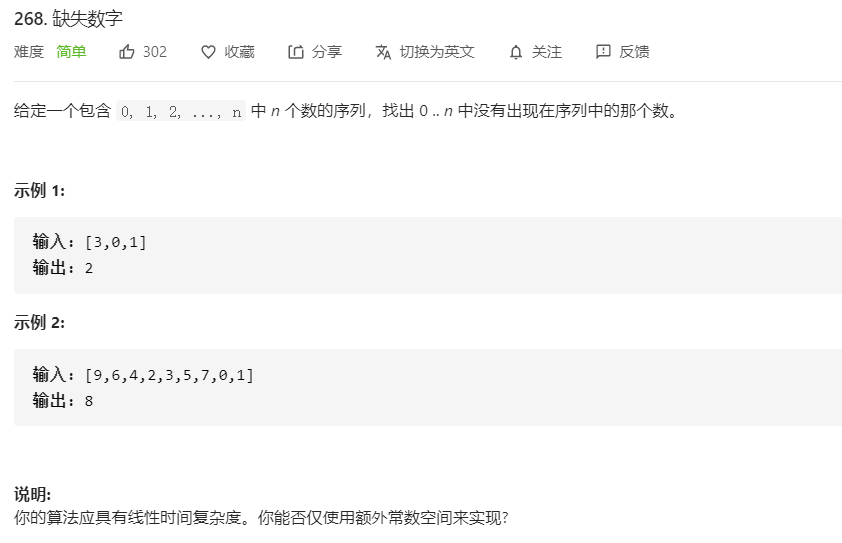
- 268.缺失数字
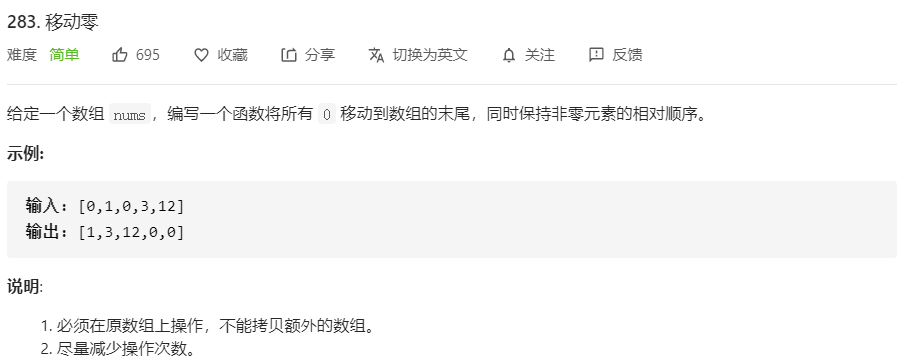
- 283.移动零
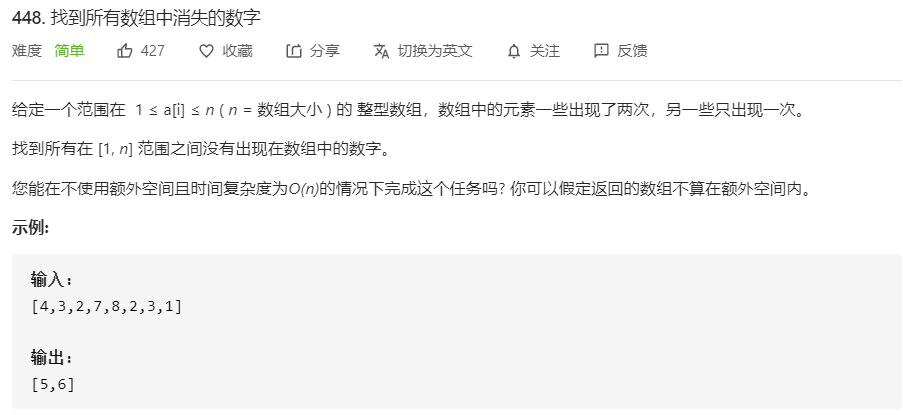
- 448.找到所有数组中消失的数字
- ---------------8.16----------------
- 485.最大连续1的个数
- 581.最短无序连续子数组
- 414.第三大的数
- 628.三个数的最大乘积
- 674.最长连续递增序列
- 665.非递减数列(不懂)
- 896.单调数列
- 1122.数组的相对排序
- --------------------8.17--------------------
- 643.子数组最大平均数
- 1200、最小绝对差
- 1470、重新排列数组
- 724、寻找数组的中心索引
- ---------------8.18------------------
- 1394.找出数组中的幸运数
- 1399.统计最大组的数目
- 1013.将数组分成和相等的三个部分
- ----------------8.19--------
- 1385.两个数组间的距离值
- 1534、统计好三元组
- ---------------8.20-------------
- 1299、将每个元素替换为右侧最大元素
- 985、查询后的偶数和(没懂)
- 1089、复写零(没懂)
- 1304、和为零的N个唯一整数
- 1331.数组序号转换
- 1356、有多少小于当前数字的数字
- 1331、数组序号转换(没看)
- -------------------8.21--------------
- 830、较大分组的位置
- 1480、一维数组的动态和
- 面试题 01.01.判定字符是否唯一
- 697、数组的度
- 面试题01.02.判定是否互为字符重排
- 1475、商品折扣后的最终价格
- 1287、有序数组中出现次数超过25%的元素
- 1450、在既定时间做作业的学生人数
- 1550.存在连续三个奇数的数组
- 面试题17.04.消失的数字(异或)
- 1512.好数对的数目
- 1539.第K个缺失的正整数
- 剑指Offer 03.数组中重复的数字
- 面试题 10.01.合并排序的数组
- 剑指Offer 53-I.在排序数组中查找数字I
- ----------------8.22------------
- 1185.一周中的第几天
- 1431、拥有最多糖果的孩子
- 1464、数组中两元素的最大乘积
- 1486、数组异或操作
- 1170、比较字符串最小字母出现频次(看不下去)
- 面试题 17.10.主要元素
- 面试题 16.17.连续数列
- 1460、通过翻转子数组使两个数组相等
- 面试题 08.03.魔术索引
- 1295、统计位数为偶数的数字
- 1413.逐步求和得到正数的最小值
- ----------------8.23----------------
- 1389、按既定顺序创建目标数组
- 747、至少是其他数字两倍的最大数
- 剑指 Offer 53-II.0~n-1中缺失的数字
- 888.公平的糖果交换
- 1346.检查整数及其两倍数是否存在
- 1160、拼写单词
- ----------------8.24--------------
- 532、数组中的K-diff数对
- 566、重塑矩阵
- 661/
- 746、使用最小花费爬楼梯(没看)
- 766。托普利茨矩阵
- 832、翻转图像
26.删除排序数组中的重复项



int removeDuplicates(int* nums, int numsSize){
if(numsSize==0){
return 0;
}
int i = 0,j;
for(j=1; j<numsSize; j++){
if(nums[j]!=nums[i]){
i++;
nums[i] = nums[j];
}
}
return i+1;
}
27.移除元素
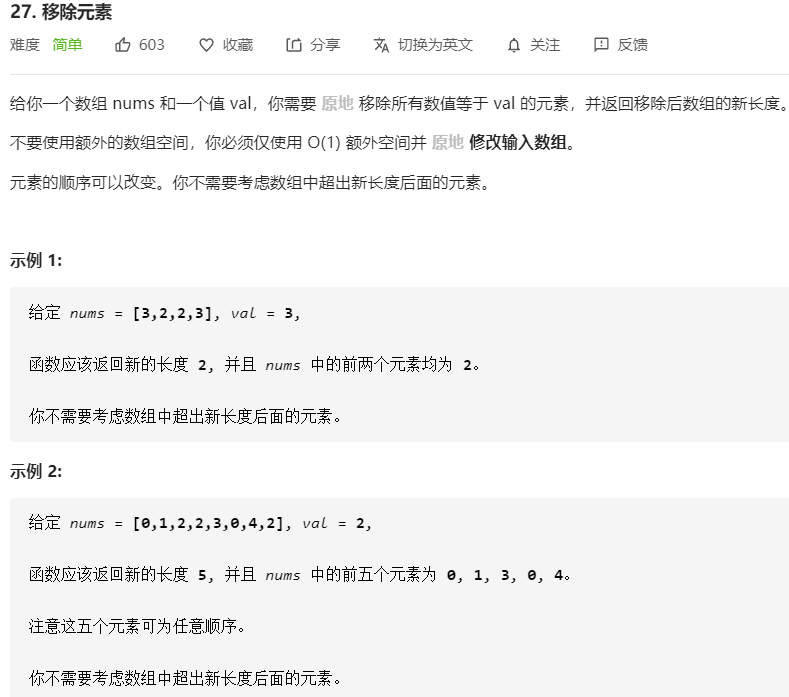

int removeElement(int* nums, int numsSize, int val){
int i = 0,j;
for(j=0; j<numsSize; j++){
if(nums[j]!=val){
nums[i]=nums[j]; //nums[i]为新数组
i++;
}
}
return i;
}
53.最大子序和
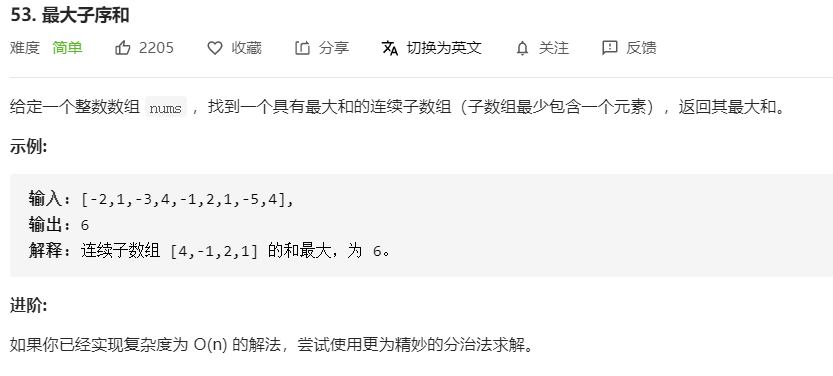
int maxSubArray(int* nums, int numsSize){
int subsum = 0, maxsum = -2147483648;
for(int i = 0; i < numsSize; i ++)
{
subsum += nums[i];
if(subsum > maxsum)
{
maxsum = subsum;
}
if(subsum < 0) subsum = 0;
}
return maxsum;
}
66.加一
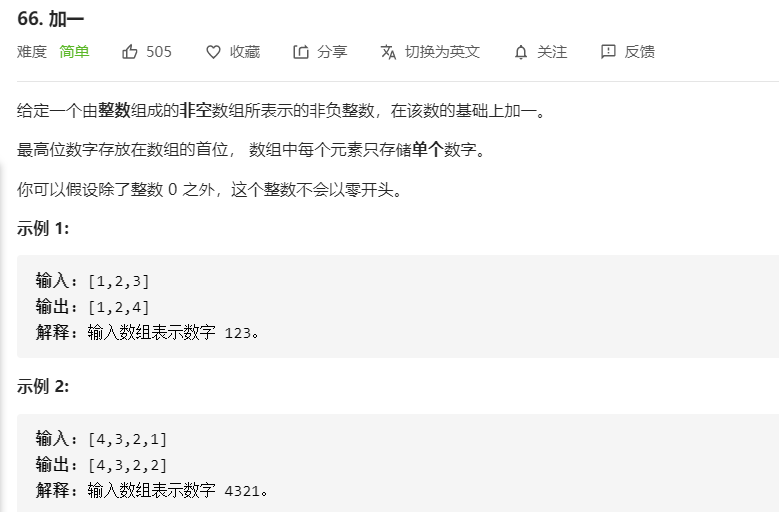
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* plusOne(int* digits, int digitsSize, int* returnSize){
if (digits == NULL && digitsSize == 0){ //传参检查
*returnSize = 0;
return NULL;
}
int flag = 0; //进位标志
int i = digitsSize - 1; //数组下标
int* res = (int*)malloc((digitsSize+1) * sizeof(int));
//申请多一位空间(最高位产生进位)
digits[i] = digits[i] + 1;//最低位 + 1
//特别注意这里改变了源数据,这点不太好,值得改进
for (; i >= 0; --i){
res[i] = digits[i] + flag;
if (res[i] >= 10){//判断有无进位
res[i] = res[i]%10;
flag = 1;
}
else{
flag = 0;
}
}
*returnSize = digitsSize + flag;
if (flag != 0){ //最高位产生了进位
int tmp;
int mid = flag; //进位数 赋给 数组第一位(新的最高位)
for (i = 0; i <= digitsSize; ++i){
tmp = res[i]; //保存当前值
res[i] = mid;
mid = tmp; //移动至下一个位置
}
}
return res;
}
88.合并两个有序数组

//由后向前排
void merge(int* nums1, int nums1Size, int m, int* nums2, int nums2Size, int n){
int tag1=m-1; //nums1最后一个元素数组下标
int tag2=n-1; //nums2最后一个元素数组下标
int end=m+n-1; //目标nums1处理下标
while(end>-1){
if(tag1<0){ //处理边界问题,防止nums[tag]数组越界
nums1[end]=nums2[tag2];
tag2--;
}
else if(tag2<0){
nums1[end]=nums1[tag1];
tag1--;
}
else if(nums1[tag1]>nums2[tag2]){
nums1[end]=nums1[tag1];
tag1--;
}
else{
nums1[end]=nums2[tag2];
tag2--;
}
end--;
}
}
题解_Java
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] nums1, int m, int[] nums2, int n) {
System.arraycopy(nums2, 0, nums1, m, n); //将俩个数组合并
Arrays.sort(nums1); //对合并后的新数组排序 缺点:没考虑俩个旧数组已经是有序的
}
}
118.杨辉三角形
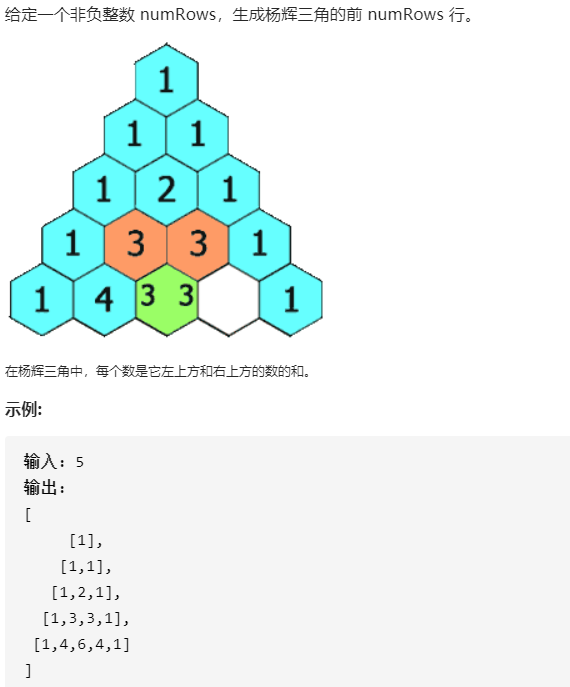
/**
* Return an array of arrays of size *returnSize.
* The sizes of the arrays are returned as *returnColumnSizes array.
* Note: Both returned array and *columnSizes array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int** generate(int numRows, int* returnSize, int** returnColumnSizes){
*returnSize = numRows;
*returnColumnSizes = (int*)malloc(4*numRows);
int i,j;
int **ret = (int**)malloc(sizeof(int*)*numRows); //声明
for(i=0; i<numRows; i++){
(*returnColumnSizes)[i] = i+1; //初始化
ret[i] = (int*)malloc(i*4+4);
ret[i][0] = 1;
ret[i][i] = 1;
}
for(i=2; i<numRows; i++){
for(j=1; j<i; j++){
ret[i][j] = ret[i-1][j-1] + ret[i-1][j]; //计算
}
}
return ret;
}
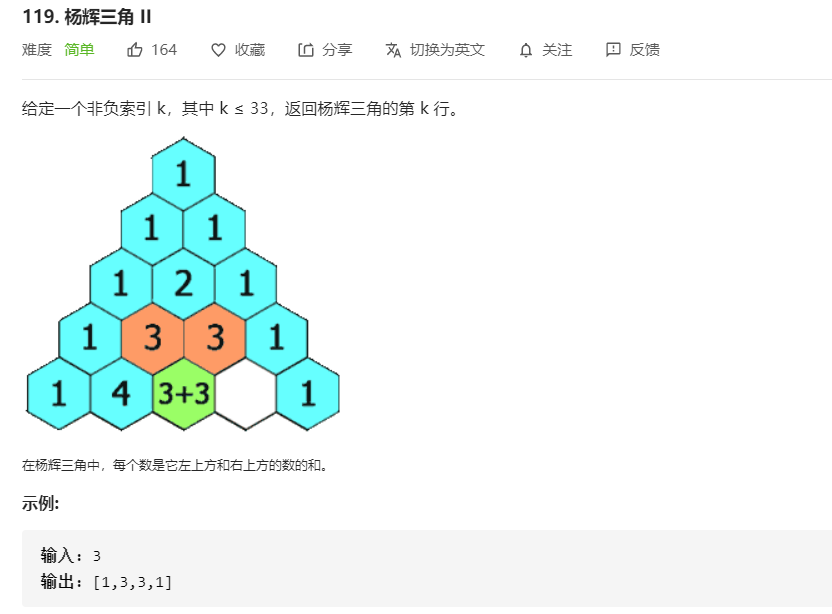
119.杨辉三角形II
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
//申请一行的空间,从后往前处理就不需要考虑数组元素被处理时被覆盖的问题。
int* getRow(int rowIndex, int* returnSize){
* returnSize = rowIndex + 1; //第k行有k个元素
int* array = (int *)malloc(sizeof(int) * (rowIndex+1));
for(int i=0; i<rowIndex+1; i++){
array[i]=1; //行末尾为1
for(int j=i-1; j>0; j--){ //每一行的更新过程
array[j] = array[j] + array[j-1];
}
array[0] = 1;
}
return array;
}
717.1比特与2比特字符
方法一:线性扫描
我们可以对 mathrm{bits}bits 数组从左到右扫描来判断最后一位是否为一比特字符。当扫描到第 ii 位时,如果 mathrm{bits}[i]=1bits[i]=1,那么说明这是一个两比特字符,将 ii 的值增加 2。如果 mathrm{bits}[i]=0bits[i]=0,那么说明这是一个一比特字符,将 ii 的值增加 1。
如果 ii 最终落在了 mathrm{bits}.mathrm{length}-1bits.length−1 的位置,那么说明最后一位一定是一比特字符。
bool isOneBitCharacter(int* bits, int bitsSize){
int i = 0;
while(i<bitsSize-1){
i += bits[i] + 1;
}
return i == bitsSize - 1;
}
989.数组形式的整数加法

思路
让我们逐位将数字加在一起。举一个例子,如果要计算 123123 与 912912 的和。我们顺次计算 3+23+2、2+12+1、1+91+9。任何时候,当加法的结果大于等于 1010,我们要将进位的 11 加入下一位的计算中去,所以最终结果等于 10351035。
算法
我们可以对以上的想法做一个小变化,让它实现起来更容易 —— 我们将整个加数加入数组表示的数的最低位。
继续之前的例子 123+912123+912,我们把它表示成 [1, 2, 3+912][1,2,3+912]。然后,我们计算 3+912 = 9153+912=915。55 留在当前这一位,将 910/10=91 以进位的形式加入下一位。
然后,我们再重复这个过程,计算 [1, 2+91, 5][1,2+91,5]。我们得到 9393,33 留在当前位,将0/10=9 以进位的形式加入下一位。继而又得到 [1+9, 3, 5][1+9,3,5],重复这个过程之后,最终得到结果 [1, 0, 3, 5][1,0,3,5]。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> addToArrayForm(int[] A, int K) {
int N = A.length;
int cur = K;
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList();
int i = N;
while (--i >= 0 || cur > 0) {
if (i >= 0)
cur += A[i];
ans.add(cur % 10);
cur /= 10;
}
Collections.reverse(ans);
return ans;
}
}
561.数组拆分I

思路:排序 相邻两个数相差最小 总和最大
public class Solution {
public int arrayPairSum(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i += 2) {
sum += nums[i];
}
return sum;
}
}
1491.去掉最低工资和最高工资后的工资平均值
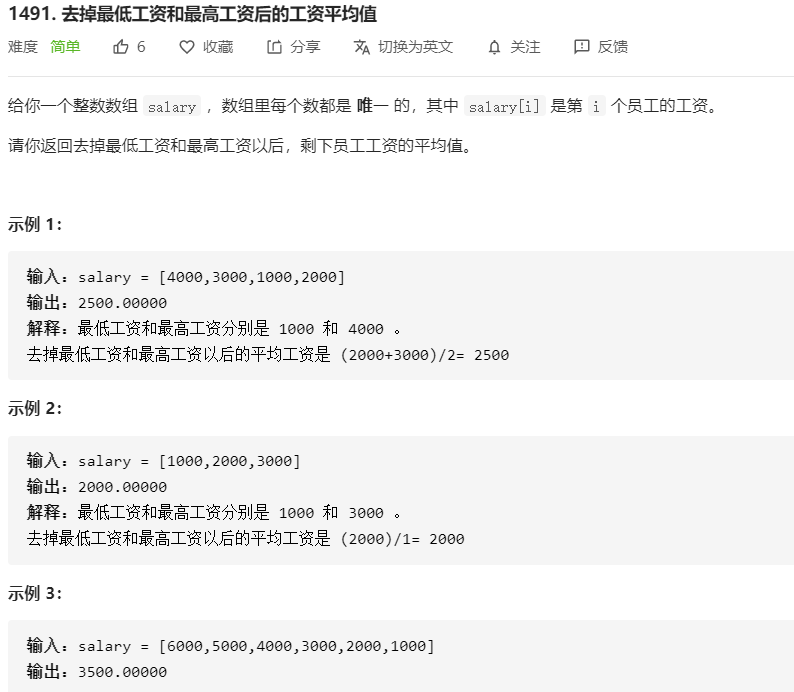
思路:对数组进行排序,去掉首尾
class Solution {
public double average(int[] salary) {
double sum = 0;
Arrays.sort(salary);
for(int i=1; i<salary.length-1; i++){
sum += salary[i];
}
return sum/(salary.length-2);
}
}
121.买卖股票的最佳时机
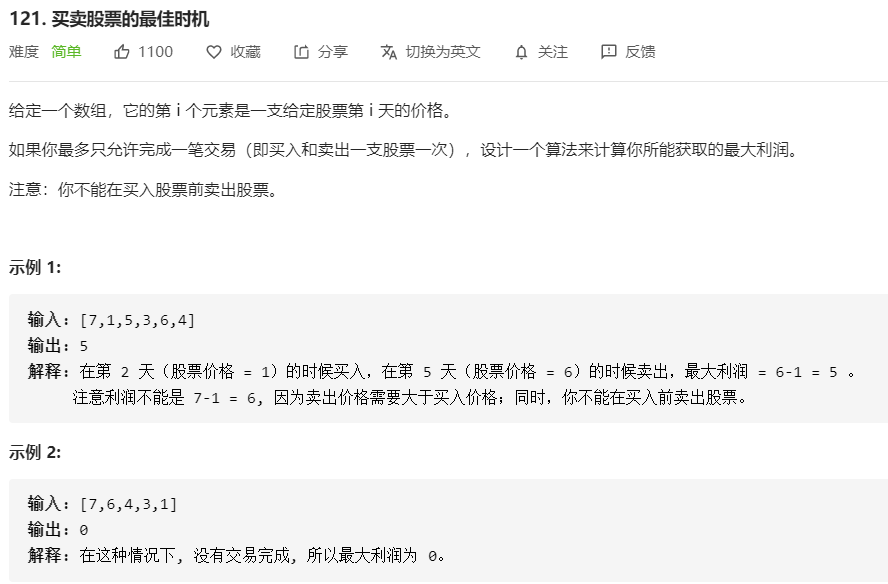
思路一:暴力法,依次求出最后比较得到最大利润
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int prices[]) {
int maxprofit = 0; //存储最大利润
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length - 1; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < prices.length; j++) { //保证买卖时间的先后顺序
int profit = prices[j] - prices[i]; //计算第i天后的每一天和第i天价格的差值
if (profit > maxprofit) //找出最大差值
maxprofit = profit;
}
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
思路2:记录历史最低点,若不是最低点,则将其与先前找到的最低点相减、找到最大利润(不过好像有问题 比如:9,2,7,1,3不适用)
求出历史最低点(买入时机),依次求每个卖出时机的的最大差值,再从中取最大值。
public class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int prices[]) {
int minprice = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
int maxprofit = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] < minprice){
minprice = prices[i];
}
else if (prices[i] - minprice > maxprofit){
maxprofit = prices[i] - minprice;
}
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
122.买卖股票的最佳时机II

我们必须确定通过交易能够获得的最大利润(对于交易次数没有限制)。为此,我们需要找出那些共同使得利润最大化的买入及卖出价格
思路1:
暴力法(官方给的代码 可 我运行后 超出时间限制):
这种情况下,我们只需要计算与所有可能的交易组合相对应的利润,并找出它们中的最大利润。
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) { //主
return calculate(prices, 0);
}
public int calculate(int prices[], int s) {
if (s >= prices.length) //数组长度小于s(s=0时数组为空) 没有股票 利润为0
return 0;
int max = 0; //多次交易后最终的最大利润
for (int start = s; start < prices.length; start++) { //遍历数组
int maxprofit = 0; //定义一次交易后的最大利润
for (int i = start + 1; i < prices.length; i++) { //遍历买入股票后的每一天
if (prices[start] < prices[i]) { //第i天股票价格大于买入时价格
int profit = calculate(prices, i + 1) + prices[i] - prices[start]; //计算此时利润
if (profit > maxprofit) //与之前的利润作比较 求出每一次交易最大利润
maxprofit = profit;
}
}
if (maxprofit > max) //多次交易后的最大利润
max = maxprofit;
}
return max;
}
}
思路2:峰谷法:
连续的峰和谷
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int i = 0;
int valley = prices[0]; //峰
int peak = prices[0]; //谷
int maxprofit = 0;
while (i < prices.length - 1) { //遍历数组
while (i < prices.length - 1 && prices[i] >= prices[i + 1]){ //找波谷
i++;
}
valley = prices[i]; //将所有的波谷值相加
while (i < prices.length - 1 && prices[i] <= prices[i + 1]){ //找波峰
i++;
}
peak = prices[i]; //将所有的波峰值相加
maxprofit += peak - valley;
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
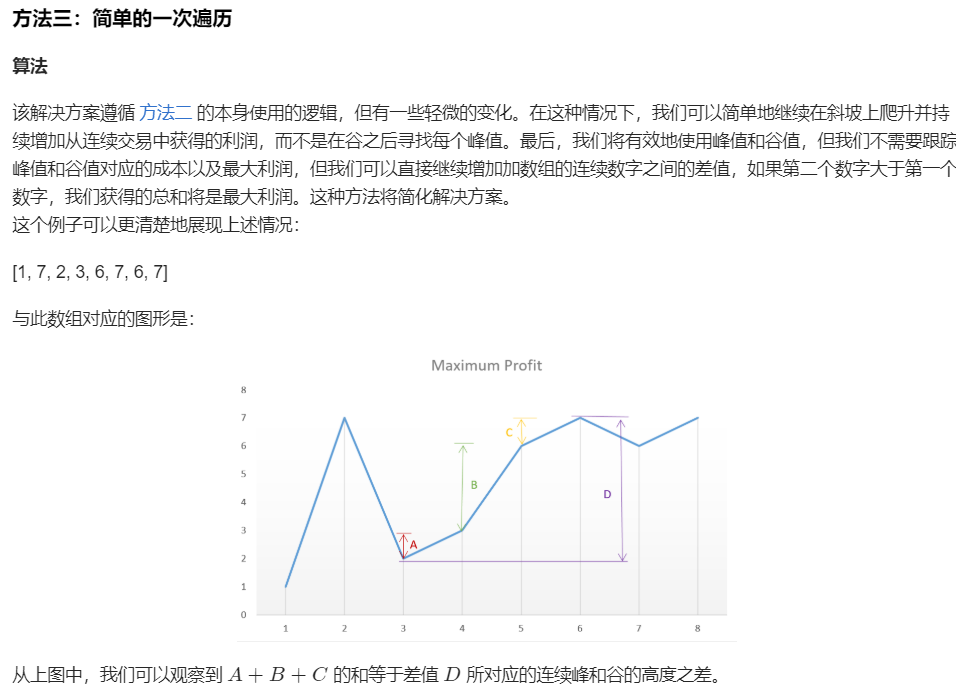
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int maxprofit = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < prices.length; i++) {
if (prices[i] > prices[i - 1])
maxprofit += prices[i] - prices[i - 1];
}
return maxprofit;
}
}
1018.可被5整除的二进制前缀(没懂)

/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
bool* prefixesDivBy5(int* A, int ASize, int* returnSize)
{
int temp = 0;
*returnSize = ASize;
bool* ret = (bool*)malloc(ASize * sizeof(bool));
for (int i = 0; i < ASize; i++) {
temp = (temp << 1) + A[i]; //换算成十进制
temp = temp % 5;
if (temp == 0) { //判断是否能被5整除
ret[i] = true;
} else {
ret[i] = false;
}
}
return ret;
}
1502.判断能否形成等差数列
思路:
先排序,后看是否满足arr[i] * 2 = arr[i - 1] + arr[i + 1]
class Solution {
public boolean canMakeArithmeticProgression(int[] arr) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length - 1; ++i) {
if (arr[i] * 2 != arr[i - 1] + arr[i + 1]) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
605.种花问题
思路:
方法一:贪心
我们从左到右扫描数组 flowerbed,如果数组中有一个 0,并且这个 0 的左右两侧都是 0,那么我们就可以在这个位置种花,即将这个位置的 0 修改成 1,并将计数器 count 增加 1。对于数组的第一个和最后一个位置,我们只需要考虑一侧是否为 0。
在扫描结束之后,我们将 count 与 n 进行比较。如果 count >= n,那么返回 True,否则返回 False。
public class Solution {
public boolean canPlaceFlowers(int[] flowerbed, int n) {
int i = 0, count = 0;
while (i < flowerbed.length) { //遍历数组
if (flowerbed[i] == 0 && (i == 0 || flowerbed[i - 1] == 0) && (i == flowerbed.length - 1 || flowerbed[i + 1] == 0)) { //判断能否种花
flowerbed[i] = 1;
count++;
}
i++;
}
return count >= n;
}
}
1351.统计有序矩阵中的负数

思路:二分法
注意到题目中给了一个性质,即矩阵中的元素无论是按行还是按列,都以非递增顺序排列,可以考虑把这个性质利用起来优化暴力。已知这个性质告诉了我们每一行的数都是有序的,所以我们通过二分查找可以找到每一行中从前往后的第一个负数,那么这个位置之后到这一行的末尾里所有的数必然是负数了,可以直接统计。
class Solution {
public int countNegatives(int[][] grid) {
int count = 0, m = grid.length, n = grid[0].length; //m:有多少组,n:一组有多少个数
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) { //一组一组遍历
int[] row = grid[i];
if (row[n - 1] >= 0){
continue;
} // 整行非负,跳过
if (row[0] < 0) { // 整行负数
count += (m - i) * n; // 后面的行也计入
break; // 无需再继续遍历
}
int first = _binarySearch(row); // 当前行二分查找第一个小于 0 的数的索引
count += n - first;
}
return count;
}
// 查找第一个小于 0 的数的索引
private int _binarySearch(int[] arr) {
int begin = 0, end = arr.length;
while (begin < end) {
int mid = begin + ((end - begin) >> 1);
if (arr[mid] >= 0) {
begin = mid + 1;
}
else { // 负数之后,还要再判断前一个不是负数(不太懂)
if (arr[mid - 1] >= 0) {
return mid;
}
end = mid;
}
}
return begin;
}
}
———————8.8————————
509.斐波那契数
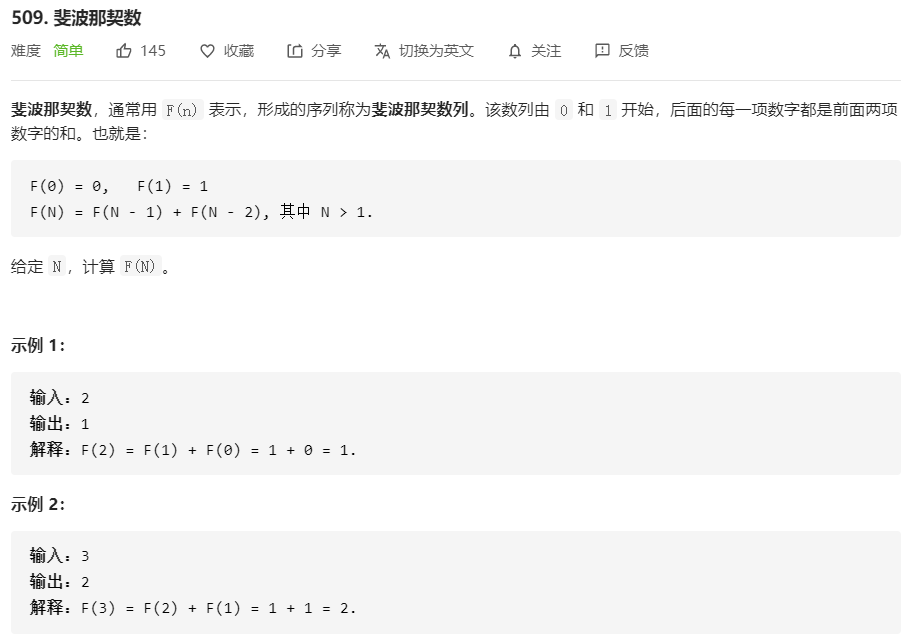

public class Solution {
public int fib(int N) {
if (N <= 1) {
return N;
}
return fib(N-1) + fib(N-2);
}
}
905.按奇偶排序数组
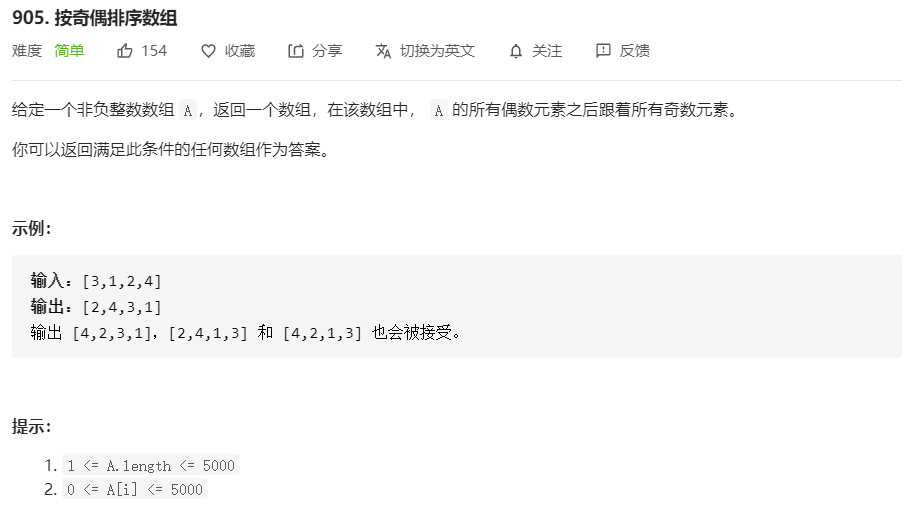
两边扫描
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParity(int[] A) {
int[] ans = new int[A.length];
int t = 0;
//第一遍扫描 输出偶数
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; ++i)
if (A[i] % 2 == 0)
ans[t++] = A[i];
//第二遍扫描 输出奇数
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; ++i)
if (A[i] % 2 == 1)
ans[t++] = A[i];
return ans;
}
}
922.按奇偶排序数组 II
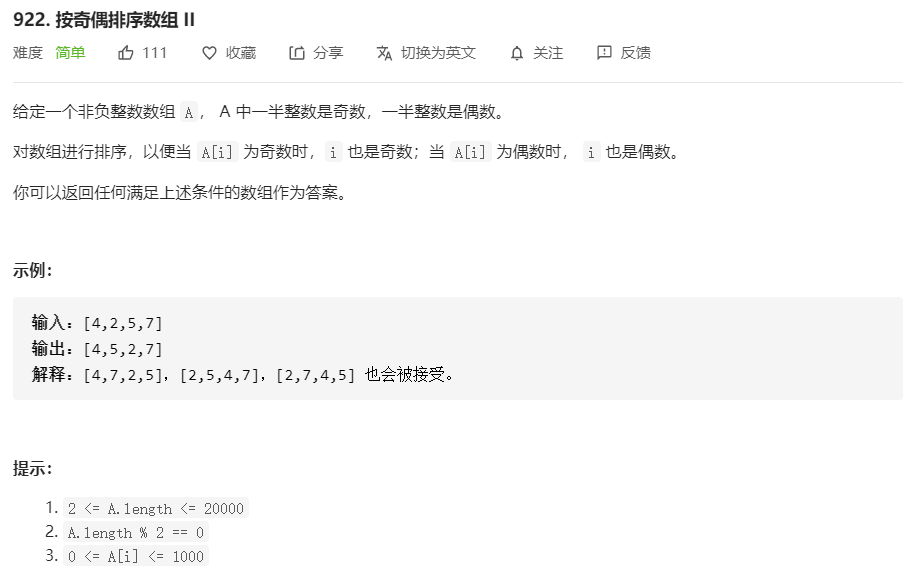
方法一: 两次遍历
思路和算法
遍历一遍数组把所有的偶数放进 ans[0],ans[2],ans[4],依次类推。
再遍历一遍数组把所有的奇数依次放进 ans[1],ans[3],ans[5],依次类推
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParityII(int[] A) {
int N = A.length;
int[] ans = new int[N];
int t = 0;
for (int x: A){
if (x % 2 == 0) {
ans[t] = x;
t += 2;
}
}
t = 1;
for (int x: A){
if (x % 2 != 0) {
ans[t] = x;
t += 2;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
方法二: 双指针
思路
我们可能会被面试官要求写出一种不需要开辟额外空间的解法。
在这个问题里面,一旦所有偶数都放在了正确的位置上,那么所有奇数也一定都在正确的位子上。所以只需要关注 A[0], A[2], A[4], … 都正确就可以了。
将数组分成两个部分,分别是偶数部分 even = A[0], A[2], A[4], … 和奇数部分 odd = A[1], A[3], A[5], …。定义两个指针 i 和 j, 每次循环都需要保证偶数部分中下标 i 之前的位置全是偶数,奇数部分中下标 j 之前的位置全是奇数。
算法
让偶数部分下标 i 之前的所有数都是偶数。为了实现这个目标,把奇数部分作为暂存区,不断增加指向奇数部分的指针,直到找到一个偶数,然后交换指针 i,j 所指的数。
class Solution {
public int[] sortArrayByParityII(int[] A) {
int j = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length; i += 2)
if (A[i] % 2 != 0) {
while (A[j] % 2 != 0)
j += 2;
// Swap A[i] and A[j]
int tmp = A[i];
A[i] = A[j];
A[j] = tmp;
}
return A;
}
}
977.有序数组的平方
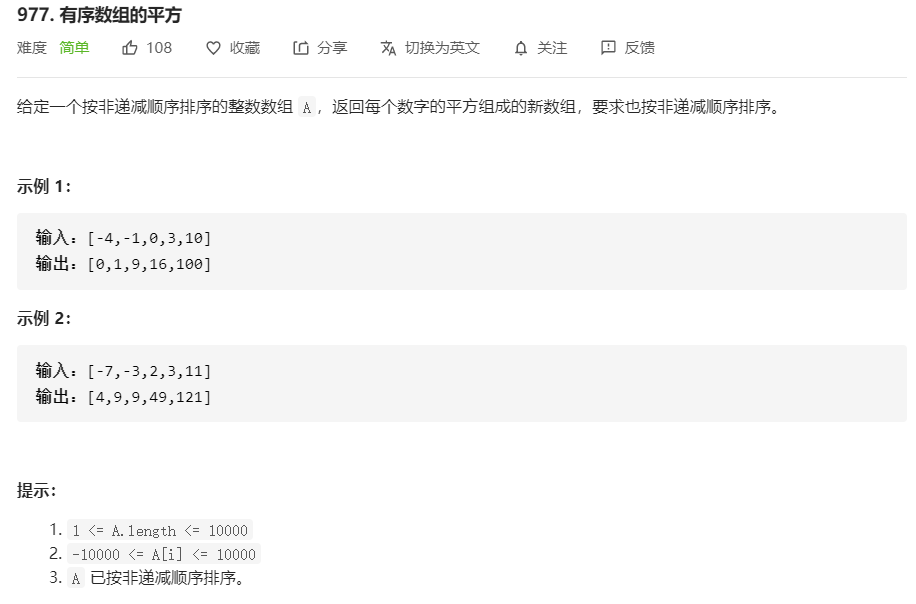
方法一:排序
思路与算法
创建一个新的数组,它每个元素是给定数组对应位置元素的平方,然后排序这个数组。
class Solution {
public int[] sortedSquares(int[] A) {
int N = A.length;
int[] ans = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
ans[i] = A[i] * A[i];
Arrays.sort(ans);
return ans;
}
}
方法二:双指针
思路
因为数组 A 已经排好序了, 所以可以说数组中的负数已经按照平方值降序排好了,数组中的非负数已经按照平方值升序排好了。
举一个例子,若给定数组为 [-3, -2, -1, 4, 5, 6],数组中负数部分 [-3, -2, -1] 的平方为 [9, 4, 1],数组中非负部分 [4, 5, 6] 的平方为 [16, 25, 36]。我们的策略就是从前向后遍历数组中的非负数部分,并且反向遍历数组中的负数部分。
算法
我们可以使用两个指针分别读取数组的非负部分与负数部分 —— 指针 i 反向读取负数部分,指针 j 正向读取非负数部分。
那么,现在我们就在使用两个指针分别读取两个递增的数组了(按元素的平方排序)。接下来,我们可以使用双指针的技巧合并这两个数组。
-------------------8.9--------------------
1051.高度检查器


class Solution {
public int heightChecker(int[] heights) {
// 值的范围是1 <= heights[i] <= 100,因此需要1,2,3,...,99,100,共101个桶
int[] arr = new int[101];
// 遍历数组heights,计算每个桶中有多少个元素,也就是数组heights中有多少个1,多少个2,。。。,多少个100
// 将这101个桶中的元素,一个一个桶地取出来,元素就是有序的
for (int height : heights) {
arr[height]++;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 1, j = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
// arr[i],i就是桶中存放的元素的值,arr[i]是元素的个数
// arr[i]-- 就是每次取出一个,一直取到没有元素,成为空桶
while (arr[i]-- > 0) {
// 从桶中取出元素时,元素的排列顺序就是非递减的,然后与heights中的元素比较,如果不同,计算器就加1
if (heights[j++] != i) count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}
169.多数元素
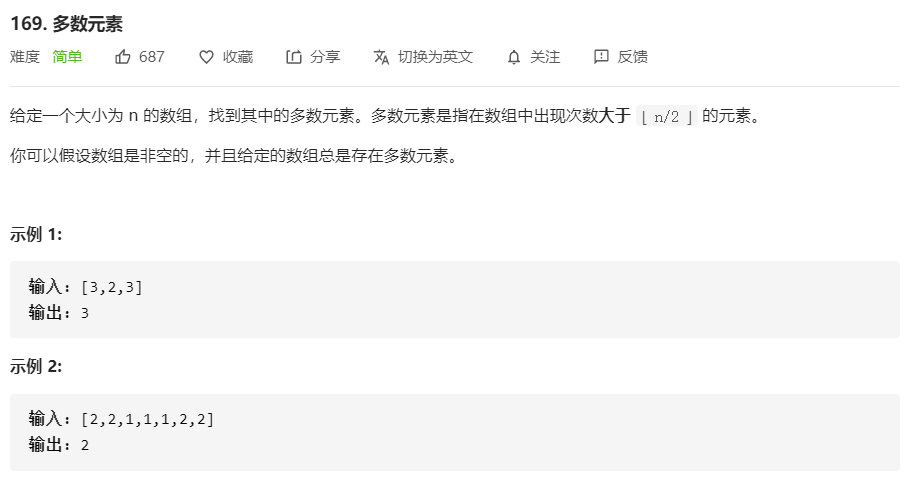

class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return nums[nums.length/2];
}
}
1002.查找常用字符(没懂)
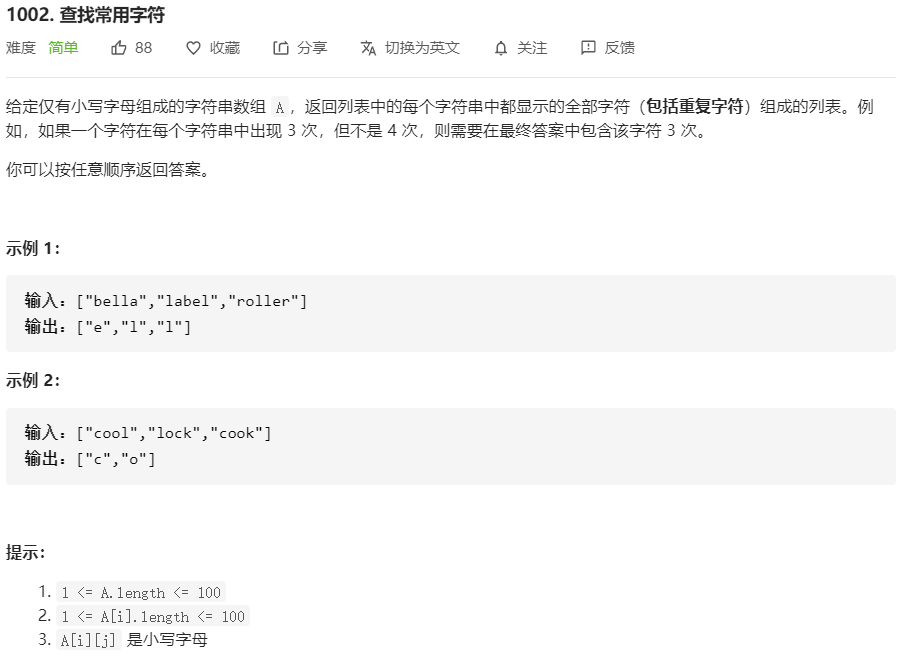

class Solution {
public List<String> commonChars(String[] A) {
//记录当前处理到的单词每个字符的出现次数
int[] hash = new int[26];
//记录已处理过的所有单词共有字符的出现次数
int[] temp = new int[26];
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
//每个字符出现次数最多100次,因为题目有限制每个单词最多含有100字符
hash[i] = 100;
//用temp更新hash
for(int i = 0; i < A.length; i++) //每个单词
{
for(char c : A[i].toCharArray()) //toCharArray()将字符串转换为字符数组
temp[c - 'a']++; //a b c d->0 1 2 3
for(int j = 0; j < 26; j++) //单词里的每个字母
{
hash[j] = Math.min(hash[j], temp[j]);
temp[j] = 0;
}
}
List<String> list = new LinkedList<String>();
for(int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
{
while(hash[i] > 0)
{
list.add(String.valueOf((char)(i + 'a')));
hash[i]--;
}
}
return list;
}
}
--------------------8.15-----------------
189.旋转元素
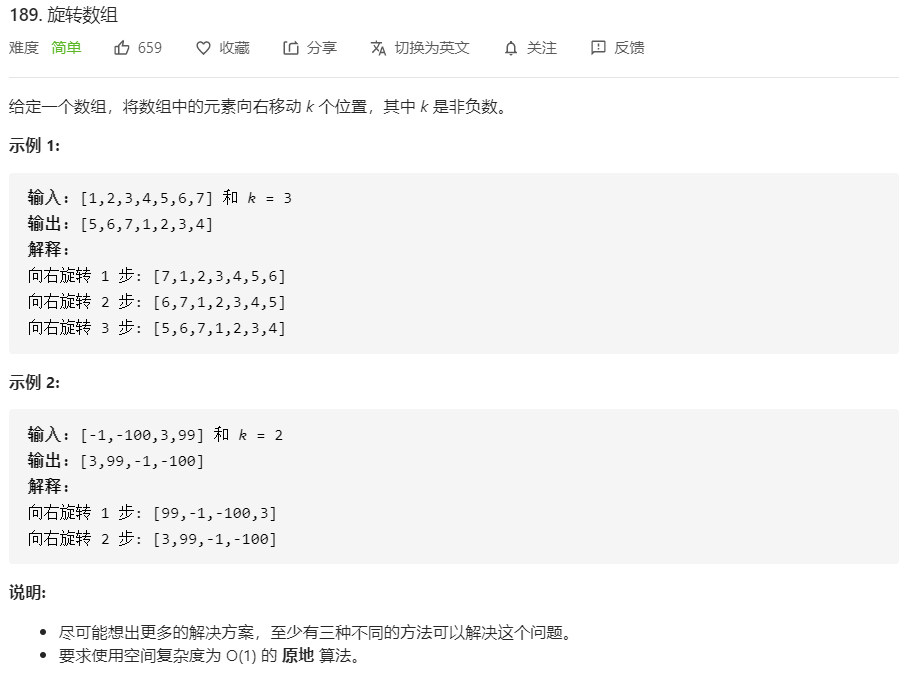
方法1:暴力法
最简单方法是旋转K次,每次将数组旋转1个元素
public class Solution {
public void rotate(int[] nums, int k) {
int temp, previous;
//向右移动k次
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
//存储数组的最后一个元素
previous = nums[nums.length - 1];
//交换第一个和最后一个元素
for (int j = 0; j < nums.length; j++) {
temp = nums[j];
nums[j] = previous;
previous = temp;
}
}
}
}
217.存在重复元素
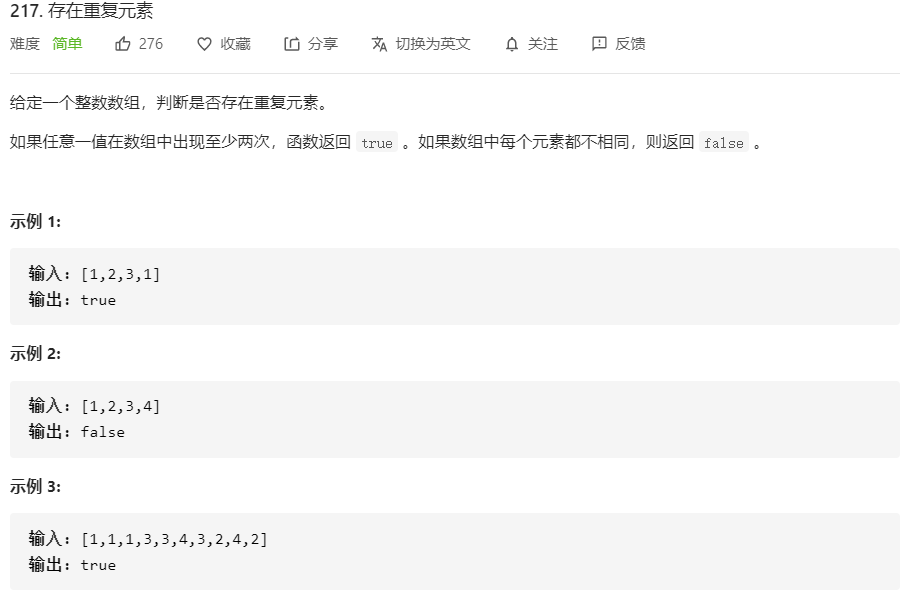

class Solution {
public boolean containsDuplicate(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length - 1; ++i) {
if (nums[i] == nums[i + 1]) return true;
}
return false;
}
}
219.存在重复元素II(哈希表)

class Solution {
public boolean containsNearbyDuplicate(int[] nums, int k) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (set.contains(nums[i])) return true;
set.add(nums[i]);
if (set.size() > k) {
set.remove(nums[i - k]);
}
}
return false;
}
}
268.缺失数字

class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
// 判断 n 是否出现在末位
if (nums[nums.length-1] != nums.length) {
return nums.length;
}
// 判断 0 是否出现在首位
else if (nums[0] != 0) {
return 0;
}
// 此时缺失的数字一定在 (0, n) 中
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
int expectedNum = nums[i-1] + 1;
if (nums[i] != expectedNum) {
return expectedNum;
}
}
// 未缺失任何数字(保证函数有返回值)
return -1;
}
}
283.移动零
思想:两次遍历
我们创建两个指针i和j,第一次遍历的时候指针j用来记录当前有多少非0元素。即遍历的时候每遇到一个非0元素就将其往数组左边挪,第一次遍历完后,j指针的下标就指向了最后一个非0元素下标。
第二次遍历的时候,起始位置就从j开始到结束,将剩下的这段区域内的元素全部置为0。
class Solution {
public void moveZeroes(int[] nums) {
if(nums==null) {
return;
}
//第一次遍历的时候,j指针记录非0的个数,只要是非0的统统都赋给nums[j]
int j = 0;
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;++i) {
if(nums[i]!=0) {
nums[j++] = nums[i];
}
}
//非0元素统计完了,剩下的都是0了
//所以第二次遍历把末尾的元素都赋为0即可
for(int i=j;i<nums.length;++i) {
nums[i] = 0;
}
}
}
448.找到所有数组中消失的数字
思想:
注意题目要求不能使用额外空间,这也是这道题的难点所在。
这道题里面其实包含了隐藏的条件,1 ≤ a[i] ≤ n,即每个数字本身都对应一个i-1的数组下标。
我们可以利用数组内容本身跟数字下标的关联找出缺失的数字。
扫描两遍数组,第一次将所有数字做标记,第二次根据标记信息找出缺失的数字。
class Solution {
public List<Integer> findDisappearedNumbers(int[] nums) {
List<Integer> res = new ArrayList<Integer>();
//第一遍扫描,根据数组的值找到对应的下标,比如3对应下标2
//将arr[i]设置成负数
for(int i=0;i<nums.length;++i) {
//abs()绝对值
int index = Math.abs(nums[i])-1;
if(nums[index]>0) {
nums[index] *= -1;
}
}
//第二遍扫描,找到所有非负数,非负数所在的下标+1,即为缺失的数字
for(int i=1;i<=nums.length;++i) {
if(nums[i-1]>0) {
res.add(i);
}
}
return res;
}
}
---------------8.16----------------
485.最大连续1的个数

class Solution {
public int findMaxConsecutiveOnes(int[] nums) {
int count = 0;
int maxCount = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
if(nums[i] == 1) {
// Increment the count of 1's by one.
count += 1;
} else {
// Find the maximum till now.
maxCount = Math.max(maxCount, count);
// Reset count of 1.
count = 0;
}
}
return Math.max(maxCount, count);
}
}
581.最短无序连续子数组
方法 3:排序
算法
另一个简单的想法是:我们将数组 numsnums 进行排序,记为 nums_sortednums_sorted 。然后我们比较 numsnums 和 nums_sortednums_sorted 的元素来决定最左边和最右边不匹配的元素。它们之间的子数组就是要求的最短无序子数组。
public class Solution {
public int findUnsortedSubarray(int[] nums) {
int[] snums = nums.clone();
Arrays.sort(snums);
int start = snums.length, end = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < snums.length; i++) {
if (snums[i] != nums[i]) {
start = Math.min(start, i);
end = Math.max(end, i);
}
}
return (end - start >= 0 ? end - start + 1 : 0);
}
}
414.第三大的数
解题思路:
先用一个循环 找出最小值
然后再用一个循环 依次找出第一大 第二大 第三大的数
int thirdMax(int* nums, int numsSize){
int i;
int one,two,three;
int min = nums[0];
//找最小值
for(i=0;i<numsSize;i++){
if(nums[i]<=min)
min = nums[i];
}
one = two = three = min;
for(i=0;i<numsSize;i++){
//注意赋值顺序 一层层往上传值 最大的值给one 下面的类似
if(nums[i]>one){
three = two;
two = one;
one = nums[i];
}
else if(nums[i] > two && nums[i] != one){
three = two;
two = nums[i];
}
else if(nums[i] > three && nums[i] != two && nums[i] != one){
three = nums[i];
}
}
//当三个层次的最值里面有两个值相等时 说明没有第三大的值 直接返回最大值
if(three == two || two == one){
return one;
}
return three;
}
628.三个数的最大乘积
方法一:排序
我们将数组进行升序排序,如果数组中所有的元素都是非负数,那么答案即为最后三个元素的乘积。
如果数组中出现了负数,那么我们还需要考虑乘积中包含负数的情况,显然选择最小的两个负数和最大的一个正数是最优的,即为前两个元素与最后一个元素的乘积。
上述两个结果中的较大值就是答案。注意我们可以不用判断数组中到底有没有正数,0 或者负数,因为上述两个结果实际上已经包含了所有情况,最大值一定在其中。
public class Solution {
public int maximumProduct(int[] nums) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
return Math.max(nums[0] * nums[1] * nums[nums.length - 1], nums[nums.length - 1] * nums[nums.length - 2] * nums[nums.length - 3]);
}
}
674.最长连续递增序列

class Solution {
public int findLengthOfLCIS(int[] nums) {
int ans = 0, anchor = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (i > 0 && nums[i-1] >= nums[i]) anchor = i;
ans = Math.max(ans, i - anchor + 1);
}
return ans;
}
}
665.非递减数列(不懂)
class Solution {
public boolean checkPossibility(int[] nums) {
int cnt = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length && cnt<=1 ; i++){
if(nums[i-1] > nums[i]){
cnt++;
if(i-2>=0 && nums[i-2]>nums[i]){
nums[i] = nums[i-1];
}
}
}
return cnt<=1;
}
}
896.单调数列

class Solution {
public boolean isMonotonic(int[] A) { //主
return increasing(A) || decreasing(A);
}
//单增
public boolean increasing(int[] A) {
for (int i = 0; i < A.length - 1; ++i)
if (A[i] > A[i+1]) return false;
return true;
}
//单减
public boolean decreasing(int[] A) {
for (int i = 0; i < A.length - 1; ++i)
if (A[i] < A[i+1]) return false;
return true;
}
}

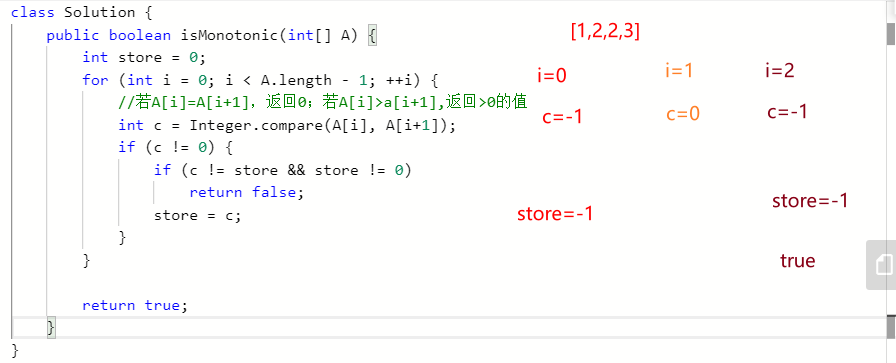
class Solution {
public boolean isMonotonic(int[] A) {
int store = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < A.length - 1; ++i) {
//若A[i]=A[i+1],返回0;若A[i]>a[i+1],返回>0的值
int c = Integer.compare(A[i], A[i+1]);
if (c != 0) {
if (c != store && store != 0)
return false;
store = c;
}
}
return true;
}
}
1122.数组的相对排序
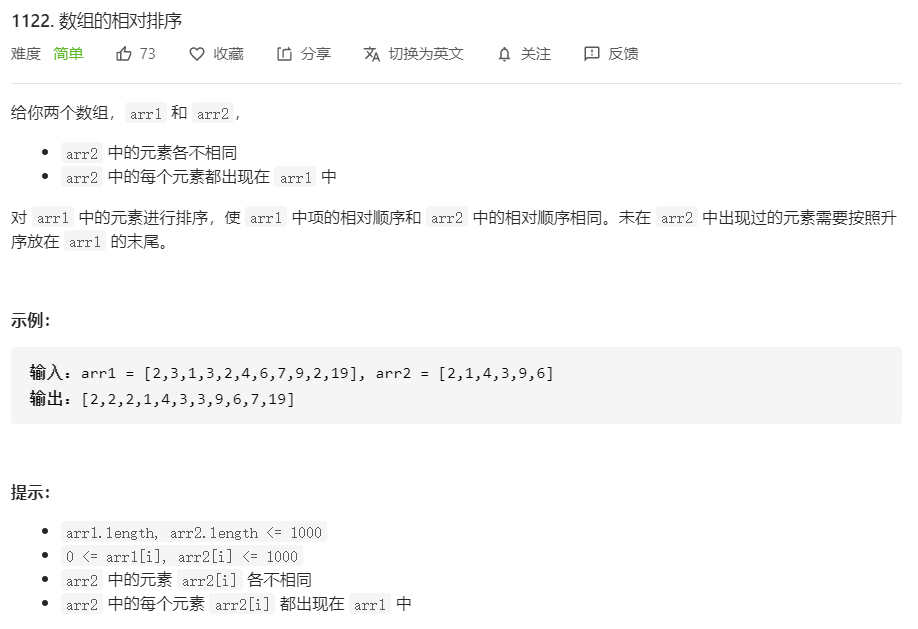
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* relativeSortArray(int* arr1, int arr1Size, int* arr2, int arr2Size, int* returnSize){
int arr[1001]={0};
int i,j=0;
//记录arr1数字出现的次数次数
for(i=0;i<arr1Size;i++){
arr[arr1[i]]++;
}
//找到在arr2和arr1都出现的数字
for(i=0;i<arr2Size;i++){
while(arr[arr2[i]]>0){
arr1[j]=arr2[i];
j++;
arr[arr2[i]]--;
}
}
//找arr1有,arr2没有的
for(i=0;i<1001;i++){
while(arr[i]>0){
arr1[j++]=i;
arr[i]--;
}
}
*returnSize=arr1Size;
return arr1;
}
--------------------8.17--------------------
643.子数组最大平均数

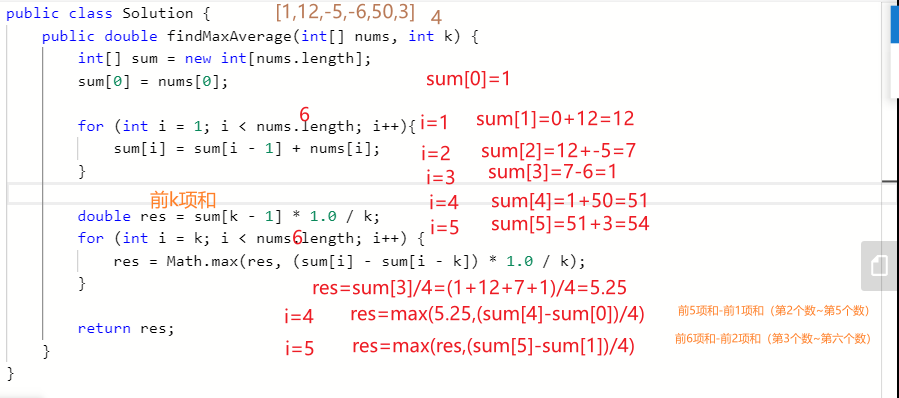
public class Solution {
public double findMaxAverage(int[] nums, int k) {
int[] sum = new int[nums.length];
sum[0] = nums[0];
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
sum[i] = sum[i - 1] + nums[i];
}
double res = sum[k - 1] * 1.0 / k;
for (int i = k; i < nums.length; i++) {
res = Math.max(res, (sum[i] - sum[i - k]) * 1.0 / k);
}
return res;
}
}
1200、最小绝对差
思想:
排序之和,最小绝对值差一定是相邻两数的差,遍历的过程中一边寻找最小差一边记录结果
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> minimumAbsDifference(int[] arr) {
Arrays.sort(arr);
List<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
int min = 99999999;
for (int i = 1; i < arr.length; i++) {
int tmp = arr[i] - arr[i - 1];
// 找到新的最小差,清空原有结果
if (tmp < min) {
min = tmp;
res.clear();
}
// 如果是最小差,记录
if (tmp == min) {
List<Integer> item = new ArrayList<>(2);
item.add(arr[i - 1]);
item.add(arr[i]);
res.add(item);
}
}
return res;
}
}
1470、重新排列数组
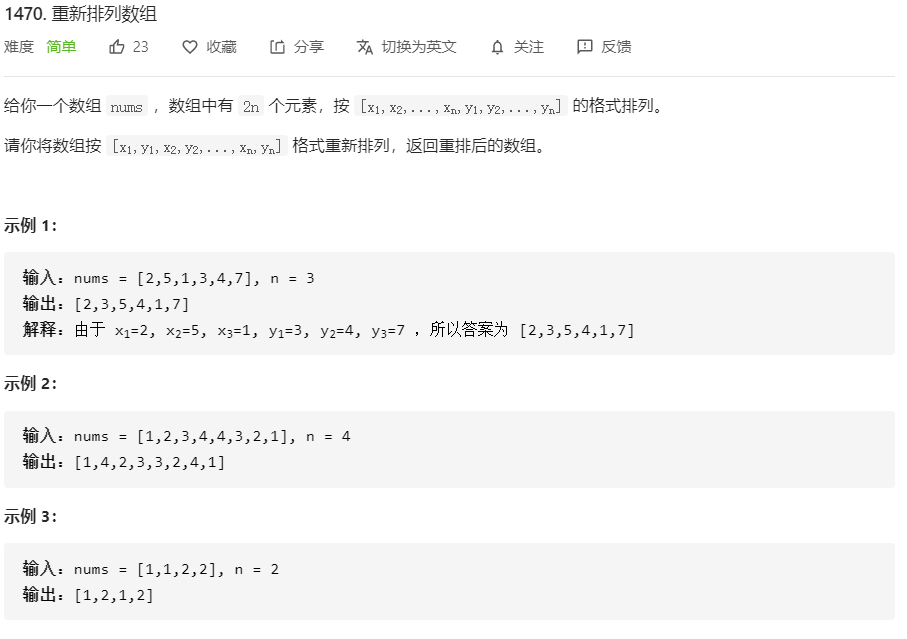

class Solution {
public int[] shuffle(int[] nums, int n) {
//1、新建一个数组用来存放排好的数
int[] arry = new int[nums.length];
//2、用for来排好
int j =0;
//循环 nums/2 次
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length/2 ; i++){
arry[j++] = nums[i]; //第一个位置放 第 i个元素,每次j++自增1
arry[j++] = nums[n +i]; //从第n+i 就是从一半开始到数组的最后
}
//3、存到新数组里
return arry;
}
}
724、寻找数组的中心索引


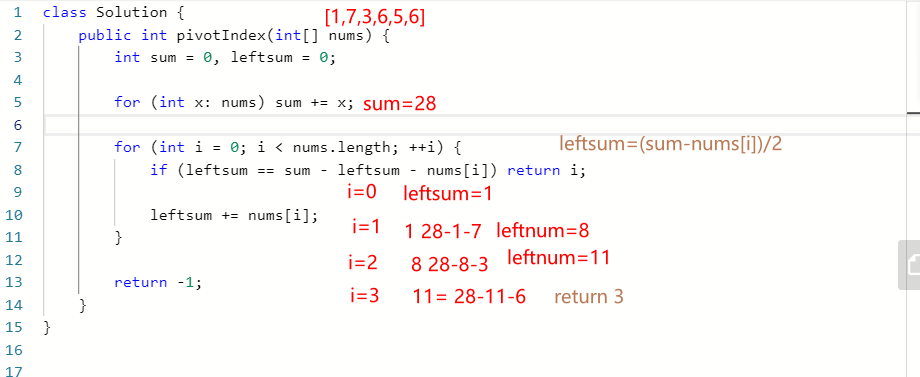
class Solution {
public int pivotIndex(int[] nums) {
int sum = 0, leftsum = 0;
for (int x: nums) sum += x;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (leftsum == sum - leftsum - nums[i]) return i;
leftsum += nums[i];
}
return -1;
}
}
---------------8.18------------------
1394.找出数组中的幸运数
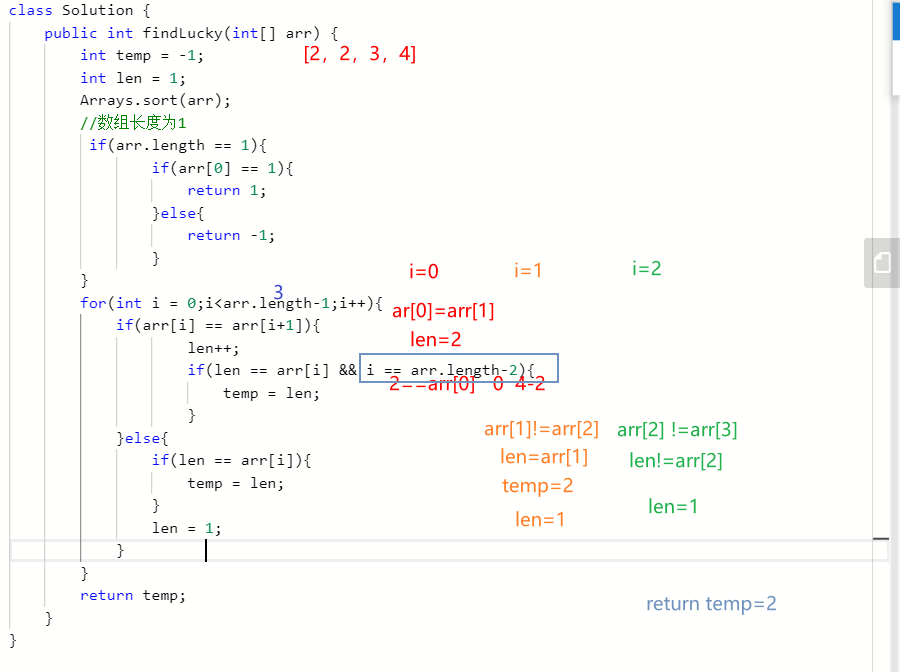
class Solution {
public int findLucky(int[] arr) {
int temp = -1;
int len = 1;
Arrays.sort(arr);
//数组长度为1
if(arr.length == 1){
if(arr[0] == 1){
return 1;
}else{
return -1;
}
}
for(int i = 0;i<arr.length-1;i++){
if(arr[i] == arr[i+1]){
len++;
if(len == arr[i] && i == arr.length-2){
temp = len;
}
}else{
if(len == arr[i]){
temp = len;
}
len = 1;
}
}
return temp;
}
}
1399.统计最大组的数目


class Solution {
public int countLargestGroup(int n) {
int ans = 0, max = 1;
// 统计数位和有多少
int[] count = new int[n + 1];
//计算1-n各个元素的数位和,例如数字i的数位和是sum[i / 10] + i % 10
int[] sum = new int[n + 1];
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
sum[i] = sum[i / 10] + i % 10;
count[sum[i]]++;
if(count[sum[i]] > max)
max = count[sum[i]];
}
for(int num : count) ans += num == max ? 1 : 0;
return ans;
}
}
1013.将数组分成和相等的三个部分


class Solution {
public boolean canThreePartsEqualSum(int[] A) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i : A){
sum += i;
}
if(sum%3 != 0){
// 总和不是3的倍数,直接返回false
return false;
}
// 使用双指针,从数组两头开始一起找,节约时间
int left = 0;
int leftSum = A[left];
int right = A.length - 1;
int rightSum = A[right];
// 使用left + 1 < right 的原因,防止只能将数组分成两个部分
// 例如:[1,-1,1,-1],使用left < right作为判断条件就会出错
while(left + 1 < right){
if(leftSum == sum/3 && rightSum == sum/3){
// 左右两边都等于 sum/3 ,中间也一定等于
return true;
}
if(leftSum != sum/3){
// left = 0赋予了初值,应该先left++,在leftSum += A[left];
leftSum += A[++left];
}
if(rightSum != sum/3){
// right = A.length - 1 赋予了初值,应该先right--,在rightSum += A[right];
rightSum += A[--right];
}
}
return false;
}
}
----------------8.19--------
1385.两个数组间的距离值




class Solution {
public int findTheDistanceValue(int[] arr1, int[] arr2, int d) {
int count =0;
for(int i=0;i<arr1.length;i++){
boolean flag = true;
for(int j =0;j<arr2.length;j++){
int value= Math.abs(arr1[i]-arr2[j]);
if(value<=d){
flag = false;
break;
}
}
if(flag){
count++;
}
}
return count;
}
}

1534、统计好三元组


class Solution {
public int countGoodTriplets(int[] arr, int a, int b, int c) {
int n = arr.length, cnt = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j) {
for (int k = j + 1; k < n; ++k) {
if (Math.abs(arr[i] - arr[j]) <= a && Math.abs(arr[j] - arr[k]) <= b && Math.abs(arr[i] - arr[k]) <= c) {
++cnt;
}
}
}
}
return cnt;
}
}
---------------8.20-------------
1299、将每个元素替换为右侧最大元素

class Solution {
public int[] replaceElements(int[] arr) {
if (arr.length == 0) return arr;
int length = arr.length;
int max = arr[length - 1];
arr[--length] = -1;
while (length > 0) {
int cur = arr[length - 1];
arr[--length] = max;
max = Math.max(max, cur);
}
return arr;
}
}
985、查询后的偶数和(没懂)



class Solution {
public int[] sumEvenAfterQueries(int[] A, int[][] queries) {
int S = 0;
for (int x: A)
if (x % 2 == 0)
S += x;
int[] ans = new int[queries.length];
for (int i = 0; i < queries.length; ++i) {
int val = queries[i][0], index = queries[i][1];
if (A[index] % 2 == 0) S -= A[index];
A[index] += val;
if (A[index] % 2 == 0) S += A[index];
ans[i] = S;
}
return ans;
}
}
1089、复写零(没懂)
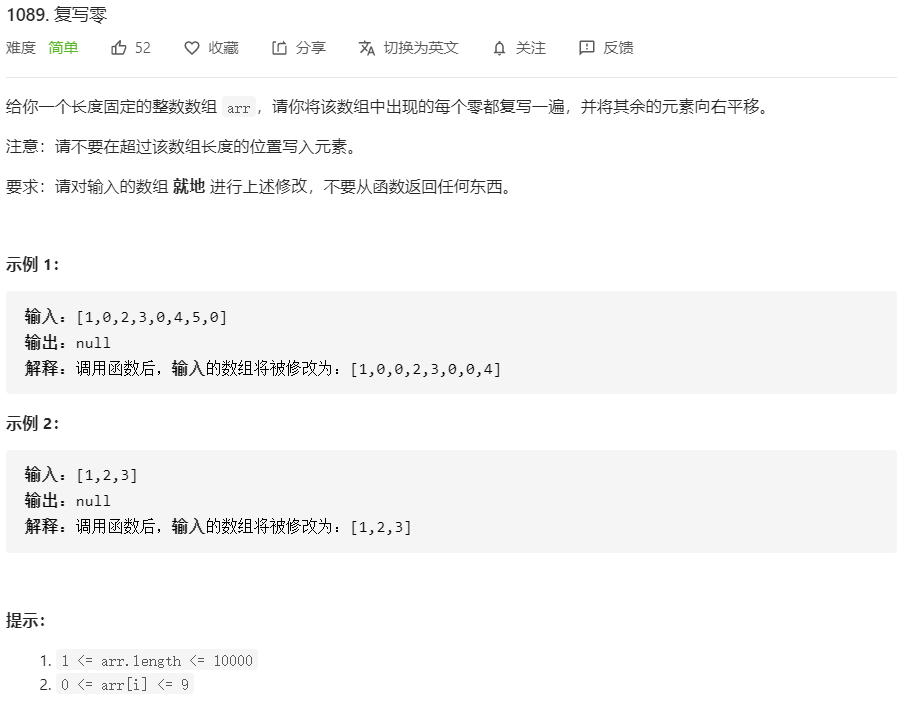
void duplicateZeros(int* arr, int arrSize){
int i;
int j;
for(i = 0; i < arrSize; i++) {
if(arr[i] == 0) {
for(j = arrSize - 1; j > i; j--) {
arr[j] = arr[j - 1];
}
//不懂i++作用
i++;
}
}
}
1304、和为零的N个唯一整数
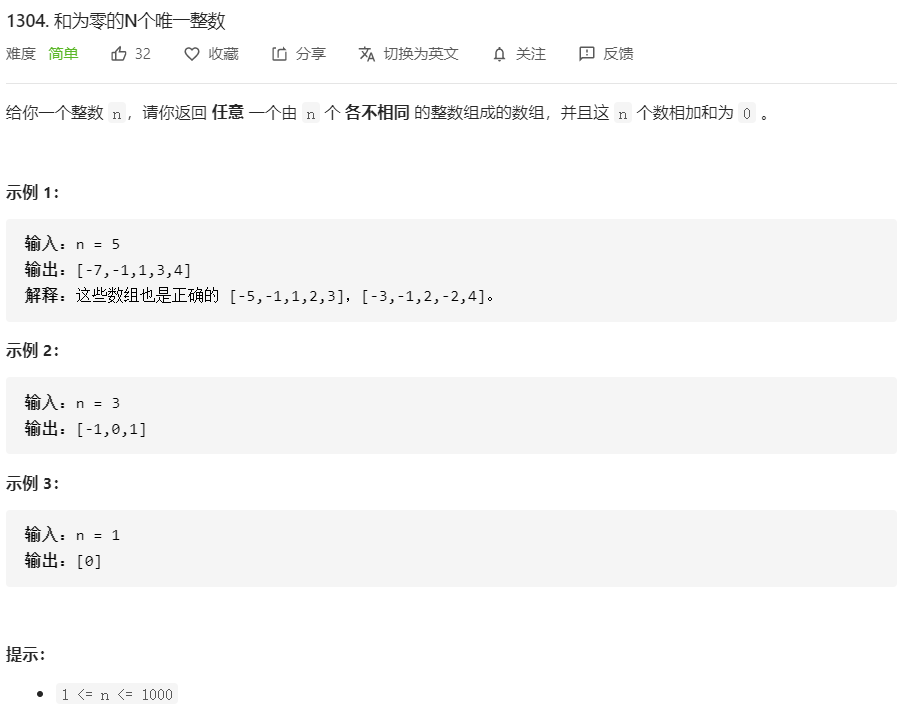
class Solution {
public int[] sumZero(int n) {
int[] arr = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n / 2; i++) {
arr[i] = i + 1;
arr[n - i - 1] = -arr[i];
}
return arr;
}
}
1331.数组序号转换
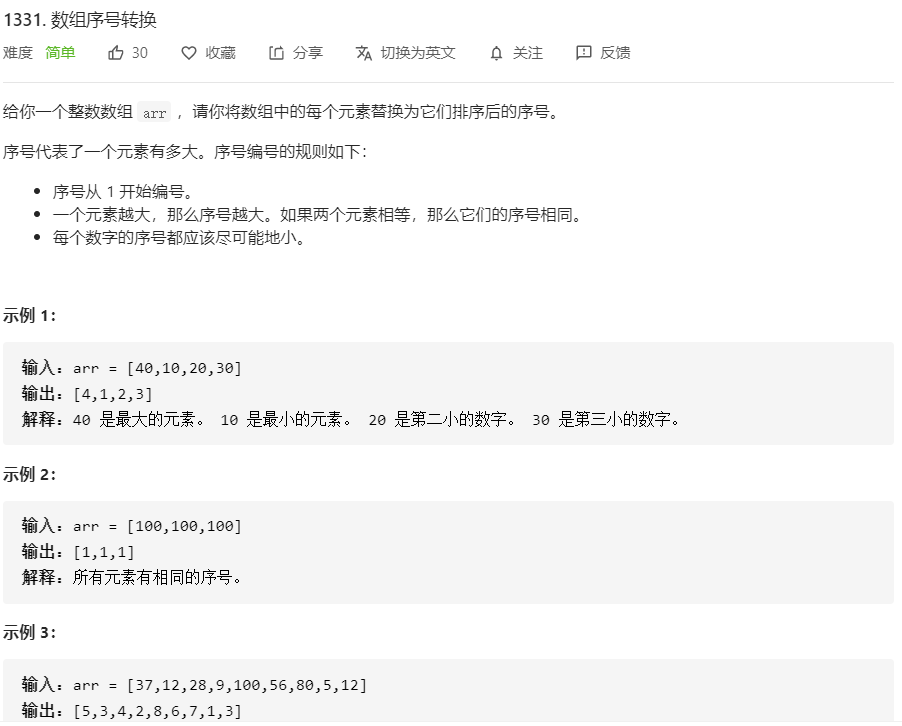

1356、有多少小于当前数字的数字

class Solution {
public int[] smallerNumbersThanCurrent(int[] nums) {
int[] s1 = new int [nums.length]; //用来存放统计个数
int ans =0; //计数
int t=0;
for(int i = 0 ; i < nums.length ; i++){
ans =0 ; // 每次循环都要 归0
for(int j = 0 ; j < nums.length ;j++){
if(nums[j] < nums[i] && j != i){
ans++;
}
}
s1[t++] = ans; //t++ 用于每一位的统计的数位置
}
//System.out.println(Arrays.toString(s1));
return s1;
}
}
1331、数组序号转换(没看)
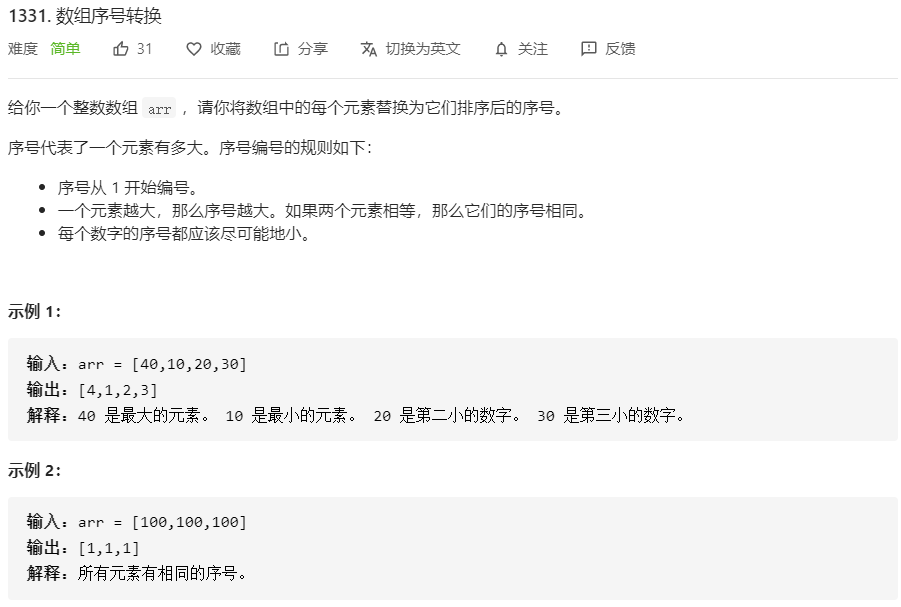

class Solution {
public int[] arrayRankTransform(int[] arr) {
int min = Integer.MAX_VALUE, max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
//找最大最小值
for(int num : arr){
if(num < min) min = num;
if(num > max) max = num;
}
//最多存在 max-min+1 个不同元素
int[] count = new int[max-min+1];
//初次遍历,找到存在的元素
for(int num : arr) count[num-min] = 1;
//二次遍历,对存在的元素进行排序
for(int i = 1; i < count.length; i++){
count[i] = count[i-1] + count[i];
}
int[] res = new int[arr.length];
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
//count数组存放着对应的排序后索引
res[i] = count[arr[i]-min];
}
return res;
}
}
-------------------8.21--------------
830、较大分组的位置


小贴士:代入数据运行
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> largeGroupPositions(String S) {
List<List<Integer>> ans = new ArrayList();
// i is the start of each group
int i = 0, N = S.length();
for (int j = 0; j < N; ++j) {
if (j == N-1 || S.charAt(j) != S.charAt(j+1)) {
// Here, [i, j] represents a group.
if (j-i+1 >= 3)
ans.add(Arrays.asList(new Integer[]{i, j}));
i = j + 1;
}
}
return ans;
}
}
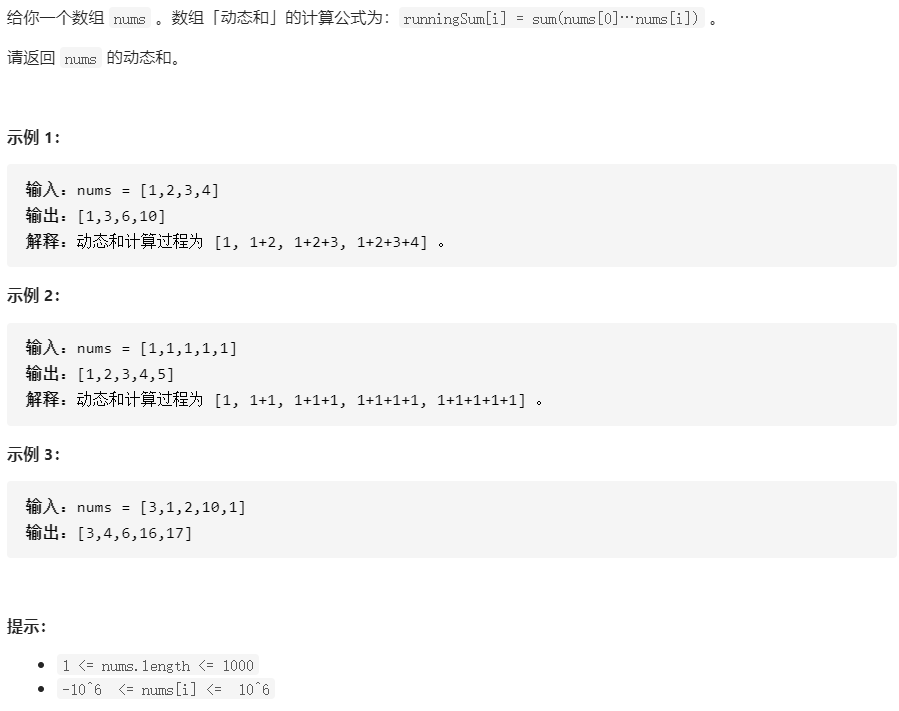
1480、一维数组的动态和
class Solution {
public int[] runningSum(int[] nums) {
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; ++i){
nums[i] += nums[i - 1];
}
return nums;
}
}
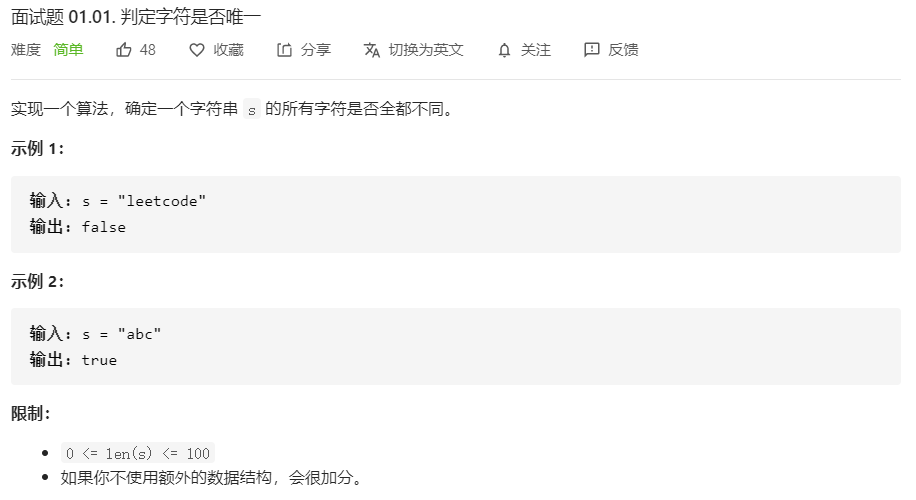
面试题 01.01.判定字符是否唯一
解题思路:
利用indexOf() 与lastIndexOf() 判断是否处于相同位置来判断是否只有一个字符
class Solution {
public boolean isUnique(String astr) {
if (astr.length() == 1 || astr.length() == 0) {
return true;
}
boolean flag = true;
for (int i = 0, len = astr.length(); i < len -1; i++){
if (astr.indexOf(astr.charAt(i)) != astr.lastIndexOf(astr.charAt(i))){
flag =false;
}
}
return flag;
}
}
相关知识:
indexOf
- public int indexOf(int ch):
返回指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回
-1。 - public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):
返回从 fromIndex
位置开始查找指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 - int indexOf(String str):
返回指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 - int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex):
返回从 fromIndex
位置开始查找指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。
lastIndexOf() 方法有以下四种形式:
- public int lastIndexOf(int ch):
返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 - public int lastIndexOf(int ch, int fromIndex):
返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引处开始进行反向搜索,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 - public int lastIndexOf(String str):
返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最右边出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 - public int lastIndexOf(String str, int fromIndex):
返回指定子字符串在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引,从指定的索引开始反向搜索,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。
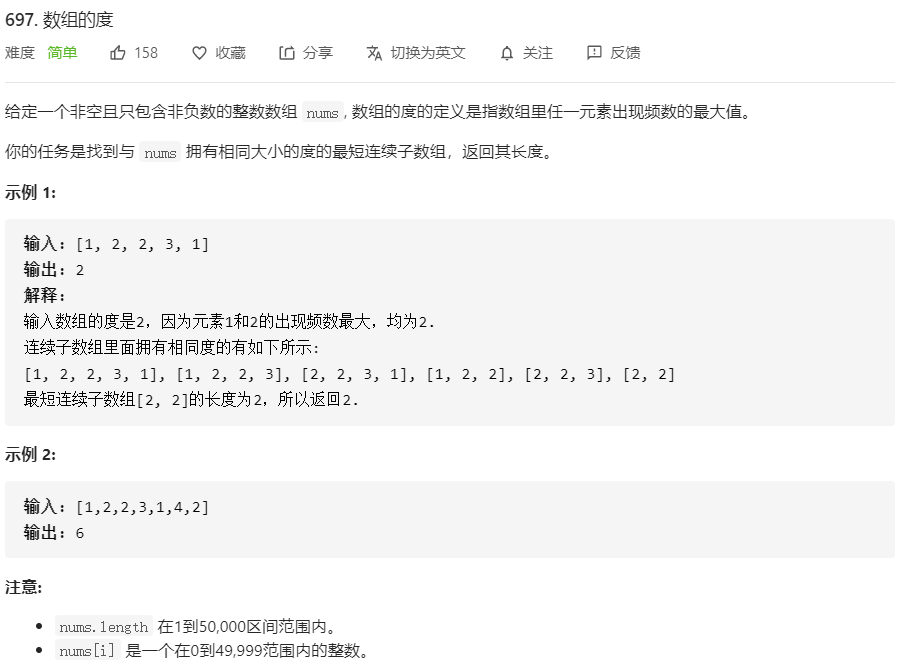
697、数组的度

小贴士:算法很好理解,代码好好看
class Solution {
public int findShortestSubArray(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> left = new HashMap(),
right = new HashMap(), count = new HashMap();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
int x = nums[i];
if (left.get(x) == null) left.put(x, i);
right.put(x, i);
count.put(x, count.getOrDefault(x, 0) + 1);
}
int ans = nums.length;
int degree = Collections.max(count.values());
for (int x: count.keySet()) {
if (count.get(x) == degree) {
ans = Math.min(ans, right.get(x) - left.get(x) + 1);
}
}
return ans;
}
}
面试题01.02.判定是否互为字符重排


tip:完全明白
class Solution {
public boolean CheckPermutation(String s1, String s2) {
if(s1.length()!=s2.length()) return false;
int[] nums = new int[26];
int len = s1.length();
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
nums[s1.charAt(i)-97]++;
nums[s2.charAt(i)-97]--;
}
for (int num : nums) {
if (num != 0) return false;
}
return true;
}
}
1475、商品折扣后的最终价格


解题思路
定义result数组
遍历数组
定义j = i + 1
如果prices[j] <= prices[i]
result[i] = prices[i] - prices[j],跳出while循环
否则result[i] = prices[i]
因为无法最后一位在循环中
最后result[prices.length - 1] = prices[prices.length - 1]
tip:代入数据运行
class Solution {
public int[] finalPrices(int[] prices) {
int[] result = new int[prices.length];
int j = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < prices.length; i++)
{
j = i + 1;
while (j < prices.length)
{
if (prices[j] <= prices[i])
{
result[i] = prices[i] - prices[j];
break;
}
else
{
result[i] = prices[i];
}
j++;
}
}
//检查最后一位
result[prices.length - 1] = prices[prices.length - 1];
return result;
}
}
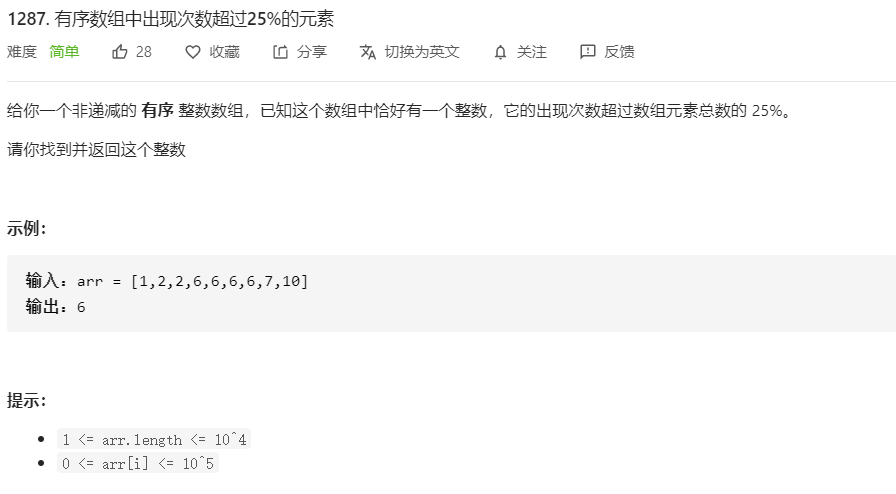
1287、有序数组中出现次数超过25%的元素
方法1:解题思路
求出 25% 对应的出现次数threshold
遍历数组
由于是有序数组,只需比较 当前位置 i 值和 i + threshold的值是否相等即可
class Solution {
public int findSpecialInteger(int[] arr) {
int threshold = arr.length / 4;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (arr[i + threshold] == arr[i]) {
return arr[i];
}
}
return 0;
}
}
方法2:用hashmap(不懂)
class Solution {
public int findSpecialInteger(int[] arr) {
Map<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap();
for(int i : arr){//先把数组中的数据存放在map中,key为元素值,value为出现的次数
map.put(i, map.getOrDefault(i, 0) + 1);
}
for(int key : map.keySet()){
Integer value = map.get(key);
if(value > arr.length / 4){//如果有满足的及时输出
return key;
}
}
return -1;
}
}
1450、在既定时间做作业的学生人数


int busyStudent(int* startTime, int startTimeSize, int* endTime, int endTimeSize, int queryTime){
int i, cnt = 0;
for(i=0;i<startTimeSize;i++)
cnt += queryTime >= startTime[i] && queryTime <= endTime[i];
return cnt;
}
1550.存在连续三个奇数的数组
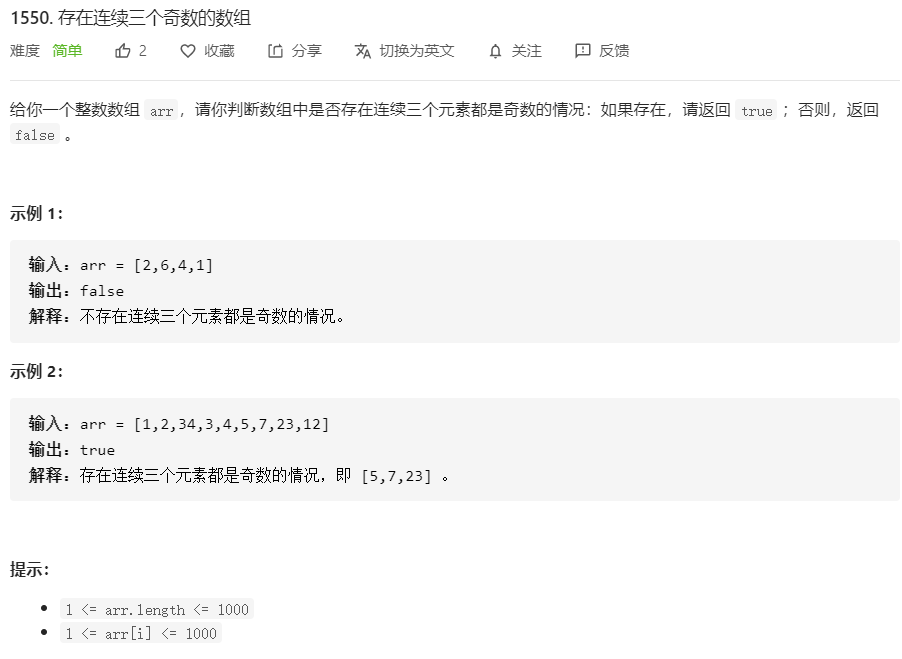
方法一:枚举
思路与算法
枚举所有的连续的三个元素,判断这三个元素是否都是奇数,如果是,则返回 true。如果所有的连续的三个元素中,没有一个满足条件,返回 false。
class Solution {
public boolean threeConsecutiveOdds(int[] arr) {
int n = arr.length;
for (int i = 0; i <= n - 3; ++i) {
//连续三个数都是奇数
if ((arr[i] & 1) != 0 && (arr[i + 1] & 1) != 0 && (arr[i + 2] & 1) != 0) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
面试题17.04.消失的数字(异或)
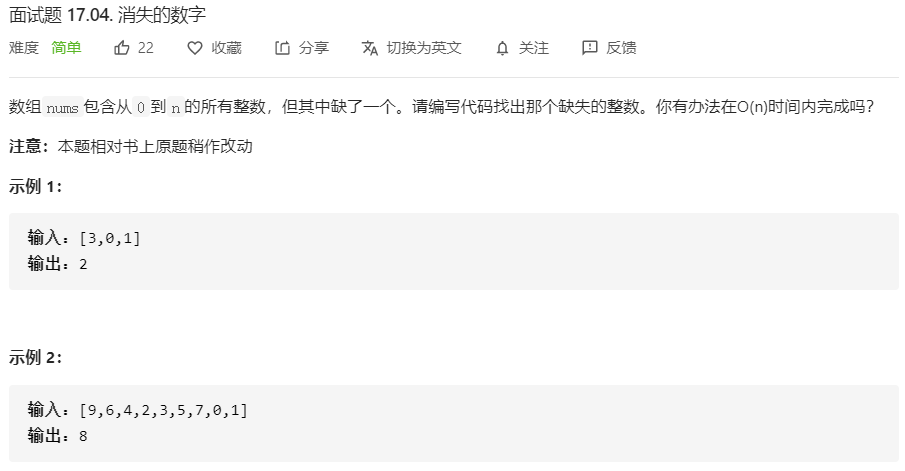
解题思路:
利用异或的特性,res = res ^ x ^ x。对同一个值异或两次,那么结果等于它本身,所以我们对res从0-nums.length进行异或,同时对nums数组中的值进行异或,出现重复的会消失,所以最后res的值是只出现一次的数字,也就是nums数组中缺失的那个数字。
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
res ^= i;
res ^= nums[i];
}
res ^= nums.length;
return res;
}
}
1512.好数对的数目



tip:两行代码理解
class Solution {
public int numIdenticalPairs(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> m = new HashMap<Integer, Integer>();
for (int num : nums) {
m.put(num, m.getOrDefault(num, 0) + 1);
}
int ans = 0;
for (Map.Entry<Integer, Integer> entry : m.entrySet()) {
int v = entry.getValue();
ans += v * (v - 1) / 2;
}
return ans;
}
}
一次循环,哈希表
解题思路
// 依据题意限定
// 1 <= nums.length <= 100
// 1 <= nums[i] <= 100
于是
1、可以利用hash table记录不同数字出现的个数;
2、当某个数字的个数出现的次数大于等于2就存在好数对;当重复的次数是n,那么好数对就增加 n(n-1)/2;
3、遍历统计好的hash table就可以得到答案;
// 依据题意限定
// 1 <= nums.length <= 100
// 1 <= nums[i] <= 100
#define HASH_SIZE 101
int fun(int n)
{
return n * (n - 1) / 2;
}
int numIdenticalPairs(int* nums, int numsSize)
{
int cnt = 0;
int numsSize1 = numsSize;
int* hashT = (int*)calloc(HASH_SIZE, sizeof(int));
for (int i = 0; i < numsSize; ++i) {
hashT[nums[i]]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < HASH_SIZE; ++i) {
if (numsSize1 < 2) { // 这个剪枝就使得提交执行双100%
break;
}
if (hashT[i] > 1) {
numsSize1 -= hashT[i];
cnt += fun(hashT[i]);
}
}
return cnt;
}
1539.第K个缺失的正整数
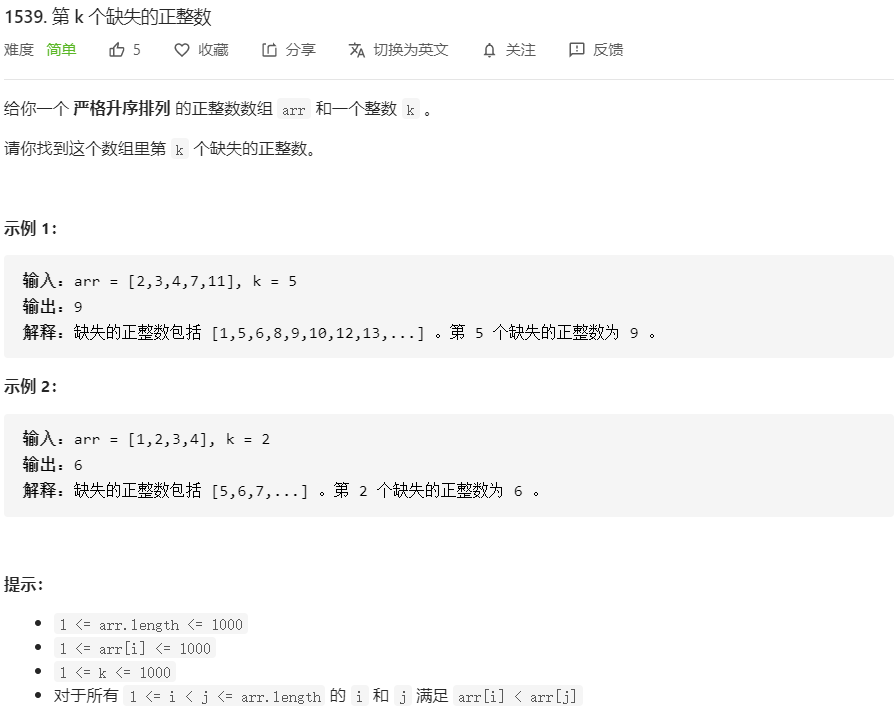

class Solution {
public int findKthPositive(int[] arr, int k) {
int len=arr.length;
for(int i=0; i<len; i++){
if(arr[i]-i-1>=k){
return k+i;
}
}
return k+len;
}
}
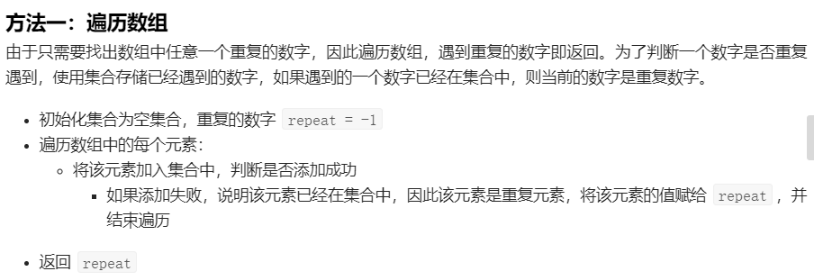
剑指Offer 03.数组中重复的数字
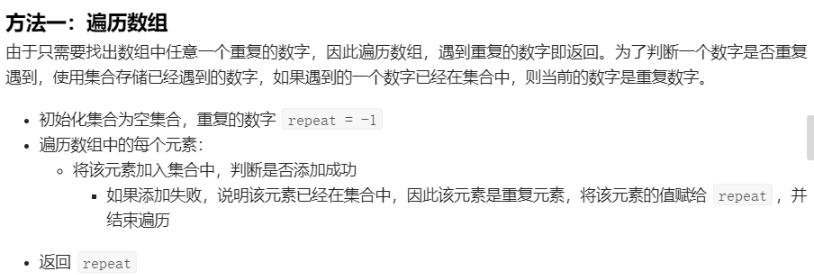
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<Integer>();
int repeat = -1;
for (int num : nums) {
if (!set.add(num)) {
repeat = num;
break;
}
}
return repeat;
}
}
面试题 10.01.合并排序的数组
方法1:直接合并后排序
算法:最直观的方法是先将数组B放进数组A的尾部,然后直接对整个数组进行排序
class Solution {
public void merge(int[] A, int m, int[] B, int n) {
for(int i=0; i!=n; i++){
A[m+i] = B[i];
}
Arrays.sort(A);
}
}
剑指Offer 53-I.在排序数组中查找数字I
class Solution {
public int search(int[] nums, int target) {
// 搜索右边界 right
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] <= target) i = m + 1;
else j = m - 1;
}
int right = i;
// 若数组中无 target ,则提前返回
if(j >= 0 && nums[j] != target) return 0;
// 搜索左边界 right
i = 0; j = nums.length - 1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] < target) i = m + 1;
else j = m - 1;
}
int left = j;
return right - left - 1;
}
}
----------------8.22------------
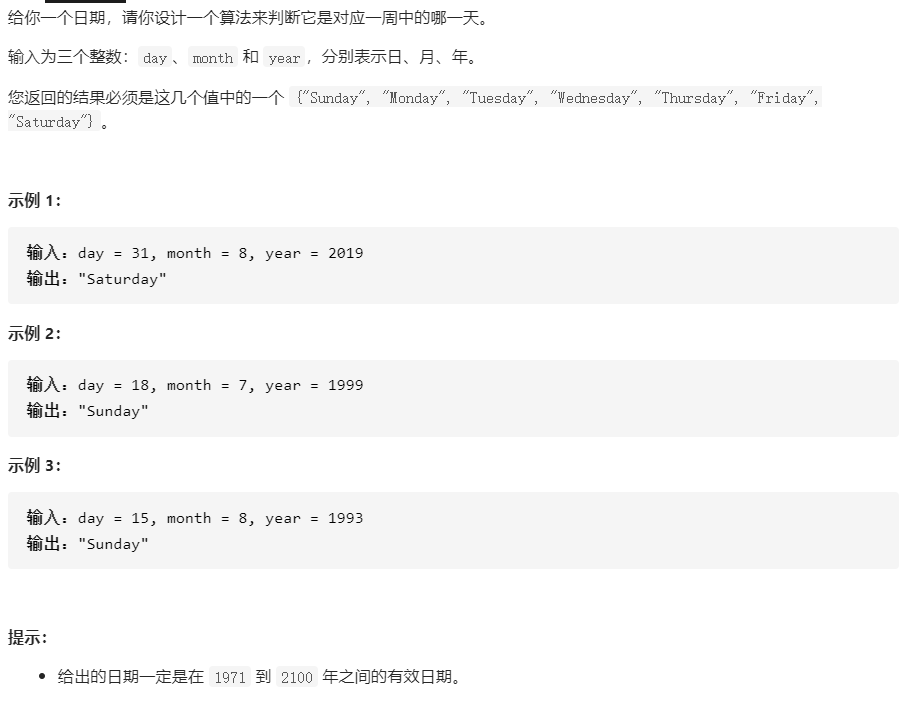
1185.一周中的第几天
class Solution {
public String dayOfTheWeek(int day, int month, int year) {
String[] weekStr = new String[]{"Sunday", "Monday", "Tuesday", "Wednesday", "Thursday", "Friday", "Saturday"};
int sum = 4;
//加年份
if (year > 1971)
for (int i = 1971; i < year; i++) {
sum += 365;
//闰年
if (i % 4 == 0 && i % 100 != 0 || i % 400 == 0) sum++;
}
//月份数组将每个月换算成对应的天数
int[] months = new int[]{31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
//加月份
for (int i = 0; i < month - 1; i++) sum += months[i];
//输入的月份至少是三月份且是闰年的时候
if (month >= 3 && (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0 || year % 400 == 0)) sum++;
//加天数
sum += day;
return weekStr[sum % 7];
}
}
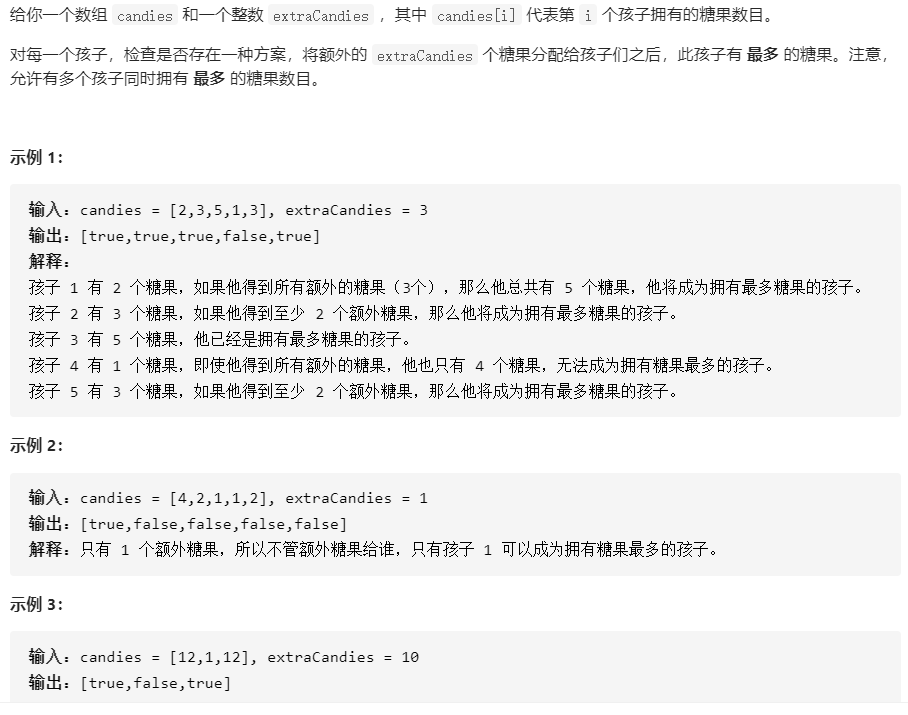
1431、拥有最多糖果的孩子

class Solution {
public List<Boolean> kidsWithCandies(int[] candies, int extraCandies) {
int n = candies.length;
//找出最多糖果数
int maxCandies = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
maxCandies = Math.max(maxCandies, candies[i]);
}
List<Boolean> ret = new ArrayList<Boolean>();
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ret.add(candies[i] + extraCandies >= maxCandies);
}
return ret;
}
}
1464、数组中两元素的最大乘积

解题思路
1、使用两个变量,一个存放最大值(默认为nums[0]),一个存放次大值(默认为0)
2、从下标为1处开始遍历nums数组,一次进行最大值和次大值的赋值。
3、注意处理下特殊情况:最大值和次大值的数值相同
class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length==2) return (nums[nums.length-1]-1)*(nums[nums.length-2]-1);
//最大值
int one = nums[0];
//次最大值
int two = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
//求最大值
if(nums[i]>one){
two = one;
one = nums[i];
}else if(nums[i] <= one){ //求次最大值
if(nums[i] >= two){
two = nums[i];
}
}
}
return (one-1)*(two-1);
}
}
1486、数组异或操作



class Solution {
public int xorOperation(int n, int start) {
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i) {
ans ^= (start + i * 2);
}
return ans;
}
}
1170、比较字符串最小字母出现频次(看不下去)

class Solution {
public int[] numSmallerByFrequency(String[] queries, String[] words) {
//count用于统计words中所有单词的最小字母出现次数,
//大小设置为12是为了避免下面进行判定的时候出现越界而做的冗余处理
int[] count = new int[12];
for (String word:words)
count[counts(word)]++;
//计算后缀和,现在count[i]表示最小字母出现次数大于或等于i的单词总数。
for (int i=9;i>=0;i--)
count[i]+=count[i+1];
//结果数组
int[] result = new int[queries.length];
//遍历queries中的每个字符串,利用前面计算得到的count数组,可以直接得到答案。
for (int i=0;i<queries.length;i++)
result[i]=count[counts(queries[i])+1];
return result;
}
//counts方法用于统计字符串s中最小字母出现的次数
private int counts(String s){
char c = s.charAt(0);
int count = 1;
for (int i=1;i<s.length();i++){
char temp = s.charAt(i);
if (temp==c)
count++;
else if (temp<c){
c=temp;
count=1;
}
}
return count;
}
}
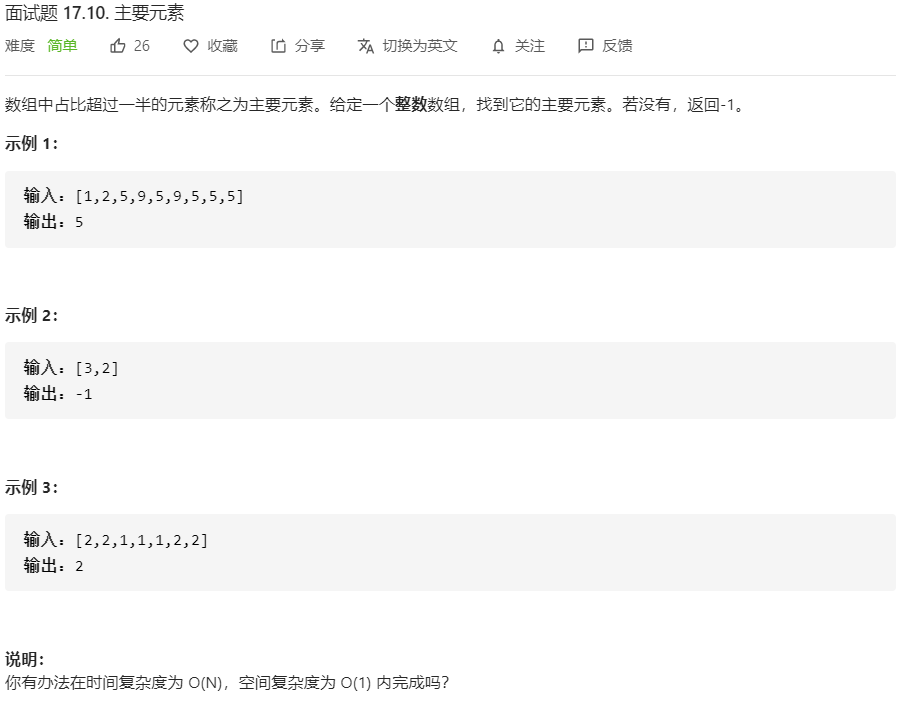
面试题 17.10.主要元素
仔细看题, 这题和多数元素那题不一样.
类似[2,7,3,5,5]这种, 直接按照投票算法, 结果是5, 但其实结果应该是并不存在.
最后加一个结果遍历验证就可以
tip:还需多看一些评论区
class Solution {
public int majorityElement(int[] nums) {
// 投票算法
int temp = nums[0];
int count = 1;
for (int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++) {
if (nums[i] == temp) {
count++;
} else {
count--;
}
if (count == 0) {
temp = nums[i];
count = 1;
}
}
// 验证是否满足要求
int t = nums.length / 2 + 1;
count = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
if (num == temp) count++;
if (count == t) return temp;
}
return -1;
}
}
面试题 16.17.连续数列

解题思路
每一个数据都有两个选择,与前面相连或者自己另立门户!
所以状态转移方程就是这个 dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i],nums[i]);
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int len = nums.length;
if(len == 0) return 0;
if(len == 1) return nums[0];
int [] dp = new int[len];
int max = nums[0];
dp[0] = nums[0];
for(int i = 1;i < len;i ++){
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i - 1] + nums[i],nums[i]);
max = Math.max(max , dp[i]);
}
return max;
}
}
1460、通过翻转子数组使两个数组相等


class Solution {
public boolean canBeEqual(int[] target, int[] arr) {
//排序
Arrays.sort(target);
Arrays.sort(arr);
//对每一位进行比较
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
if (target[i]!=arr[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
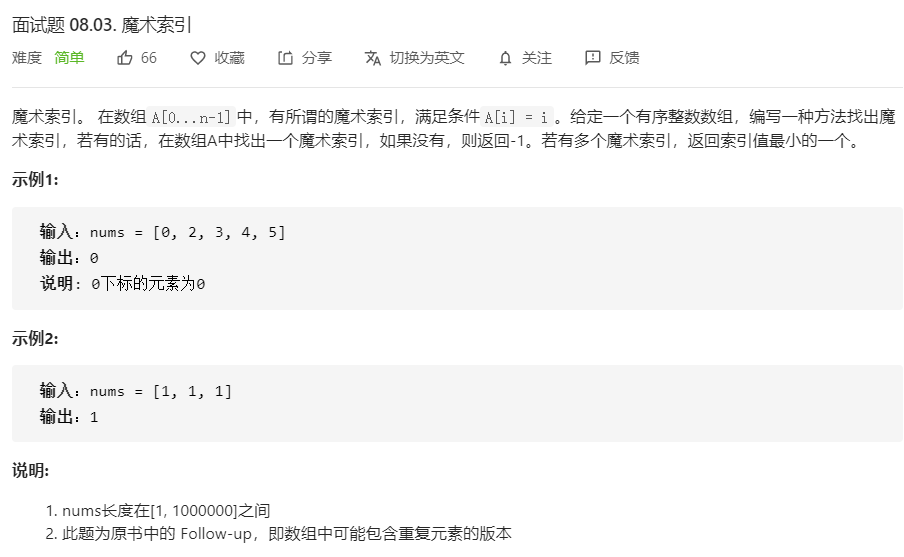
面试题 08.03.魔术索引
方法一:二分剪枝
思路与算法
此问题如果用暴力的方法来解决,我们只需要对原数组从前往后进行一次遍历,找到第一个可行的位置返回即可,这里不再赘述。而本方法会进行一定程度的剪枝,在一些情况下会达到较优的时间复杂度,在最差情况下仍会退化成线性的时间复杂度,这里我们分两种情况讨论。
第一种情况是数组中只有一个满足条件的答案。我们假设这个答案为 ii,那么意味着 [0 ldots i-1][0…i−1] 的值均小于自身的下标,[i+1 ldots n-1][i+1…n−1] 的值均大于自身的下标。我们将整个数组每个元素减去其自身所在的下标,那么最后的答案即为 00 所在的下标,且在 00 之前的元素均为负数,00 之后的元素均为正数。以 [-1,0,2,4,5][−1,0,2,4,5] 为例,减去自身下标以后以后得到 [-1,-1,0,1,1][−1,−1,0,1,1],整个数组以 00 为分界点,前半部分均为负数,后半部分均为负数,因此我们可以使用二分查找在 O(log n)O(logn) 的时间内找到答案 00 所在的下标,具体做法就是碰到负数舍弃左半边,碰到正数舍弃右半边即可。
第二种情况是数组中存在多个满足条件的答案,此时我们发现整个数组不具有任何性质。以 [0,0,2,2,5][0,0,2,2,5] 为例,我们仍进行一次将每个元素减去其自身下标的操作,得到 [0,-1,0,-1,1][0,−1,0,−1,1]。目标是要找到第一个出现的 00,而由于数组中出现 00 的位置不确定,因此无法使用二分查找,但是我们可以依据此来进行一定程度的剪枝,我们剪枝的策略为:
每次我们选择数组的中间元素,如果当前中间元素是满足条件的答案,那么这个位置往后的元素我们都不再考虑,只要寻找左半部分是否有满足条件的答案即可。
否则我们需要查看左半部分是否有满足条件的答案,如果没有的话我们仍然需要在右半边寻找,使用的策略同上。
我们可以依靠此策略定义一个递归函数:getAnswer(nums, left, right) 返回数组 textit{nums}nums 的下标范围 [textit{left},textit{right}][left,right] 中第一个满足条件的答案,如果没有返回 -1−1。每次选择中间的位置 textit{mid}mid,此时直接先递归调用数组左半部分 getAnswer(nums, left, mid - 1) 得到返回值 textit{leftAnswer}leftAnswer,如果存在则直接返回,如果不存在则比较 textit{nums}[textit{mid}]nums[mid] 和 textit{mid}mid 是否相等,如果相等则返回 textit{mid}mid,否则需要递归调用 getAnswer(nums, mid + 1, right)。
显然,此剪枝策略在 [-1,0,1,2,4][−1,0,1,2,4] 这种答案为数组的最后一个元素的情况下会退化成线性的时间复杂度,但是在一些情况下会有不错的表现。
tip:代入数字进去运行
class Solution {
public int findMagicIndex(int[] nums) { //主
return getAnswer(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public int getAnswer(int[] nums, int left, int right) {
if (left > right) {
return -1;
}
int mid = (right - left) / 2 + left;
int leftAnswer = getAnswer(nums, left, mid - 1);
if (leftAnswer != -1) {
return leftAnswer;
} else if (nums[mid] == mid) {
return mid;
}
return getAnswer(nums, mid + 1, right);
}
}
1295、统计位数为偶数的数字
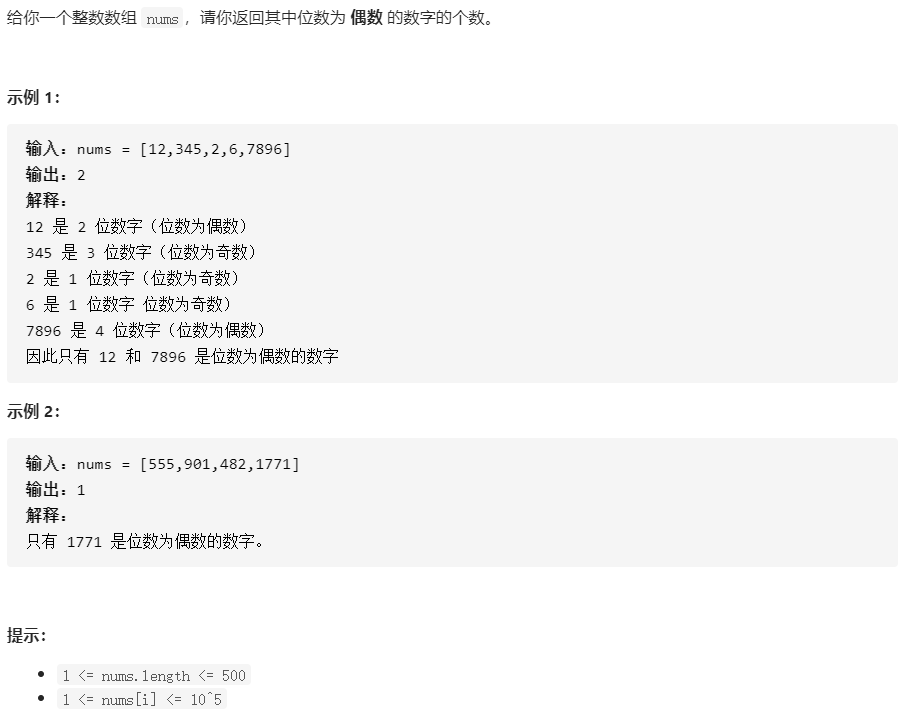
方法一:枚举 + 字符串
我们枚举数组 nums 中的整数,并依次判断每个整数 x 是否包含偶数个数字。
一种简单的方法是使用语言内置的整数转字符串函数,将 x 转换为字符串后,判断其长度是否为偶数即可。
class Solution {
public:
int findNumbers(vector<int>& nums) {
int ans = 0;
for (int num: nums) {
if (to_string(num).size() % 2 == 0) {
++ans;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
1413.逐步求和得到正数的最小值
学习此题的算法思想
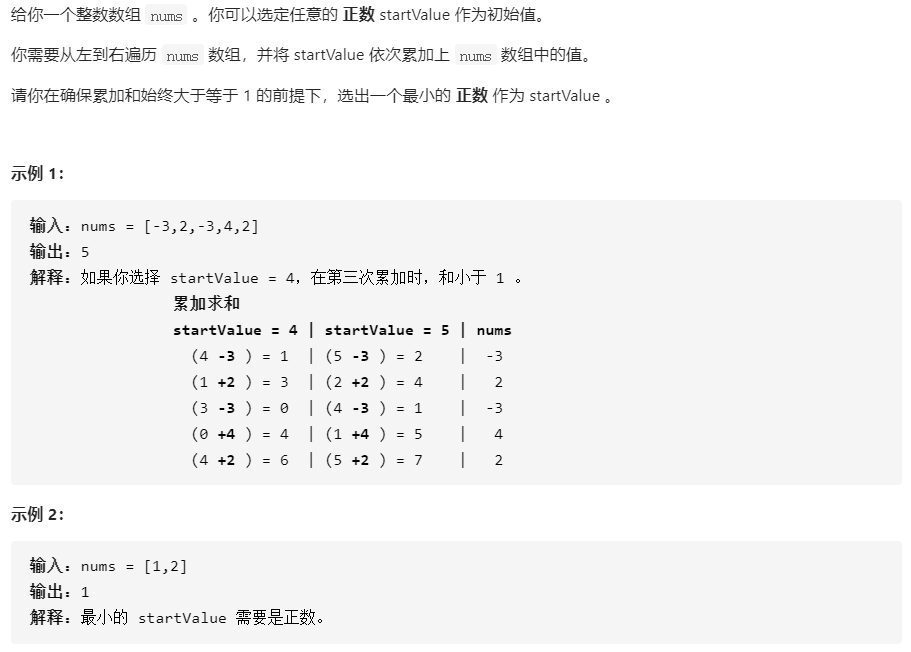

思路:
将数组中的值依次相加,寻找到和为最小值时的最小值,用1减去最小值即为答案
class Solution {
public int minStartValue(int[] nums) {
int min = 0;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
sum = sum + nums[i];
if (sum<min)
min = sum;
}
return 1-min;
}
}
----------------8.23----------------
1389、按既定顺序创建目标数组
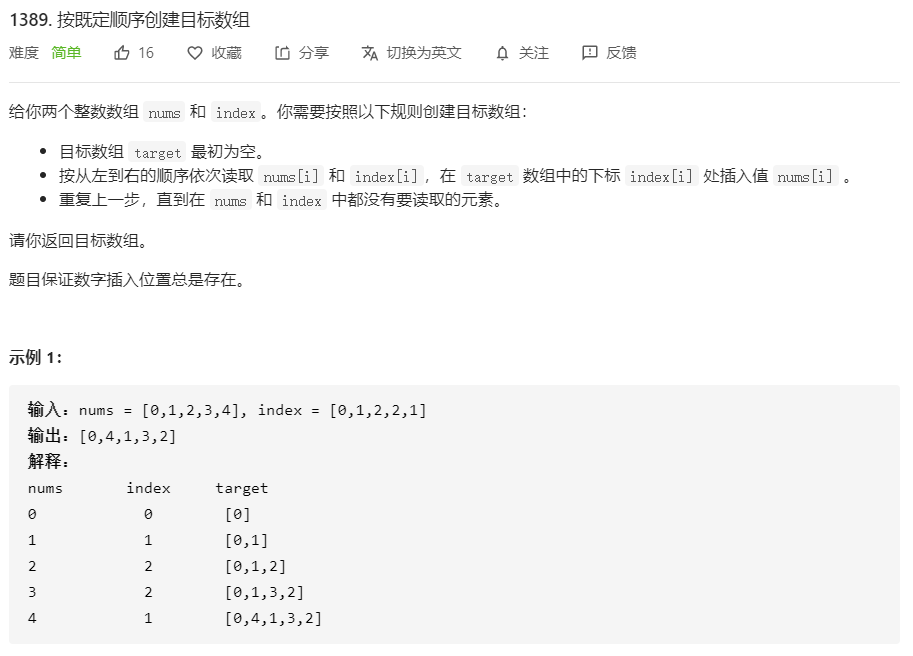

方法一:模拟
思路
使用顺序表作为答案的存储结构,按照题意模拟即可。具体的方法是:要在当前的下标从 00 开始长度为 nn 的顺序表的 ii 位置插入元素,就要先把原来表中区间 [i, n][i,n] 中的元素从全部向后移动一位,然后在 ii 位置插入带插入的元素。当然很多语言中都有现成的方法可以调用,比如 C++ vector 类中的 insert、Python 列表中的 insert 等。
tip:代入数据运行代码
/**
* Note: The returned array must be malloced, assume caller calls free().
*/
int* createTargetArray(int* nums, int numsSize, int* index, int indexSize, int* returnSize){
int* ret = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * indexSize);
int tail = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < indexSize; ++i) {
++tail;
//后面的全部往后移
for (int j = tail; j > index[i]; --j) {
ret[j] = ret[j - 1];
}
//插入值
ret[index[i]] = nums[i];
}
*returnSize = indexSize;
return ret;
}
747、至少是其他数字两倍的最大数

class Solution {
public int dominantIndex(int[] nums) {
//找最大元素
int maxIndex = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (nums[i] > nums[maxIndex])
maxIndex = i;
}
//判断是否至少是是数组中每个其他数字的两倍
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
if (maxIndex != i && nums[maxIndex] < 2 * nums[i])
return -1;
}
return maxIndex;
}
}
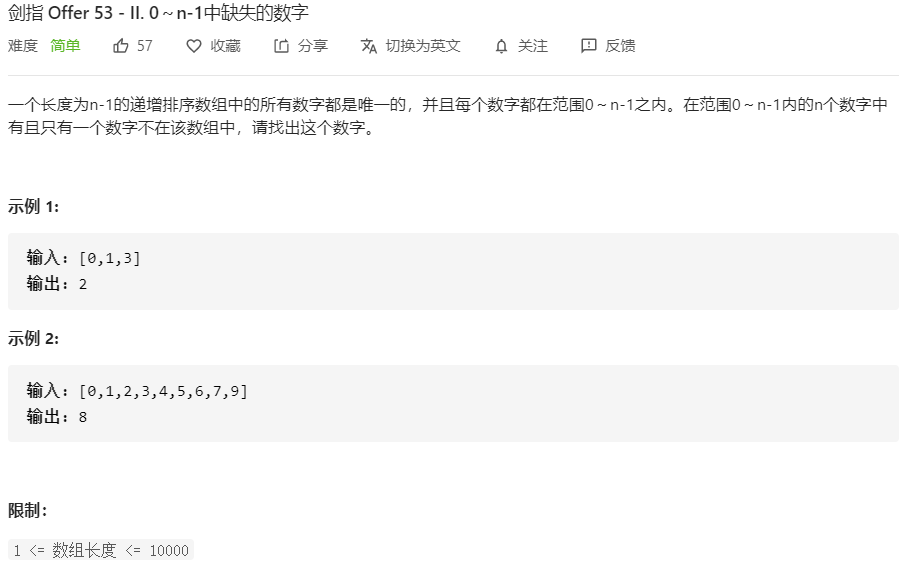
剑指 Offer 53-II.0~n-1中缺失的数字
class Solution {
public int missingNumber(int[] nums) {
int i = 0, j = nums.length - 1;
while(i <= j) {
int m = (i + j) / 2;
if(nums[m] == m) i = m + 1;
else j = m - 1;
}
return i;
}
}
888.公平的糖果交换


class Solution {
public int[] fairCandySwap(int[] A, int[] B) {
int sa = 0, sb = 0; // sum of A, B respectively
for (int x: A) sa += x;
for (int x: B) sb += x;
int delta = (sb - sa) / 2;
// If Alice gives x, she expects to receive x + delta
Set<Integer> setB = new HashSet();
for (int x: B) setB.add(x);
for (int x: A)
if (setB.contains(x + delta))
return new int[]{x, x + delta};
throw null;
}
}
1346.检查整数及其两倍数是否存在



class Solution {
public:
bool checkIfExist(vector<int>& arr) {
sort(arr.begin(), arr.end());
for (auto i = arr.begin(), j = arr.begin(); i != arr.end(); ++i) {
while (j != arr.end() && *i * 2 > *j)
++j;
if (j != arr.end() && i != j && *i * 2 == *j)
return true;
}
for (auto i = arr.rbegin(), j = arr.rbegin(); i != arr.rend(); ++i) {
while (j != arr.rend() && *i * 2 < *j)
++j;
if (j != arr.rend() && i != j && *i * 2 == *j)
return true;
}
return false;
}
};
1160、拼写单词

class Solution {
public int countCharacters(String[] words, String chars) {
//一个哈希表存储chars中每个字母的数量
Map<Character,Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
for(char c:chars.toCharArray()){
map.put(c,map.getOrDefault(c,0)+1);
}
int length = 0;
//另一个哈希表存储word中的字母拼写出的word
Map<Character,Integer> tmpMap;
for(String word:words){
boolean flag = true;
tmpMap = new HashMap<>();
for(char c:word.toCharArray()){
int count =tmpMap.getOrDefault(c,0)+1;
if(count>map.getOrDefault(c,0)){
flag = false;
break;
}
tmpMap.put(c,count);
}
if(flag){
length +=word.length();
}
}
return length;
}
}
----------------8.24--------------
532、数组中的K-diff数对


class Solution {
public int findPairs(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums.length < 2) return 0;
Arrays.sort(nums);
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < nums.length - 1;i++){
/***这条判断语句很重要,小编也是改了好几遍才解决了这个判断条件
若为if(nums[i]==nums[i+1]) continue; 这样k=0时会出错
若为if(nums[i]==nums[i-1]) continue; 这样系统会判错 因为最开始的i=0,i-1=-1
**/
if(i >= 1 && nums[i] == nums[i -1]) continue;
for(int j = i + 1;j < nums.length;j++){
if(nums[j] - k > nums[i]){
break;
}
if(nums[j] - k == nums[i]){
count++;
break;
}
}
}
return count;
}
}
566、重塑矩阵


public class Solution {
public int[][] matrixReshape(int[][] nums, int r, int c) {
//存储新的矩阵
int[][] res = new int[r][c];
//不能形成所得矩阵时
if (nums.length == 0 || r * c != nums.length * nums[0].length)
return nums;
//用队列放置提取的元素
int count = 0;
Queue < Integer > queue = new LinkedList < > ();
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < nums[0].length; j++) {
queue.add(nums[i][j]);
}
}
//按行逐列排列得到的所需矩阵元素
for (int i = 0; i < r; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < c; j++) {
res[i][j] = queue.remove();
}
}
return res;
}
}
661/
class Solution {
public int[][] imageSmoother(int[][] M) {
int R = M.length, C = M[0].length;
int[][] ans = new int[R][C];
for (int r = 0; r < R; ++r)
for (int c = 0; c < C; ++c) {
int count = 0;
for (int nr = r-1; nr <= r+1; ++nr)
for (int nc = c-1; nc <= c+1; ++nc) {
if (0 <= nr && nr < R && 0 <= nc && nc < C) {
ans[r][c] += M[nr][nc];
count++;
}
}
ans[r][c] /= count;
}
return ans;
}
}
746、使用最小花费爬楼梯(没看)


class Solution {
public int minCostClimbingStairs(int[] cost) {
int f1 = 0, f2 = 0;
for (int i = cost.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
int f0 = cost[i] + Math.min(f1, f2);
f2 = f1;
f1 = f0;
}
return Math.min(f1, f2);
}
}
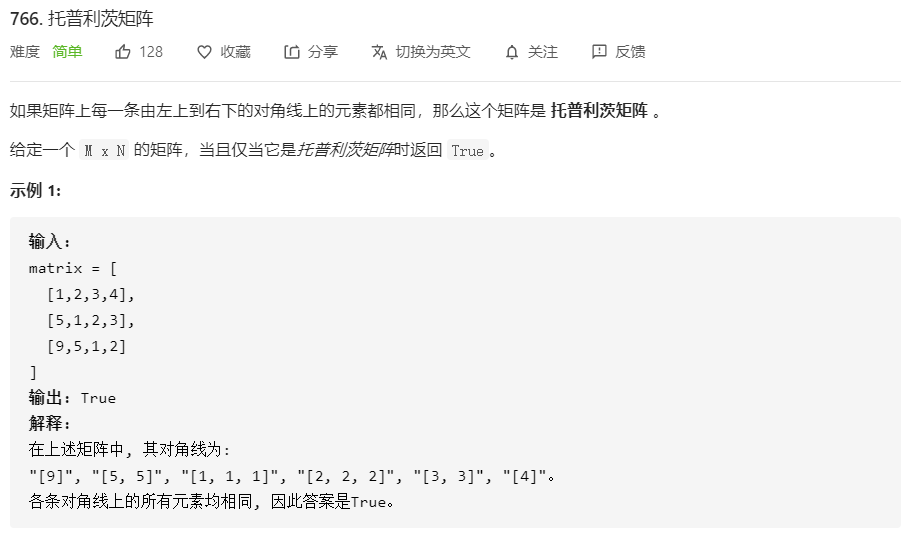
766。托普利茨矩阵


class Solution {
public boolean isToeplitzMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
Map<Integer, Integer> groups = new HashMap();
for (int r = 0; r < matrix.length; ++r) {
for (int c = 0; c < matrix[0].length; ++c) {
if (!groups.containsKey(r-c))
groups.put(r-c, matrix[r][c]);
else if (groups.get(r-c) != matrix[r][c])
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
}
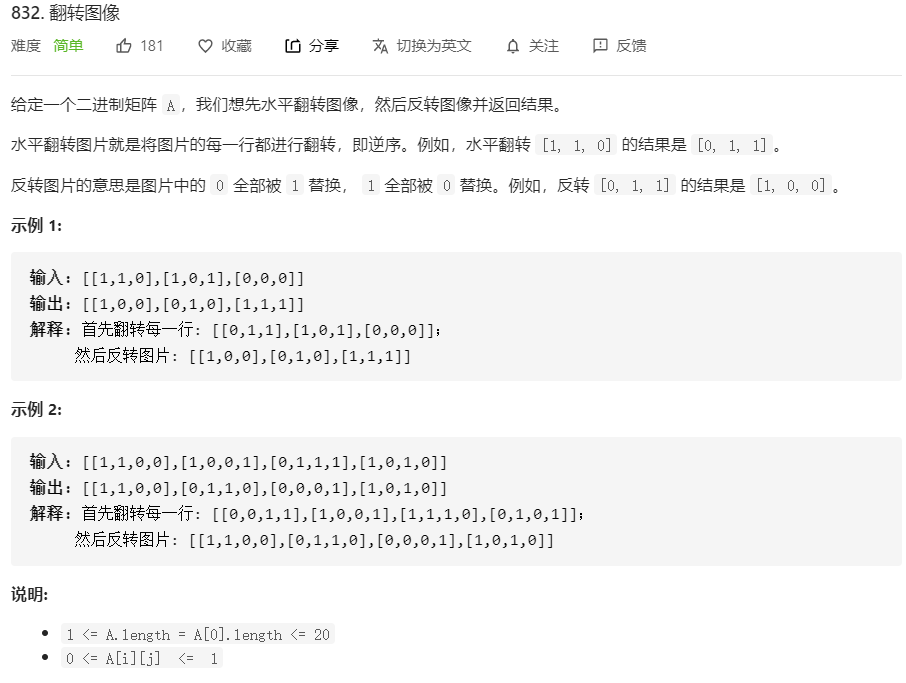
832、翻转图像
class Solution {
public int[][] flipAndInvertImage(int[][] A) {
int C = A[0].length;
for (int[] row: A)
for (int i = 0; i < (C + 1) / 2; ++i) {
int tmp = row[i] ^ 1;
row[i] = row[C - 1 - i] ^ 1;
row[C - 1 - i] = tmp;
}
return A;
}
}
最后
以上就是俊逸马里奥最近收集整理的关于LeetCode_数组_简单题26.删除排序数组中的重复项27.移除元素53.最大子序和66.加一88.合并两个有序数组118.杨辉三角形119.杨辉三角形II717.1比特与2比特字符989.数组形式的整数加法561.数组拆分I1491.去掉最低工资和最高工资后的工资平均值121.买卖股票的最佳时机122.买卖股票的最佳时机II1018.可被5整除的二进制前缀(没懂)1502.判断能否形成等差数列605.种花问题1351.统计有序矩阵中的负数———————8.8————————509.斐波那契的全部内容,更多相关LeetCode_数组_简单题26.删除排序数组中内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复