本文为复现B站视频,方便自己回看。
B站视频链接:搭建yolov3+tensorflow2.0开发环境 模型训练 小白篇 机器视觉 神经网络学习
步骤如下:
1·建立数据集文件夹
在对应路径下新建一个文件夹:JPEGImages,并存入自己的数据集
如图(以识别火焰为例):
2·添加图片并且标注(labellmg软件)
labelImg软件的安装比较简单,可以自己百度查找教程安装,我记得是要提前安装一些python的第三方库,然后才是安装labelImg。这些安装都可以在cmd窗口中完成,值得注意的是,labelImg可能要求附加第三方库是特定版本的。安装完成之后,可以在cmd窗口中直接输入:labelImg,就能打开这个软件。
软件打开之后的界面是这样的:

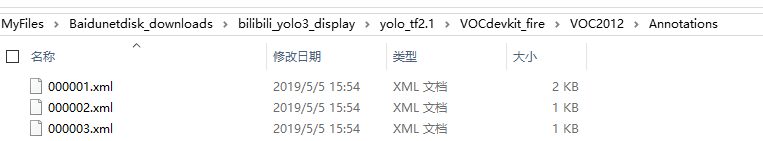
软件使用也比较简单,自己琢磨也能明白。用labelImg标注之后生成的是xml格式的标签文件:
博主还知道另一个标注工具:labelme,用这个软件标注得到的是json格式的文件,这个看自己的需求选择使用就行,安装过程也和labelImg的安装过程类似。
生成txt文件:
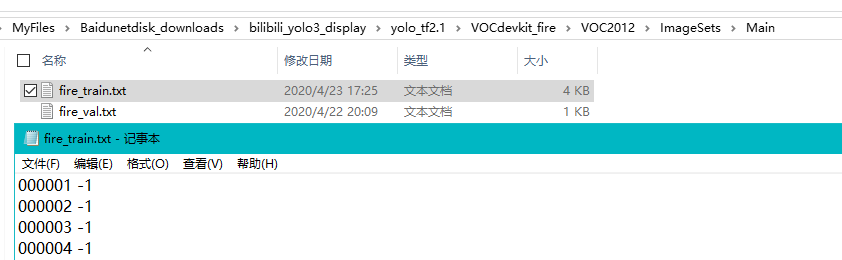
可以自己写个脚本生成序号,然后复制保存在txt里就行。(我也不知道为啥要有个-1,如果有大神知道欢迎指出)
接着,要建立标签文件。
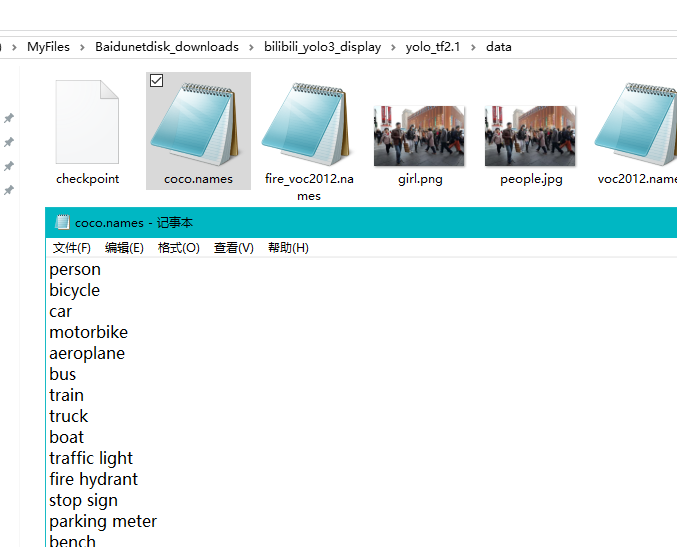
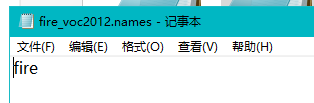
官方文件coco.names里保存了80分类的名称,可以自己复制一个,然后修改名称,例如这里改为fire_voc2012.names,然后在fire_voc2012.names里保存自己的标签名。
3.生成tensorflow易读的tfrecord文件(train和val)
先在文件里找到voc2012.py,并打开。
代码voc2012.py如下:
import time
import os
import hashlib
from absl import app, flags, logging
from absl.flags import FLAGS
import tensorflow as tf
import lxml.etree
import tqdm
flags.DEFINE_string('data_dir', './data/voc2012_raw/VOCdevkit/VOC2012/',
'path to raw PASCAL VOC dataset')
flags.DEFINE_enum('split', 'train', [
'train', 'val'], 'specify train or val spit')
#./data/voc2012_train.tfrecord为生成路径,可以自己定义
flags.DEFINE_string('output_file', './data/voc2012_train.tfrecord', 'outpot dataset')
flags.DEFINE_string('classes', './data/voc2012.names', 'classes file')
def build_example(annotation, class_map):
img_path = os.path.join(
FLAGS.data_dir, 'JPEGImages', annotation['filename'])
img_raw = open(img_path, 'rb').read()
key = hashlib.sha256(img_raw).hexdigest()
width = int(annotation['size']['width'])
height = int(annotation['size']['height'])
xmin = []
ymin = []
xmax = []
ymax = []
classes = []
classes_text = []
truncated = []
views = []
difficult_obj = []
if 'object' in annotation:
for obj in annotation['object']:
difficult = bool(int(obj['difficult']))
difficult_obj.append(int(difficult))
xmin.append(float(obj['bndbox']['xmin']) / width)
ymin.append(float(obj['bndbox']['ymin']) / height)
xmax.append(float(obj['bndbox']['xmax']) / width)
ymax.append(float(obj['bndbox']['ymax']) / height)
classes_text.append(obj['name'].encode('utf8'))
classes.append(class_map[obj['name']])
truncated.append(int(obj['truncated']))
views.append(obj['pose'].encode('utf8'))
example = tf.train.Example(features=tf.train.Features(feature={
'image/height': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[height])),
'image/width': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=[width])),
'image/filename': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[
annotation['filename'].encode('utf8')])),
'image/source_id': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[
annotation['filename'].encode('utf8')])),
'image/key/sha256': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[key.encode('utf8')])),
'image/encoded': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=[img_raw])),
'image/format': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=['jpeg'.encode('utf8')])),
'image/object/bbox/xmin': tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=xmin)),
'image/object/bbox/xmax': tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=xmax)),
'image/object/bbox/ymin': tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=ymin)),
'image/object/bbox/ymax': tf.train.Feature(float_list=tf.train.FloatList(value=ymax)),
'image/object/class/text': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=classes_text)),
'image/object/class/label': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=classes)),
'image/object/difficult': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=difficult_obj)),
'image/object/truncated': tf.train.Feature(int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(value=truncated)),
'image/object/view': tf.train.Feature(bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(value=views)),
}))
return example
def parse_xml(xml):
if not len(xml):
return {xml.tag: xml.text}
result = {}
for child in xml:
child_result = parse_xml(child)
if child.tag != 'object':
result[child.tag] = child_result[child.tag]
else:
if child.tag not in result:
result[child.tag] = []
result[child.tag].append(child_result[child.tag])
return {xml.tag: result}
def main(_argv):
class_map = {name: idx for idx, name in enumerate(
open(FLAGS.classes).read().splitlines())}
logging.info("Class mapping loaded: %s", class_map)
writer = tf.io.TFRecordWriter(FLAGS.output_file)
image_list = open(os.path.join(
#fire_%s.txt是自己建立的两个txt文件,如果名称不同,在调用voc2012.py前,需要先修改fire_%s.txt字符串
FLAGS.data_dir, 'ImageSets', 'Main', 'fire_%s.txt' % FLAGS.split)).read().splitlines()
logging.info("Image list loaded: %d", len(image_list))
for image in tqdm.tqdm(image_list):
name, _ = image.split()
annotation_xml = os.path.join(
FLAGS.data_dir, 'Annotations', name + '.xml')
annotation_xml = lxml.etree.fromstring(open(annotation_xml).read())
annotation = parse_xml(annotation_xml)['annotation']
tf_example = build_example(annotation, class_map)
writer.write(tf_example.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
logging.info("Done")
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(main)
注意:fire_%s.txt是自己建立的两个txt文件,如果名称不同,在调用voc2012.py前,需要先修改fire_%s.txt字符串
在cmd里执行程序之前,文件夹里的文件是这样的:
现在可以在cmd终端里分别输入一下内容并回车:
python tools/voc2012.py --data_dir ./VOCdevkit_fire/VOC2012 --split train --output_file ./data/voc2012_train_fire.tfrecord --classes ./data/fire_voc2012.names
python tools/voc2012.py --data_dir ./VOCdevkit_fire/VOC2012 --split val --output_file ./data/voc2012_val_fire.tfrecord --classes ./data/fire_voc2012.names
如图:


运行完毕之后文件夹里就生成了两个tfrecord格式的文件:
4.进行迁移训练
在cmd窗口里输入以下内容:
python train.py --dataset ./data/voc2012_train_fire.tfrecord --val_dataset ./data/voc2012_val_fire.tfrecord --classes ./data/fire_voc2012.names --num_classes 1
–mode fit --transfer darknet --batch_size 4 --epochs 20 --weights ./checkpoints/yolov3.tf
–weights_num_classes 80
train.py:是文件夹下的代码:
–dataset ./data/voc2012_train_fire.tfrecord --val_dataset ./data/voc2012_val_fire.tfrecord:
加载刚才生成的两个tfrecord格式的文件。
–classes ./data/fire_voc2012.names --num_classes 1:分类,因为只是识别火焰,因此是1分类
–transfer darknet:使用darknet框架。
–batch_size 4:一次装入数据的尺寸大小,可以根据自己显卡性能适当调整
–epochs 20:迭代次数
**–weights ./checkpoints/yolov3.tf:**加载官方权重
–weights_num_classes 80:官方权重是80分类,无需修改。
训练之前:
训练之后(部分截图):
训练之后的文件在这里生成。
5.进行模型测试
5.1预测图片
在cmd窗口里输入:python detect.py --classes ./data/fire_voc2012.names --num_classes 1 --weights ./checkpoints/yolov3_train_20.tf --image ./fire.jpg --yolo_score_threshold 0.3
yolov3_train_20.tf中的20是自己电脑上实际迭代的次数,我的是迭代了20次,有些是在到20次之前就会提前停下来了,这是为了防止过拟合。
另外,–yolo_score_threshold 0.3中的0.3是自己设置的阈值。如果不添加则默认是0.5,参见代码models.py(在yolov3_tf2文件夹里):
# models.py
from absl import flags
from absl.flags import FLAGS
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.keras import Model
from tensorflow.keras.layers import (
Add,
Concatenate,
Conv2D,
Input,
Lambda,
LeakyReLU,
MaxPool2D,
UpSampling2D,
ZeroPadding2D,
)
from tensorflow.keras.regularizers import l2
from tensorflow.keras.losses import (
binary_crossentropy,
sparse_categorical_crossentropy
)
from .batch_norm import BatchNormalization
from .utils import broadcast_iou
flags.DEFINE_integer('yolo_max_boxes', 250,
'maximum number of boxes per image')
#默认0.5阈值
flags.DEFINE_float('yolo_iou_threshold', 0.5, 'iou threshold')
flags.DEFINE_float('yolo_score_threshold', 0.5, 'score threshold')
yolo_anchors = np.array([(10, 13), (16, 30), (33, 23), (30, 61), (62, 45),
(59, 119), (116, 90), (156, 198), (373, 326)],
np.float32) / 416
yolo_anchor_masks = np.array([[6, 7, 8], [3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]])
yolo_tiny_anchors = np.array([(10, 14), (23, 27), (37, 58),
(81, 82), (135, 169), (344, 319)],
np.float32) / 416
yolo_tiny_anchor_masks = np.array([[3, 4, 5], [0, 1, 2]])
def DarknetConv(x, filters, size, strides=1, batch_norm=True): #Darknet卷积
if strides == 1:
padding = 'same'
else:
x = ZeroPadding2D(((1, 0), (1, 0)))(x) # top left half-padding
padding = 'valid'
x = Conv2D(filters=filters, kernel_size=size,
strides=strides, padding=padding,
use_bias=not batch_norm, kernel_regularizer=l2(0.0005))(x)
if batch_norm:
x = BatchNormalization()(x)
x = LeakyReLU(alpha=0.1)(x)
return x
def DarknetResidual(x, filters):
prev = x
x = DarknetConv(x, filters // 2, 1)
x = DarknetConv(x, filters, 3)
x = Add()([prev, x])
return x
def DarknetBlock(x, filters, blocks): #卷积块
x = DarknetConv(x, filters, 3, strides=2)
for _ in range(blocks):
x = DarknetResidual(x, filters)
return x
def Darknet(name=None):#Darknet 主体部分
x = inputs = Input([None, None, 3])
x = DarknetConv(x, 32, 3)
x = DarknetBlock(x, 64, 1)
x = DarknetBlock(x, 128, 2) # skip connection
x = x_36 = DarknetBlock(x, 256, 8) # skip connection
x = x_61 = DarknetBlock(x, 512, 8)
x = DarknetBlock(x, 1024, 4)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs, (x_36, x_61, x), name=name)
def DarknetTiny(name=None):
x = inputs = Input([None, None, 3])
x = DarknetConv(x, 16, 3)
x = MaxPool2D(2, 2, 'same')(x)
x = DarknetConv(x, 32, 3)
x = MaxPool2D(2, 2, 'same')(x)
x = DarknetConv(x, 64, 3)
x = MaxPool2D(2, 2, 'same')(x)
x = DarknetConv(x, 128, 3)
x = MaxPool2D(2, 2, 'same')(x)
x = x_8 = DarknetConv(x, 256, 3) # skip connection
x = MaxPool2D(2, 2, 'same')(x)
x = DarknetConv(x, 512, 3)
x = MaxPool2D(2, 1, 'same')(x)
x = DarknetConv(x, 1024, 3)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs, (x_8, x), name=name)
def YoloConv(filters, name=None):
def yolo_conv(x_in):
if isinstance(x_in, tuple):
inputs = Input(x_in[0].shape[1:]), Input(x_in[1].shape[1:])
x, x_skip = inputs
# concat with skip connection
x = DarknetConv(x, filters, 1)
x = UpSampling2D(2)(x)
x = Concatenate()([x, x_skip])
else:
x = inputs = Input(x_in.shape[1:])
x = DarknetConv(x, filters, 1)
x = DarknetConv(x, filters * 2, 3)
x = DarknetConv(x, filters, 1)
x = DarknetConv(x, filters * 2, 3)
x = DarknetConv(x, filters, 1)
return Model(inputs, x, name=name)(x_in)
return yolo_conv
def YoloConvTiny(filters, name=None):
def yolo_conv(x_in):
if isinstance(x_in, tuple):
inputs = Input(x_in[0].shape[1:]), Input(x_in[1].shape[1:])
x, x_skip = inputs
# concat with skip connection
x = DarknetConv(x, filters, 1)
x = UpSampling2D(2)(x)
x = Concatenate()([x, x_skip])
else:
x = inputs = Input(x_in.shape[1:])
x = DarknetConv(x, filters, 1)
return Model(inputs, x, name=name)(x_in)
return yolo_conv
def YoloOutput(filters, anchors, classes, name=None):
def yolo_output(x_in):
x = inputs = Input(x_in.shape[1:])
x = DarknetConv(x, filters * 2, 3)
x = DarknetConv(x, anchors * (classes + 5), 1, batch_norm=False)
x = Lambda(lambda x: tf.reshape(x, (-1, tf.shape(x)[1], tf.shape(x)[2],
anchors, classes + 5)))(x)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs, x, name=name)(x_in)
return yolo_output
def yolo_boxes(pred, anchors, classes):
# pred: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors, (x, y, w, h, obj, ...classes))
grid_size = tf.shape(pred)[1]
box_xy, box_wh, objectness, class_probs = tf.split(
pred, (2, 2, 1, classes), axis=-1)
box_xy = tf.sigmoid(box_xy)
objectness = tf.sigmoid(objectness)
class_probs = tf.sigmoid(class_probs)
pred_box = tf.concat((box_xy, box_wh), axis=-1) # original xywh for loss
# !!! grid[x][y] == (y, x)
grid = tf.meshgrid(tf.range(grid_size), tf.range(grid_size))
grid = tf.expand_dims(tf.stack(grid, axis=-1), axis=2) # [gx, gy, 1, 2]
box_xy = (box_xy + tf.cast(grid, tf.float32)) /
tf.cast(grid_size, tf.float32)
box_wh = tf.exp(box_wh) * anchors
box_x1y1 = box_xy - box_wh / 2
box_x2y2 = box_xy + box_wh / 2
bbox = tf.concat([box_x1y1, box_x2y2], axis=-1)
return bbox, objectness, class_probs, pred_box
def yolo_nms(outputs, anchors, masks, classes):
# boxes, conf, type
b, c, t = [], [], []
for o in outputs:
b.append(tf.reshape(o[0], (tf.shape(o[0])[0], -1, tf.shape(o[0])[-1])))
c.append(tf.reshape(o[1], (tf.shape(o[1])[0], -1, tf.shape(o[1])[-1])))
t.append(tf.reshape(o[2], (tf.shape(o[2])[0], -1, tf.shape(o[2])[-1])))
bbox = tf.concat(b, axis=1)
confidence = tf.concat(c, axis=1)
class_probs = tf.concat(t, axis=1)
scores = confidence * class_probs
boxes, scores, classes, valid_detections = tf.image.combined_non_max_suppression(
boxes=tf.reshape(bbox, (tf.shape(bbox)[0], -1, 1, 4)),
scores=tf.reshape(
scores, (tf.shape(scores)[0], -1, tf.shape(scores)[-1])),
max_output_size_per_class=FLAGS.yolo_max_boxes,
max_total_size=FLAGS.yolo_max_boxes,
iou_threshold=FLAGS.yolo_iou_threshold,
score_threshold=FLAGS.yolo_score_threshold
)
return boxes, scores, classes, valid_detections
def YoloV3(size=None, channels=3, anchors=yolo_anchors,
masks=yolo_anchor_masks, classes=80, training=False):
x = inputs = Input([size, size, channels], name='input')
x_36, x_61, x = Darknet(name='yolo_darknet')(x)
x = YoloConv(512, name='yolo_conv_0')(x)
output_0 = YoloOutput(512, len(masks[0]), classes, name='yolo_output_0')(x)
x = YoloConv(256, name='yolo_conv_1')((x, x_61))
output_1 = YoloOutput(256, len(masks[1]), classes, name='yolo_output_1')(x)
x = YoloConv(128, name='yolo_conv_2')((x, x_36))
output_2 = YoloOutput(128, len(masks[2]), classes, name='yolo_output_2')(x)
if training:
return Model(inputs, (output_0, output_1, output_2), name='yolov3')
boxes_0 = Lambda(lambda x: yolo_boxes(x, anchors[masks[0]], classes),
name='yolo_boxes_0')(output_0)
boxes_1 = Lambda(lambda x: yolo_boxes(x, anchors[masks[1]], classes),
name='yolo_boxes_1')(output_1)
boxes_2 = Lambda(lambda x: yolo_boxes(x, anchors[masks[2]], classes),
name='yolo_boxes_2')(output_2)
outputs = Lambda(lambda x: yolo_nms(x, anchors, masks, classes),
name='yolo_nms')((boxes_0[:3], boxes_1[:3], boxes_2[:3]))
return Model(inputs, outputs, name='yolov3')
def YoloV3Tiny(size=None, channels=3, anchors=yolo_tiny_anchors,
masks=yolo_tiny_anchor_masks, classes=80, training=False):
x = inputs = Input([size, size, channels], name='input')
x_8, x = DarknetTiny(name='yolo_darknet')(x)
x = YoloConvTiny(256, name='yolo_conv_0')(x)
output_0 = YoloOutput(256, len(masks[0]), classes, name='yolo_output_0')(x)
x = YoloConvTiny(128, name='yolo_conv_1')((x, x_8))
output_1 = YoloOutput(128, len(masks[1]), classes, name='yolo_output_1')(x)
if training:
return Model(inputs, (output_0, output_1), name='yolov3')
boxes_0 = Lambda(lambda x: yolo_boxes(x, anchors[masks[0]], classes),
name='yolo_boxes_0')(output_0)
boxes_1 = Lambda(lambda x: yolo_boxes(x, anchors[masks[1]], classes),
name='yolo_boxes_1')(output_1)
outputs = Lambda(lambda x: yolo_nms(x, anchors, masks, classes),
name='yolo_nms')((boxes_0[:3], boxes_1[:3]))
return Model(inputs, outputs, name='yolov3_tiny')
def YoloLoss(anchors, classes=80, ignore_thresh=0.5):
def yolo_loss(y_true, y_pred):
# 1. transform all pred outputs
# y_pred: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors, (x, y, w, h, obj, ...cls))
pred_box, pred_obj, pred_class, pred_xywh = yolo_boxes(
y_pred, anchors, classes)
pred_xy = pred_xywh[..., 0:2]
pred_wh = pred_xywh[..., 2:4]
# 2. transform all true outputs
# y_true: (batch_size, grid, grid, anchors, (x1, y1, x2, y2, obj, cls))
true_box, true_obj, true_class_idx = tf.split(
y_true, (4, 1, 1), axis=-1)
true_xy = (true_box[..., 0:2] + true_box[..., 2:4]) / 2
true_wh = true_box[..., 2:4] - true_box[..., 0:2]
# give higher weights to small boxes
box_loss_scale = 2 - true_wh[..., 0] * true_wh[..., 1]
# 3. inverting the pred box equations
grid_size = tf.shape(y_true)[1]
grid = tf.meshgrid(tf.range(grid_size), tf.range(grid_size))
grid = tf.expand_dims(tf.stack(grid, axis=-1), axis=2)
true_xy = true_xy * tf.cast(grid_size, tf.float32) -
tf.cast(grid, tf.float32)
true_wh = tf.math.log(true_wh / anchors)
true_wh = tf.where(tf.math.is_inf(true_wh),
tf.zeros_like(true_wh), true_wh)
# 4. calculate all masks
obj_mask = tf.squeeze(true_obj, -1)
# ignore false positive when iou is over threshold
best_iou = tf.map_fn(
lambda x: tf.reduce_max(broadcast_iou(x[0], tf.boolean_mask(
x[1], tf.cast(x[2], tf.bool))), axis=-1),
(pred_box, true_box, obj_mask),
tf.float32)
ignore_mask = tf.cast(best_iou < ignore_thresh, tf.float32)
# 5. calculate all losses
xy_loss = obj_mask * box_loss_scale *
tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(true_xy - pred_xy), axis=-1)
wh_loss = obj_mask * box_loss_scale *
tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(true_wh - pred_wh), axis=-1)
obj_loss = binary_crossentropy(true_obj, pred_obj)
obj_loss = obj_mask * obj_loss +
(1 - obj_mask) * ignore_mask * obj_loss
# TODO: use binary_crossentropy instead
class_loss = obj_mask * sparse_categorical_crossentropy(
true_class_idx, pred_class)
# 6. sum over (batch, gridx, gridy, anchors) => (batch, 1)
xy_loss = tf.reduce_sum(xy_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
wh_loss = tf.reduce_sum(wh_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
obj_loss = tf.reduce_sum(obj_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
class_loss = tf.reduce_sum(class_loss, axis=(1, 2, 3))
return xy_loss + wh_loss + obj_loss + class_loss
return yolo_loss
测试之后会在文件夹下看到测试结果:

(记得要加阈值,否则看不到预测框)

5.2 预测视频流:
在cmd里输入以下内容:
python detect_video.py --classes ./data/fire_voc2012.names --num_classes 1 --weights ./checkpoints/yolov3_train_20.tf
–video fire.mp4 --yolo_score_threshold 0.3 --output ./test_output.avi
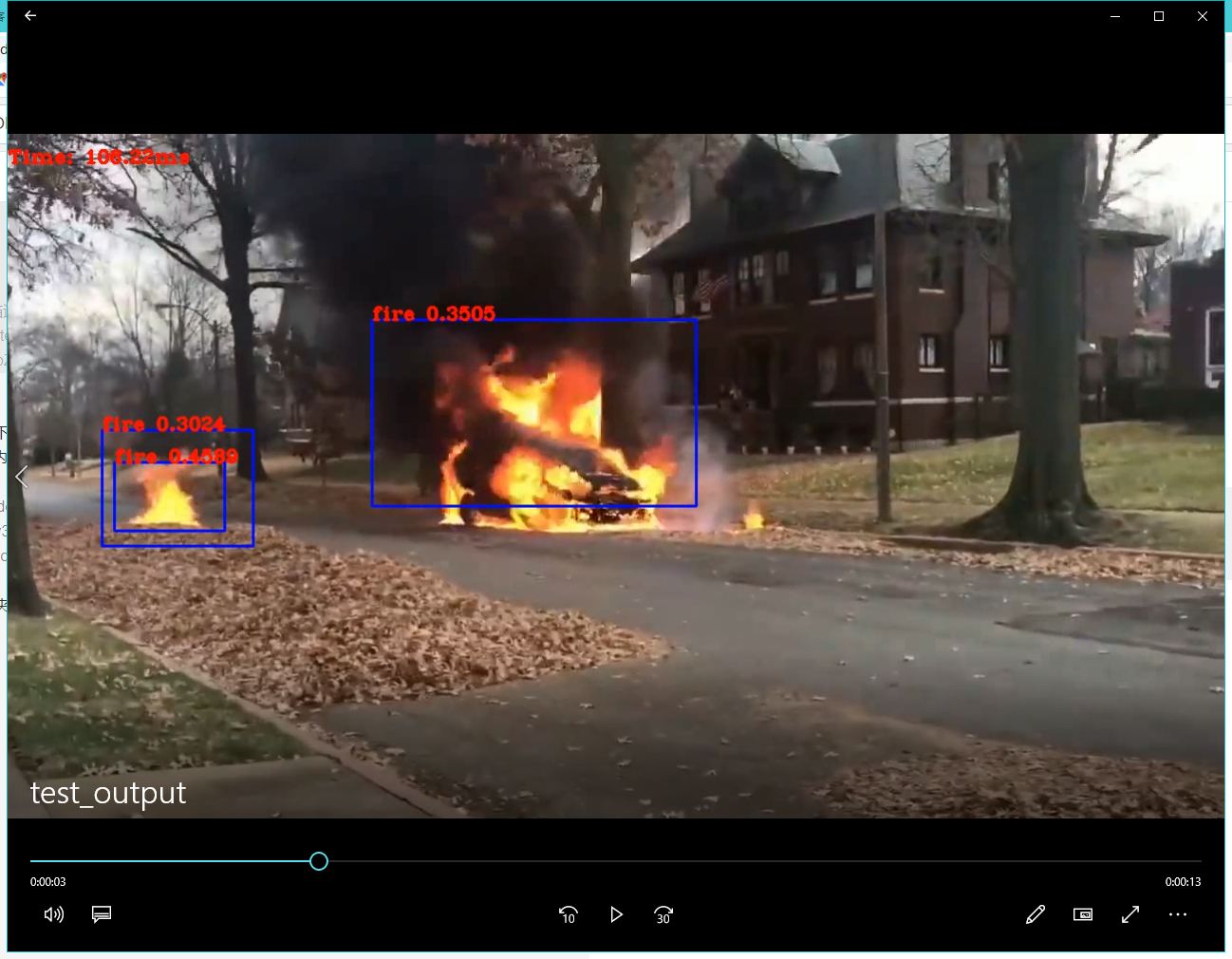
运行之后会在文件夹下生成一个test_output.avi。打开截图如下:
如果看不懂的可以先看看我的第一篇:
YOLO3—1利用官方权重进行识别
最后
以上就是冷傲绿草最近收集整理的关于YOLO3--2训练自己的模型并识别的全部内容,更多相关YOLO3--2训练自己内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。





![[Pytorch]YOLO目标检测目录一、经典算法与阶段(Stage)二、真实框(Ground Truth)、预测框(Prediction)与交并比(IoU)三、精确率(Precision)与召回率(Recall)四、置信度(Confidence)与置信度阈值(Confidence Threshold)五、AP(Average Precision)、mAP(Mean Average Precision)、所有点插值法(Interpolation Performed in all Points)与](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg9.png)


发表评论 取消回复