我是靠谱客的博主 陶醉月光,这篇文章主要介绍视觉SLAM学习笔记3——eigen库的基础编程 一、头文件二、矩阵与向量的定义三、矩阵的输入与输出 四、矩阵的加减乘除五、随机数、数乘、转置、行列式、逆 等六、特征值与特征向量七、解方程八、矩阵的角操作九、均值、求和、最值、迹 等,现在分享给大家,希望可以做个参考。
一、头文件
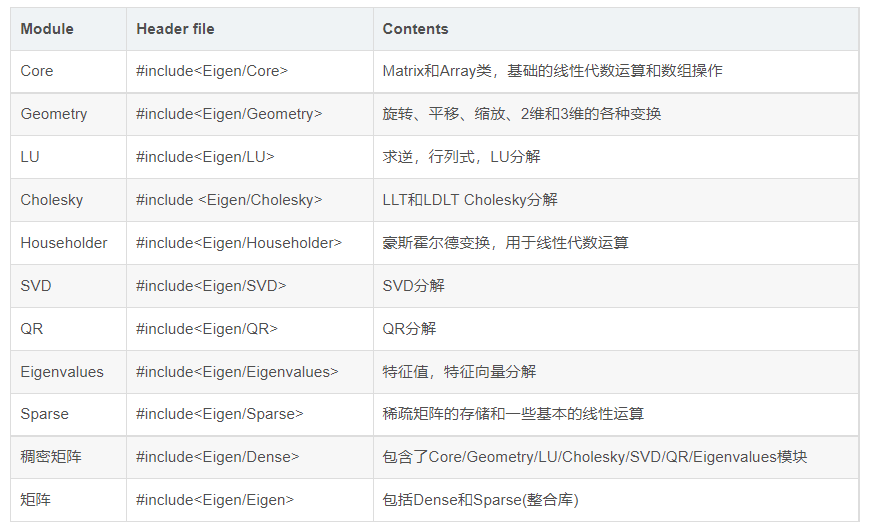
一般情况下,只需要:
#include <Eigen/Core>
#include <Eigen/Dense>
二、矩阵与向量的定义
Eigen 中所有向量和矩阵都是Eigen::Matrix,它是一个模板类。
它的前三个参数为:数据类型,行,列。
// 声明一个2*3的float矩阵
Eigen::Matrix<float, 2, 3> matrix_23;
//声明一个5*1的double向量
Eigen::Matrix<double, 5, 1> matrix_51;后面的名称为变量名,按自己习惯定义即可。
同时,Eigen 通过 typedef 提供了许多内置类型,不过底层仍是Eigen::Matrix,比如以下两种d定义向量的方式是一样的:
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 1> v_3d; //即三维double向量
Eigen::Vector3d v_3d;
以下两种定义3*3方阵的方式也是一定的:
Eigen::Matrix<double, 3, 3> matrix_33 ;
Eigen::Matrix3d matrix_33 ;初始化为0:
matrix_33 = Eigen::Matrix3d::Zero(); 若不确定矩阵大小,可以使用动态大小的矩阵:
Eigen::Matrix< double, Eigen::Dynamic, Eigen::Dynamic > matrix_dynamic;
// 更简单的
Eigen::MatrixXd matrix_x;三、矩阵的输入与输出
例如定义2*3矩阵:
Eigen::Matrix<float, 2, 3> matrix_23;矩阵初始化(输入):
matrix_23 << 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6;矩阵显示(输出):
cout << matrix_23 << endl;
1 2 3
4 5 6与matlab类似,可以用括号访问矩阵中的元素:
for (int i=0; i<2; i++)
{
for (int j=0; j<3; j++)
cout<<matrix_23(i,j)<<"t";
cout<<endl;
}1 2 3
4 5 6
也可以基于整行或整列操作:
Eigen::MatrixXf m(3,3);
m << 1,2,3,
4,5,6,
7,8,9;
cout << "Here is the matrix m:" << endl << m << endl;
cout << "2nd Row: " << m.row(1) << endl;
m.col(2) += 3 * m.col(0);
cout << "After adding 3 times the first column into the third column, the matrix m is:n";
cout << m << endl;Here is the matrix m:
1 2 3
4 5 6
7 8 9
2nd Row: 4 5 6
After adding 3 times the first column into the third column, the matrix m is:
1 2 6
4 5 18
7 8 30四、矩阵的加减乘除
需要注意此类操作数据类型应该一致,矩阵维度也要满足运算要求,以乘法操作为例:
Eigen::Vector3d v_3d;
Eigen::Matrix<float,3,1> vd_3d;
v_3d << 3, 2, 1;
vd_3d << 4,5,6;
Eigen::Matrix<double, 2, 1> result = matrix_23.cast<double>() * v_3d; //数据类型转换
cout << result << endl;
Eigen::Matrix<float, 2, 1> result2 = matrix_23 * vd_3d;
cout << result2 << endl;
10
28
32
77
其它四则运算类似,改用+-*/即可。
五、随机数、数乘、转置、行列式、逆 等
matrix_33 = Eigen::Matrix3d::Random(); // 随机数矩阵
cout << matrix_33 << endl << endl;
cout << matrix_33.transpose() << endl; // 转置
cout << matrix_33.sum() << endl; // 各元素和
cout << matrix_33.trace() << endl; // 迹
cout << 10*matrix_33 << endl; // 数乘
cout << matrix_33.inverse() << endl; // 逆
cout << matrix_33.determinant() << endl; // 行列式
输出为:
0.680375 0.59688 -0.329554
-0.211234 0.823295 0.536459
0.566198 -0.604897 -0.444451
0.680375 -0.211234 0.566198
0.59688 0.823295 -0.604897
-0.329554 0.536459 -0.444451
1.61307
1.05922
6.80375 5.9688 -3.29554
-2.11234 8.23295 5.36459
5.66198 -6.04897 -4.44451
-0.198521 2.22739 2.8357
1.00605 -0.555135 -1.41603
-1.62213 3.59308 3.28973
0.208598
六、特征值与特征向量
// 实对称矩阵可以保证对角化成功
Eigen::SelfAdjointEigenSolver<Eigen::Matrix3d> eigen_solver ( matrix_33.transpose()*matrix_33 );
cout << "Eigen values = n" << eigen_solver.eigenvalues() << endl;
cout << "Eigen vectors = n" << eigen_solver.eigenvectors() << endl;
输出:
Eigen values =
0.0242899
0.992154
1.80558
Eigen vectors =
-0.549013 -0.735943 0.396198
0.253452 -0.598296 -0.760134
-0.796459 0.316906 -0.514998
七、解方程
求解 matrix_NN * x = v_Nd 这个方程
定义
#define MATRIX_SIZE 5 Eigen::Matrix< double, MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE > matrix_NN;
matrix_NN = Eigen::MatrixXd::Random( MATRIX_SIZE, MATRIX_SIZE );
Eigen::Matrix< double, MATRIX_SIZE, 1> v_Nd;
v_Nd = Eigen::MatrixXd::Random( MATRIX_SIZE,1 );直接求逆求解直接但运算量大:
Eigen::Matrix<double,MATRIX_SIZE,1> x = matrix_NN.inverse()*v_Nd;
cout << "x=" << x <<endl;x=-0.745267
-1.09144
-0.737525
-1.21405
-1.18348
通常用矩阵分解来求,例如QR分解,速度会快很多:
x = matrix_NN.colPivHouseholderQr().solve(v_Nd);
cout << "x=" << x <<endl;x=-0.745267
-1.09144
-0.737525
-1.21405
-1.18348
运算结果当然是一致的。
八、矩阵的角操作
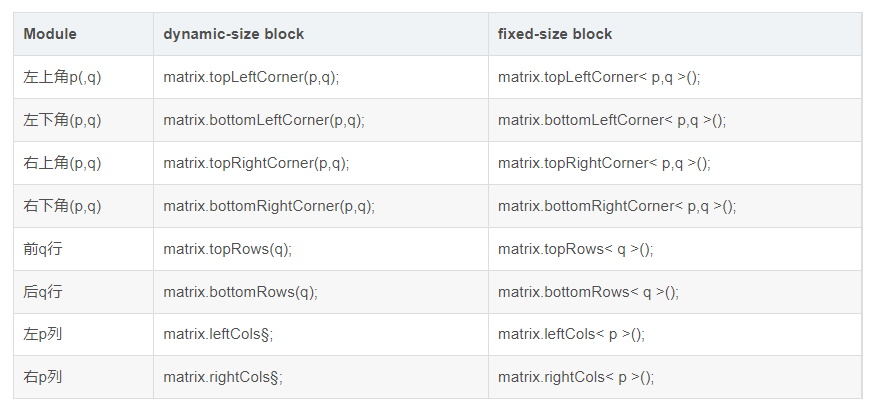
Eigen::Matrix4f m_44;
m_44 << 1, 2, 3, 4,
5, 6, 7, 8,
9, 10,11,12,
13,14,15,16;
cout << "m_44.leftCols(2) =" << endl << m_44.leftCols(2) << endl << endl;
cout << "m_44.bottomRows<2>() =" << endl << m_44.bottomRows<2>() << endl << endl;
m_44.topLeftCorner(1,3) = m_44.bottomRightCorner(3,1).transpose();
cout << "After assignment, m_44 = " << endl << m_44 << endl;
输出为:
m_44.leftCols(2) =
1 2
5 6
9 10
13 14
m_44.bottomRows<2>() =
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
After assignment, m_44 =
8 12 16 4
5 6 7 8
9 10 11 12
13 14 15 16
九、均值、求和、最值、迹 等
Eigen::Matrix2d mat;
mat << 1, 2,3, 4;
cout << "Here is mat.sum(): " << mat.sum() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.prod(): " << mat.prod() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.mean(): " << mat.mean() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.minCoeff(): " << mat.minCoeff() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.maxCoeff(): " << mat.maxCoeff() << endl;
cout << "Here is mat.trace(): " << mat.trace() << endl;输出为:
Here is mat.sum(): 10
Here is mat.prod(): 24
Here is mat.mean(): 2.5
Here is mat.minCoeff(): 1
Here is mat.maxCoeff(): 4
Here is mat.trace(): 5
最后
以上就是陶醉月光最近收集整理的关于视觉SLAM学习笔记3——eigen库的基础编程 一、头文件二、矩阵与向量的定义三、矩阵的输入与输出 四、矩阵的加减乘除五、随机数、数乘、转置、行列式、逆 等六、特征值与特征向量七、解方程八、矩阵的角操作九、均值、求和、最值、迹 等的全部内容,更多相关视觉SLAM学习笔记3——eigen库的基础编程 一、头文件二、矩阵与向量的定义三、矩阵的输入与输出 四、矩阵的加减乘除五、随机数、数乘、转置、行列式、逆 内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复