torch.nn.functional.interpolate实现插值和上采样
torch.nn.functional.interpolate(input, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None, recompute_scale_factor=None)功能:根据给定的size或scale_factor参数来对输入进行下/上采样,使用的插值算法取决于参数mode的设置。
支持目前的temporal(1D, 如向量数据), spatial(2D, 如jpg、png等图像数据)和volumetric(3D, 如点云数据)类型的采样数据作为输入,输入数据的格式为minibatch x channels x [optional depth] x [optional height] x width,具体为:
- 对于一个temporal输入,期待着3D张量的输入,即minibatch x channels x width;
- 对于一个空间spatial输入,期待着4D张量的输入,即minibatch x channels x height x width;
- 对于体积volumetric输入,则期待着5D张量的输入,即minibatch x channels x depth x height x width。
可用于重置大小的mode有:最近邻、线性(3D-only),、双线性, 双三次(bicubic,4D-only)和三线性(trilinear,5D-only)插值算法和area算法。
参数
-
input (Tensor) – 输入张量。
-
size (int or Tuple[int] or Tuple[int, int] or Tuple[int, int, int]) –输出大小。
-
scale_factor (float or Tuple[float]) – 指定输出为输入的多少倍数。如果输入为tuple,其也要制定为tuple类型。
-
mode (str) –
可使用的上采样算法,有'nearest','linear','bilinear','bicubic','trilinear'和'area'.默认使用'nearest'。 -
align_corners (bool, optional) –
几何上,我们认为输入和输出的像素是正方形,而不是点。如果设置为True,则输入和输出张量由其角像素的中心点对齐,从而保留角像素处的值。如果设置为False,则输入和输出张量由它们的角像素的角点对齐,插值使用边界外值的边值填充;当scale_factor保持不变时,使该操作独立于输入大小。仅当使用的算法为'linear','bilinear', 'bilinear'or'trilinear'时可以使用。默认设置为False。 -
recompute_scale_facto(bool):重新计算用于插值计算的 scale_factor。当scale_factor作为参数传递时,它用于计算output_size。如果recompute_scale_factor的False或没有指定,传入的scale_factor将在插值计算中使用。否则,将根据用于插值计算的输出和输入大小计算新的scale_factor(即,如果计算的output_size显式传入,则计算将相同 )。注意当scale_factor 是浮点数,由于舍入和精度问题,重新计算的 scale_factor 可能与传入的不同。
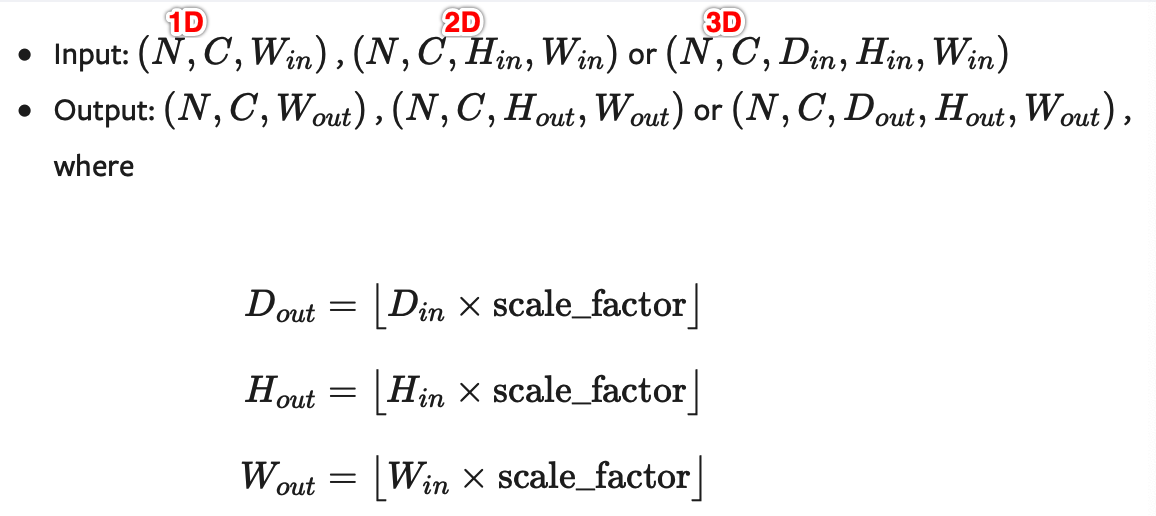
注意
- 输入的张量数组里面的数据类型必须是float。
- 输入的数组维数只能是3、4或5,分别对应于时间、空间、体积采样。
- 不对输入数组的前两个维度(批次和通道)采样,从第三个维度往后开始采样处理。
- 输入的维度形式为:批量(batch_size)×通道(channel)×[可选深度]×[可选高度]×宽度(前两个维度具有特殊的含义,不进行采样处理)
- size与scale_factor两个参数只能定义一个,即两种采样模式只能用一个。要么让数组放大成特定大小、要么给定特定系数,来等比放大数组。
- 如果size或者scale_factor输入序列,则必须匹配输入的大小。如果输入四维,则它们的序列长度必须是2,如果输入是五维,则它们的序列长度必须是3。
- 如果size输入整数x,则相当于把3、4维度放大成(x,x)大小(输入以四维为例,下面同理)。
- 如果scale_factor输入整数x,则相当于把3、4维度都等比放大x倍。
- mode是’linear’时输入必须是3维的;是’bicubic’时输入必须是4维的;是’trilinear’时输入必须是5维的
- 如果align_corners被赋值,则mode必须是'linear','bilinear','bicubic'或'trilinear'中的一个。
- 插值方法不同,结果就不一样,需要结合具体任务,选择合适的插值方法。
-
使用mode='bicubic'时,可能会导致overshoot问题,即它可以为图像生成负值或大于255的值。如果你想在显示图像时减少overshoot问题,可以显式地调用result.clamp(min=0,max=255)。
When using the CUDA backend, this operation may induce nondeterministic behaviour in be backward that is not easily switched off. Please see the notes on Reproducibility for background.
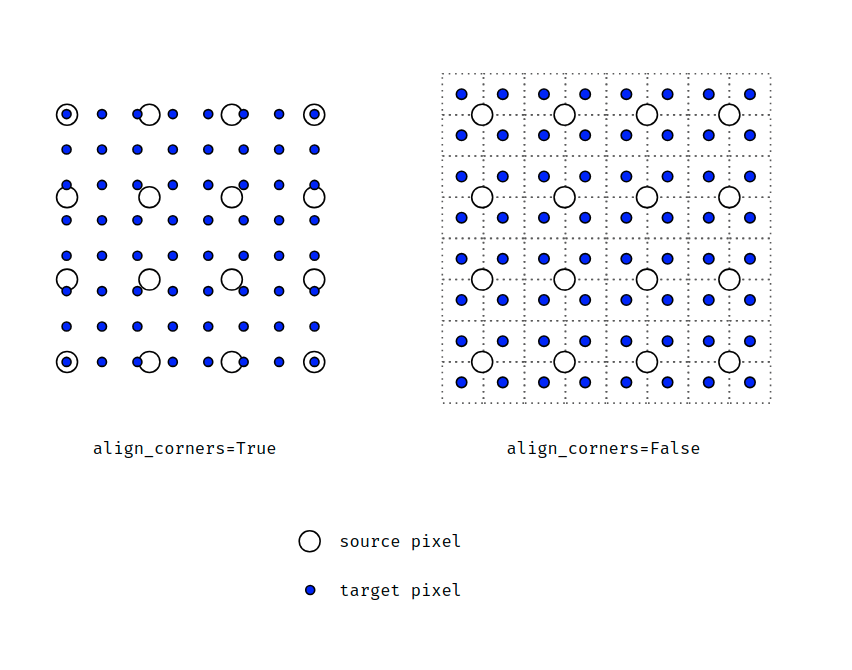
一图看懂align_corners=True与False的区别,从4×4上采样成8×8。一个是按四角的像素点中心对齐,另一个是按四角的像素角点对齐。
当align_corners = True时,线性插值模式(线性、双线性、双三线性和三线性)不按比例对齐输出和输入像素,因此输出值可以依赖于输入的大小。默认行为是align_corners = False。
实例
一般用法
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
a=torch.arange(12,dtype=torch.float32).reshape(1,2,2,3)
b=F.interpolate(a,size=(4,4),mode='bilinear')
# 这里的(4,4)指的是将后两个维度放缩成4*4的大小
print(a)
print(b)
print('原数组尺寸:',a.shape)
print('size采样尺寸:',b.shape)
# 输出结果。一、二维大小不会变化。
# 原数组
tensor([[[[ 0., 1., 2.],
[ 3., 4., 5.]],
[[ 6., 7., 8.],
[ 9., 10., 11.]]]])
# 采样后的数组
tensor([[[[ 0.0000, 0.6250, 1.3750, 2.0000],
[ 0.7500, 1.3750, 2.1250, 2.7500],
[ 2.2500, 2.8750, 3.6250, 4.2500],
[ 3.0000, 3.6250, 4.3750, 5.0000]],
[[ 6.0000, 6.6250, 7.3750, 8.0000],
[ 6.7500, 7.3750, 8.1250, 8.7500],
[ 8.2500, 8.8750, 9.6250, 10.2500],
[ 9.0000, 9.6250, 10.3750, 11.0000]]]])
原数组尺寸: torch.Size([1, 2, 2, 3])
size采样尺寸: torch.Size([1, 2, 4, 4])
# 规定三四维度放缩成4*4大小size与scale_factor的区别:输入序列时
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
a=torch.arange(4*512*14*14,dtype=torch.float32).reshape(4,512,14,14)
b=F.interpolate(a,size=(28,56),mode='bilinear')
c=F.interpolate(a,scale_factor=(4,8),mode='bilinear')
print('原数组尺寸:',a.shape)
print('size采样尺寸:',b.shape)
print('scale_factor采样尺寸:',c.shape)
# 输出结果
原数组尺寸: torch.Size([4, 512, 14, 14])
size采样尺寸: torch.Size([4, 512, 28, 56])
# 第三维度放大成28,第四维度放大成56
scale_factor采样尺寸: torch.Size([4, 512, 56, 112])
# 第三维度放大4倍,第四维度放8倍size与scale_factor的区别:输入整数时
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
a=torch.arange(4*512*14*14,dtype=torch.float32).reshape(4,512,14,14)
b=F.interpolate(a,size=28,mode='bilinear')
c=F.interpolate(a,scale_factor=4,mode='bilinear')
print('原数组尺寸:',a.shape)
print('size采样尺寸:',b.shape)
print('scale_factor采样尺寸:',c.shape)
# 输出结果
原数组尺寸: torch.Size([4, 512, 14, 14])
size采样尺寸: torch.Size([4, 512, 28, 28])
# 三四维度数组被放大成28*28
scale_factor采样尺寸: torch.Size([4, 512, 56, 56])
# 三四维度数组被放大了4倍align_corners=True与False的区别
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch
a=torch.arange(18,dtype=torch.float32).reshape(1,2,3,3)
b=F.interpolate(a,size=(4,4),mode='bicubic',align_corners=True)
c=F.interpolate(a,size=(4,4),mode='bicubic',align_corners=False)
print(a)
print(b)
print(c)
# 输出结果,具体效果会因mode插值方法而异
tensor([[[[ 0., 1., 2.],
[ 3., 4., 5.],
[ 6., 7., 8.]],
[[ 9., 10., 11.],
[12., 13., 14.],
[15., 16., 17.]]]])
# align_corners=True
tensor([[[[ 0.0000, 0.5741, 1.4259, 2.0000],
[ 1.7222, 2.2963, 3.1481, 3.7222],
[ 4.2778, 4.8519, 5.7037, 6.2778],
[ 6.0000, 6.5741, 7.4259, 8.0000]],
[[ 9.0000, 9.5741, 10.4259, 11.0000],
[10.7222, 11.2963, 12.1481, 12.7222],
[13.2778, 13.8519, 14.7037, 15.2778],
[15.0000, 15.5741, 16.4259, 17.0000]]]])
# align_corners=False
tensor([[[[-0.2871, 0.3145, 1.2549, 1.8564],
[ 1.5176, 2.1191, 3.0596, 3.6611],
[ 4.3389, 4.9404, 5.8809, 6.4824],
[ 6.1436, 6.7451, 7.6855, 8.2871]],
[[ 8.7129, 9.3145, 10.2549, 10.8564],
[10.5176, 11.1191, 12.0596, 12.6611],
[13.3389, 13.9404, 14.8809, 15.4824],
[15.1436, 15.7451, 16.6855, 17.2871]]]])实际使用
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
img = torch.randint(0, 255, (3, 2, 2)) # 默认为torch.int64类型
img = img.type(torch.float32) # 使用F.interpolate函数前需要将img转成float32类型
img = img.unsqueeze(0) # 需要将三维图片(C, H, W)变为四维(N, C, H, W),必须有批量N
img_ = F.interpolate(img, size=(4, 4), mode='nearest') # size是img_的尺寸大小
print("img: n", img)
print("img_: n", img_)备注
在计算机视觉中,interpolate函数常用于图像的放大(即上采样操作)。比如在细粒度识别领域中,注意力图有时候会对特征图进行裁剪操作,将有用的部分裁剪出来,裁剪后的图像往往尺寸小于原始特征图,这时候如果强制转换成原始图像大小,往往是无效的,会丢掉部分有用的信息。所以这时候就需要用到interpolate函数对其进行上采样操作,在保证图像信息不丢失的情况下,放大图像,从而放大图像的细节,有利于进一步的特征提取工作。
参考博客
F.interpolate——数组采样操作_视觉萌新、的博客-CSDN博客_interpolate scale_factor
pytorch torch.nn.functional实现插值和上采样 - 慢行厚积 - 博客园 (cnblogs.com)
官方文档
torch.nn.functional.interpolate — PyTorch 1.11.0 documentation
TORCH.NN.FUNCTIONAL.INTERPOLATE
torch.nn.functional.interpolate(input, size=None, scale_factor=None, mode='nearest', align_corners=None, recompute_scale_factor=None, antialias=False)[SOURCE]
- Down/up samples the input to either the given
sizeor the givenscale_factor - The algorithm used for interpolation is determined by
mode. - Currently temporal, spatial and volumetric sampling are supported, i.e. expected inputs are 3-D, 4-D or 5-D in shape.
- The input dimensions are interpreted in the form: mini-batch x channels x [optional depth] x [optional height] x width.
- The modes available for resizing are: nearest, linear (3D-only), bilinear, bicubic (4D-only), trilinear (5D-only), area, nearest-exact
Parameters
-
input (Tensor) – the input tensor
-
size (int or Tuple[int] or Tuple[int, int] or Tuple[int, int, int]) – output spatial size.
-
scale_factor (float or Tuple[float]) – multiplier for spatial size. If scale_factor is a tuple, its length has to match input.dim().
-
mode (str) – algorithm used for upsampling:
'nearest'|'linear'|'bilinear'|'bicubic'|'trilinear'|'area'|'nearest-exact'. Default:'nearest' -
align_corners (bool, optional) – Geometrically, we consider the pixels of the input and output as squares rather than points. If set to
True, the input and output tensors are aligned by the center points of their corner pixels, preserving the values at the corner pixels. If set toFalse, the input and output tensors are aligned by the corner points of their corner pixels, and the interpolation uses edge value padding for out-of-boundary values, making this operation independent of input size whenscale_factoris kept the same. This only has an effect whenmodeis'linear','bilinear','bicubic'or'trilinear'. Default:False -
recompute_scale_factor (bool, optional) – recompute the scale_factor for use in the interpolation calculation. If recompute_scale_factor is
True, then scale_factor must be passed in and scale_factor is used to compute the output size. The computed output size will be used to infer new scales for the interpolation. Note that when scale_factor is floating-point, it may differ from the recomputed scale_factor due to rounding and precision issues. If recompute_scale_factor isFalse, then size or scale_factor will be used directly for interpolation. Default:None. -
antialias (bool, optional) – flag to apply anti-aliasing. Default:
False. Using anti-alias option together withalign_corners=False, interpolation result would match Pillow result for downsampling operation. Supported modes:'bilinear','bicubic'.
NOTE
- With
mode='bicubic', it’s possible to cause overshoot, in other words it can produce negative values or values greater than 255 for images. Explicitly callresult.clamp(min=0, max=255)if you want to reduce the overshoot when displaying the image. - Mode
mode='nearest-exact'matches Scikit-Image and PIL nearest neighbours interpolation algorithms and fixes known issues withmode='nearest'. This mode is introduced to keep backward compatibility. Modemode='nearest'matches buggy OpenCV’sINTER_NEARESTinterpolation algorithm. - This operation may produce nondeterministic gradients when given tensors on a CUDA device. See Reproducibility for more information.
最后
以上就是热情泥猴桃最近收集整理的关于torch.nn.functional.interpolate函数torch.nn.functional.interpolate实现插值和上采样实例备注参考博客官方文档 的全部内容,更多相关torch内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复