参考链接:https://blog.csdn.net/Maggie_zhangxin/article/details/73481417
实现的内容很简单,存为.m文件可以直接在matlab上运行,就是利用Q学习(Q learning)完成自主路径寻优简单示例,并进行可视化,Q学习部分参考了如上链接中的内容,供大家交流学习使用,请多提宝贵意见
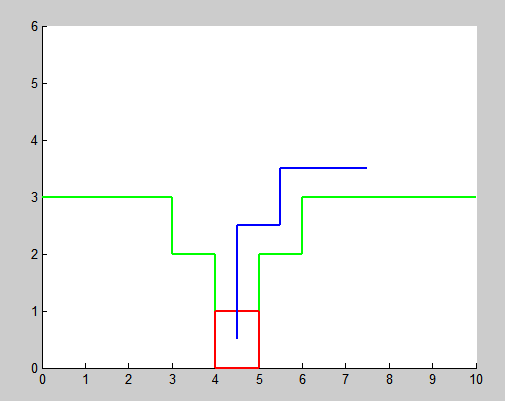
如图为最终路径,红色方框代表机器人,绿色区域代表障碍,中间底部位置(图示红色方框位置)为目标位置,蓝色为运动轨迹
本程序对训练过程进行了可视化,方便理解学习过程,代码如下:
clc;
clear all;
% define state
R=ones(60,60)*-inf;
for i=1:30
if i-10>0
R(i,i-10)=0;
end
if i+10<31
R(i,i+10)=0;
end
if mod(i,10)~=1
R(i,i-1)=0;
end
if mod(i,10)~=0;
R(i,i+1)=0;
end
end
R(24,34)=0;R(25,35)=0;R(26,36)=0;
R(34,24)=0;R(35,25)=0;R(36,26)=0;
R(34,35)=0;R(35,36)=0;R(35,34)=0;R(36,35)=0;
R(35,45)=0;R(45,35)=0;
R(45,55)=100;R(55,45)=0;
% reinforcement learning parameters
gamma=0.9;
q=zeros(size(R)); % q matrix
q1=ones(size(R))*inf; % previous q matrix
count=0;
% visualize obstacle
axis([0,10,0,6]);
hold on;
plot([0,3],[3,3],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([6,10],[3,3],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([3,3],[2,3],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([6,6],[2,3],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([4,4],[0,2],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([5,5],[0,2],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([3,4],[2,2],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([5,6],[2,2],'g','linewidth',2);
% intial state
y=randperm(30);
state=y(1);
% q learning
tic
for episode=0:50000
qma=max(q(state,:));
if qma~=0
x=find(q(state,:)==qma);
else
x=find(R(state,:)>=0);
end
% choose action
if size(x,1)>0
x1=RandomPermutation(x);
x1=x1(1);
end
% update q matrix
qMax=max(q,[],2);
q(state,x1)=R(state,x1)+gamma*qMax(x1);
Y(i)=5.5-floor((x1-1)/10);
X(i)=0.5+rem(x1-1,10);
% visualization
A=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)-0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
B=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)+0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
C=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)-0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
D=plot([X(i)+0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
pause(0.05);
% break if converged: small deviation on q for 1000 consecutive
if sum(sum(abs(q1-q)))<0.0001 && sum(sum(q))>190
if count>500,
episode % report last episode
break % for
else
count=count+1; % set counter if deviation of q is small
end
else
q1=q;
count=0;
end
if(R(state,x1)==100)
y=randperm(30);
state=y(1);
pause(0.4);
else
state=x1;
end
delete(A);
delete(B);
delete(C);
delete(D);
end
toc
%normalization
g=max(max(q));
if g>0,
q=100*q/g;
end
需要配合函数使用,函数 RandomPermutation.m 在参考链接中给出,原作者:
Copyright Kardi Teknomo(c) 2005
(http://people.revoledu.com/kardi/)
这里一并给出
function y=RandomPermutation(A)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% return random permutation of matrix A
% unlike randperm(n) that give permutation of integer 1:n only,
% RandomPermutation rearrange member of matrix A randomly
% This function is useful for MonteCarlo Simulation,
% Bootstrap sampling, game, etc.
%
% Copyright Kardi Teknomo(c) 2005
% (http://people.revoledu.com/kardi/)
%
% example: A = [ 2, 1, 5, 3]
% RandomPermutation(A) may produce [ 1, 5, 3, 2] or [ 5, 3, 2, 3]
%
% example:
% A=magic(3)
% RandomPermutation(A)
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
[r,c]=size(A);
b=reshape(A,r*c,1); % convert to column vector
x=randperm(r*c); % make integer permutation of similar array as key
w=[b,x']; % combine matrix and key
d=sortrows(w,2); % sort according to key
y=reshape(d(:,1),r,c); % return back the matrix
--------------------- 2019-4-24 更新 ----------------------------------
感谢scxDAWN的提醒,示意图里面画训练结束后最终轨迹的程序附在下面,蓝线表示走过的轨迹,如果迭代次数不够多,可能会出现不太合理的轨迹,如果只希望看最终结果而不关心过程,可以把之前 q-learning 训练程序中画图的部分都去掉,可以很快得到最终收敛的结果,然后用下面程序检验训练效果即可:
axis([0,10,0,6]);
%grid on;
%axis equal;
hold on;
plot([0,3],[3,3],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([6,10],[3,3],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([3,3],[2,3],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([6,6],[2,3],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([4,4],[0,2],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([5,5],[0,2],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([3,4],[2,2],'g','linewidth',2);
plot([5,6],[2,2],'g','linewidth',2);
st=randperm(30);
s=st(1);
%s=28;
i=1;
while s~=55
%商
Y(i)=5.5-floor((s-1)/10);
%余数
X(i)=0.5+rem(s-1,10);
%plot(X,Y,'*');
A=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)-0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
B=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)+0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
C=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)-0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
D=plot([X(i)+0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
pause(0.2);
if i>1;
plot([X(i-1),X(i)],[Y(i-1),Y(i)],'b-','linewidth',2);
end
qm=max(q(s,:));
if qm~=0
ac=find(q(s,:)==qm);
else
ac=find(R(s,:)>=0);
end
if size(ac,2)>1
act=RandomPermutation(ac);
act=act(1);
else
act=ac;
end
delete(A);
delete(B);
delete(C);
delete(D);
s=act;
i=i+1;
end
%商
Y(i)=5.5-floor((s-1)/10);
%余数
X(i)=0.5+rem(s-1,10);
A=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)-0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
B=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)+0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
C=plot([X(i)-0.5,X(i)-0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
D=plot([X(i)+0.5,X(i)+0.5],[Y(i)-0.5,Y(i)+0.5],'r-','linewidth',2);
if i>1;
plot([X(i-1),X(i)],[Y(i-1),Y(i)],'b-','linewidth',2);
end
最后
以上就是优美大山最近收集整理的关于Q学习(Q learning) 强化学习的简单例子 Matlab实现 可视化的全部内容,更多相关Q学习(Q内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复