1 内容介绍
Hough变换在图像处理中占有重要地位,是一种检测曲线的有效方法.但使用传统的Hough变换来检测椭圆具有存储空间大计算时间长的缺点.为此提出了一种新的基于Hough变换的椭圆轮廓检测方法,利用椭圆的斜率特性,降低了Hough参数空间的维度,提高了运算运效率,并能良好地对图像中多个椭圆进行检测.
2 仿真代码
function [ellipses, L, posi] = ellipseDetectionByArcSupportLSs(I, Tac, Tr, specified_polarity)
%input:
% I: input image
% Tac: elliptic angular coverage (completeness degree)
% Tr: ratio of support inliers on an ellipse
%output:
% ellipses: N by 5. (center_x, center_y, a, b, phi)
% reference:
% 1、von Gioi R Grompone, Jeremie Jakubowicz, Jean-
% Michel Morel, and Gregory Randall, “Lsd: a fast line
% segment detector with a false detection control.,” IEEE
% transactions on pattern analysis and machine intelligence,
% vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 722–732, 2010.
angleCoverage = Tac;%default 165°
Tmin = Tr;%default 0.6
unit_dis_tolerance = 2; %max([2, 0.005 * min([size(I, 1), size(I, 2)])]);%内点距离的容忍差小于max(2,0.5%*minsize)
normal_tolerance = pi/9; %法线容忍角度20°= pi/9
t0 = clock;
if(size(I,3)>1)
I = rgb2gray(I);
[candidates, edge, normals, lsimg] = generateEllipseCandidates(I, 2, specified_polarity);%1,sobel; 2,canny
else
[candidates, edge, normals, lsimg] = generateEllipseCandidates(I, 2, specified_polarity);%1,sobel; 2,canny
end
% figure; imshow(edge);
% return;
% subplot(1,2,1);imshow(edge);%show edge image
% subplot(1,2,2);imshow(lsimg);%show LS image
t1 = clock;
disp(['the time of generating ellipse candidates:',num2str(etime(t1,t0))]);
candidates = candidates';%ellipse candidates matrix Transposition
if(candidates(1) == 0)%表示没有找到候选圆
candidates = zeros(0, 5);
end
posi = candidates;
normals = normals';%norams matrix transposition
[y, x]=find(edge);%找到非0元素的行(y)、列(x)的索引
% ellipses = [];L=[];
% return;
[mylabels,labels, ellipses] = ellipseDetection(candidates ,[x, y], normals, unit_dis_tolerance, normal_tolerance, Tmin, angleCoverage, I);%后四个参数 0.5% 20° 0.6 180°
disp('-----------------------------------------------------------');
disp(['running time:',num2str(etime(clock,t0)),'s']);
% labels
% size(labels)
% size(y)
warning('on', 'all');
L = zeros(size(I, 1), size(I, 2));%创建与输入图像I一样大小的0矩阵L
L(sub2ind(size(L), y, x)) = mylabels;%labels,长度等于edge_pixel_n x 1,如果第i个边缘点用于识别了第j个圆,则该行标记为j,否则为0。大小 edge_pixel_n x 1;现在转化存到图像中,在图像中标记
% figure;imshow(L==2);%LLL
% imwrite((L==2),'D:Graduate Design画图edge_result.jpg');
end
%% ================================================================================================================================
%函数1
%输入
%candidates: ncandidates x 5
%points: 边缘像素点的坐标(x,y),nx2,n为总共的边缘点数
%lineLabels: 对相应的坐标(xi,yi)标记,对应靠近相应的线段,nx1,未标记则为0
%lines: 线段参数,-B,A,xmid,ymid,其中(xmid,ymid)对应相应的线段中点,mx4,m为总共m条线段
%输出
%labels: 长度等于n x 1,如果第i个边缘点用于识别了第j个圆,则该行标记为j,否则为0。大小 n x 1
%C: 识别出来的对称中心,长半轴,短半轴,和倾角,每一行格式是(x,y,a,b,phi)
function [mylabels,labels, ellipses] = ellipseDetection(candidates, points, normals, distance_tolerance, normal_tolerance, Tmin, angleCoverage, E)
labels = zeros(size(points, 1), 1);
mylabels = zeros(size(points, 1), 1);%测试
ellipses = zeros(0, 5);
%% 对于显著性很大的候选椭圆,且满足极其严格要求,直接检测出来,SE(salient ellipses);同时对~SE按照goodness进行pseudo order
goodness = zeros(size(candidates, 1), 1);%初始化时为0,当检测到显著椭圆时直接提取,相应位置的goodness(i) = -1标记。
for i = 1 : size(candidates,1)
%ellipse circumference is approximate pi * (1.5*sum(ellipseAxes)-sqrt(ellipseAxes(1)*ellipseAxes(2))
ellipseCenter = candidates(i, 1 : 2);
ellipseAxes = candidates(i, 3:4);
tbins = min( [ 180, floor( pi * (1.5*sum(ellipseAxes)-sqrt(ellipseAxes(1)*ellipseAxes(2)) ) * Tmin ) ] );%选分区
%ellipse_normals = computePointAngle(candidates(i,:),points);
%inliers = find( labels == 0 & dRosin_square(candidates(i,:),points) <= 1 ); % +-1个像素内找支持内点
%加速计算,只挑出椭圆外接矩形内的边缘点(椭圆中的长轴a>b),s_dx存储的是相对points的索引
s_dx = find( points(:,1) >= (ellipseCenter(1)-ellipseAxes(1)-1) & points(:,1) <= (ellipseCenter(1)+ellipseAxes(1)+1) & points(:,2) >= (ellipseCenter(2)-ellipseAxes(1)-1) & points(:,2) <= (ellipseCenter(2)+ellipseAxes(1)+1));
inliers = s_dx(dRosin_square(candidates(i,:),points(s_dx,:)) <= 1);
ellipse_normals = computePointAngle(candidates(i,:),points(inliers,:));
p_dot_temp = dot(normals(inliers,:), ellipse_normals, 2); %加速后ellipse_normals(inliers,:)改为加速后ellipse_normals
p_cnt = sum(p_dot_temp>0);%无奈之举,做一次极性统计,当改为C代码时注意拟合圆时内点极性的选取问题
if(p_cnt > size(inliers,1)*0.5)
%极性相异,也就是内黑外白
%ellipse_polarity = -1;
inliers = inliers(p_dot_temp>0 & p_dot_temp >= 0.923879532511287 );%cos(pi/8) = 0.923879532511287, 夹角小于22.5°
else
%极性相同,也就是内白外黑
%ellipse_polarity = 1;
inliers = inliers(p_dot_temp<0 & (-p_dot_temp) >= 0.923879532511287 );
end
inliers = inliers(takeInliers(points(inliers, :), ellipseCenter, tbins));
support_inliers_ratio = length(inliers)/floor( pi *
% size(labels)
% size(dRosin_square(list(i,:),points) )
% ppp = (dRosin_square(list(i,:),points) <= 4*distance_tolerance_square)
% if( i == 11 && angleCoverage == 165)
% drawEllipses(list(i,:)',E);
% end
%此处非常重要,距离应该要比之前的更狭小的范围寻找内点
%ellipse_normals = computePointAngle(list(i,:),points);
%inliers = find(labels == 0 & (dRosin_square(list(i,:),points) <= distance_tolerance_square) ); % 2.25 * distance_tolerance_square , 4*distance_tolerance_square.
%加速计算,只挑出椭圆外接矩形内的边缘点(椭圆中的长轴a>b),i_dx存储的是相对在points中的索引.
i_dx = find( points(:,1) >= (ellipseCenter(1)-ellipseAxes(1)-distance_tolerance) & points(:,1) <= (ellipseCenter(1)+ellipseAxes(1)+distance_tolerance) & points(:,2) >= (ellipseCenter(2)-ellipseAxes(1)-distance_tolerance) & points(:,2) <= (ellipseCenter(2)+ellipseAxes(1)+distance_tolerance));
inliers = i_dx(labels(i_dx) == 0 & (dRosin_square(list(i,:),points(i_dx,:)) <= distance_tolerance_square) );
ellipse_normals = computePointAngle(list(i,:),points(inliers,:));%ellipse_normals长度与inliers长度一致
% if( i == 11 && angleCoverage == 165)
% testim = zeros(size(E,1),size(E,2));
% testim(sub2ind(size(E),points(inliers,2),points(inliers,1))) = 1;
% figure;imshow(testim);
% end
p_dot_temp = dot(normals(inliers,:), ellipse_normals, 2);
p_cnt = sum(p_dot_temp>0);%无奈之举,做一次极性统计,当改为C代码时注意拟合圆时内点极性的选取问题
if(p_cnt > size(inliers,1)*0.5)
%极性相异,也就是内黑外白
ellipse_polarity = -1;
inliers = inliers(p_dot_temp>0 & p_dot_temp >= 0.923879532511287 );%cos(pi/8) = 0.923879532511287, 夹角小于22.5°
else
%极性相同,也就是内白外黑
ellipse_polarity = 1;
inliers = inliers(p_dot_temp<0 & (-p_dot_temp) >= 0.923879532511287 );
end
% if( i == 11 && angleCoverage == 165)
% testim = zeros(size(E,1),size(E,2));
% testim(sub2ind(size(E),points(inliers,2),points(inliers,1))) = 1;
% figure;imshow(testim);
% end
inliers2 = inliers;
inliers3 = 0;
%=================================================================================================================================================================
%连通域分析,inliers为存的是在边缘点的行下标
% size(points)
% size(inliers)
% size(points(inliers, :))
% size(takeInliers(points(inliers, :), circleCenter, tbins))
%连通域分析,得到有效的内点,内点提纯,也就是inliers中进一步产出有效的inliers,个数会减少,大小inlier_n2 x 1。注意注意:inliers中存的是在points中的行下标
inliers = inliers(takeInliers(points(inliers, :), ellipseCenter, tbins));
% if( i == 11 && angleCoverage == 165)
% testim = zeros(size(E,1),size(E,2));
% testim(sub2ind(size(E),points(inliers,2),points(inliers,1))) = 1;
% figure;imshow(testim);
% end
[new_ellipse,new_info] = fitEllipse(points(inliers,1),points(inliers,2));
% if( i == 11 && angleCoverage == 165)
% drawEllipses(new_ellipse',E);
% end
% if angleLoop == 2 %mycode
% dispimg = zeros(size(E,1),size(E,2),3);
% dispimg(:,:,1) = E.*255;%边缘提取出来的是0-1图像
% dispimg(:,:,2) = E.*255;
% dispimg(:,:,3) = E.*255;
% for i = 1:length(inliers)
% dispimg(points(inliers(i),2),points(inliers(i),1),:)=[0 0 255];
% end
% dispimg = drawCircle(dispimg,[newa newb],newr);
% figure;
% imshow(uint8(dispimg));
% end
if (new_info == 1)%如果是用最小二乘法拟合的而得出的结果
%新对称中心和老对称中心的距离小于4*distance_tolerance, (a,b)的距离也是小于4*distance_tolerance,倾角phi小于0.314159265358979 = 0.1pi = 18°,因为新拟合出来的不能和原来的椭圆中心差很多,
if ( (((new_ellipse(1) - ellipseCenter(1))^2 + (new_ellipse(2) - ellipseCenter(2))^2 ) <= 16 * distance_tolerance_square) ...
&& (((new_ellipse(3) - ellipseAxes(1))^2 + (new_ellipse(4) - ellipseAxes(2))^2 ) <= 16 * distance_tolerance_square) ...
&& (abs(new_ellipse(5) - ellipsePhi) <= 0.314159265358979) )
ellipse_normals = computePointAngle(new_ellipse,points);
%重新做一次找内点,连通性分析的内点提纯,这次的新的内点会用于后面的完整度分析
%newinliers = find( (labels == 0) & (dRosin_square(new_ellipse,points) <= distance_tolerance_square) ...
% & ((dot(normals, ellipse_normals, 2)*(-ellipse_polarity)) >= 0.923879532511287) ); % (2*distance_tolerance)^2, cos(pi/8) = 0.923879532511287, 夹角小于22.5°
%加速计算,只挑出椭圆外接矩形内的边缘点(椭圆中的长轴a>b),i_dx存储的是相对在points中的索引
i_dx = find( points(:,1) >= (new_ellipse(1)-new_ellipse(3)-distance_tolerance) & points(:,1) <= (new_ellipse(1)+new_ellipse(3)+distance_tolerance) & points(:,2) >= (new_ellipse(2)-new_ellipse(3)-distance_tolerance) & points(:,2) <= (new_ellipse(2)+new_ellipse(3)+distance_tolerance));
ellipse_normals = computePointAngle(new_ellipse,points(i_dx,:));%ellipse_normals长度与i_dx长度一致
newinliers = i_dx(labels(i_dx) == 0 & (dRosin_square(new_ellipse,points(i_dx,:)) <= distance_tolerance_square & ((dot(normals(i_dx,:), ellipse_normals, 2)*(-ellipse_polarity)) >= 0.923879532511287) ) );
newinliers = newinliers(takeInliers(points(newinliers, :), new_ellipse(1:2), tbins));
if (length(newinliers) >= length(inliers))
%a = newa; b = newb; r = newr; cnd = newcnd;
inliers = newinliers;
inliers3 = newinliers;%my code,just test
%======================================================================
%二次拟合
%[newa, newb, newr, newcnd] = fitCircle(points(inliers, :));
[new_new_ellipse,new_new_info] = fitEllipse(points(inliers,1),points(inliers,2));
if(new_new_info == 1)
new_ellipse = new_new_ellipse;
end
%=======================================================================
end
end
else
new_ellipse = list(i,:); %candidates
end
%内点数量大于圆周上的一定比例,Tmin为比例阈值
% length(inliers)
% floor( pi * (1.5*sum(new_ellipse(3:4))-sqrt(new_ellipse(3)*new_ellipse(4))) * Tmin )
if (length(inliers) >= floor( pi * (1.5*sum(new_ellipse(3:4))-sqrt(new_ellipse(3)*new_ellipse(4))) * Tmin ))
convergence(i, :) = new_ellipse;
%与之前的圆心和半径参数几乎一致,重复了,因此把这个圆淘汰(排在最开头的和它重复的圆不一定会被淘汰)
if (any( (sqrt(sum((convergence(1 : i - 1, 1 : 2) - repmat(new_ellipse(1:2), i - 1, 1)) .^ 2, 2)) <= distance_tolerance) ...
& (sqrt(sum((convergence(1 : i - 1, 3 : 4) - repmat(new_ellipse(3:4), i - 1, 1)) .^ 2, 2)) <= distance_tolerance) ...
& (abs(convergence(1 : i - 1, 5) - repmat(new_ellipse(5), i - 1, 1)) <= 0.314159265358979) ))
validCandidates(i) = false;
end
%如果内点在圆周上满足angleCoverage的完整度
%completeOrNot = isComplete(points(inliers, :), new_ellipse(1:2), tbins, angleCoverage);
completeOrNot = calcuCompleteness(points(inliers,:),new_ellipse(1:2),tbins) >= angleCoverage;
if (new_info == 1 && new_ellipse(3) < maxSemiMajor && new_ellipse(4) < maxSemiMinor && completeOrNot )
%且满足和其它圆参数大于distance_tolerance,也就是指和其它圆是不同的
if (all( (sqrt(sum((ellipses(:, 1 : 2) - repmat(new_ellipse(1:2), size(ellipses, 1), 1)) .^ 2, 2)) > distance_tolerance) ...
| (sqrt(sum((ellipses(:, 3 : 4) - repmat(new_ellipse(3:4), size(ellipses, 1), 1)) .^ 2, 2)) > distance_tolerance) ...
| (abs(ellipses(:, 5) - repmat(new_ellipse(5), size(ellipses, 1), 1)) >= 0.314159265358979 ) )) %0.1 * pi = 0.314159265358979 = 18°
%size(inliers)
%line_normal = pca(points(inliers, :));%得到2x2的pca变换矩阵,因此第二列便是由内点统计出的梯度
%line_normal = line_normal(:, 2)';%取出第二列并且变为1 x 2 的行向量
%line_point = mean(points(inliers, :));%内点取平均
%防止数据点过于集中
%if (sum(abs(dot(points(inliers, :) - repmat(line_point, length(inliers), 1), repmat(line_normal, length(inliers), 1), 2)) <= distance_tolerance & radtodeg(real(acos(abs(dot(normals(inliers, :), repmat(line_normal, length(inliers), 1), 2))))) <= normal_tolerance) / length(inliers) < 0.8)
labels(inliers) = size(ellipses, 1) + 1;%标记,这些内点已经用过了,构成了新检测到圆周
%==================================================================
if(all(inliers3) == 1)
mylabels(inliers3) = size(ellipses,1) + 1; %显示拟合出圆时所用的内点 SSS
end
%==================================================================
ellipses = [ellipses; new_ellipse];%将该圆参数加入进去
validCandidates(i) = false;%第i个候选圆检测完毕
%disp([angleCoverage,i]);
%drawEllipses(new_ellipse',E);
%end
end
end
else
validCandidates(i) = false;%其它情况,淘汰该候选圆
end
end %for
end%fun
%% ================================================================================================================================
%函数4
%圆的最小二乘法拟合(此处可以改用快速圆拟合方法)
%输入:
%points: 联通性分析后的提纯后的内点,设大小为 fpn x 2,格式(xi,yi)
%输出:
%a :拟合后的圆心横坐标x
%b :拟合后的圆心纵坐标y
%c :拟合后的圆心半径r
%cnd :1表示数据代入方程后是奇异的,直接用平均值估计;0表示数据是用最小二乘法拟合的
function [a, b, r, cnd] = fitCircle(points)
%{
A = [sum(points(:, 1)), sum(points(:, 2)), size(points, 1); sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 2)), sum(points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2)), sum(points(:, 2)); sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1)), sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 2)), sum(points(:, 1))];
%用最小二乘法时,A'A正则矩阵如果接近0,则意味着方程组线性,求平均值即可
if (abs(det(A)) < 1e-9)
cnd = 1;
a = mean(points(:, 1));
b = mean(points(:, 2));
r = min(max(points) - min(points));
return;
end
cnd = 0;
B = [-sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1) + points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2)); -sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1) .* points(:, 2) + points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2)); -sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1) + points(:, 1) .* points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2))];
t = A B;
a = -0.5 * t(1);
b = -0.5 * t(2);
r = sqrt((t(1) .^ 2 + t(2) .^ 2) / 4 - t(3));
%}
A = [sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1)),sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 2)),sum(points(:, 1)); sum(points(:, 1) .* points(:, 2)),sum(points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2)),sum(points(:, 2)); sum(points(:, 1)),sum(points(:, 2)),size(points, 1)];
%用最小二乘法时,A'A正则矩阵如果接近0,则意味着方程组线性,求平均值即可
if (abs(det(A)) < 1e-9)
cnd = 1;
a = mean(points(:, 1));
b = mean(points(:, 2));
r = min(max(points) - min(points));
return;
end
cnd = 0;
B = [sum(-points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1) - points(:, 1) .* points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2));sum(-points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1) .* points(:, 2) - points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2)); sum(-points(:, 1) .* points(:, 1) - points(:, 2) .* points(:, 2))];
t = A B;
a = -0.5 * t(1);
b = -0.5 * t(2);
r = sqrt((t(1) .^ 2 + t(2) .^ 2) / 4 - t(3));
end
%% ================================================================================================================================
%函数5
%输入
%x : 连通性分析后,满足数量2piRT的提纯后的内点(x,y),将参与到完整度分析环节.num x 2
%center: 圆心(x,y) 1 x 2
%tbins :分区总数
%angleCoverage: 需要达到的圆完整度
%输出
%result: true or false,表示该圆完整与不完整
%longest_inliers:
function [result, longest_inliers] = isComplete(x, center, tbins, angleCoverage)
[theta, ~] = cart2pol(x(:, 1) - center(1), x(:, 2) - center(2));%theta为(-pi,pi)的角度,num x 1
tmin = -pi; tmax = pi;
tt = round((theta - tmin) / (tmax - tmin) * tbins + 0.5);%theta的第i个元素落在第j个bin,则tt第i行标记为j,大小num x 1
tt(tt < 1) = 1; tt(tt > tbins) = tbins;
h = histc(tt, 1 : tbins);
longest_run = 0;
start_idx = 1;
end_idx = 1;
while (start_idx <= tbins)
if (h(start_idx) > 0)%找到bin中vote第一个大于0的
end_idx = start_idx;
while (start_idx <= tbins && h(start_idx) > 0)%直到bin第一个小于0的
start_idx = start_idx + 1;
end
inliers = [end_idx, start_idx - 1];%此区间为连通区域
inliers = find(tt >= inliers(1) & tt <= inliers(2));%在tt中找到落在此区间的内点的索引
run = max(theta(inliers)) - min(theta(inliers));%角度差
if (longest_run < run)%此举是为了找到最大的完整的且连通的跨度
longest_run = run;
longest_inliers = inliers;
end
end
start_idx = start_idx + 1;
end
if (h(1) > 0 && h(tbins) > 0)%如果第一个bin和最后一个bin都大于0,有可能最大连通区域是头尾相连的这种情况
start_idx = 1;
while (start_idx < tbins && h(start_idx) > 0)%找到bin中vote第一个大于0的
start_idx = start_idx + 1;
end
end_idx = tbins;%end_idx直接从最尾部开始往回找
while (end_idx > 1 && end_idx > start_idx && h(end_idx) > 0)
end_idx = end_idx - 1;
end
inliers = [start_idx - 1, end_idx + 1];
run = max(theta(tt <= inliers(1)) + 2 * pi) - min(theta(tt >= inliers(2)));
inliers = find(tt <= inliers(1) | tt >= inliers(2));
if (longest_run < run)
longest_run = run;
longest_inliers = inliers;
end
end
%最大的连通的跨度大于了angleCoverage,或者虽然最大连通跨度小于,但完整度足够了
longest_run_deg = radtodeg(longest_run);
h_greatthanzero_num = sum(h>0);
result = longest_run_deg >= angleCoverage || h_greatthanzero_num * (360 / tbins) >= min([360, 1.2*angleCoverage]); %1.2 * angleCoverage
end
function [completeness] = calcuCompleteness(x, center, tbins)
[theta, ~] = cart2pol(x(:, 1) - center(1), x(:, 2) - center(2));%theta为(-pi,pi)的角度,num x 1
tmin = -pi; tmax = pi;
tt = round((theta - tmin) / (tmax - tmin) * tbins + 0.5);%theta的第i个元素落在第j个bin,则tt第i行标记为j,大小num x 1
tt(tt < 1) = 1; tt(tt > tbins) = tbins;
h = histc(tt, 1 : tbins);
h_greatthanzero_num = sum(h>0);
completeness = h_greatthanzero_num*(360 / tbins);
end
%% ================================================================================================================================
%函数6
%连通性分析,对圆周上的内点进行提纯
%输入
%x:椭圆周上的内点(x,y),设为inlier_n x 2
%center:一个椭圆的中心(x,y) 1x2
%tbins: 分区 = min( 180 , pi*(1.5*(a+b)-sqrt(a*b)) )
%输出
%idx:为与x一样长的,inlier_n x 1的logical向量,返回有效的满足一定连通长度的内点,对应位置有效则为1,否则为0
function idx = takeInliers(x, center, tbins)
[theta, ~] = cart2pol(x(:, 1) - center(1), x(:, 2) - center(2));%得到[-pi,pi]的方位角,等价于 theta = atan2(x(:, 2) - center(2) , x(:, 1) - center(1));
tmin = -pi; tmax = pi;
tt = round((theta - tmin) / (tmax - tmin) * tbins + 0.5);%将内点分区到[1 tbins]
tt(tt < 1) = 1; tt(tt > tbins) = tbins;
h = histc(tt, 1 : tbins);%h为直方图[1 tbins]的统计结果
mark = zeros(tbins, 1);
compSize = zeros(tbins, 1);
nComps = 0;
queue = zeros(tbins, 1);
du = [-1, 1];
for i = 1 : tbins
if (h(i) > 0 && mark(i) == 0)%如果落在第i个分区内的值大于0,且mark(i)为0
nComps = nComps + 1;
mark(i) = nComps;%标记第nComps个连通区域
front = 1; rear = 1;
queue(front) = i;%将该分区加入队列,并以此开始任务
while (front <= rear)
u = queue(front);
front = front + 1;
for j = 1 : 2
v = u + du(j);
if (v == 0)
v = tbins;
end
if (v > tbins)
v = 1;
end
if (mark(v) == 0 && h(v) > 0)
rear = rear + 1;
queue(rear) = v;
mark(v) = nComps;%标记第nComps个连通区域
end
end
end
compSize(nComps) = sum(ismember(tt, find(mark == nComps)));%得到构成连通域为nComps的内点数量
end
end
compSize(nComps + 1 : end) = [];
maxCompSize = max(compSize);
validComps = find(compSize >= maxCompSize * 0.1 & compSize > 10);%大于等于最大连通长度的0.1倍的连通区域是有效的
validBins = find(ismember(mark, validComps));%有效的分区
idx = ismember(tt, validBins);%有效的内点
end
%% compute the points' normals belong to an ellipse, the normals have been already normalized.
%param: [x0 y0 a b phi].
%points: [xi yi], n x 2
function [ellipse_normals] = computePointAngle(ellipse, points)
%convert [x0 y0 a b phi] to Ax^2+Bxy+Cy^2+Dx+Ey+F = 0
a_square = ellipse(3)^2;
b_square = ellipse(4)^2;
sin_phi = sin(ellipse(5));
cos_phi = cos(ellipse(5));
sin_square = sin_phi^2;
cos_square = cos_phi^2;
A = b_square*cos_square+a_square*sin_square;
B = (b_square-a_square)*sin_phi*cos_phi*2;
C = b_square*sin_square+a_square*cos_square;
D = -2*A*ellipse(1)-B*ellipse(2);
E = -2*C*ellipse(2)-B*ellipse(1);
% F = A*ellipse(1)^2+C*ellipse(2)^2+B*ellipse(1)*ellipse(2)-(ellipse(3)*ellipse(4)).^2;
% A = A/F;
% B = B/F;
% C = C/F;
% D = D/F;
% E = E/F;
% F = 1;
%calculate points' normals to ellipse
angles = atan2(C*points(:,2)+B/2*points(:,1)+E/2, A*points(:,1)+B/2*points(:,2)+D/2);
ellipse_normals = [cos(angles),sin(angles)];
end
%% param为[x0 y0 a b Phi],1 x 5 或者 5 x 1
%points为待计算rosin distance的点,每一行为(xi,yi),size是 n x 2
%dmin为输出估计距离的平方.
%调用注意,当a = b时,也就是椭圆退化成圆时,dmin会变成无穷大NAN,不能用此函数
function [dmin]= dRosin_square(param,points)
ae2 = param(3).*param(3);
be2 = param(4).*param(4);
x = points(:,1) - param(1);
y = points(:,2) - param(2);
xp = x*cos(-param(5))-y*sin(-param(5));
yp = x*sin(-param(5))+y*cos(-param(5));
fe2 = ae2-be2;
X = xp.*xp;
Y = yp.*yp;
delta = (X+Y+fe2).^2-4*fe2*X;
A = (X+Y+fe2-sqrt(delta))/2;
ah = sqrt(A);
bh2 = fe2-A;
term = A*be2+ae2*bh2;
xi = ah.*sqrt(ae2*(be2+bh2)./term);
yi = param(4)*sqrt(bh2.*(ae2-A)./term);
d = zeros(size(points,1),4);%n x 4
d(:,1) = (xp-xi).^2+(yp-yi).^2;
d(:,2) = (xp-xi).^2+(yp+yi).^2;
d(:,3) = (xp+xi).^2+(yp-yi).^2;
d(:,4) = (xp+xi).^2+(yp+yi).^2;
dmin = min(d,[],2); %返回距离的平方
%[dmin, ii] = min(d,[],2); %返回距离的平方
% for jj = 1:length(dmin)
% if(ii(jj) == 1)
% xi(jj) = xi(jj);
% yi(jj) = yi(jj);
% elseif (ii(jj) == 2)
% xi(jj) = xi(jj);
% yi(jj) = -yi(jj);
% elseif (ii(jj) == 3)
% xi(jj) = -xi(jj);
% yi(jj) = yi(jj);
% elseif(ii(jj) == 4)
% xi(jj) = -xi(jj);
% yi(jj) = -yi(jj);
% end
% end
%
% xi = xi*cos(param(5))-yi*sin(param(5));
% yi = xi*sin(param(5))+yi*cos(param(5));
%
% testim = zeros(300,300);
% testim(sub2ind([300 300],uint16(yi+param(2)),uint16(xi+param(1)))) = 1;
% figure;imshow(uint8(testim).*255);
end
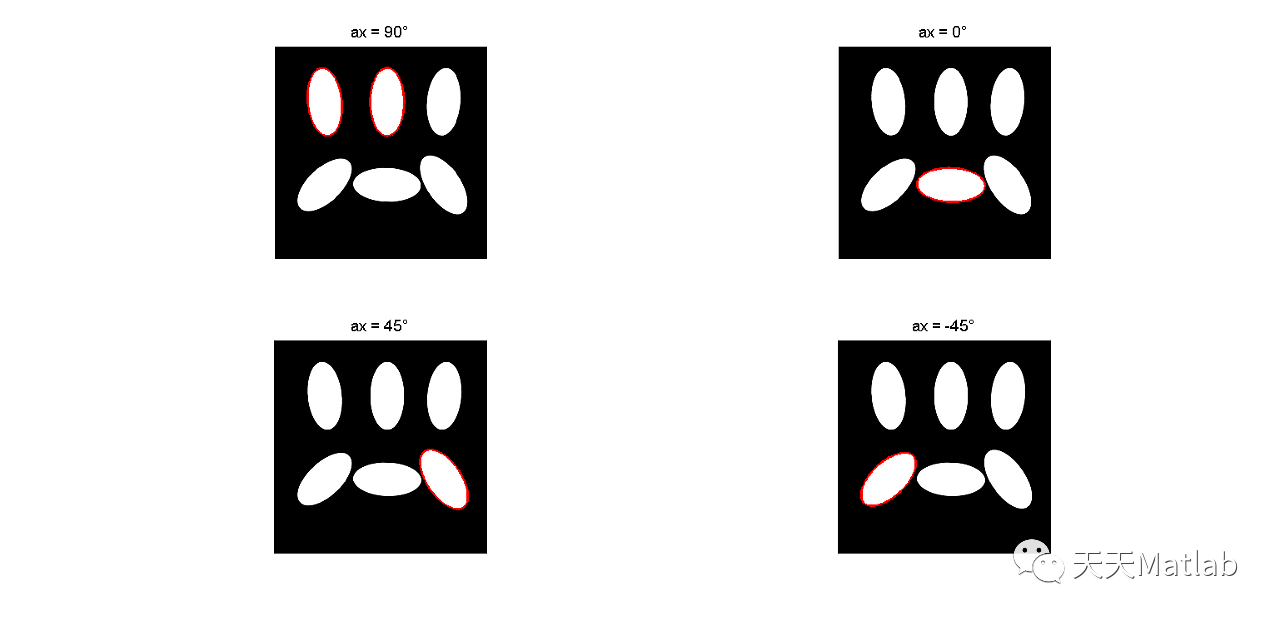
3 运行结果
4 参考文献
[1]张治斌, 刘桂玲, and 程玉华. "基于计算机视觉的图像检测方案设计." 数字技术与应用 3(2012):2.
[2]屈稳太. 基于弦中点Hough变换的椭圆检测方法[J]. 浙江大学学报:工学版, 2005, 39(8):5.
博主简介:擅长智能优化算法、神经网络预测、信号处理、元胞自动机、图像处理、路径规划、无人机等多种领域的Matlab仿真,相关matlab代码问题可私信交流。
部分理论引用网络文献,若有侵权联系博主删除。
最后
以上就是寒冷自行车最近收集整理的关于【图像检测】基于计算机视觉实现椭圆检测附matlab代码的全部内容,更多相关【图像检测】基于计算机视觉实现椭圆检测附matlab代码内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复