verilog的设计文件:
module BPSK(
input clk,
input [7:0] indata,
output reg [15 : 0] myout,
output wire [15:0] fir_out_my
);
wire m_axis_data_tvalid;
wire s_axis_data_tready;
reg [9 : 0] addra = 0;
wire [19 : 0] outdata;
fir_compiler_0 fir_compiler_0 (
.aclk(clk), // input wire aclk 输入时钟
.s_axis_data_tvalid(1), // input wire s_axis_data_tvalid
.s_axis_data_tready(s_axis_data_tready), // output wire s_axis_data_tready
.s_axis_data_tdata(indata), // input wire [7 : 0] s_axis_data_tdata(输入数据) 8位
.m_axis_data_tvalid(m_axis_data_tvalid), // output wire m_axis_data_tvalid
.m_axis_data_tdata(fir_out_my) // output wire [15 : 0] fir_out_my(输出数据16位)
);
/*
aresetn:复位引脚,低电平复位FIR IP核;
aclk:时钟引脚,工程中输入500MHz时钟信号;
s_axis_data_tdata:输入采样数据;
s_axis_data_tready:1 表示IP核准备好接收采样数据;
s_axis_data_tvalid:1 表示s_axis_data_tdata输入的采样数据有效;
fir_out_my:输出滤波后的数据;
m_axis_data_tvalid:1 表示fir_out_my输出的数据有效。
*/
//生成正弦波
wire [9 : 0] sin_out;
blk_mem_gen_0 blk_mem_gen_0 (
.clka(clk), // input wire clka
.ena(1), // input wire ena
.addra(addra), // input wire [9 : 0] addra
.douta(sin_out) // output wire [9 : 0]
);
//乘法器
sinmult sinmult (
.CLK(clk), // input wire CLK
.A(fir_out_my), // input wire [9 : 0] A
.B(sin_out), // input wire [9 : 0] B
.P(outdata) // output wire [19 : 0] P
);
always@(posedge clk)begin
addra <= addra + 256;
myout <= outdata[17:2];
end
endmodule
tb文件:
`timescale 1ns / 1ps
// fclk = 500MHZ
module tb();
reg [7:0] indata = 7'b0;
wire [15 : 0] myout;
reg clk;
reg [5-1:0] sps = 5'd0;
wire [15:0] fir_out_my;
reg [1-1:0] DataMem [0:8000-1];
reg [13-1:0] AddrMem = 13'd0; //8064
BPSK BPSK(
.clk ( clk ),
.indata ( indata ),
.myout ( myout ),
.fir_out_my(fir_out_my)
);
always #1 clk = ~ clk;
integer dout_file1;
initial begin
clk = 0;
$readmemh("../../../../SimData/CSV/FrmBin.txt", DataMem);
dout_file1=$fopen("../../../../SimData/CSV/rcos.txt"); //打开所创建的文件
if(dout_file1 == 0)begin
$display ("can not open the file!"); //创建文件失败,显示can not open the file!
$stop;
end
end
always@(posedge clk)begin
//$fdisplay(dout_file1,"%d",$signed(myout));
$fdisplay(dout_file1,"%d", $signed(fir_out_my));
if(sps==0)begin
indata <= {5'd0,DataMem[AddrMem],1'b1};
sps <= sps + 1;
AddrMem <= AddrMem + 1;
end
else if(sps<15)begin
indata <= 7'd0;
sps <= sps + 1;
end
else if(sps == 15)begin
indata <= 7'd0;
sps <= 0;
end
end
endmodule
verilog的fir实现的根升余弦滤波器的输出与matlab的根升余弦滤波器输出的代码:
clc;
close all;
clear;
b = rcosdesign(0.35,6,16,'sqrt');
bb = round(255.*b./max(b));
fs = 500*10e6;
fc = fs/4;
msg_source = load('D:vivado_documentproject_3SimDataCSVFrmBin.txt');
bipolar_msg_source = -2.*msg_source'+1;%0,1映射为1,-1
rcos_msg_source = upfirdn(bipolar_msg_source,bb,16);
n = 1:length(rcos_msg_source);
verilog_seq = load('D:vivado_documentproject_3SimDataCSVrcos.txt');
xmin = 1;
xmax = 500;
ymax = 500;
delay = 59;
xend = 500;%为了确保matlab的结果和verilog的结果长度一致能够作差
verilog_seq_delay = verilog_seq(delay:end)';
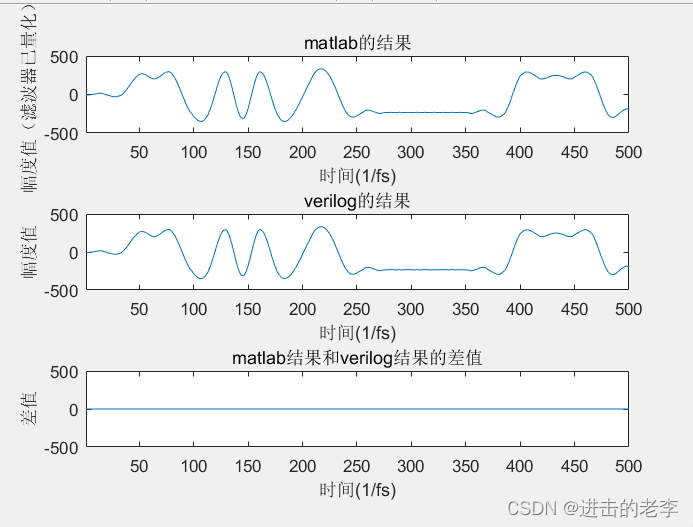
figure;
subplot(3,1,1)
plot(rcos_msg_source);%%%
axis([xmin xmax -ymax ymax]);
title('matlab的结果')
xlabel('时间(1/fs)');
ylabel('幅度值(滤波器已量化)');
subplot(3,1,2)
plot(verilog_seq_delay);%%%
axis([xmin xmax -ymax ymax]);
title('verilog的结果')
xlabel('时间(1/fs)');
ylabel('幅度值');
subplot(3,1,3)
y=rcos_msg_source(1:xend) - verilog_seq_delay(1:xend);
plot(y);
axis([xmin xmax -ymax ymax]);
title('matlab结果和verilog结果的差值');
xlabel('时间(1/fs)');
ylabel('差值');
接下来是最终的发送波形的对比
clc;
close all;
clear;
b = rcosdesign(0.35,6,16,'sqrt');
bb = round(255.*b./max(b));
fs = 500*10e6;
fc = fs/4;
msg_source = load('D:vivado_documentproject_3SimDataCSVFrmBin.txt');
bipolar_msg_source = -2.*msg_source'+1;%0,1映射为1,-1,因为verilog就是这么弄得
rcos_msg_source = upfirdn(bipolar_msg_source,bb,16);
n = 1:length(rcos_msg_source);
rcos_msg_source_carrier = rcos_msg_source.*cos(2*pi*fc.*n/fs);
%存放verilog载波乘法器的输出的地方
verilog_seq = load('D:vivado_documentproject_3SimDataCSVmyFrmBin.txt');
xmin = 1;
xmax = 1500;
ymax = 500;
delay = 62;
xend = 1500;%为了确保matlab的结果和verilog的结果长度一致能够作差
verilog_seq_delay = verilog_seq(delay:end)'/64;
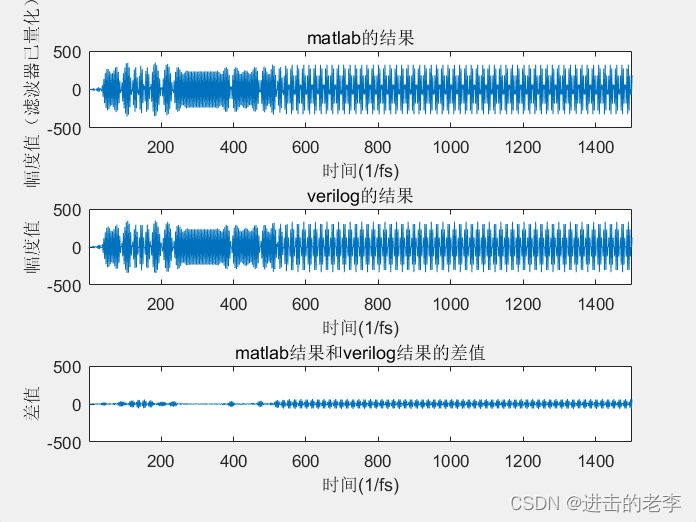
figure;
subplot(3,1,1)
plot(rcos_msg_source_carrier);%%%
axis([xmin xmax -ymax ymax]);
title('matlab的结果')
xlabel('时间(1/fs)');
ylabel('幅度值(滤波器已量化)');
subplot(3,1,2)
plot(verilog_seq_delay);%%%
axis([xmin xmax -ymax ymax]);
title('verilog的结果')
xlabel('时间(1/fs)');
ylabel('幅度值');
subplot(3,1,3)
y=rcos_msg_source_carrier(1:xend) - verilog_seq_delay(1:xend);
plot(y);
axis([xmin xmax -ymax ymax]);
title('matlab结果和verilog结果的差值');
xlabel('时间(1/fs)');
ylabel('差值');
结果如下:
最后
以上就是陶醉面包最近收集整理的关于verilog实现bpsk的发送并与matlab的bpsk仿真进行对比的全部内容,更多相关verilog实现bpsk内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复