aarch32 linux4.9
红外模块使用了input子系统向上层提供IR的key值和PAD的key值,debug之余了解下input的原理
以一个简单的input子系统为例,allocate 跟register 初始化完成之后,在需要上报事件的地方比如IR中断,调用函数input_event
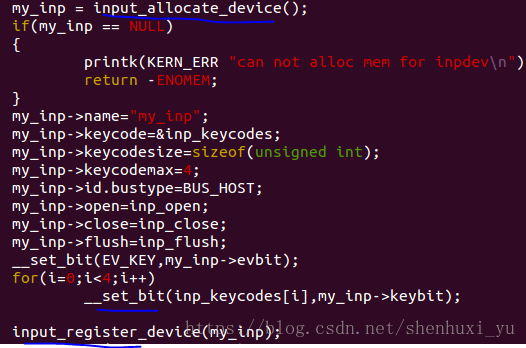
register device后会在sysfs里面产生/dev/input/event* 文件,cat /proc/bus/input/devices 可以dump 所有的input device信息
user space获取input事件并打印key值的简易代码如下
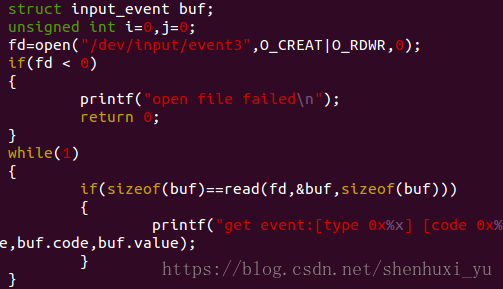
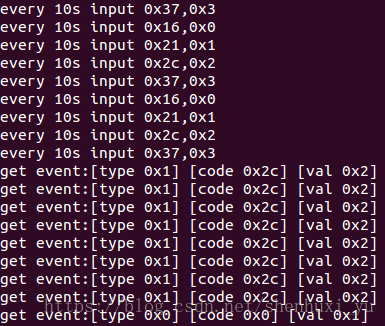
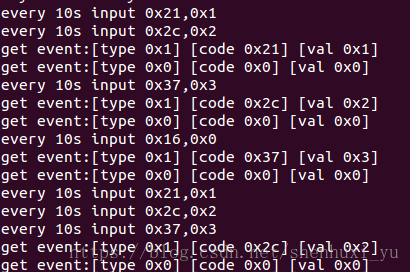
input register 是把event 跟每一个input device关联起来,驱动层再通过input device 找到event client 把事件传递给sysfs, 如果input driver 上报事件的时候只是调用了input_event的话driver并不会每一个key值flush一次,就会看到如下图中的LOG,即使user 在while 的读取文件,也会等好久才会收到一次消息,如果在每一次input_event的时候调用一次input sync结果就是user 会很快收到input event.
![]()
![]()
不妨带着这个问题点去探寻下linux input 子系统
input_sync 其实也是调用的input_event 只不过向上层传送的key的类型和key值分别是EV_SYN ,SYN_MT_REPORT 也就是0
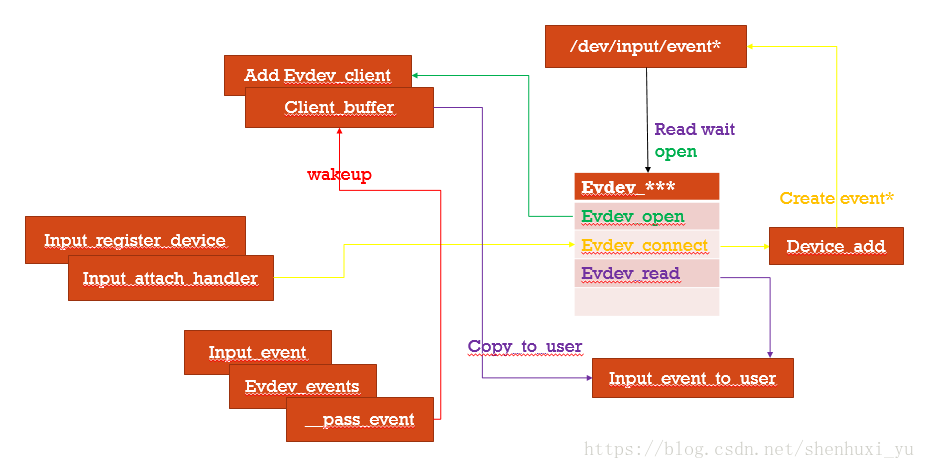
附上简图,方便理解如下的code flow
user space的进程每一次open event* 都会创建一个event_client,可以理解为某次读取event的行为
user space要取的数据就被driver存放在client_buffer中
input消息的处理者 input_handler 就是evdev,evdev就是/dev/input/event*, 链表维护evdev_client
对event*的read操作driver会检查当前的Client的buffer size是否满足要读的size
input_event和input_sync会把消息交给evdev,evdev再把消息填充到它的evdev_client客户们的buffer中
static inline void input_sync(struct input_dev *dev)
{
input_event(dev, EV_SYN, SYN_REPORT, 0);
}
void input_event(struct input_dev *dev,unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
if (is_event_supported(type, dev->evbit, EV_MAX))
input_handle_event(dev, type, code, value);
}
"input_sync 也是调用的 input_event 参数是EV_SYN SYN_REPORT可以作为查flow的关键字"
static void input_handle_event(struct input_dev *dev,
unsigned int type, unsigned int code, int value)
{
int disposition = input_get_disposition(dev, type, code, &value);
if ((disposition & INPUT_PASS_TO_DEVICE) && dev->event)
dev->event(dev, type, code, value);
if (disposition & INPUT_FLUSH) {
if (dev->num_vals >= 2)
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);
dev->num_vals = 0;
} else if (dev->num_vals >= dev->max_vals - 2) {
dev->vals[dev->num_vals++] = input_value_sync;
input_pass_values(dev, dev->vals, dev->num_vals);
dev->num_vals = 0;
}
}
"input_get_disposition 函数是根据input事件的类型EV_XXX决定后面处理流程的状态机"
"EV_SYN 的返回值是INPUT_FLUSH,所以dev->num_vals >= 2(some key + sync key)的时候"
"就会调用input_pass_values传递key值到到event,如果不是INPUT_FLUSH则判断条件是key nums 快要接近max vals,linux3.18上面这个max的值是10”
static void input_pass_values(struct input_dev *dev,struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count)
{
handle = rcu_dereference(dev->grab);
/* @grab: input handle that currently has the device grabbed (via
* EVIOCGRAB ioctl). When a handle grabs a device it becomes sole
* recipient for all input events coming from the device*/
"/dev/input/event*的ioctl可以grab或者ungrab 某个input device,sole recipient 即唯一接受者"
if (handle) {
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);
} else {
list_for_each_entry_rcu(handle, &dev->h_list, d_node)
/* @h_list: list of input handles associated with the device. When
* accessing the list dev->mutex must be held*/
if (handle->open) {
count = input_to_handler(handle, vals, count);
if (!count)
break;
}
}
}
static unsigned int input_to_handler(struct input_handle *handle,
struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count)
{
if (handler->events)
handler->events(handle, vals, count);
else if (handler->event)
for (v = vals; v != vals + count; v++)
handler->event(handle, v->type, v->code, v->value);
}
"handler->event 在input_register_device的时候input_attach_handler"
"然后match后通把handler赋值为evdev_handler,match的时候同时会调用"
"device_add添加/input/event*的设备节点"
static struct input_handler evdev_handler = {
.event = evdev_event,
.events = evdev_events,
.connect = evdev_connect,
.disconnect = evdev_disconnect,
.legacy_minors = true,
.minor = EVDEV_MINOR_BASE,
.name = "evdev",
.id_table = evdev_ids,
};
static void evdev_events(struct input_handle *handle,
const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count)
{
client = rcu_dereference(evdev->grab);
if (client)
evdev_pass_values(client, vals, count, ev_time);
else
list_for_each_entry_rcu(client, &evdev->client_list, node)
evdev_pass_values(client, vals, count, ev_time);
}
static void evdev_pass_values(struct evdev_client *client,
const struct input_value *vals, unsigned int count,
ktime_t *ev_time)
{
/* Interrupts are disabled, just acquire the lock. */
spin_lock(&client->buffer_lock);
for (v = vals; v != vals + count; v++) {
if (__evdev_is_filtered(client, v->type, v->code))
continue;
if (v->type == EV_SYN && v->code == SYN_REPORT) {
/* drop empty SYN_REPORT */
if (client->packet_head == client->head)
continue;
wakeup = true;
}
event.type = v->type;
event.code = v->code;
event.value = v->value;
__pass_event(client, &event);
}
spin_unlock(&client->buffer_lock);
if (wakeup)
wake_up_interruptible(&evdev->wait);
}
"__pass_event将event的消息放到对应的client 的buffer链表中"
"当发生evdev_read的时候就会从这个buffer的链表中将消息回给userspace"
"通过copy_to_user input_event结构体的方式"
static ssize_t evdev_read(struct file *file, char __user *buffer,
size_t count, loff_t *ppos)
{
for (;;) {
if (!evdev->exist || client->revoked)
return -ENODEV;
if (client->packet_head == client->tail &&
(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK))
return -EAGAIN;
/*
* count == 0 is special - no IO is done but we check
* for error conditions (see above).
*/
if (count == 0)
break;
while (read + input_event_size() <= count &&
evdev_fetch_next_event(client, &event)) {
if (input_event_to_user(buffer + read, &event))
return -EFAULT;
read += input_event_size();
}
if (read)
break;
if (!(file->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)) {
error = wait_event_interruptible(evdev->wait,
client->packet_head != client->tail ||
!evdev->exist || client->revoked);
if (error)
return error;
}
}
return read;
}
int input_event_to_user(char __user *buffer,
const struct input_event *event)
{
if (copy_to_user(buffer, event, sizeof(struct input_event)))
return -EFAULT;
}
最后
以上就是默默汽车最近收集整理的关于linux input子系统原理分析的全部内容,更多相关linux内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复