1、常微分方程(Lorenze混沌系统):
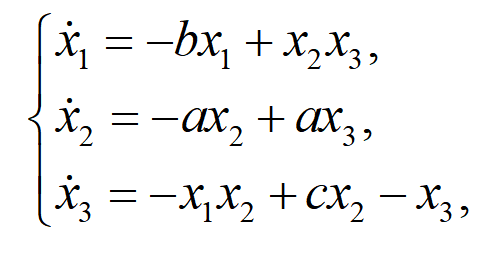
方法1:m文件实现
function exam1
x0=[0;0;1e-3];
[t,x]=ode45(@lorenzfun,[0,100],x0);
figure(1)
plot(t,x)
figure(2)
plot3(x(:,1),x(:,2),x(:,3))function dx=lorenzfun(t,x)
a=10;c=28;b=8/3;
dx=zeros(3,1);
dx(1)=-b*x(1)+x(2)*x(3);
dx(2)=-a*x(2)+10*x(3);
dx(3)=-x(1)*x(2)+c*x(2)-x(3);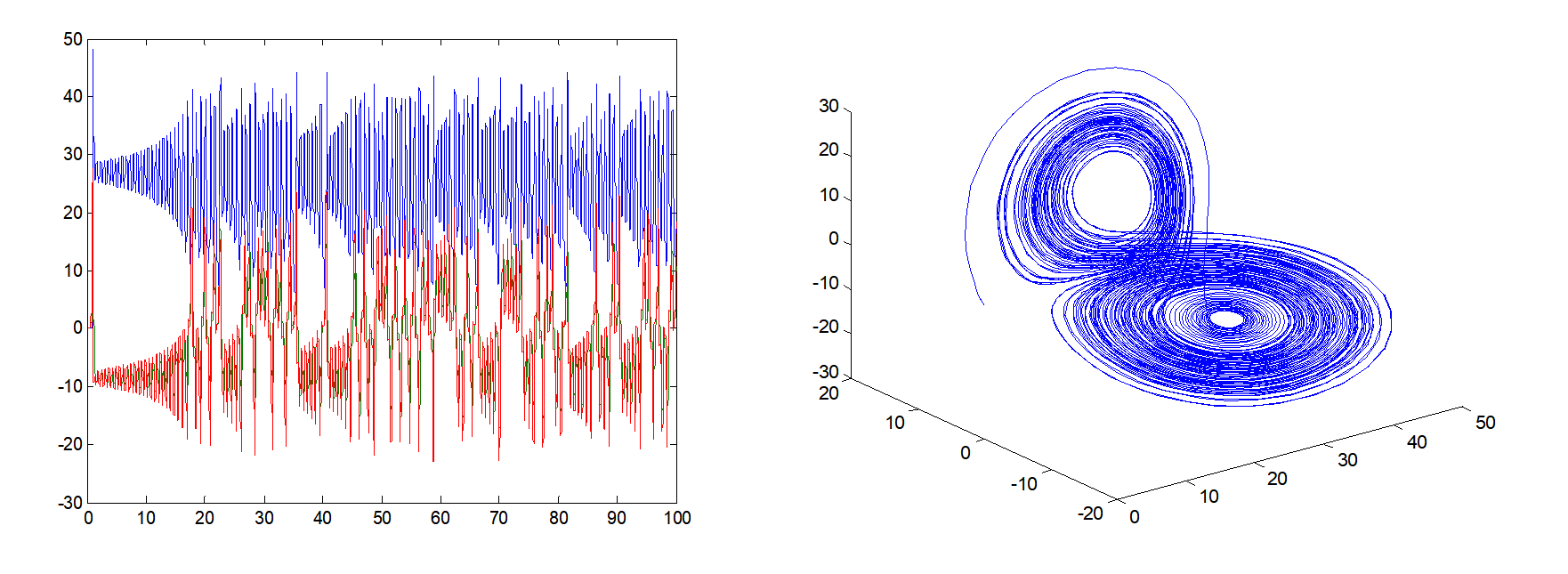
方法2:Simulink模糊实现
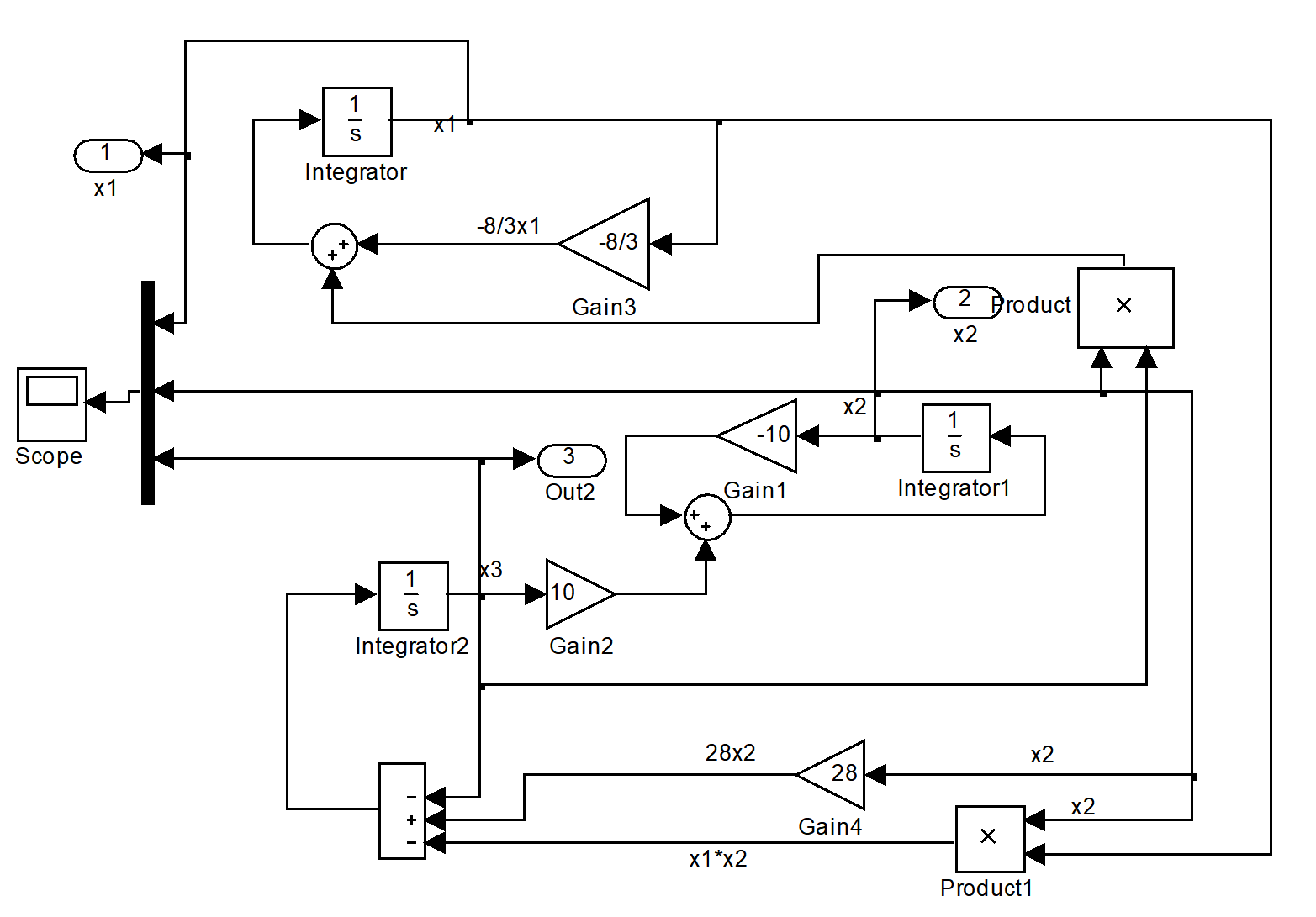
其中三个积分模块的初始值设置与exam1相同,仿真时长为100s。精度设置:Simulation--Configuration Parameters—Relative tolerance, 1e-3改为1e-5(试试不作此修改的结果比较)。运行后双击示波器scope后可看到:
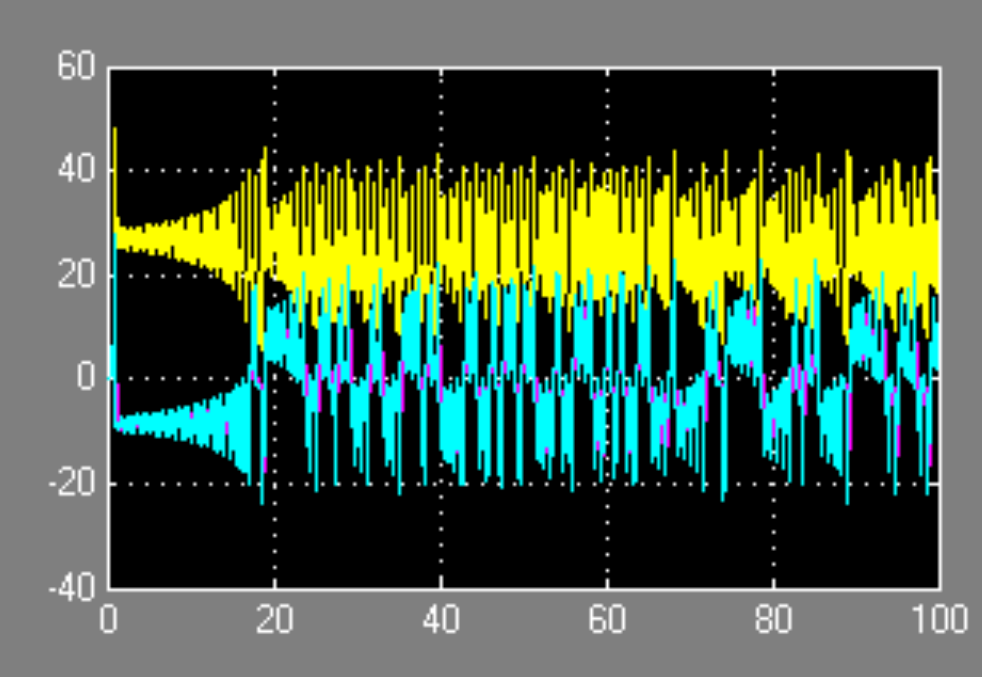
在matlab命令窗口输入画图命令:
figure
plot(tout,yout)
figure
plot3(yout(:,2),yout(:,3),yout(:,1))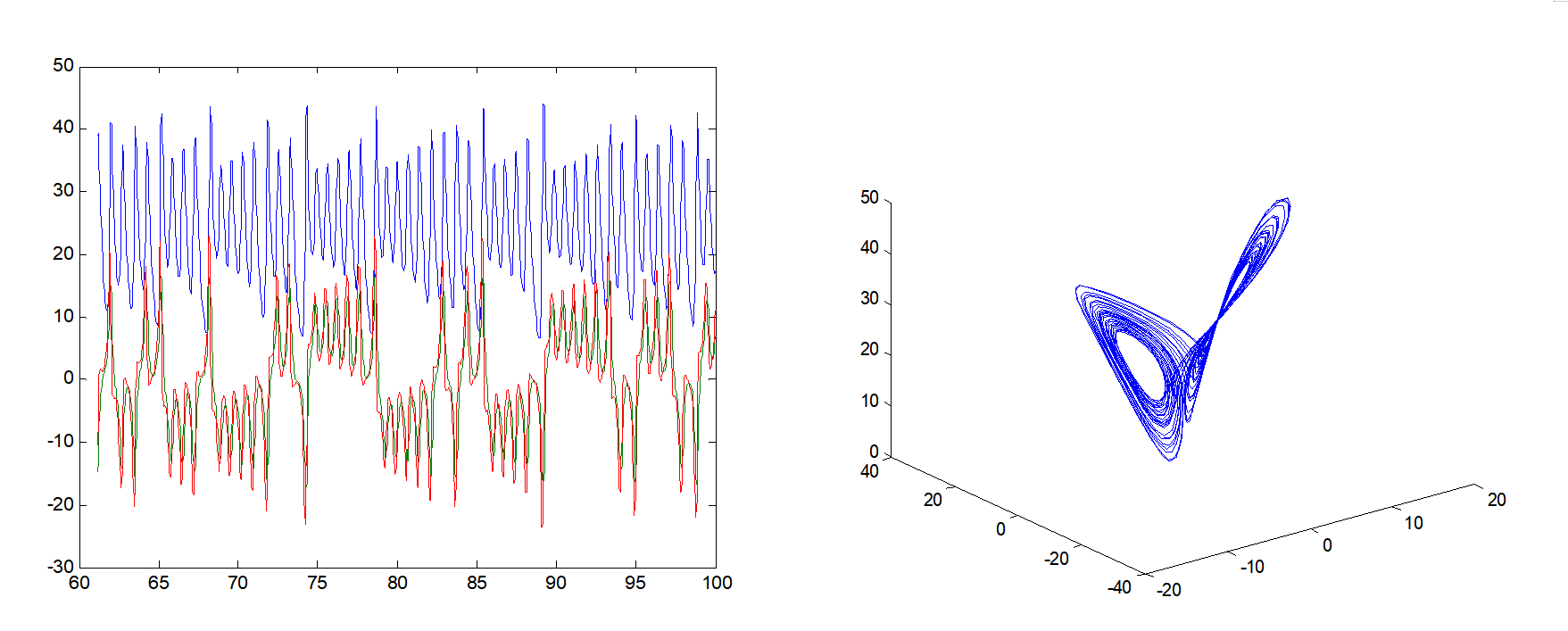
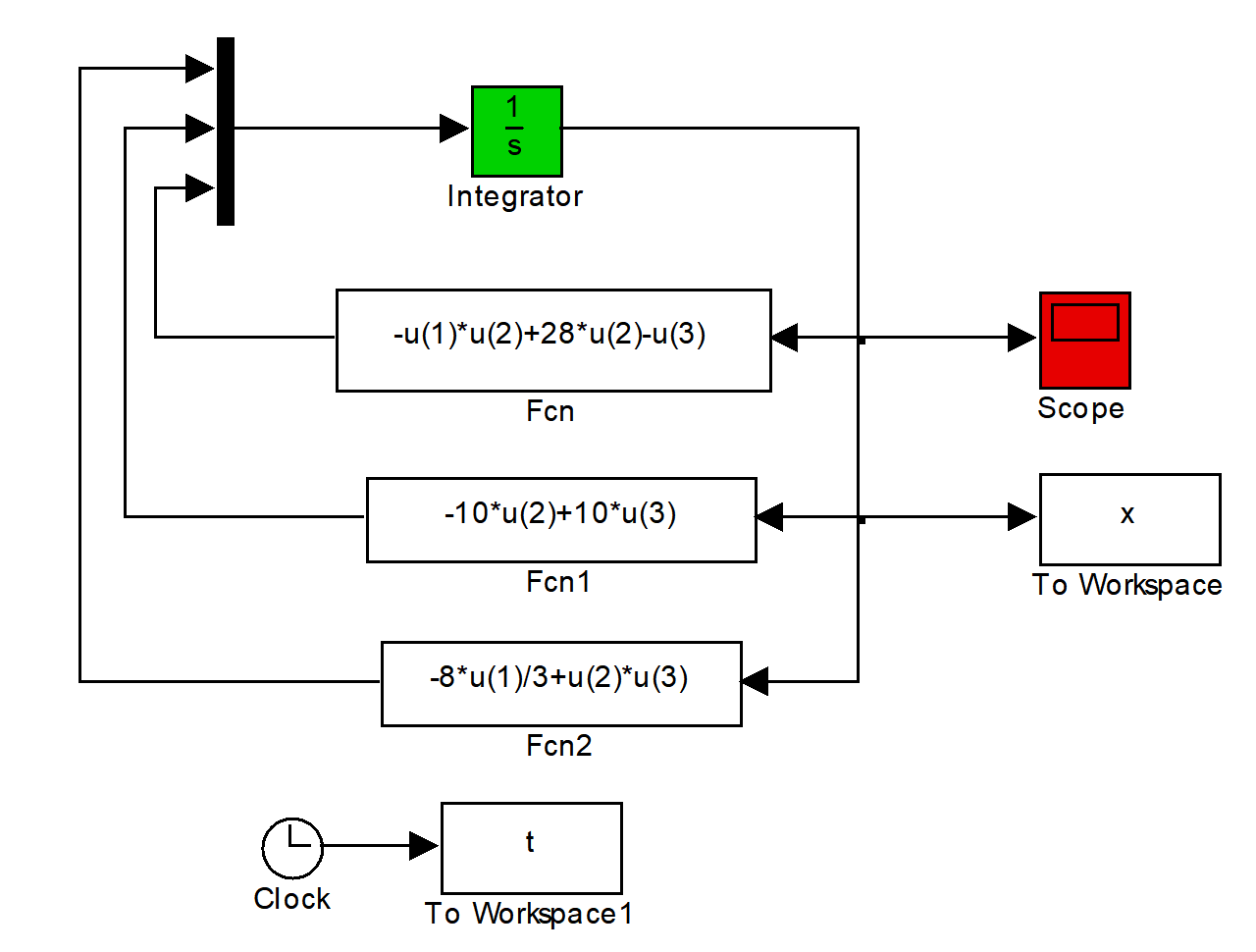
方法3:simulink向量模块
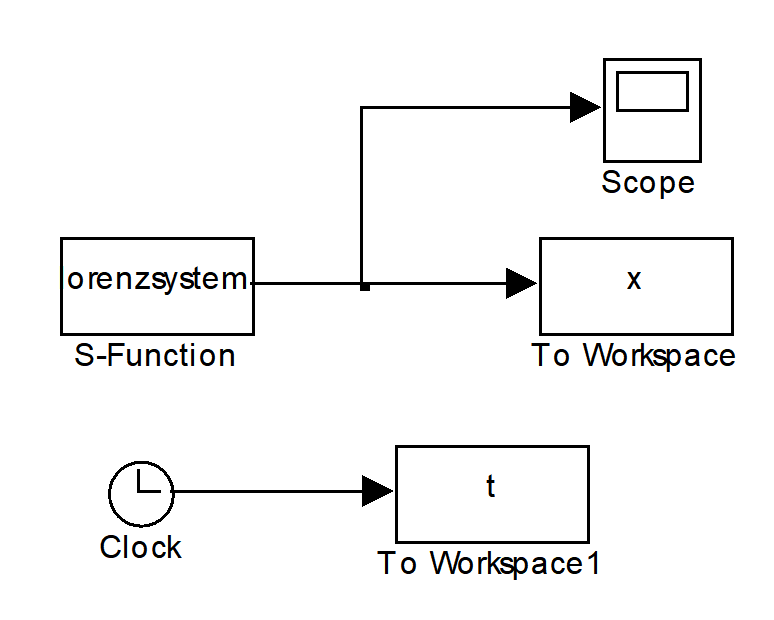
方法4:Simulink中S函数的实现
2、常时滞微分方程
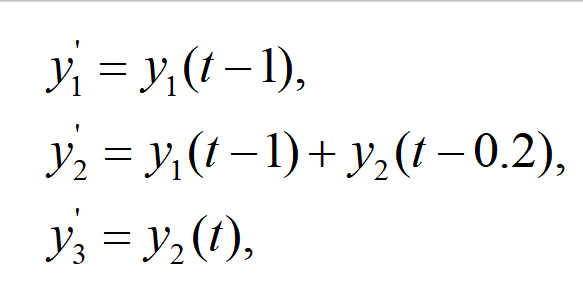
方法1:m文件需调用dde23来求解
function exam2
sol = dde23('exam1f',[1, 0.2],ones(3,1),[0, 5]);
plot(sol.x,sol.y);
title('Example 2')
xlabel('time t');
ylabel('y(t)');function v = exam1f(t,y,Z)
ylag1 = Z(:,1);
ylag2 = Z(:,2);
v = zeros(3,1);
v(1) = ylag1(1);
v(2) = ylag1(1) + ylag2(2);
v(3) = y(2);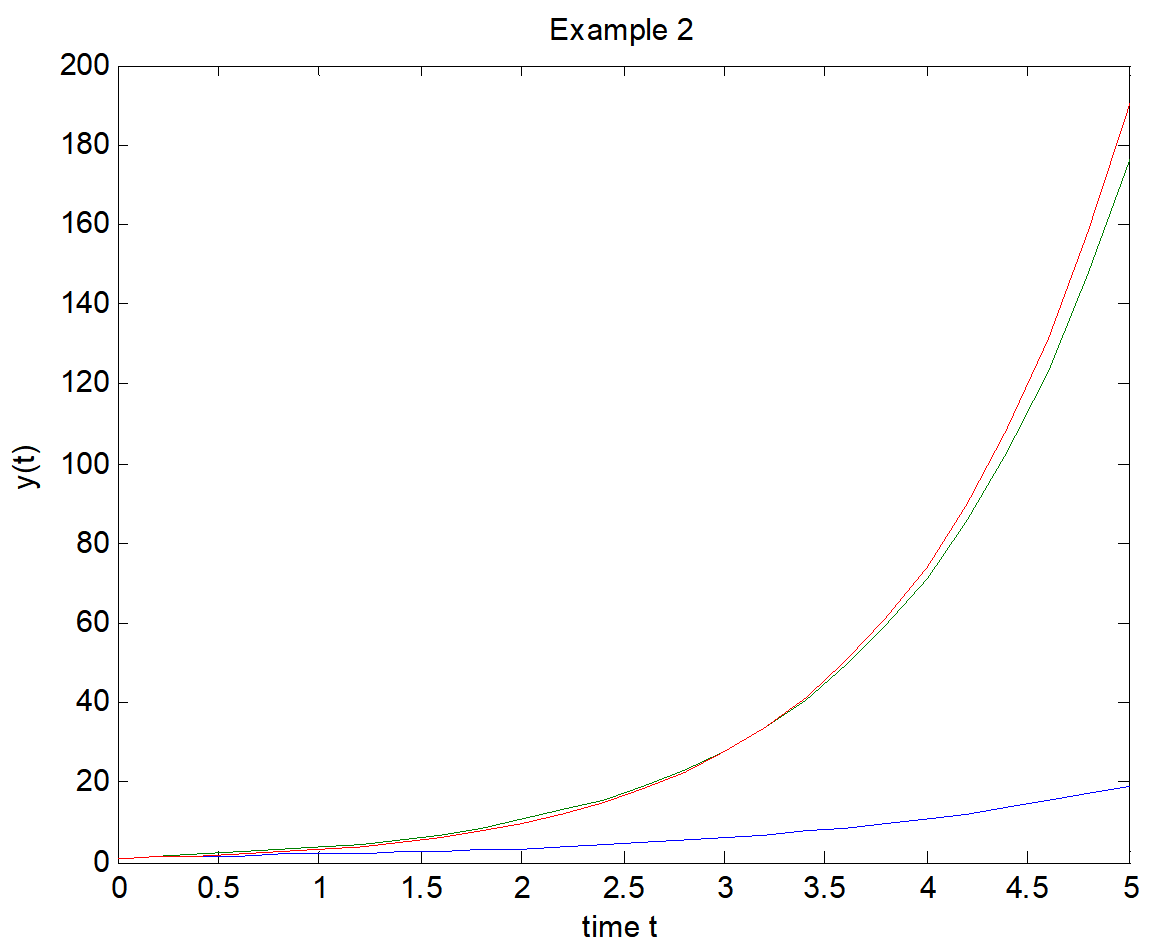
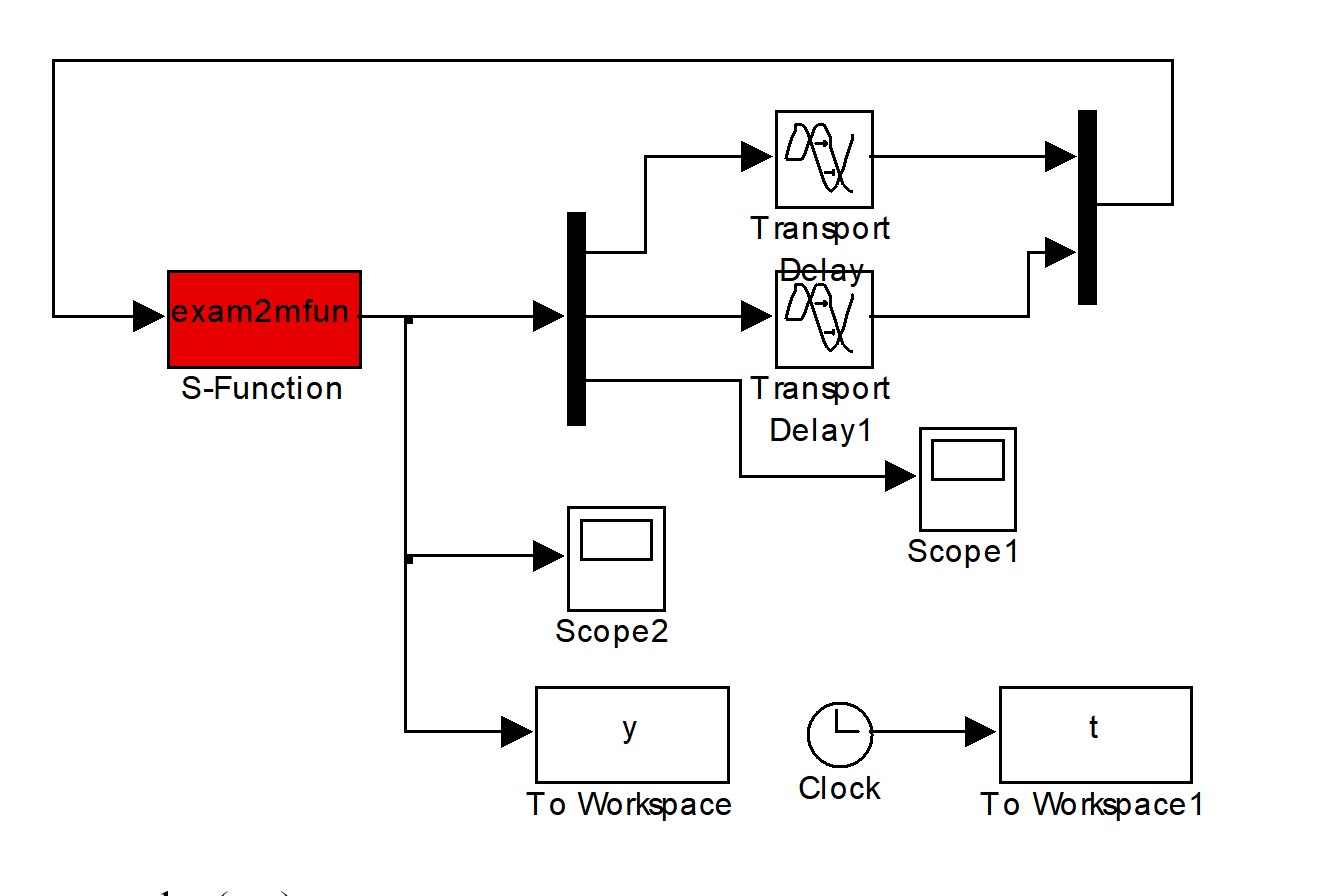
方法2:Simulink中S函数来实现:
注:用Simulink中S函数求解时滞微分方程的核心思想在于:将时滞变量作为S函数的外部输入。
最后
以上就是背后保温杯最近收集整理的关于matlab simulink 求解连续微分系统 混沌系统的全部内容,更多相关matlab内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复