先来回顾一下rowspan和colspan
<td>元素的colspan属性来实现单元格跨列操作,使用<td>元素的rowspan属性来实现单元格的跨行操作。
colspan属性规定单元格可横跨的列数,所有浏览器都支持colspan属性。其取值为number,
如下图所示:
例如:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>星期一</th>
<th>星期二</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2">星期天</td>
</tr>
</table>
实现结果如下图所示:
rowspan属性规定单元格可横跨的列数,所有浏览器都支持rowspan属性。其取值为number,如下图所示:
例如:
<table border="1">
<tr>
<td rowspan="2">星期一</td>
<td>星期二</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>星期三</td>
</tr>
</table>
实现结果如下图所示:
总结colspan和rowspan的使用如下:
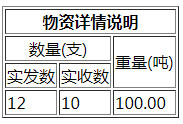
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th colspan="3">物资详情说明</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<td colspan="2" align="center">数量(支)</td>
<td rowspan="2">重量(吨)</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>实发数</td>
<td>实收数</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>12</td>
<td>10</td>
<td>100.00</td>
</tr>
</table>实现结果如下图所示:
下面进入正题:
假设没有rowspan的时候,首行下面有三行,如果执行了rowspan=4(rowspan=1,表示占用一行,其本身就是占用一行,所以如果要额外占用其他的三行,那么rowspasn=1+3),这个时候会占用下面三行的,看起来的效果就是合并了其余三行(使用rowspan,那么它本身和它即将要合并的行必须在不同的行,并且处于相同的列)
<html>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>第一行</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>第二行</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>第三行</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>第四行</th>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
效果图:
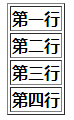
如果合并三面的三行:
<html>
<body>
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th rowspan="4">第一行</th>//合并三面的三行,会把下面三行的位置占据,下面的三行将会被挤到右边去
</tr>
<tr>
<th>第二行</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>第三行</th>
</tr>
<tr>
<th>第四行</th>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>
效果图:

碰到项目中的一个问题:
有个树结构的数据,它有多个顶级节点(AuditorInfoObject),每个顶级可能有子节点(TaskObject),子节点可能还有自己的子节点(BaseObject),如何形成合并行的table:
解决步骤:
1.计算最顶级节点占用的行数(即rowspan)
private Map<Integer,Integer> countMap = new HashMap<>();//key为顶级节点的索引值,value为rowspan的数量
if(this.auditorList != null) {
//计算页面合并行的总个数
for(int i = 0;i < this.auditorList.size();i++) {
int total = 1;//每个顶级节点自己原本就占有一行
List<TaskObject> childrens = this.auditorList.get(i).getChildren();
if(childrens != null && childrens.size() > 0) {
for(TaskObject child:childrens) {
total++;//每个子节点占一行
List<BaseObject<?>> processElenmentList = child.getProcessElenmentList();
if(processElenmentList != null && processElenmentList.size() > 0) {
total += processElenmentList.size();//每个子节点的子节点又占一行
}
}
}
countMap.put(i, total);
}
}2.在页面写好三层循环结构:
jsp代码:
<table class="table" style="width:100%;border:0px;" id="shcx_table">
<tbody>
<tr>
<th height="18px;" style="text-align:center">顶级节点</th>
<th style="text-align:center;" id="myStep">一级节点</th>
<th style="text-align:center;" id="myName">二级节点</th>
</tr>
<s:iterator value="auditorList" var="obj" status="l">
<tbody title="<s:property value="#obj.processName" />">
<tr><!-- 顶级节点 -->
<th rowspan="<s:property value="countMap.get(#l.index)"/>" style="text-align:center; width:80px;">
<s:property value="#obj.processName"/>
</th>
</tr>
<s:iterator value="#obj.children" var="c"><!-- 一级节点 -->
<s:if test="#c.processElenmentList != null && #c.processElenmentList.size() > 0">
<tr>
<th rowspan="<s:property value="#c.processElenmentList.size()+1"/>" style="text-align:left; width:80px;">
<s:property value="#c.stepName"/>
</th>
</tr>
<s:iterator value="#c.processElenmentList" var="r"><!-- 二级节点 -->
<tr>
<th style="text-align:left; font-weight:normal;width:400px"><s:property value="#r.elementName"/></th>
</tr>
</s:iterator>
</s:if>
<s:else>
<tr><!-- 一级节点没有子节点走这里 -->
<th style="text-align:left; font-weight:normal;width:10px"><s:property value="#c.stepName"/></th>
<th style="text-align:left; font-weight:normal;width:400px">无子节点</th>
</tr>
</s:else>
</s:iterator>
</tbody>
</s:iterator>
</tbody>
</table>
显示效果:
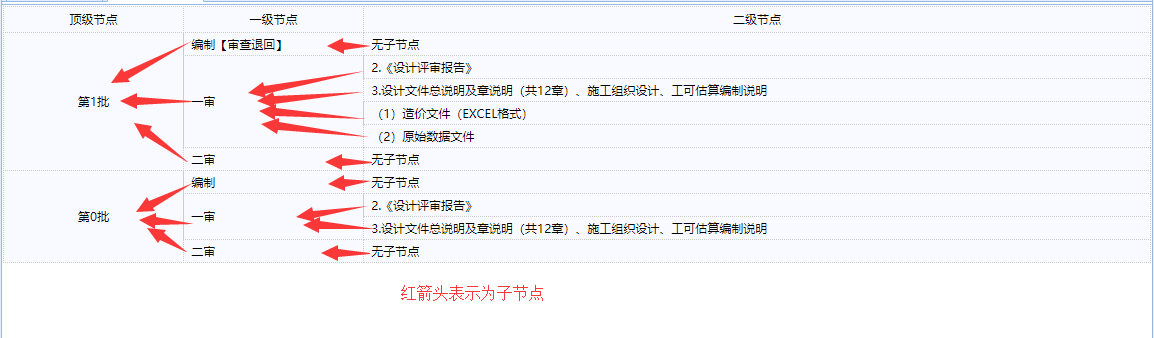
红色箭头表示父节点方向,对于这种结构树,
可以这么做:
(1)可以先不考虑合并行,把每个tr从父节点到子节点都一一用td列出来
即:每一行tr都是从顶级节点到最后一个节点都一一用td装入进来
(2)在顶级节点使用rowspan,这个时候会发现:顶级节点的rowspan=1(root本身占1行)+该节点拥有的一级子节点(root.getChildren().size())+每一个子节点拥有的子节点树(child.getProcessElenmentList().size())
(3)在使用的rowspan之后,把被挤到右侧的节点的顶级节点删除掉(被合并的行不再需要root节点,只有第一行需要,其他的行和第一行公用root节点)
(4)因为一级节点也有子节点,此时再合并一级节点,步骤同顶级节点...
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/u012724595/article/details/79401401
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/u/2331760/blog/3072727
最后
以上就是温婉马里奥最近收集整理的关于strus2在jsp页面利用利用s:iterator三层循环合并多行的全部内容,更多相关strus2在jsp页面利用利用s内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。







![JSP 2.0: The New Deal, Part 1 [转载]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg1.png)




发表评论 取消回复