基于 RTC 场景下要解决的声音的问题,WebRTC 有一个大体如下图所示的音频处理流水线:
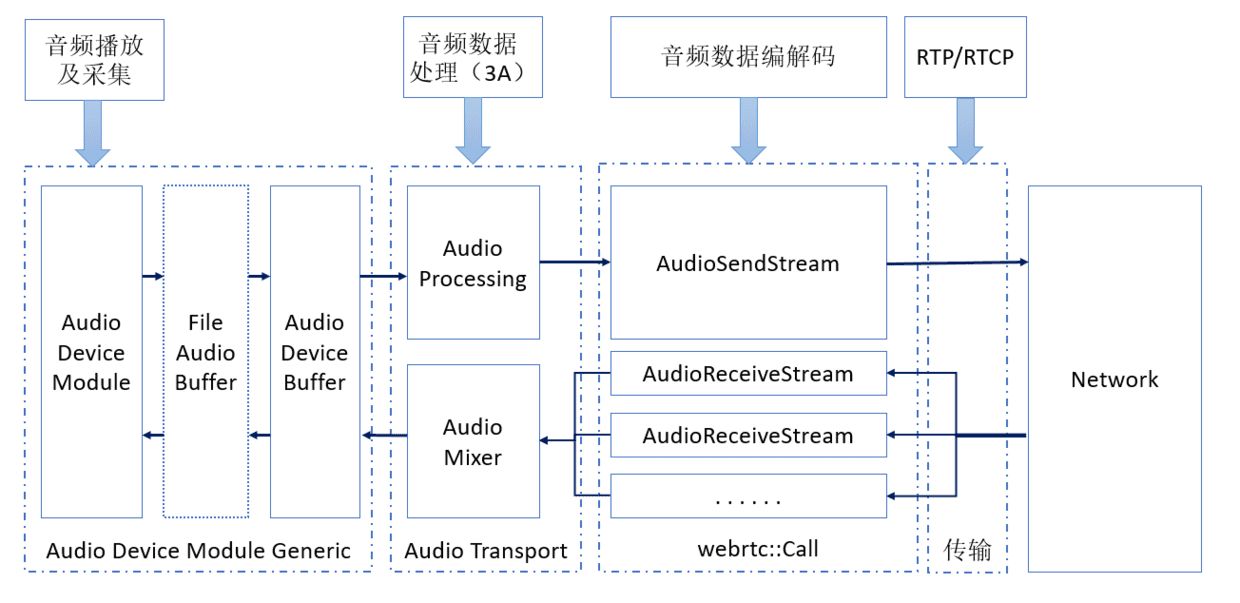
WebRTC 的音频处理流水线,不是一次性建立起来的,而是分阶段分步骤建立的。整体而言,可以认为这个流水线分两个阶段建立,或者可以认为这个流水线分为两部分:一部分可称为静态流水线,另一部分可称为动态流水线,或者也可以称为前端和后端。静态流水线,在某个时间点建立一次,随后在整个 WebRTC 通信过程中基本保持不变;动态流水线则在通信过程中,可能出现较为频繁的变动,如本地打开或禁用录制启动发送或停止发送音频数据,远端发送者加入或退出频道等,都会改变动态流水线。
如此,WebRTC 的音频处理流水线大致如下图所示:
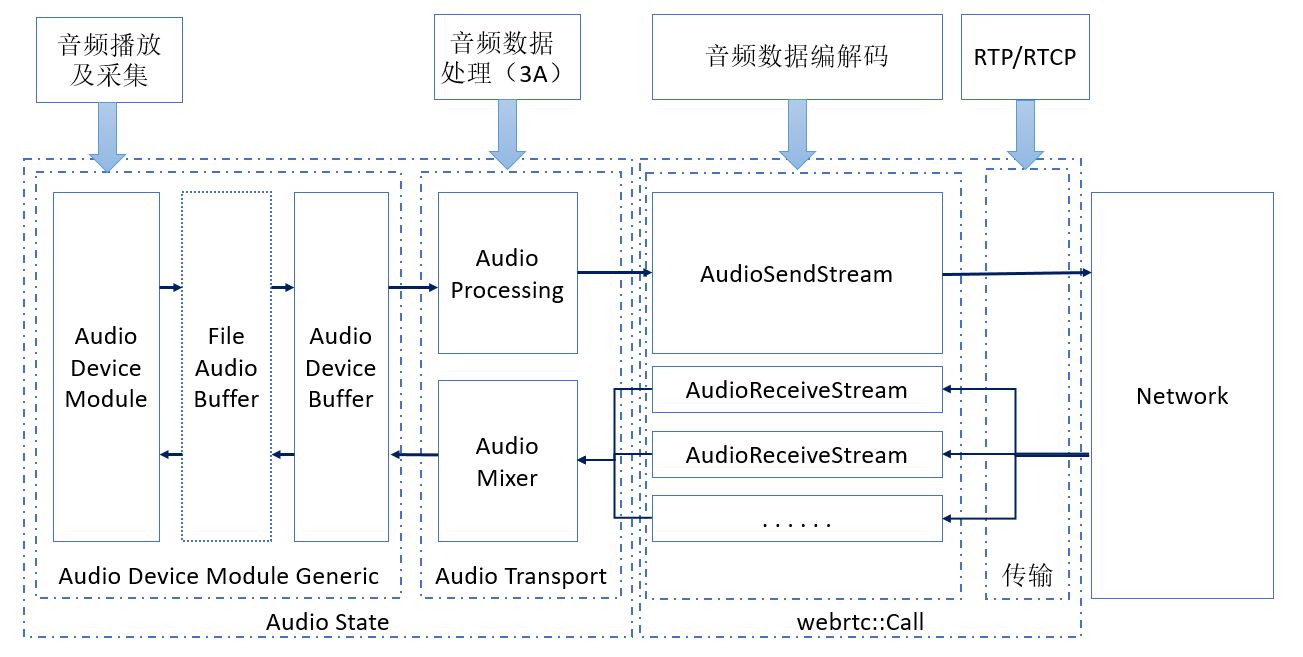
WebRTC 音频的静态流水线,建立之后,其相关节点状态由 AudioState 维护和管理。WebRTC 音频的静态流水线,主要包括 AudioDeviceModule,AudioProcessing,和 AudioMixer 等,其中 AudioDeviceModule 用于采集和播放音频数据,AudioProcessing 主要用于对录制的音频数据做初始处理,如回声消除,降噪等,AudioMixer 主要用于对远端发送过来的音频数据做混音。
WebRTC 音频的静态流水线在 WebRtcVoiceEngine 初始化时建立:
void WebRtcVoiceEngine::Init() {
RTC_DCHECK(worker_thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "WebRtcVoiceEngine::Init";
// TaskQueue expects to be created/destroyed on the same thread.
low_priority_worker_queue_.reset(
new rtc::TaskQueue(task_queue_factory_->CreateTaskQueue(
"rtc-low-prio", webrtc::TaskQueueFactory::Priority::LOW)));
// Load our audio codec lists.
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Supported send codecs in order of preference:";
send_codecs_ = CollectCodecs(encoder_factory_->GetSupportedEncoders());
for (const AudioCodec& codec : send_codecs_) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << ToString(codec);
}
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << "Supported recv codecs in order of preference:";
recv_codecs_ = CollectCodecs(decoder_factory_->GetSupportedDecoders());
for (const AudioCodec& codec : recv_codecs_) {
RTC_LOG(LS_INFO) << ToString(codec);
}
#if defined(WEBRTC_INCLUDE_INTERNAL_AUDIO_DEVICE)
// No ADM supplied? Create a default one.
if (!adm_) {
adm_ = webrtc::AudioDeviceModule::Create(
webrtc::AudioDeviceModule::kPlatformDefaultAudio, task_queue_factory_);
}
#endif // WEBRTC_INCLUDE_INTERNAL_AUDIO_DEVICE
RTC_CHECK(adm());
webrtc::adm_helpers::Init(adm());
webrtc::apm_helpers::Init(apm());
// Set up AudioState.
{
webrtc::AudioState::Config config;
if (audio_mixer_) {
config.audio_mixer = audio_mixer_;
} else {
config.audio_mixer = webrtc::AudioMixerImpl::Create();
}
config.audio_processing = apm_;
config.audio_device_module = adm_;
audio_state_ = webrtc::AudioState::Create(config);
}
// Connect the ADM to our audio path.
adm()->RegisterAudioCallback(audio_state()->audio_transport());
// Set default engine options.
{
AudioOptions options;
options.echo_cancellation = true;
options.auto_gain_control = true;
options.noise_suppression = true;
options.highpass_filter = true;
options.stereo_swapping = false;
options.audio_jitter_buffer_max_packets = 200;
options.audio_jitter_buffer_fast_accelerate = false;
options.audio_jitter_buffer_min_delay_ms = 0;
options.audio_jitter_buffer_enable_rtx_handling = false;
options.typing_detection = true;
options.experimental_agc = false;
options.extended_filter_aec = false;
options.delay_agnostic_aec = false;
options.experimental_ns = false;
options.residual_echo_detector = true;
bool error = ApplyOptions(options);
RTC_DCHECK(error);
}
initialized_ = true;
}WebRTC 音频静态流水线的几个节点,由外部创建好注入进来,并通过 AudioState 创建的 AudioTransport 连接起来:WebRtcVoiceEngine::Init()
根据需要创建 AudioDeviceModule,然后创建 AudioState,AudioState 用注入的 AudioMixer 和 AudioProcessing 创建 AudioTransport,WebRtcVoiceEngine::Init() 随后将 AudioState 创建的 AudioTransport 作为 AudioCallback 注册给 AudioDeviceModule。WebRTC 音频静态流水线在 WebRtcVoiceEngine::Init() 中建立。动态流水线和静态流水线在 AudioState 和 AudioTransport 处交汇。
AudioTransport
AudioDeviceModule 在录到音频数据时,将音频数据送给 AudioTransport,在播放音频时,也向 AudioTransport 拿要播放的音频数据。AudioTransport 是录制的音频数据和播放的音频数据的交汇点。
AudioTransport 接口的定义 (位于 webrtc/src/modules/audio_device/include/audio_device_defines.h) 如下:
class AudioTransport {
public:
virtual int32_t RecordedDataIsAvailable(const void* audioSamples,
const size_t nSamples,
const size_t nBytesPerSample,
const size_t nChannels,
const uint32_t samplesPerSec,
const uint32_t totalDelayMS,
const int32_t clockDrift,
const uint32_t currentMicLevel,
const bool keyPressed,
uint32_t& newMicLevel) = 0; // NOLINT
// Implementation has to setup safe values for all specified out parameters.
virtual int32_t NeedMorePlayData(const size_t nSamples,
const size_t nBytesPerSample,
const size_t nChannels,
const uint32_t samplesPerSec,
void* audioSamples,
size_t& nSamplesOut, // NOLINT
int64_t* elapsed_time_ms,
int64_t* ntp_time_ms) = 0; // NOLINT
// Method to pull mixed render audio data from all active VoE channels.
// The data will not be passed as reference for audio processing internally.
virtual void PullRenderData(int bits_per_sample,
int sample_rate,
size_t number_of_channels,
size_t number_of_frames,
void* audio_data,
int64_t* elapsed_time_ms,
int64_t* ntp_time_ms) = 0;
protected:
virtual ~AudioTransport() {}
};WebRTC 中的 AudioTransport 接口实现 AudioTransportImpl 定义 (位于 webrtc/src/audio/audio_transport_impl.h) 如下:
namespace webrtc {
class AudioSendStream;
class AudioTransportImpl : public AudioTransport {
public:
AudioTransportImpl(AudioMixer* mixer, AudioProcessing* audio_processing);
~AudioTransportImpl() override;
int32_t RecordedDataIsAvailable(const void* audioSamples,
const size_t nSamples,
const size_t nBytesPerSample,
const size_t nChannels,
const uint32_t samplesPerSec,
const uint32_t totalDelayMS,
const int32_t clockDrift,
const uint32_t currentMicLevel,
const bool keyPressed,
uint32_t& newMicLevel) override;
int32_t NeedMorePlayData(const size_t nSamples,
const size_t nBytesPerSample,
const size_t nChannels,
const uint32_t samplesPerSec,
void* audioSamples,
size_t& nSamplesOut,
int64_t* elapsed_time_ms,
int64_t* ntp_time_ms) override;
void PullRenderData(int bits_per_sample,
int sample_rate,
size_t number_of_channels,
size_t number_of_frames,
void* audio_data,
int64_t* elapsed_time_ms,
int64_t* ntp_time_ms) override;
void UpdateSendingStreams(std::vector<AudioSendStream*> streams,
int send_sample_rate_hz,
size_t send_num_channels);
void SetStereoChannelSwapping(bool enable);
bool typing_noise_detected() const;
const voe::AudioLevel& audio_level() const { return audio_level_; }
private:
// Shared.
AudioProcessing* audio_processing_ = nullptr;
// Capture side.
rtc::CriticalSection capture_lock_;
std::vector<AudioSendStream*> sending_streams_ RTC_GUARDED_BY(capture_lock_);
int send_sample_rate_hz_ RTC_GUARDED_BY(capture_lock_) = 8000;
size_t send_num_channels_ RTC_GUARDED_BY(capture_lock_) = 1;
bool typing_noise_detected_ RTC_GUARDED_BY(capture_lock_) = false;
bool swap_stereo_channels_ RTC_GUARDED_BY(capture_lock_) = false;
PushResampler<int16_t> capture_resampler_;
voe::AudioLevel audio_level_;
TypingDetection typing_detection_;
// Render side.
rtc::scoped_refptr<AudioMixer> mixer_;
AudioFrame mixed_frame_;
// Converts mixed audio to the audio device output rate.
PushResampler<int16_t> render_resampler_;
RTC_DISALLOW_IMPLICIT_CONSTRUCTORS(AudioTransportImpl);
};
} // namespace webrtcAudioTransportImpl 实现的 AudioTransport 接口的要求的操作:将录制的音频数据送出去,及获取播放的音频数据。
AudioTransportImpl 对象创建时保存注入的 AudioMixer 和 AudioProcessing 对象指针:
AudioTransportImpl::AudioTransportImpl(AudioMixer* mixer,
AudioProcessing* audio_processing)
: audio_processing_(audio_processing), mixer_(mixer) {
RTC_DCHECK(mixer);
RTC_DCHECK(audio_processing);
}
AudioTransportImpl::~AudioTransportImpl() {}播放
AudioDeviceModule 可以通过 AudioTransportImpl 的 NeedMorePlayData() 和 PullRenderData() 获取用于播放的音频数据:
// Resample audio in |frame| to given sample rate preserving the
// channel count and place the result in |destination|.
int Resample(const AudioFrame& frame,
const int destination_sample_rate,
PushResampler<int16_t>* resampler,
int16_t* destination) {
const int number_of_channels = static_cast<int>(frame.num_channels_);
const int target_number_of_samples_per_channel =
destination_sample_rate / 100;
resampler->InitializeIfNeeded(frame.sample_rate_hz_, destination_sample_rate,
number_of_channels);
// TODO(yujo): make resampler take an AudioFrame, and add special case
// handling of muted frames.
return resampler->Resample(
frame.data(), frame.samples_per_channel_ * number_of_channels,
destination, number_of_channels * target_number_of_samples_per_channel);
}
. . . . . .
// Mix all received streams, feed the result to the AudioProcessing module, then
// resample the result to the requested output rate.
int32_t AudioTransportImpl::NeedMorePlayData(const size_t nSamples,
const size_t nBytesPerSample,
const size_t nChannels,
const uint32_t samplesPerSec,
void* audioSamples,
size_t& nSamplesOut,
int64_t* elapsed_time_ms,
int64_t* ntp_time_ms) {
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(sizeof(int16_t) * nChannels, nBytesPerSample);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(nChannels, 1);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(nChannels, 2);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(
samplesPerSec,
static_cast<uint32_t>(AudioProcessing::NativeRate::kSampleRate8kHz));
// 100 = 1 second / data duration (10 ms).
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(nSamples * 100, samplesPerSec);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(nBytesPerSample * nSamples * nChannels,
AudioFrame::kMaxDataSizeBytes);
mixer_->Mix(nChannels, &mixed_frame_);
*elapsed_time_ms = mixed_frame_.elapsed_time_ms_;
*ntp_time_ms = mixed_frame_.ntp_time_ms_;
const auto error = audio_processing_->ProcessReverseStream(&mixed_frame_);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(error, AudioProcessing::kNoError);
nSamplesOut = Resample(mixed_frame_, samplesPerSec, &render_resampler_,
static_cast<int16_t*>(audioSamples));
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(nSamplesOut, nChannels * nSamples);
return 0;
}
// Used by Chromium - same as NeedMorePlayData() but because Chrome has its
// own APM instance, does not call audio_processing_->ProcessReverseStream().
void AudioTransportImpl::PullRenderData(int bits_per_sample,
int sample_rate,
size_t number_of_channels,
size_t number_of_frames,
void* audio_data,
int64_t* elapsed_time_ms,
int64_t* ntp_time_ms) {
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(bits_per_sample, 16);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(number_of_channels, 1);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(sample_rate, AudioProcessing::NativeRate::kSampleRate8kHz);
// 100 = 1 second / data duration (10 ms).
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(number_of_frames * 100, sample_rate);
// 8 = bits per byte.
RTC_DCHECK_LE(bits_per_sample / 8 * number_of_frames * number_of_channels,
AudioFrame::kMaxDataSizeBytes);
mixer_->Mix(number_of_channels, &mixed_frame_);
*elapsed_time_ms = mixed_frame_.elapsed_time_ms_;
*ntp_time_ms = mixed_frame_.ntp_time_ms_;
auto output_samples = Resample(mixed_frame_, sample_rate, &render_resampler_,
static_cast<int16_t*>(audio_data));
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(output_samples, number_of_channels * number_of_frames);
}NeedMorePlayData() 执行如下操作:
通过 AudioMixer 对远端的音频流做混音。AudioTransportImpl 没有直接与 AudioReceiveStream 建立连接,但 AudioMixer 的 source 实际上是 AudioReceiveStream。
把混音后的音频数据送进 AudioProcessing。主要用于回声消除。
对混音后的音频数据重采样。如我们前面看到的 AudioMixerImpl 的实现,它的混音输出采样率有它自己的决定逻辑,可能与 AudioDeviceModule 设备需要的不一致,这里需要按照设备的需要,将混音后的数据重采样到设备需要的采样率。
返回重采样的数据。
PullRenderData() 的操作与 NeedMorePlayData() 仅有的区别在于,没有上面的第 2 步。如注释中所说,在某些情况下,混音之后的数据无需送进 AudioProcessing。此外,PullRenderData() 要求调用者只能请求单通道的音频数据,NeedMorePlayData() 的调用者则可以请求单通道或立体声的。
重采样和混音的更多细节,这里不再赘述。
录制
AudioDeviceModule 可以通过 AudioTransport 的 RecordedDataIsAvailable() 把录制的数据送出去:
// We want to process at the lowest sample rate and channel count possible
// without losing information. Choose the lowest native rate at least equal to
// the minimum of input and codec rates, choose lowest channel count, and
// configure the audio frame.
void InitializeCaptureFrame(int input_sample_rate,
int send_sample_rate_hz,
size_t input_num_channels,
size_t send_num_channels,
AudioFrame* audio_frame) {
RTC_DCHECK(audio_frame);
int min_processing_rate_hz = std::min(input_sample_rate, send_sample_rate_hz);
for (int native_rate_hz : AudioProcessing::kNativeSampleRatesHz) {
audio_frame->sample_rate_hz_ = native_rate_hz;
if (audio_frame->sample_rate_hz_ >= min_processing_rate_hz) {
break;
}
}
audio_frame->num_channels_ = std::min(input_num_channels, send_num_channels);
}
void ProcessCaptureFrame(uint32_t delay_ms,
bool key_pressed,
bool swap_stereo_channels,
AudioProcessing* audio_processing,
AudioFrame* audio_frame) {
RTC_DCHECK(audio_processing);
RTC_DCHECK(audio_frame);
audio_processing->set_stream_delay_ms(delay_ms);
audio_processing->set_stream_key_pressed(key_pressed);
int error = audio_processing->ProcessStream(audio_frame);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(0, error) << "ProcessStream() error: " << error;
if (swap_stereo_channels) {
AudioFrameOperations::SwapStereoChannels(audio_frame);
}
}
. . . . . .
// Not used in Chromium. Process captured audio and distribute to all sending
// streams, and try to do this at the lowest possible sample rate.
int32_t AudioTransportImpl::RecordedDataIsAvailable(
const void* audio_data,
const size_t number_of_frames,
const size_t bytes_per_sample,
const size_t number_of_channels,
const uint32_t sample_rate,
const uint32_t audio_delay_milliseconds,
const int32_t /*clock_drift*/,
const uint32_t /*volume*/,
const bool key_pressed,
uint32_t& /*new_mic_volume*/) { // NOLINT: to avoid changing APIs
RTC_DCHECK(audio_data);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(number_of_channels, 1);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(number_of_channels, 2);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(2 * number_of_channels, bytes_per_sample);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(sample_rate, AudioProcessing::NativeRate::kSampleRate8kHz);
// 100 = 1 second / data duration (10 ms).
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(number_of_frames * 100, sample_rate);
RTC_DCHECK_LE(bytes_per_sample * number_of_frames * number_of_channels,
AudioFrame::kMaxDataSizeBytes);
int send_sample_rate_hz = 0;
size_t send_num_channels = 0;
bool swap_stereo_channels = false;
{
rtc::CritScope lock(&capture_lock_);
send_sample_rate_hz = send_sample_rate_hz_;
send_num_channels = send_num_channels_;
swap_stereo_channels = swap_stereo_channels_;
}
std::unique_ptr<AudioFrame> audio_frame(new AudioFrame());
InitializeCaptureFrame(sample_rate, send_sample_rate_hz, number_of_channels,
send_num_channels, audio_frame.get());
voe::RemixAndResample(static_cast<const int16_t*>(audio_data),
number_of_frames, number_of_channels, sample_rate,
&capture_resampler_, audio_frame.get());
ProcessCaptureFrame(audio_delay_milliseconds, key_pressed,
swap_stereo_channels, audio_processing_,
audio_frame.get());
// Typing detection (utilizes the APM/VAD decision). We let the VAD determine
// if we're using this feature or not.
// TODO(solenberg): GetConfig() takes a lock. Work around that.
bool typing_detected = false;
if (audio_processing_->GetConfig().voice_detection.enabled) {
if (audio_frame->vad_activity_ != AudioFrame::kVadUnknown) {
bool vad_active = audio_frame->vad_activity_ == AudioFrame::kVadActive;
typing_detected = typing_detection_.Process(key_pressed, vad_active);
}
}
// Measure audio level of speech after all processing.
double sample_duration = static_cast<double>(number_of_frames) / sample_rate;
audio_level_.ComputeLevel(*audio_frame, sample_duration);
// Copy frame and push to each sending stream. The copy is required since an
// encoding task will be posted internally to each stream.
{
rtc::CritScope lock(&capture_lock_);
typing_noise_detected_ = typing_detected;
RTC_DCHECK_GT(audio_frame->samples_per_channel_, 0);
if (!sending_streams_.empty()) {
auto it = sending_streams_.begin();
while (++it != sending_streams_.end()) {
std::unique_ptr<AudioFrame> audio_frame_copy(new AudioFrame());
audio_frame_copy->CopyFrom(*audio_frame);
(*it)->SendAudioData(std::move(audio_frame_copy));
}
// Send the original frame to the first stream w/o copying.
(*sending_streams_.begin())->SendAudioData(std::move(audio_frame));
}
}
return 0;
}
. . . . . .
void AudioTransportImpl::UpdateSendingStreams(
std::vector<AudioSendStream*> streams,
int send_sample_rate_hz,
size_t send_num_channels) {
rtc::CritScope lock(&capture_lock_);
sending_streams_ = std::move(streams);
send_sample_rate_hz_ = send_sample_rate_hz;
send_num_channels_ = send_num_channels;
}AudioTransportImpl 的 RecordedDataIsAvailable() 拿到录音得到的音频数据,对音频数据执行如下操作:
重采样。AudioDeviceModule 送进来的音频数据的采样率是设备采集的原始采样率,这里需要把采集的音频数据转换为适合 WebRTC 的音频处理模块如降噪和回声消除等模块及编码器处理的采样率。
对音频数据做回声消除,降噪等处理。
把音频数据送出去,给注入的 AudioSendStream。
AudioState
AudioState 既是 WebRTC 音频流水线节点的容器,也可用于对这些节点做一些管理和控制,以及将不同节点粘起来构成流水线。AudioState 接口的定义 (位于 webrtc/src/call/audio_state.h) 如下:
namespace webrtc {
class AudioTransport;
// AudioState holds the state which must be shared between multiple instances of
// webrtc::Call for audio processing purposes.
class AudioState : public rtc::RefCountInterface {
public:
struct Config {
Config();
~Config();
// The audio mixer connected to active receive streams. One per
// AudioState.
rtc::scoped_refptr<AudioMixer> audio_mixer;
// The audio processing module.
rtc::scoped_refptr<webrtc::AudioProcessing> audio_processing;
// TODO(solenberg): Temporary: audio device module.
rtc::scoped_refptr<webrtc::AudioDeviceModule> audio_device_module;
};
struct Stats {
// Audio peak level (max(abs())), linearly on the interval [0,32767].
int32_t audio_level = -1;
// See:
// https://w3c.github.io/webrtc-stats/#dom-rtcmediastreamtrackstats-totalaudioenergy
double total_energy = 0.0f;
double total_duration = 0.0f;
};
virtual AudioProcessing* audio_processing() = 0;
virtual AudioTransport* audio_transport() = 0;
// Enable/disable playout of the audio channels. Enabled by default.
// This will stop playout of the underlying audio device but start a task
// which will poll for audio data every 10ms to ensure that audio processing
// happens and the audio stats are updated.
virtual void SetPlayout(bool enabled) = 0;
// Enable/disable recording of the audio channels. Enabled by default.
// This will stop recording of the underlying audio device and no audio
// packets will be encoded or transmitted.
virtual void SetRecording(bool enabled) = 0;
virtual Stats GetAudioInputStats() const = 0;
virtual void SetStereoChannelSwapping(bool enable) = 0;
static rtc::scoped_refptr<AudioState> Create(
const AudioState::Config& config);
~AudioState() override {}
};
} // namespace webrtc作为音频处理流水线的容器,AudioState 接口主要包含了 AudioMixer、AudioProcessing 和 AudioDeviceModule。AudioState 对象的创建主要通过静态工厂方法完成。
WebRTC 提供了 AudioState 接口的实现,该实现的定义 (位于 webrtc/src/audio/audio_state.h ) 如下:
namespace webrtc {
class AudioSendStream;
class AudioReceiveStream;
namespace internal {
class AudioState : public webrtc::AudioState {
public:
explicit AudioState(const AudioState::Config& config);
~AudioState() override;
AudioProcessing* audio_processing() override;
AudioTransport* audio_transport() override;
void SetPlayout(bool enabled) override;
void SetRecording(bool enabled) override;
Stats GetAudioInputStats() const override;
void SetStereoChannelSwapping(bool enable) override;
AudioDeviceModule* audio_device_module() {
RTC_DCHECK(config_.audio_device_module);
return config_.audio_device_module.get();
}
bool typing_noise_detected() const;
void AddReceivingStream(webrtc::AudioReceiveStream* stream);
void RemoveReceivingStream(webrtc::AudioReceiveStream* stream);
void AddSendingStream(webrtc::AudioSendStream* stream,
int sample_rate_hz,
size_t num_channels);
void RemoveSendingStream(webrtc::AudioSendStream* stream);
private:
void UpdateAudioTransportWithSendingStreams();
rtc::ThreadChecker thread_checker_;
rtc::ThreadChecker process_thread_checker_;
const webrtc::AudioState::Config config_;
bool recording_enabled_ = true;
bool playout_enabled_ = true;
// Transports mixed audio from the mixer to the audio device and
// recorded audio to the sending streams.
AudioTransportImpl audio_transport_;
// Null audio poller is used to continue polling the audio streams if audio
// playout is disabled so that audio processing still happens and the audio
// stats are still updated.
std::unique_ptr<NullAudioPoller> null_audio_poller_;
std::unordered_set<webrtc::AudioReceiveStream*> receiving_streams_;
struct StreamProperties {
int sample_rate_hz = 0;
size_t num_channels = 0;
};
std::map<webrtc::AudioSendStream*, StreamProperties> sending_streams_;
RTC_DISALLOW_IMPLICIT_CONSTRUCTORS(AudioState);
};
} // namespace internal 如上面看到的,AudioState对象在WebRtcVoiceEngine::Init()创建。AudioState的Create()函数定义 (位于webrtc/src/audio/audio_state.cpp) 如下:
rtc::scoped_refptr<AudioState> AudioState::Create(
const AudioState::Config& config) {
return new rtc::RefCountedObject<internal::AudioState>(config);
}WebRTC 中实际在用的 AudioState 对象为 webrtc::internal::AudioState 的对象。
AudioState 完成的工作主要为:
音频流水线的节点的 Getter
管理音频静态流水线和动态流水线的连接,也就是添加和移除 AudioSendStream 和 AudioReceiveStream:把 AudioSendStream 注入给 AudioTransportImpl 或从中移除,把 AudioReceiveStream 添加到 AudioMixer 或从中移除。这些接口主要由 webrtc::Call 使用。
控制播放和录制的启动和停止。
webrtc::internal::AudioState 的具体实现 (位于 webrtc/src/audio/audio_state.cpp) 如下:
namespace webrtc {
namespace internal {
AudioState::AudioState(const AudioState::Config& config)
: config_(config),
audio_transport_(config_.audio_mixer, config_.audio_processing.get()) {
process_thread_checker_.Detach();
RTC_DCHECK(config_.audio_mixer);
RTC_DCHECK(config_.audio_device_module);
}
AudioState::~AudioState() {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
RTC_DCHECK(receiving_streams_.empty());
RTC_DCHECK(sending_streams_.empty());
}
AudioProcessing* AudioState::audio_processing() {
RTC_DCHECK(config_.audio_processing);
return config_.audio_processing.get();
}
AudioTransport* AudioState::audio_transport() {
return &audio_transport_;
}
bool AudioState::typing_noise_detected() const {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
return audio_transport_.typing_noise_detected();
}
void AudioState::AddReceivingStream(webrtc::AudioReceiveStream* stream) {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(0, receiving_streams_.count(stream));
receiving_streams_.insert(stream);
if (!config_.audio_mixer->AddSource(
static_cast<internal::AudioReceiveStream*>(stream))) {
RTC_DLOG(LS_ERROR) << "Failed to add source to mixer.";
}
// Make sure playback is initialized; start playing if enabled.
auto* adm = config_.audio_device_module.get();
if (!adm->Playing()) {
if (adm->InitPlayout() == 0) {
if (playout_enabled_) {
adm->StartPlayout();
}
} else {
RTC_DLOG_F(LS_ERROR) << "Failed to initialize playout.";
}
}
}
void AudioState::RemoveReceivingStream(webrtc::AudioReceiveStream* stream) {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
auto count = receiving_streams_.erase(stream);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(1, count);
config_.audio_mixer->RemoveSource(
static_cast<internal::AudioReceiveStream*>(stream));
if (receiving_streams_.empty()) {
config_.audio_device_module->StopPlayout();
}
}
void AudioState::AddSendingStream(webrtc::AudioSendStream* stream,
int sample_rate_hz,
size_t num_channels) {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
auto& properties = sending_streams_[stream];
properties.sample_rate_hz = sample_rate_hz;
properties.num_channels = num_channels;
UpdateAudioTransportWithSendingStreams();
// Make sure recording is initialized; start recording if enabled.
auto* adm = config_.audio_device_module.get();
if (!adm->Recording()) {
if (adm->InitRecording() == 0) {
if (recording_enabled_) {
adm->StartRecording();
}
} else {
RTC_DLOG_F(LS_ERROR) << "Failed to initialize recording.";
}
}
}
void AudioState::RemoveSendingStream(webrtc::AudioSendStream* stream) {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
auto count = sending_streams_.erase(stream);
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(1, count);
UpdateAudioTransportWithSendingStreams();
if (sending_streams_.empty()) {
config_.audio_device_module->StopRecording();
}
}
void AudioState::SetPlayout(bool enabled) {
RTC_LOG(INFO) << "SetPlayout(" << enabled << ")";
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
if (playout_enabled_ != enabled) {
playout_enabled_ = enabled;
if (enabled) {
null_audio_poller_.reset();
if (!receiving_streams_.empty()) {
config_.audio_device_module->StartPlayout();
}
} else {
config_.audio_device_module->StopPlayout();
null_audio_poller_ =
absl::make_unique<NullAudioPoller>(&audio_transport_);
}
}
}
void AudioState::SetRecording(bool enabled) {
RTC_LOG(INFO) << "SetRecording(" << enabled << ")";
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
if (recording_enabled_ != enabled) {
recording_enabled_ = enabled;
if (enabled) {
if (!sending_streams_.empty()) {
config_.audio_device_module->StartRecording();
}
} else {
config_.audio_device_module->StopRecording();
}
}
}
AudioState::Stats AudioState::GetAudioInputStats() const {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
const voe::AudioLevel& audio_level = audio_transport_.audio_level();
Stats result;
result.audio_level = audio_level.LevelFullRange();
RTC_DCHECK_LE(0, result.audio_level);
RTC_DCHECK_GE(32767, result.audio_level);
result.total_energy = audio_level.TotalEnergy();
result.total_duration = audio_level.TotalDuration();
return result;
}
void AudioState::SetStereoChannelSwapping(bool enable) {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
audio_transport_.SetStereoChannelSwapping(enable);
}
void AudioState::UpdateAudioTransportWithSendingStreams() {
RTC_DCHECK(thread_checker_.IsCurrent());
std::vector<webrtc::AudioSendStream*> sending_streams;
int max_sample_rate_hz = 8000;
size_t max_num_channels = 1;
for (const auto& kv : sending_streams_) {
sending_streams.push_back(kv.first);
max_sample_rate_hz = std::max(max_sample_rate_hz, kv.second.sample_rate_hz);
max_num_channels = std::max(max_num_channels, kv.second.num_channels);
}
audio_transport_.UpdateSendingStreams(std::move(sending_streams),
max_sample_rate_hz, max_num_channels);
}
} // namespace internal总结一下:
WebRtcVoiceEngine::Init()建立了 WebRTC 音频处理的静态流水线。AudioTransport将音频处理静态流水线的各个节点粘起来。webrtc::Call使用AudioState将音频处理流水线的静态部分和动态部分连接起来。
最后
以上就是认真大船最近收集整理的关于WebRTC的音频处理流水线的全部内容,更多相关WebRTC内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
![WebRTC[40]- WebRTC 如何在安卓系统上采集音频数据](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg2.png)







发表评论 取消回复