一.算法原理
A* 算法,就是解决在一个平面 grid地图中寻找起点到终点的最短路径问题的算法,类似于Dijkstra算法和BFS算法一样,属于广度优先搜索。实际上它还是一个启发式搜索算法,什么叫启发式搜索算法?不同于BFS和DFS在子节点选择上其实是盲目的,启发式搜索就是利用评估函数在平面中对所有的待搜索点进行评估,找出最佳的搜索点问题。那么A* 算法是如何利用这些思想的呢?
1.评估函数
对于地图中的每一个点,都有一个评估标准值F,评估函数为:F= G+H
而G表示的是从起点到现在所在方格的总代价,计算G我们通常采用搜索树的深度,及此节点的上一个节点G+1来计算,源点本身G=0;
H代表着从当前点到目的地点的预计代价,计算H我们通常采用“曼哈端距离算法”(译注:Manhattan distance method),这个算法仅仅只是计算了当前点到终点的水平方向和竖直方向上的方格数,而没有将障碍物或不同地形考虑进来。 如果你在游戏中采用此算法,则需要注意将地形的情况考虑到H的计算之中,假设是在grid地图中,目的地坐标(4,4),当前坐标(0,0),当前坐标的 H = 8 H=8 H=8
2.待测点与已测点的存储
我们使用closeList(闭表)来储存那些我们被探测过的点和障碍点,当我们的终点被加入closeList中的时候,意味着我们已经得到最短路径,我们停止扩散搜索。
我们使用openList(开表)来记录我们的待测点,我们通常将当前点A的上下左右(其他的斜角方向是否考虑在内处于你的要求)中的那些没有被搜索过且不为障碍点的节点加入到openList中,同时设置这些点的parent引用指向当前节点A,用于记录路径,便于最后输出路径,并设置他们的F= H + G,H根据此节点的实际情况进行计算,G取当前节点A的G再加1,如果这些点中有的已经加入到openList中,我们将他的F值与根据节点A计算的F进行比较,如果新计算的评估值F小,我们就更新那个节点的F值。每次从开表中选择评估值F最小的点,使每一次的搜索点为最优点。
伪代码:
closeList:= set contains barriers nodes at the beginning
openList:= set contains the source node at the beginning
while(!openList isEmpty())
node = get_node_with_minF(openList)
if(node == end_node)
getPathTo(end_node)
break
for(each neighbor node的相邻节点)
//如果相邻节点在闭表中,直接跳过
if(neighbor in closeList)
continue
//计算相邻节点的H和G
int G = node.G + 1
int H = calcuH_from_neighbor_to_end(neighbor, end)
//已在开表中,需要更新
if(neighbor in openList)
if(neighbor.F > G + H)
neighbor.F = G+H
neighbor.parent = node
else
neighbor.F = G+H
neighbor.parent = node
openList.add(neighbor)
openList.remove(node)
closeList.add(node)
二.算法实现
package com.example.astar;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.Comparator;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @author 玄木.
*/
public class AStar {
private Node source;
private Node end;
private List<Node> openList;
private List<Node> closeList;
/**
*
* @param map 0:for source node, 1:for nothing, 2:for barriers, 3:for end node, 4:for path
* @return the path from source to end
* @throws NotFoundException
*/
public void aStar(int[][] map) throws NotFoundException{
//异常处理
if(map.length==0||map[0].length==0){
throw new NotFoundException("parameters invalid");
}
init(map);
while(!openList.isEmpty()){
Node node = getNodeWithMinF(openList);
if(node.equals(end)){
for(Node tmp : getPathTo(node)){
map[tmp.y][tmp.x] = 4;
}
printMap(map);
return;
}
for(Node neighbor : getNeighbors(node, map)){
if (closeList.contains(neighbor)){
continue;
}
int G = node.getG() + 1;
int H = calcuH(neighbor, end);
if(openList.contains(neighbor)) {
if (neighbor.getF() > G + H) {
neighbor.setG(G);
neighbor.setH(H);
neighbor.setF(G + H);
neighbor.setParent(node);
}
}
else{
neighbor.setG(G);
neighbor.setH(H);
neighbor.setF(G + H);
neighbor.setParent(node);
openList.add(neighbor);
}
}
openList.remove(node);
closeList.add(node);
}
throw new NotFoundException("not found");
}
/**
* init the openList,closeList,source,end node
* @param map
*/
public void init(int[][] map){
openList = new ArrayList<Node>();
closeList = new ArrayList<Node>();
for(int row=0;row<map.length;row++){
for(int column=0;column<map[0].length;column++){
//add the barriers nodes to the closeList
if(map[row][column]==2){
closeList.add(new Node(column, row));
}
else if(map[row][column]==1){
source = new Node(column, row);
}
else if(map[row][column]==3){
end = new Node(column, row);
}
}
}
source.setG(0);
source.setH(calcuH(source, end));
source.setF(source.getG()+source.getH());
openList.add(source);
}
/**
* return the path from source node to end node
* @param end
* @return
*/
public List<Node> getPathTo(Node end){
List<Node> pathTo = new ArrayList<Node>();
Node temp = end;
while(temp!=null){
pathTo.add(temp);
temp = temp.parent;
}
Collections.reverse(pathTo);
return pathTo;
}
/**
* get neighbors of node
* @param node
* @param map
* @return
*/
public List<Node> getNeighbors(Node node, int[][] map){
List<Node> list = new ArrayList<Node>();
if(node.x>0 && node.x<map[0].length-1){
list.add(new Node(node.x-1,node.y));
list.add(new Node(node.x+1,node.y));
}
else if(node.x == 0){
list.add(new Node(node.x+1,node.y));
}
else{
list.add(new Node(node.x-1,node.y));
}
if(node.y>0 && node.y<map.length-1){
list.add(new Node(node.x,node.y+1));
list.add(new Node(node.x,node.y-1));
}
else if(node.y == 0){
list.add(new Node(node.x,node.y+1));
}
else{
list.add(new Node(node.x,node.y-1));
}
return list;
}
/**
* calculate H
* @param node
* @param end
* @return
*/
public int calcuH(Node node, Node end){
return Math.abs(node.x-end.x)+Math.abs(node.y-end.y);
}
/**
* get the node with minimum F in openList
* @param list
* @return
*/
public Node getNodeWithMinF(List<Node> list){
Collections.sort(list, Comparator.comparingInt(o -> o.F));
return list.get(0);
}
/**
* print the map
* @param map
*/
public void printMap(int[][] map){
int row=0,column=0;
for(row=0;row<map.length;row++){
for (column=0;column<map[0].length;column++){
switch (map[row][column]){
case 0:
System.out.print("[]");
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("##");
break;
case 1:
case 3:
System.out.print("@@");
break;
case 4:
System.out.print("->");
break;
default:break;
}
}
System.out.println();
}
System.out.println();
}
/**
* static inner class Node
*/
public static class Node{
private int x;
private int y;
private int G;
private int H;
private int F;
private Node parent;
public Node(int x, int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.G = 0;
this.H = 0;
this.F = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
this.parent = null;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Node){
Node other = (Node)obj;
return other.x==this.x && other.y==this.y;
}
return false;
}
public int getG() {
return G;
}
public void setG(int g) {
G = g;
}
public int getH() {
return H;
}
public void setH(int h) {
H = h;
}
public int getF() {
return F;
}
public void setF(int f) {
F = f;
}
public Node getParent() {
return parent;
}
public void setParent(Node parent) {
this.parent = parent;
}
}
/**
* static inner Exception class
*/
public static class NotFoundException extends Exception{
public NotFoundException(String mess) {
super(mess);
}
}
}
三.实验测试
1. 基础测试
@Test
public void aStarTest(){
int[][] map = {
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 2, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 3},
};
try {
aStar.printMap(map);
aStar.aStar(map);
}catch (AStar.NotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
[]表示可以行走的空地
##表示障碍
->表示路径
@ 表示起点和终点
实验结果
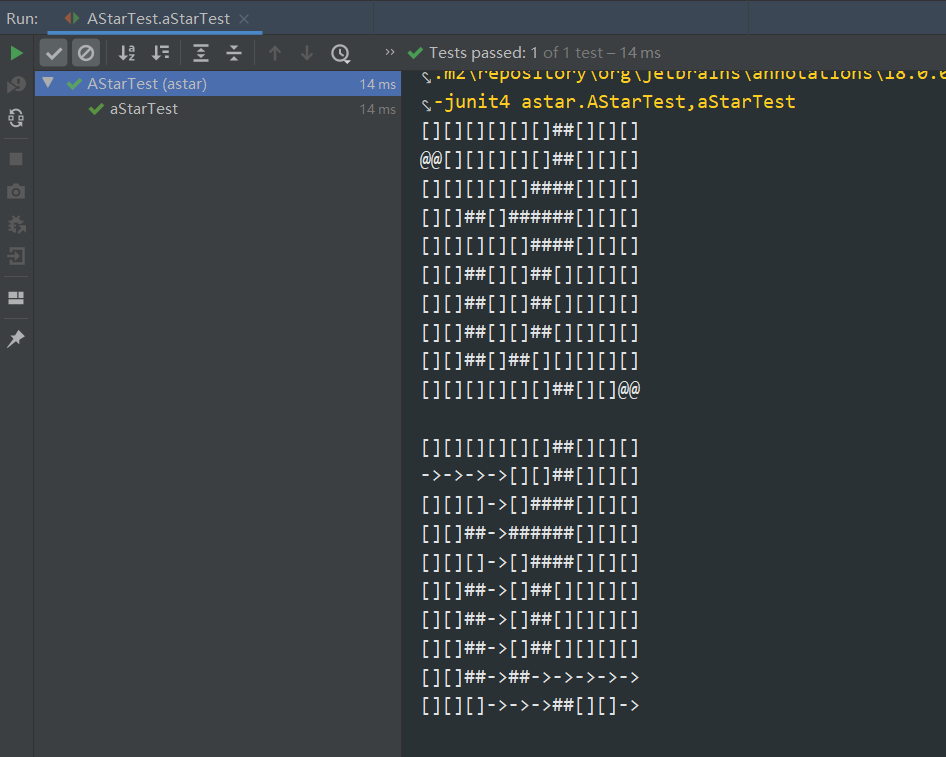
测试通过
2.异常测试
@Test
public void aStarTest(){
int[][] map = {
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 0},
{0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 2, 0, 0, 3},
};
try {
aStar.printMap(map);
aStar.aStar(map);
}catch (AStar.NotFoundException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
实验结果
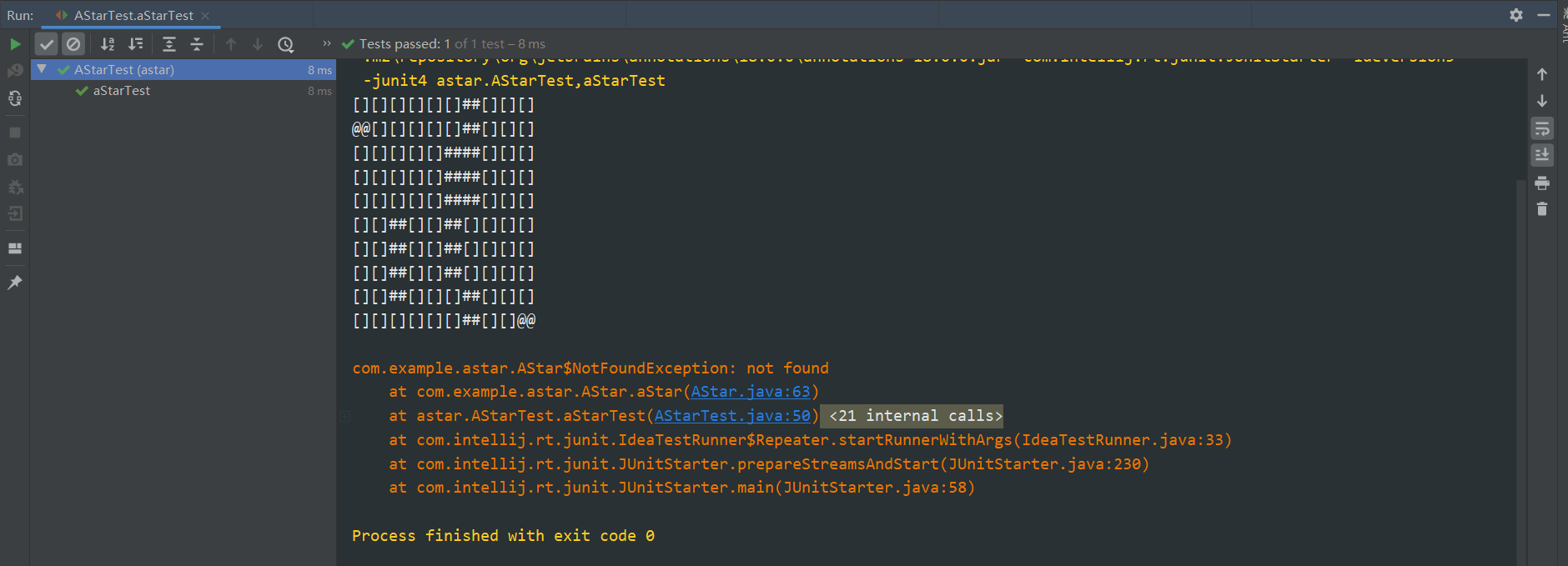
测试通过
你可能还敢兴趣的图论算法(均附Java实现代码):
-
算法实验–主函数只有五行的Floyed的算法以及最短路径输出
-
你必须会的–Dijkstra算法–单源最短路径问题
-
你必须会的DFS的递归实现与堆栈实现
-
你了解欧拉回路吗?
最后
以上就是温婉柚子最近收集整理的关于你必须会的启发式搜索算法--A*算法一.算法原理二.算法实现三.实验测试的全部内容,更多相关你必须会内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复