表是按位置保存的一个元素序列。因为不允许下标访问,因此为了访问元素的值,我们必须通过其前面的一个元素。然而,所有的插入和删除操作的是ian复杂度均为O(1),即使是那些在表内部执行的操作也是如此。想比较而言,在序列中相应的向量操作的时间复杂度为O(n).
List类熟悉的操作偶: push_back()和pop_back()。然而,表为表头front()增加了相应的操作push_front()和pop_front()。就像对每个容器类的情况一样,表提供了size()和empty(),访问操作。还有back(),front()
例如:
intList.push_front(5);//在表首增加元素5
intList.push_front(3); //在表首增加元素3
intList.push_back(4);//在表为增加元素4
intList.push_back(6); //在表尾增加元素6
intList.back(); //返回表尾元素
intList.front(); //返回表头元素
intList.pop_front(); //删除表头元素
intList.pop_back(); //删除表尾元素
n=intList.size(); //捕获表的长度,并赋值给n
intList.empty(); //判断是否为空表迭代器是一种一般的指针,它正向或反向在表中逐个元素移动。 *运算符访问在任意点表项的值。
list类有两种迭代器类型:iterator和const_iterator。 const_inerator必须用于常量表访问。 *运算符不能在赋值语句左边和const_iterator一起使用。
用表成员函数begin()给迭代器一个初始值,它指向第一个元素。成员函数end()返回个一个迭代器,它指向表尾部元素的下一个位置。
通过使用迭代器范围[frist,last],可以很好地实现表对象的顺序查找。其实现返回一个指向目标值的迭代器,或当目标值不再表中时,返回last。
list类成员函数insert()和erase() 用一个迭代器参数来更改表。函数insert(pos value)把value放在表中迭代器pos指向的数据千米那。函数erase(pos)从表中删除pos指向的数据项。
用#include<list>包含所要的模版
下面用一个程序(没有重复的有序表)来说明表的操作:
该程序主要说明了迭代器的用法以及insert()和erase()的用法
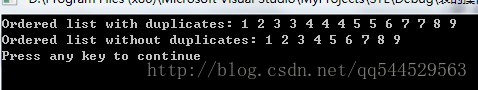
//此程序通过扫描数组和调用insertOrder()函数,生成了有序表intList,
//在调用removeDuplicates()函数删除重复数值前后,程序用函数writeList()输出表
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
template<typename T>
void insertOrder(list<T> & orderedList,const T& item) //在有序表中插入新项
{
list<T>::iterator curr = orderedList.begin();//curr从第一个表元素开始,stop表示结束
list<T>::iterator stop = orderedList.end();
while((curr!=stop)&& (*curr < item)) //查找插入点
curr++;
orderedList.insert(curr,item); //使用insert()插入
}
template<typename T>
void writeList(const list<T> & orderedList) //输出表的内容
{
list<T>::const_iterator iter=orderedList.begin();//由于不改变表的内容,所以使用常量迭代器
list<T>::const_iterator stop=orderedList.end();
while(iter!=stop)
{
cout<<*iter<<" ";
iter++;
}
cout<<endl;
}
template<typename T>
void removeDuplicates(list<T> & aList) //移除重复项
{
T currValue; //当前数据值
list<T>::iterator curr=aList.begin();//使用几个迭代器
list<T>::iterator stop=aList.end();
list<T>::iterator p;
while(curr!=stop) //从表头开始,在表中循环
{
currValue=*curr; //记录当前表数据值
p=curr; //将p设置为curr右边的元素
p++;
while(p!=stop) //向后移动,删除currValue的所有出现
{
if(*p==currValue) //删除当前元素,将p向后移一项
aList.erase(p++);
else p++;//移向下一个表元素
}
//删除currValue的重复值,移动到下一个数据值,并重复此过程
curr++;
}
}
int main()
{
//声明具有重复值的无序数组
int arr[]={7,5,9,4,3,8,1,6,2,4,4,7,5,3},i;
int arrsize=sizeof(arr)/sizeof(int);
list<int> intList;
//使用数组中的元素生成有序表
for(i=0;i<arrsize;i++)
insertOrder(intList,arr[i]);
//输出具有重复数值的有序表
cout<<"Ordered list with duplicates: ";
writeList(intList);
//删除重复值
removeDuplicates(intList);
//输出没有重复值的有序表
cout<<"Ordered list without duplicates: ";
writeList(intList);
}
表的排序sort();
#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[]={1,23,4,7,3,11,12,0};
int size=sizeof(a)/sizeof(int);
list<int> l(a,a+size);
l.sort();
//cout<<size;
list<int>::iterator iter=l.begin();
while(iter!=l.end())
{
cout<<*iter<<endl;
iter++;
}
return 0;
}#include<iostream>
#include<list>
#include<string>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct Student
{ private:
string name;
int score;
public:
Student(string name ,int score)
{
this->name=name;
this->score=score;
}
string getname()
{
return name;
}
int getscore()
{
return score;
}
};
int main()
{
string name;
int score;
list<Student> stu;
Student stu1("htp",100);
Student stu2("htp1",101);
stu.push_back (stu1);
stu.push_back (stu2);
name="aaa";
score=100;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
// cin>>name>>score;
Student stu1(name,++score);
stu.push_back(stu1);
}
list<Student>::iterator iter=stu.begin();
while(iter!=stu.end ())
{
cout<<iter->getname() <<" "<<iter->getscore()<<endl ;
iter++;
}
return 0;
}最后
以上就是小巧睫毛最近收集整理的关于数据结构应用标准模版库STL——表的操作(没有重复的有序表)的全部内容,更多相关数据结构应用标准模版库STL——表内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。





![[数组][哈希表]leetcode167:两数之和Ⅱ-输入有序数组(easy)](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg8.png)


发表评论 取消回复