| 静态方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Imgproc.findContours | 轮廓检索方式,是形状分析和对象检测和识别的有用工具,参考 PCAExample示例 |
| Imgproc.drawContours | 绘制轮廓轮廓或填充轮廓,与findContours 合用,参数== contourIdx==:-1为全部绘制,根据contours数量填写,thickness:线条粗细,LineTypes 参数层次结构有关层次结构的可选信息。仅当您只想绘制一些轮廓时才需要它参数 ,maxLevel 绘制轮廓的最大级别。如果为 0,则仅绘制指定的轮廓。如果为 1,则该函数绘制等高线和所有嵌套的等高线。如果为 2,则函数绘制轮廓、所有嵌套轮廓、所有嵌套到嵌套轮廓,依此类推。仅当有可用的层次结构时才考虑此参数 |
| Imgproc.contourArea | 轮廓区域,计算轮廓面积 |
| Imgproc.arcLength | 计算轮廓周长或曲线长度,该函数计算曲线长度或闭合轮廓周长。 |
| Imgproc.approxPolyDP | 以指定的精度逼近多边形曲线。近似函数 |
| Imgproc.boundingRect | 计算灰度图像的点集或非零像素的右上边界矩形 |
| Imgproc.matchTemplate | 模板匹配,将模板与重叠的图像区域进行比较。参考场景示例== MatchTemplateExample== |
| Imgproc.calcHist | 直方图计算 |
| Imgproc.equalizeHist | 均衡灰度图像的直方图 |
| Imgproc.createCLAHE | 对一张图进行区域划分,然后再做智能直方图均衡化 |
| Imgproc.getStructuringElement | 自己定义一个核的大小,参数shape:形状 Imgproc.MORPH_RECT矩形等等,ksize:核的大小,anchor:核的锚点,默认(-1,-1) |
| Core.minMaxLoc | 查找数组中的全局最小值和最大值 |
一.图像轮廓
① 轮廓检索
Imgproc.findContours(image, contours, hierarchy, mode, method)参数解释
1.mode
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Imgproc.RETR_EXTERNAL | 只检测最外面的轮廓 |
| Imgproc.RETR_LIST | 检测所有轮廓,并保存到一条链表当中 |
| Imgproc.RETR_CCOMP | 检测所有轮廓,并分为两层 |
| Imgproc.RETR_TREE | 检测所有轮廓,并重构嵌套轮廓的整个层次 |
2.method
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE | 以Freeman链码的方式输出轮廓 |
| Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE | 压缩水平,垂直和斜的部分 |
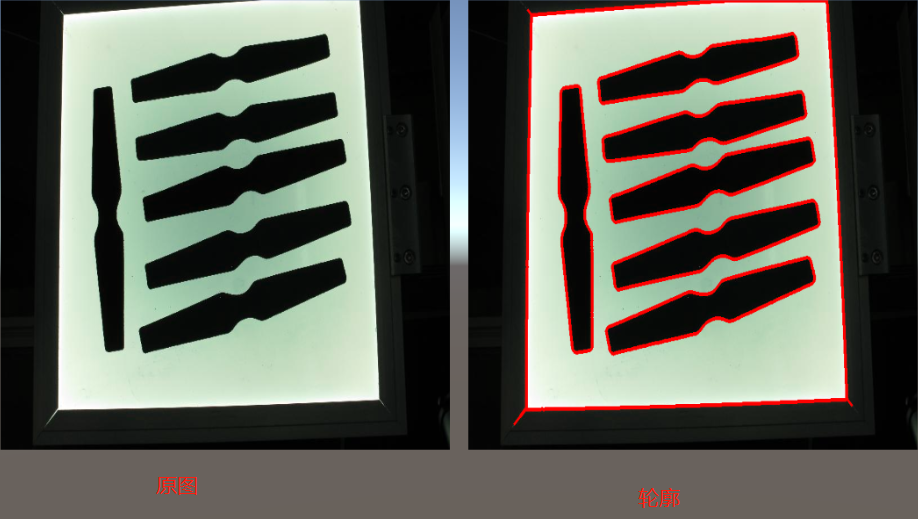

void TestContours()
{
//读取灰度图
Mat mat = Imgcodecs.imread(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/pca_test1.jpg");
Mat mat1 = new Mat();
//转为灰度图
Imgproc.cvtColor(mat, mat1, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//阈值处理,作用是为了更好的去做轮廓检测
Imgproc.threshold(mat1, mat1, 50, 255, Imgproc.THRESH_BINARY | Imgproc.THRESH_OTSU);
List<MatOfPoint> matOfPoints = new List<MatOfPoint>();
Mat hierarchy = new Mat();
//matOfPoints取得轮廓数据
Imgproc.findContours(mat1, matOfPoints, hierarchy, Imgproc.RETR_LIST, Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
Mat Apply = new Mat();
mat.copyTo(Apply);
// for (int i=0;i< matOfPoints.Count;i++)
//{
// Imgproc.drawContours(Apply, matOfPoints, i, new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
//}
//把全部轮廓绘制到原图上
Imgproc.drawContours(Apply, matOfPoints, -1, new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
//计算第1个轮廓面积
//Imgproc.drawContours(Apply, matOfPoints, 0, new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
//double area= Imgproc.contourArea(matOfPoints[0]);
计算第1个轮廓周长
//MatOfPoint2f ofPoint2F = new MatOfPoint2f(matOfPoints[0].toArray());
//double arclength = Imgproc.arcLength(ofPoint2F, true);
//Debug.Log(area);
//Debug.Log(arclength);
//轮廓图
Texture2D texture = new Texture2D(Apply.cols(), Apply.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(Apply, texture);
rawImage.texture = texture;
//原图
Texture2D texture1 = new Texture2D(mat.cols(), mat.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(mat, texture1);
GetRaw.texture = texture1;
}
② 轮廓近似
| 参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| approxCurve | 返回一个近似结果 |
| epsilon | 指定近似精度的参数。这是原始曲线与其近似值之间的最大距离 |
| closed | 如果为true,近似曲线是闭合的 |
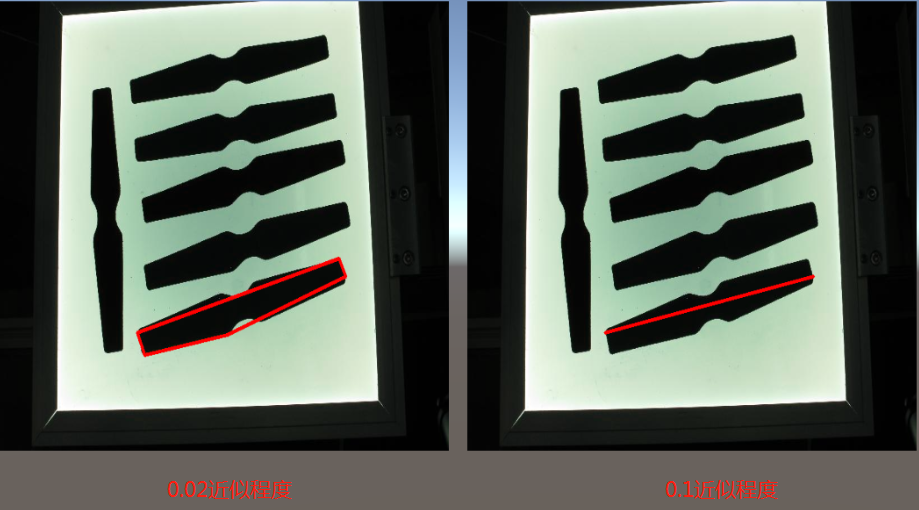

//轮廓近似
void TestapproxPolyDP()
{
//读取灰度图
Mat mat = Imgcodecs.imread(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/pca_test1.jpg");
Mat mat1 = new Mat();
//转为灰度图
Imgproc.cvtColor(mat, mat1, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//阈值处理,作用是为了更好的去做轮廓检测
Imgproc.threshold(mat1, mat1, 50, 255, Imgproc.THRESH_BINARY | Imgproc.THRESH_OTSU);
List<MatOfPoint> matOfPoints = new List<MatOfPoint>();
Mat hierarchy = new Mat();
//matOfPoints取得轮廓数据
Imgproc.findContours(mat1, matOfPoints, hierarchy, Imgproc.RETR_LIST, Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
Mat Apply1f = new Mat();
mat.copyTo(Apply1f);
Mat Apply2f = new Mat();
mat.copyTo(Apply2f);
//取其中一条轮廓对比
MatOfPoint2f ofPoint2F = new MatOfPoint2f(matOfPoints[0].toArray());
//0.1的近似程度
double epsilon1=0.1f* Imgproc.arcLength(ofPoint2F, true);
MatOfPoint2f first1f= new MatOfPoint2f();
Imgproc.approxPolyDP(ofPoint2F, first1f, epsilon1, true);
MatOfPoint matOf1f = new MatOfPoint(first1f.toArray());
Imgproc.drawContours(Apply1f, new List<MatOfPoint> { matOf1f }, -1, new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
Texture2D texture = new Texture2D(Apply1f.cols(), Apply1f.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(Apply1f, texture);
rawImage.texture = texture;
//0.02的近似程度
double epsilon2 = 0.02f * Imgproc.arcLength(ofPoint2F, true);
MatOfPoint2f first2f = new MatOfPoint2f();
Imgproc.approxPolyDP(ofPoint2F, first2f, epsilon2, true);
MatOfPoint matOf2f = new MatOfPoint(first2f.toArray());
Imgproc.drawContours(Apply2f, new List<MatOfPoint> { matOf2f }, -1, new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
Texture2D texture1 = new Texture2D(Apply2f.cols(), Apply2f.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(Apply2f, texture1);
GetRaw.texture = texture1;
//
}
③边界矩形和外接圆

void TestShape()
{
Mat mat = Imgcodecs.imread(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/pca_test1.jpg");
Mat mat1 = new Mat();
//转为灰度图
Imgproc.cvtColor(mat, mat1, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
//阈值处理,作用是为了更好的去做轮廓检测
Imgproc.threshold(mat1, mat1, 50, 255, Imgproc.THRESH_BINARY | Imgproc.THRESH_OTSU);
List<MatOfPoint> matOfPoints = new List<MatOfPoint>();
Mat hierarchy = new Mat();
//matOfPoints取得轮廓数据
Imgproc.findContours(mat1, matOfPoints, hierarchy, Imgproc.RETR_LIST, Imgproc.CHAIN_APPROX_NONE);
Rect rect= Imgproc.boundingRect(matOfPoints[0]);
Mat Apply1f = new Mat();
mat.copyTo(Apply1f);
Debug.Log(rect);
//矩形框 外接圆
Imgproc.rectangle(Apply1f, new Point(rect.x, rect.y),new Point(rect.x+rect.width,rect.y+rect.height), new Scalar(255, 0, 0),3);
MatOfPoint2f matOfPoint2F = new MatOfPoint2f(matOfPoints[1].toArray());
Point center = new Point();
float[] radius = new float[1] ;
Imgproc.minEnclosingCircle(matOfPoint2F, center, radius);
Imgproc.circle(Apply1f, center,(int) radius[0], new Scalar(255, 0, 0), 3);
Texture2D texture = new Texture2D(Apply1f.cols(), Apply1f.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(Apply1f, texture);
rawImage.texture = texture;
//原图
Texture2D texture1 = new Texture2D(mat.cols(), mat.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(mat, texture1);
GetRaw.texture = texture1;
}
二.模板匹配
参考文档 https://www.w3cschool.cn/opencv/opencv-pswj2dbc.html
参数method解释
| 填写参数 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF | 计算平方,值越小与相关 |
| Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED | 计算归一化的平方值,值越接近0,越相关 |
| Imgproc. TM_CCORR | 计算相关性,值越大越相关 |
| Imgproc.TM_CCORR_NORMED | 计算归一化相关性,值越接近1,越相关 |
| Imgproc.TM_CCOEFF | 计算相关系数,值越大,越相关 |
| Imgproc. TM_CCOEFF_NORMED | 计算归一化相关系数,值越接近1,越相关 |
输出resultmat=(A-a+1,B-b+1) 其中(A,B)为大图,(a,b)为小图

//模板匹配
void TestMatchTemplate()
{
Texture2D imgTexture = Resources.Load("lena") as Texture2D;
Texture2D tempTexture = Resources.Load("template2") as Texture2D;
Mat imgMat = new Mat(imgTexture.height, imgTexture.width, CvType.CV_8UC4);
Mat tempMat = new Mat(tempTexture.height, tempTexture.width, CvType.CV_8UC4);
Utils.texture2DToMat(imgTexture, imgMat);
Utils.texture2DToMat(tempTexture, tempMat);
//创建一个返回结果的mat
int result_cols = imgMat.cols() - tempMat.cols() + 1;
int result_rows = imgMat.rows() - tempMat.rows() + 1;
Mat result = new Mat(result_rows, result_cols, CvType.CV_32FC1);
/*The mask应具有CV_8U或CV_32F深度和与模板图像相同数量的通道。在CV_8U情况下,
* mask值被视为二进制,即零和非零。在CV_32F情况下,值应该落在[0..1]范围内,
* 并且模板像素将乘以相应的The mask像素值。由于样本中的输入图像具有CV_8UC3类型,
* 因此屏蔽也被读取为彩色图像。*/
/*目前只有两种匹配方法接受掩码:CV_TM_SQDIFF和CV_TM_CCORR_NORMED*/
/* if( match_method == Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF || match_method == Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED )
{ matchLoc = mmr.minLoc; }
else
{ matchLoc = mmr.maxLoc; } 这是文档java描述*/
Imgproc.matchTemplate(imgMat, tempMat, result, Imgproc.TM_SQDIFF_NORMED);
Mat mask = new Mat();
//返回最大值和最小值
MinMaxLocResult minMaxLoc= Core.minMaxLoc(result);
double minx = minMaxLoc.minLoc.x;
double miny = minMaxLoc.minLoc.y;
Debug.Log(new Point(minx + tempMat.cols(), miny + tempMat.rows()));
Debug.Log(minMaxLoc.minLoc);
Imgproc.rectangle(imgMat, minMaxLoc.minLoc, new Point(minx + tempMat.cols(),miny+tempMat.rows()), new Scalar(0, 255, 0, 255), 2);
Texture2D texture = new Texture2D(imgMat.cols(), imgMat.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(imgMat, texture);
rawImage.texture = texture;
//原图
Texture2D texture1 = new Texture2D(tempMat.cols(), tempMat.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(tempMat, texture1);
GetRaw.texture = texture1;
}
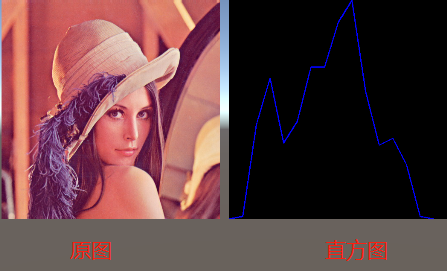
三.直方图
什么是直方图?
- 直方图是将数据组织成一组预定义仓的收集计数
- 当我们说数据时,我们并不把它限制为强度值(正如我们在前面的教程中看到的)。收集的数据可以是您发现有用的描述您的图像的任何功能。

方法 Imgproc.calcHist ( List< Mat > images,MatOfInt channels,Mat mask,Mat hist,MatOfInt histSize,MatOfFloat ranges,bool accumulate )
对应参数解释 - image:传入一个数组,对原图像格式像素采集,bins
- channels:如果是灰度图 new MatOfInt (0),如果是彩色图像传入new MatOfInt (0,1,2) 分别对应BGR
- mask : 掩膜图像 ,统计自己划定的区域
- hist : 输出参数 ,得到mat信息
- histSize :bins的数量,详情在图片里
- ranges:像素取值范围[0,255]
void TestCalchist()
{
//读取灰度图
Mat mat = Imgcodecs.imread(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/lena.jpg");
Mat mat1 = new Mat();
//转为灰度图
Imgproc.cvtColor(mat, mat1, Imgproc.COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
List<Mat> mats = new List<Mat>();
mats.Add(mat1);
Mat b_hist = new Mat();
//取16个区域
Imgproc.calcHist(mats, new MatOfInt(0), new Mat(), b_hist, new MatOfInt(16), new MatOfFloat(0, 255));
Debug.Log(b_hist);
int hist_w = (int)mat.size().width; int hist_h = (int)mat.size().height;
//每一条数据的间隔
int bin_w = (int)Mathf.Round(hist_w / b_hist.rows());
Mat histImage = new Mat(mat.size(), CvType.CV_8UC3, new Scalar(0,0,0));
//归一化
Core.normalize(b_hist, b_hist, 0, histImage.rows(), Core.NORM_MINMAX, -1, new Mat());
for (int i = 0; i < b_hist.rows()-1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < b_hist.cols(); j++)
{
//得到对应像素的b值
int b_first= (int)b_hist.get(i, j)[0];
int b_Second = (int)b_hist.get(i+1, j)[0];
Debug.Log(bin_w * i + " "+ bin_w * (i + 1));
Point point1 = new Point(bin_w *i, hist_h - b_first);
Point point2 = new Point(bin_w*(i+1), hist_h- b_Second);
//画线
Imgproc.line(histImage, point1, point2, new Scalar(0, 0, 255,1), 2, 8, 0);
}
}
Texture2D texture = new Texture2D(histImage.cols(), histImage.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(histImage, texture);
rawImage.texture = texture;
}
均衡化原理
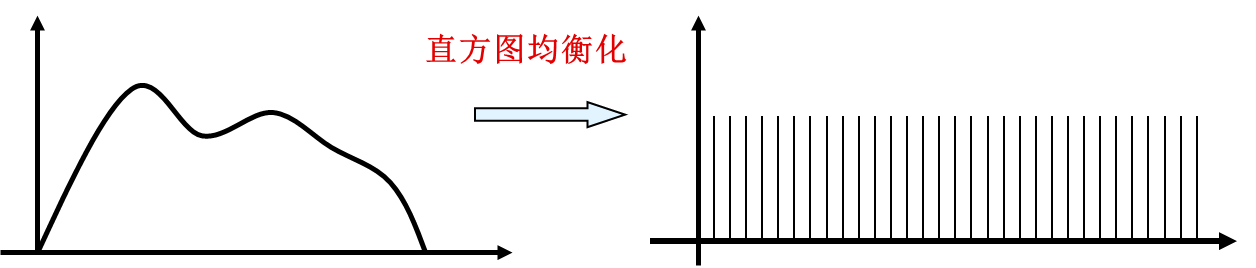
| 灰度值[0,255] | 像素个数 | 概率 | 累计概率 | 映射后灰度值 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 4 | 4/16=0.25 | 0.25+0=0.25 | 0.25*(255-0)=63.75 |
| 128 | 3 | 0.1875 | 0.25+0.1875=0.4375 | 0.4375*(255-0)=111.56 |
| 200 | 5 | 0.3125 | 0.75 | 191.25 |
| 255 | 4 | 0.25 | 1 | 255 |
映射完后的值再取整
①测试
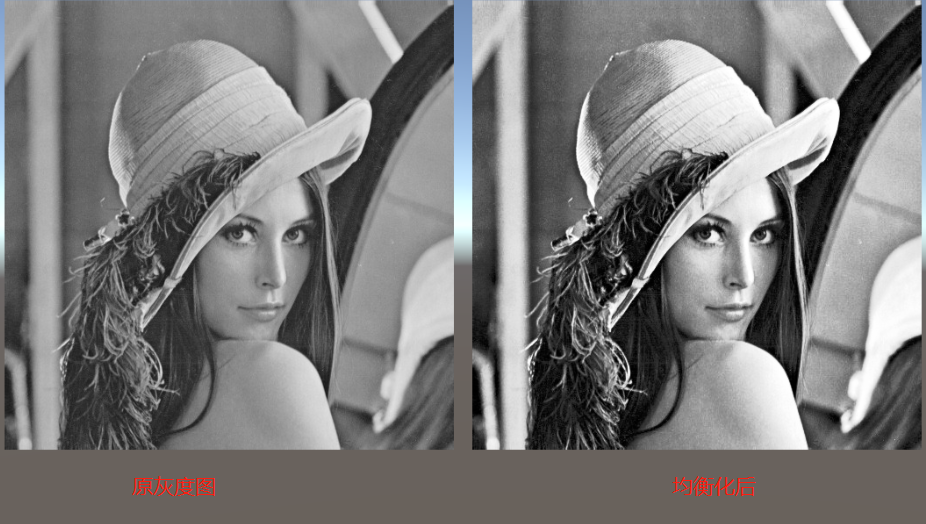

//均衡化
void TestEqualizeHist()
{
//输出灰度图
Mat mat = Imgcodecs.imread(Application.streamingAssetsPath + "/lena.jpg",0);
Mat mat1 = new Mat();
mat.copyTo(mat1);
Imgproc.equalizeHist(mat1, mat1);
Texture2D texture = new Texture2D(mat1.cols(), mat1.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(mat1, texture);
rawImage.texture = texture;
//原图
Texture2D texture1 = new Texture2D(mat.cols(), mat.rows(), TextureFormat.BGRA32, false);
Utils.matToTexture2D(mat, texture1);
GetRaw.texture = texture1;
}
②自适应直方图均衡化
在上面代码添加自适应均衡化代码,看看效果吧
CLAHE cLAHE= Imgproc.createCLAHE(2, new Size(8, 8));
cLAHE.apply(mat1, mat1);
最后
以上就是长情往事最近收集整理的关于unity3d OpenCVForUnity(二)的全部内容,更多相关unity3d内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。


![[opencv]利用鼠标事件选取坐标进行透视变换矫正图像](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg7.png)





发表评论 取消回复