2019独角兽企业重金招聘Python工程师标准>>> 
官方的:
我们上个版本的:

可以看出谷歌的是有位移效果,而我们的是原地扩散的效果,当然动画速度这个与PS的设置有关,不做比较,实际速度比上面的略快。
下面咱们就来试试做做位移的特效,先画个图给大家看看:
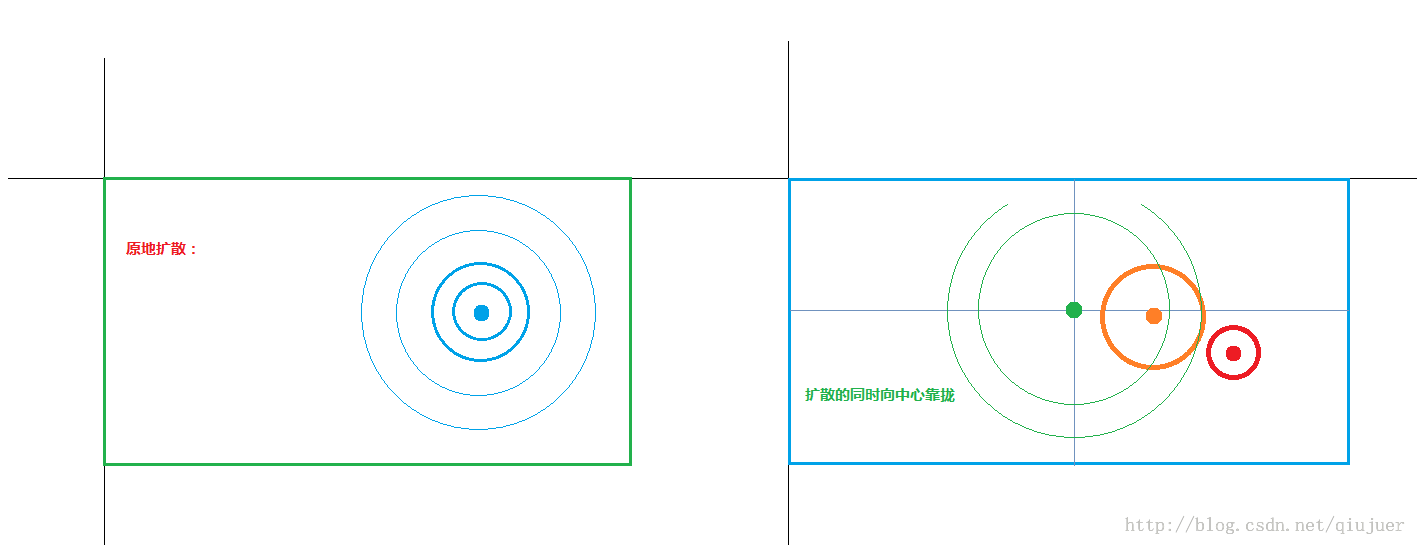
相信大家都能看懂,第一种就是之前的实现方式,只是在原地扩散,第二种就是新的,将在扩散的同时向中心靠拢,且为了达到更加好的视觉效果,靠拢中心的XY轴速度并不是一样的,X轴的靠拢时间=整个扩散时间,向Y轴靠拢的时间~=整个扩散时间*0.3(且都是先快后慢),现在来看看成品效果:
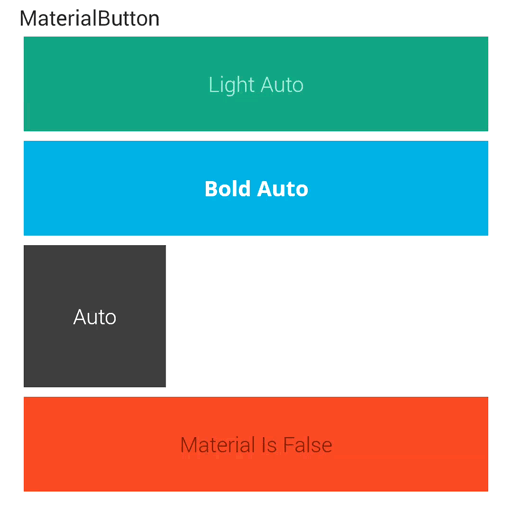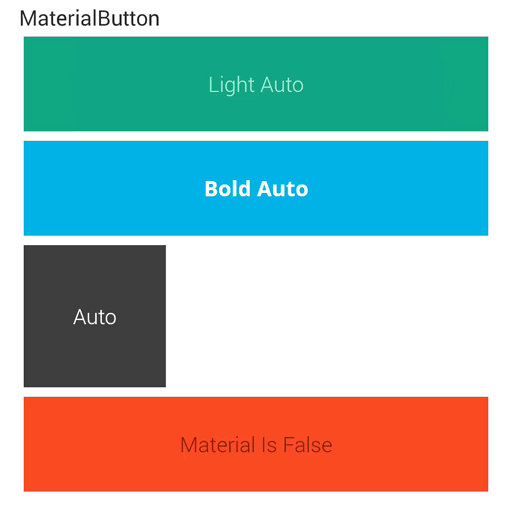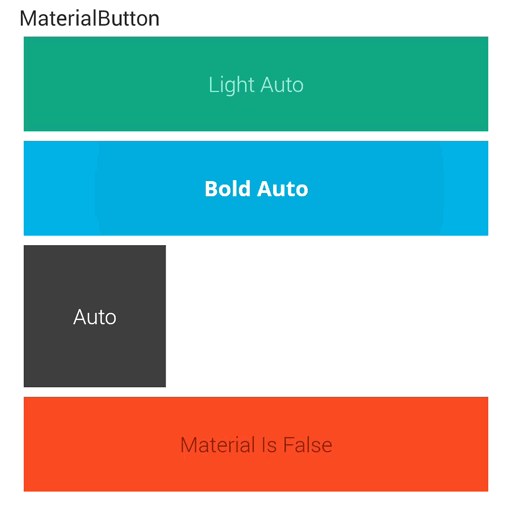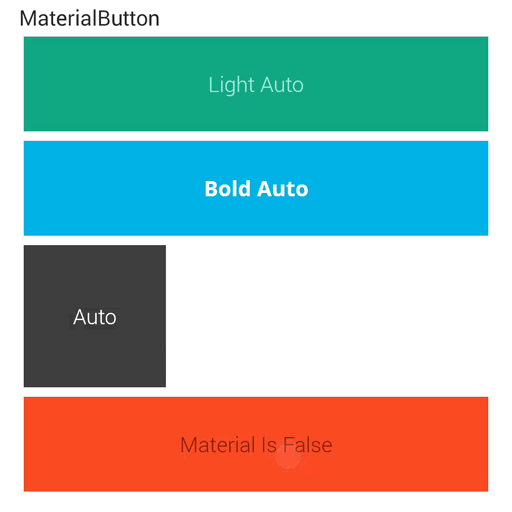
点击中间的时候与第一种差距不大,但是点击两边的时候将会有明显的差距,能感觉到向中心靠拢的触觉。是不是和谷歌的相比起来又近了一些了?
说了这个多的理论与演示,下面来说说整个的实现:
首先我们抽取上一篇文章的成果作为这篇的开头,具体怎么新建控件就不再做介绍了,先看看上一篇的代码成果(该代码进行了一定的修改):
public class MaterialButton extends Button {
private static final Interpolator ANIMATION_INTERPOLATOR = new DecelerateInterpolator();
private static final long ANIMATION_TIME = 600;
private Paint backgroundPaint;
private static ArgbEvaluator argbEvaluator = new ArgbEvaluator();
private float paintX, paintY, radius;
public MaterialButton(Context context) {
super(context);
init(null, 0);
}
public MaterialButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(attrs, 0);
}
public MaterialButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init(attrs, defStyle);
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
private void init(AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
...
}
@SuppressWarnings("NullableProblems")
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.save();
canvas.drawCircle(paintX, paintY, radius, backgroundPaint);
canvas.restore();
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
@SuppressWarnings("NullableProblems")
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
paintX = event.getX();
paintY = event.getY();
startRoundAnimator();
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
/**
* =============================================================================================
* The Animator methods
* =============================================================================================
*/
/**
* Start Round Animator
*/
private void startRoundAnimator() {
float start, end, height, width;
long time = (long) (ANIMATION_TIME * 1.85);
//Height Width
height = getHeight();
width = getWidth();
//Start End
if (height < width) {
start = height;
end = width;
} else {
start = width;
end = height;
}
float startRadius = (start / 2 > paintY ? start - paintY : paintY) * 1.15f;
float endRadius = (end / 2 > paintX ? end - paintX : paintX) * 0.85f;
//If The approximate square approximate square
if (startRadius > endRadius) {
startRadius = endRadius * 0.6f;
endRadius = endRadius / 0.8f;
time = (long) (time * 0.5);
}
AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet();
set.playTogether(
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, mRadiusProperty, startRadius, endRadius),
ObjectAnimator.ofObject(this, mBackgroundColorProperty, argbEvaluator, attributes.getColor(1), attributes.getColor(2))
);
// set Time
set.setDuration((long) (time / end * endRadius));
set.setInterpolator(ANIMATION_INTERPOLATOR);
set.start();
}
/**
* =============================================================================================
* The custom properties
* =============================================================================================
*/
private Property<MaterialButton, Float> mRadiusProperty = new Property<MaterialButton, Float>(Float.class, "radius") {
@Override
public Float get(MaterialButton object) {
return object.radius;
}
@Override
public void set(MaterialButton object, Float value) {
object.radius = value;
invalidate();
}
};
private Property<MaterialButton, Integer> mBackgroundColorProperty = new Property<MaterialButton, Integer>(Integer.class, "bg_color") {
@Override
public Integer get(MaterialButton object) {
return object.backgroundPaint.getColor();
}
@Override
public void set(MaterialButton object, Integer value) {
object.backgroundPaint.setColor(value);
}
};
}
在上述代码中我们实现了点击时进行扩散的效果,初始化控件部分由于我加入了许多的代码这里删除了,具体可以看看我的项目实现,最后会给出地址。
现在基于此开工!
首先我们建立 两个新的属性 分别X坐标与Y坐标属性:
private Property<MaterialButton, Float> mPaintXProperty = new Property<MaterialButton, Float>(Float.class, "paintX") {
@Override
public Float get(MaterialButton object) {
return object.paintX;
}
@Override
public void set(MaterialButton object, Float value) {
object.paintX = value;
}
};
private Property<MaterialButton, Float> mPaintYProperty = new Property<MaterialButton, Float>(Float.class, "paintY") {
@Override
public Float get(MaterialButton object) {
return object.paintY;
}
@Override
public void set(MaterialButton object, Float value) {
object.paintY = value;
}
};
在这两个属性中并未调用第一篇所说的 “ invalidate();”方法进行界面刷新,因为该方法应该放在持续时间最长的半径属性中调用。
之后我们获取到高宽 以及根据高和宽 计算出对应的 开始半径与结束半径:
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>float start, end, height, width, speed = 0.3f;
long time = ANIMATION_TIME;
//Height Width
height = getHeight();
width = getWidth();
//Start End
if (height < width) {
start = height;
end = width;
} else {
start = width;
end = height;
}
start = start / 2 > paintY ? start - paintY : paintY;
end = end * 0.8f / 2f;
//If The approximate square approximate square
if (start > end) {
start = end * 0.6f;
end = end / 0.8f;
time = (long) (time * 0.65);
speed = 1f;
}
我们首先比较了高与宽的长度 把短的赋予为开始半径 长的赋予为结束半径。
第二步,我们把开始长度除以2 得出其一半的长度 然后与 点击时的Y轴坐标比较,如果Y轴较长则取Y,如果不够则取其相减结果。这样能保证点击开始时的半径能刚好大于其高或者宽(短的一边),这样就不会出现小圆扩散的效果,看起来将会由椭圆的效果(当然以后将会直接画出椭圆)
第三步,我们运算出结束半径,同时保证结束半径为长的一边的一半的8/10 这样的效果是不会出现布满整个控件的情况。8/10 的空间刚好是个不错的选择。
第四步,判断开始长度是否大于结束长度,如果是(近似正方形情况),进行一定规则的重新运算,保证其开始半径能刚好与控件长度差不多(0.48左右),结束半径能刚刚布满控件,同时减少动画时间
当然,我现在才发现了一个BUG,在第二步的地方的BUG,大家看看,希望能提出是哪里的BUG;就当是一个互动!该BUG将会在下个版本修复。
之后我们建立每个属性的动画,并给每个属性动画设置对应的时间:
//PaintX
ObjectAnimator aPaintX = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, mPaintXProperty, paintX, width / 2);
aPaintX.setDuration(time);
//PaintY
ObjectAnimator aPaintY = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, mPaintYProperty, paintY, height / 2);
aPaintY.setDuration((long) (time * speed));
//Radius
ObjectAnimator aRadius = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, mRadiusProperty, start, end);
aRadius.setDuration(time);
//Background
ObjectAnimator aBackground = ObjectAnimator.ofObject(this, mBackgroundColorProperty, argbEvaluator, attributes.getColor(1), attributes.getColor(2));
aBackground.setDuration(time);
可以看见Y轴的时间乘以了一个speed变量,该变量默认是0.3 如果是近似正方形将初始化为1以便能同时对齐到中心位置,在上一步中有对应变量。
然后咱们把所有的属性动画添加到一个动画集并设置其速度方式为:先快后慢。最后启动该动画集。
//AnimatorSet
AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet();
set.playTogether(aPaintX, aPaintY, aRadius, aBackground);
set.setInterpolator(ANIMATION_INTERPOLATOR);
set.start();
以上就是最新的动画效果的实现原理及代码了,当然我们可以将其合并到第一篇的代码中,并使用一个 Bool 属性来控制使用哪一种动画:
public class MaterialButton extends Button {
private static final Interpolator ANIMATION_INTERPOLATOR = new DecelerateInterpolator();
private static final long ANIMATION_TIME = 600;
private Paint backgroundPaint;
private static ArgbEvaluator argbEvaluator = new ArgbEvaluator();
private float paintX, paintY, radius;
private Attributes attributes;
public MaterialButton(Context context) {
super(context);
init(null, 0);
}
public MaterialButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init(attrs, 0);
}
public MaterialButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
super(context, attrs, defStyle);
init(attrs, defStyle);
}
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
private void init(AttributeSet attrs, int defStyle) {
...
}
@SuppressWarnings("NullableProblems")
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
canvas.save();
canvas.drawCircle(paintX, paintY, radius, backgroundPaint);
canvas.restore();
super.onDraw(canvas);
}
@SuppressWarnings("NullableProblems")
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
if (attributes.isMaterial() && event.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
paintX = event.getX();
paintY = event.getY();
if (attributes.isAutoMove())
startMoveRoundAnimator();
else
startRoundAnimator();
}
return super.onTouchEvent(event);
}
/**
* =============================================================================================
* The Animator methods
* =============================================================================================
*/
/**
* Start Round Animator
*/
private void startRoundAnimator() {
float start, end, height, width;
long time = (long) (ANIMATION_TIME * 1.85);
//Height Width
height = getHeight();
width = getWidth();
//Start End
if (height < width) {
start = height;
end = width;
} else {
start = width;
end = height;
}
float startRadius = (start / 2 > paintY ? start - paintY : paintY) * 1.15f;
float endRadius = (end / 2 > paintX ? end - paintX : paintX) * 0.85f;
//If The approximate square approximate square
if (startRadius > endRadius) {
startRadius = endRadius * 0.6f;
endRadius = endRadius / 0.8f;
time = (long) (time * 0.5);
}
AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet();
set.playTogether(
ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, mRadiusProperty, startRadius, endRadius),
ObjectAnimator.ofObject(this, mBackgroundColorProperty, argbEvaluator, attributes.getColor(1), attributes.getColor(2))
);
// set Time
set.setDuration((long) (time / end * endRadius));
set.setInterpolator(ANIMATION_INTERPOLATOR);
set.start();
}
/**
* Start Move Round Animator
*/
private void startMoveRoundAnimator() {
float start, end, height, width, speed = 0.3f;
long time = ANIMATION_TIME;
//Height Width
height = getHeight();
width = getWidth();
//Start End
if (height < width) {
start = height;
end = width;
} else {
start = width;
end = height;
}
start = start / 2 > paintY ? start - paintY : paintY;
end = end * 0.8f / 2f;
//If The approximate square approximate square
if (start > end) {
start = end * 0.6f;
end = end / 0.8f;
time = (long) (time * 0.65);
speed = 1f;
}
//PaintX
ObjectAnimator aPaintX = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, mPaintXProperty, paintX, width / 2);
aPaintX.setDuration(time);
//PaintY
ObjectAnimator aPaintY = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, mPaintYProperty, paintY, height / 2);
aPaintY.setDuration((long) (time * speed));
//Radius
ObjectAnimator aRadius = ObjectAnimator.ofFloat(this, mRadiusProperty, start, end);
aRadius.setDuration(time);
//Background
ObjectAnimator aBackground = ObjectAnimator.ofObject(this, mBackgroundColorProperty, argbEvaluator, attributes.getColor(1), attributes.getColor(2));
aBackground.setDuration(time);
//AnimatorSet
AnimatorSet set = new AnimatorSet();
set.playTogether(aPaintX, aPaintY, aRadius, aBackground);
set.setInterpolator(ANIMATION_INTERPOLATOR);
set.start();
}
/**
* =============================================================================================
* The custom properties
* =============================================================================================
*/
private Property<MaterialButton, Float> mPaintXProperty = new Property<MaterialButton, Float>(Float.class, "paintX") {
@Override
public Float get(MaterialButton object) {
return object.paintX;
}
@Override
public void set(MaterialButton object, Float value) {
object.paintX = value;
}
};
private Property<MaterialButton, Float> mPaintYProperty = new Property<MaterialButton, Float>(Float.class, "paintY") {
@Override
public Float get(MaterialButton object) {
return object.paintY;
}
@Override
public void set(MaterialButton object, Float value) {
object.paintY = value;
}
};
private Property<MaterialButton, Float> mRadiusProperty = new Property<MaterialButton, Float>(Float.class, "radius") {
@Override
public Float get(MaterialButton object) {
return object.radius;
}
@Override
public void set(MaterialButton object, Float value) {
object.radius = value;
invalidate();
}
};
private Property<MaterialButton, Integer> mBackgroundColorProperty = new Property<MaterialButton, Integer>(Integer.class, "bg_color") {
@Override
public Integer get(MaterialButton object) {
return object.backgroundPaint.getColor();
}
@Override
public void set(MaterialButton object, Integer value) {
object.backgroundPaint.setColor(value);
}
};
}
在最后附上两种方式运行后的效果对比图:
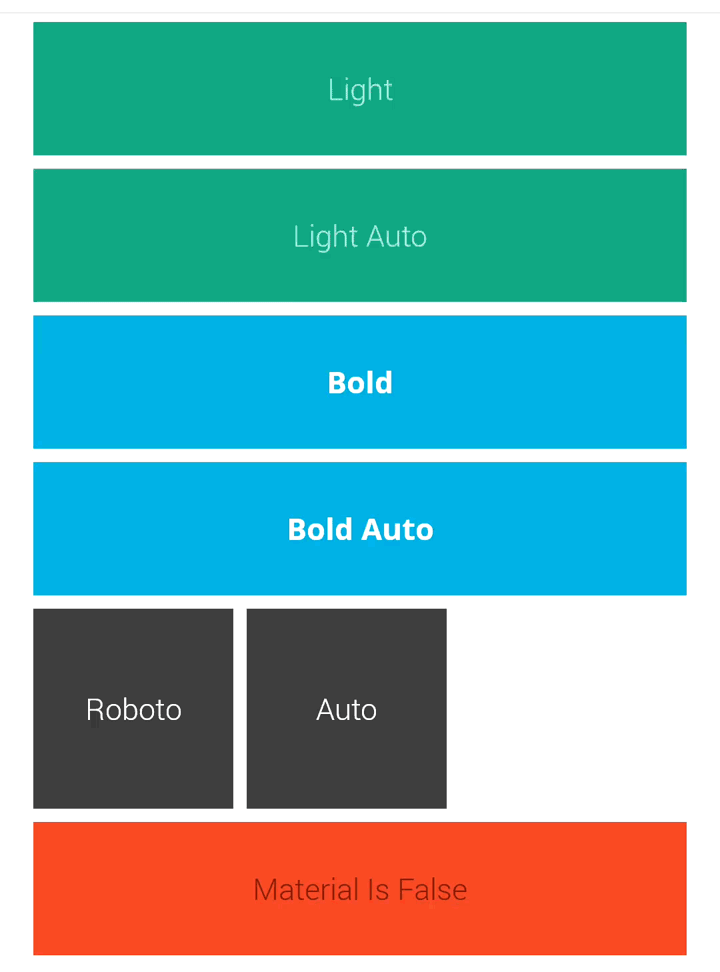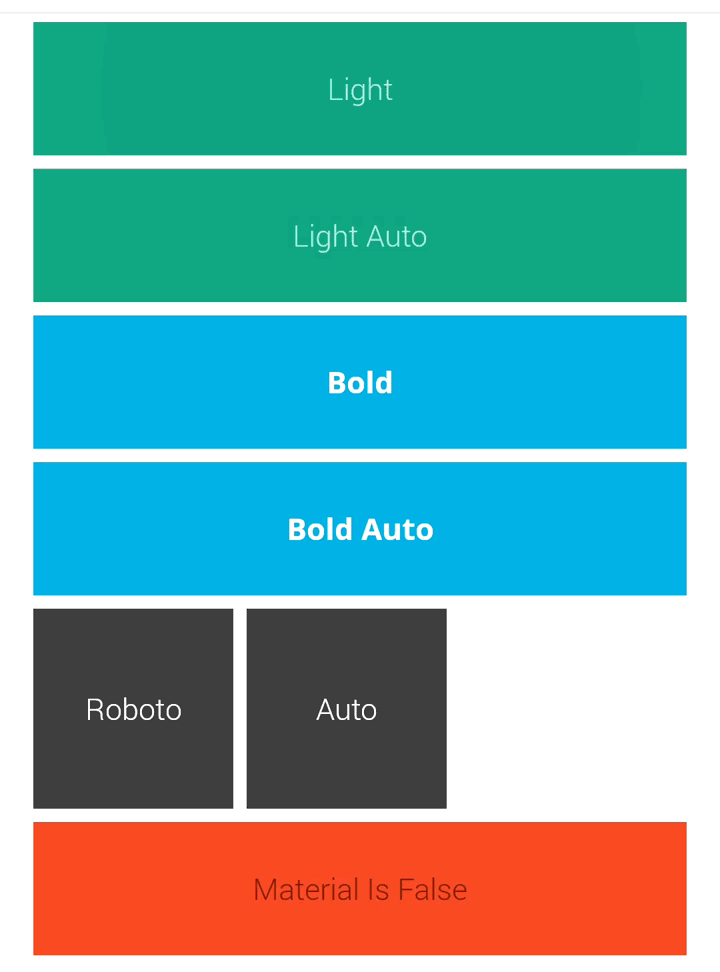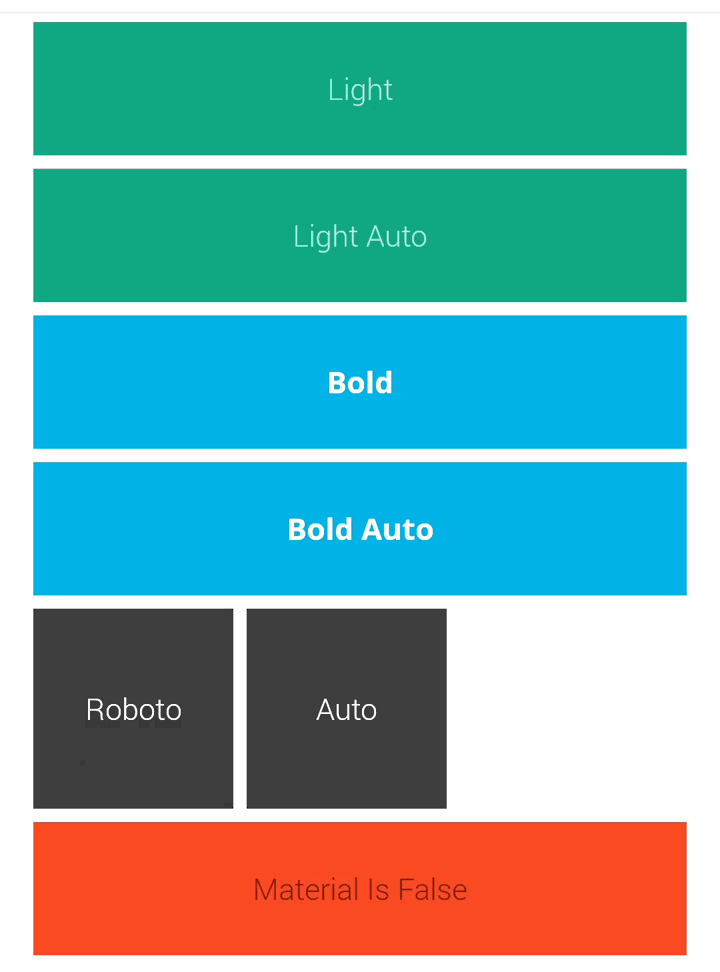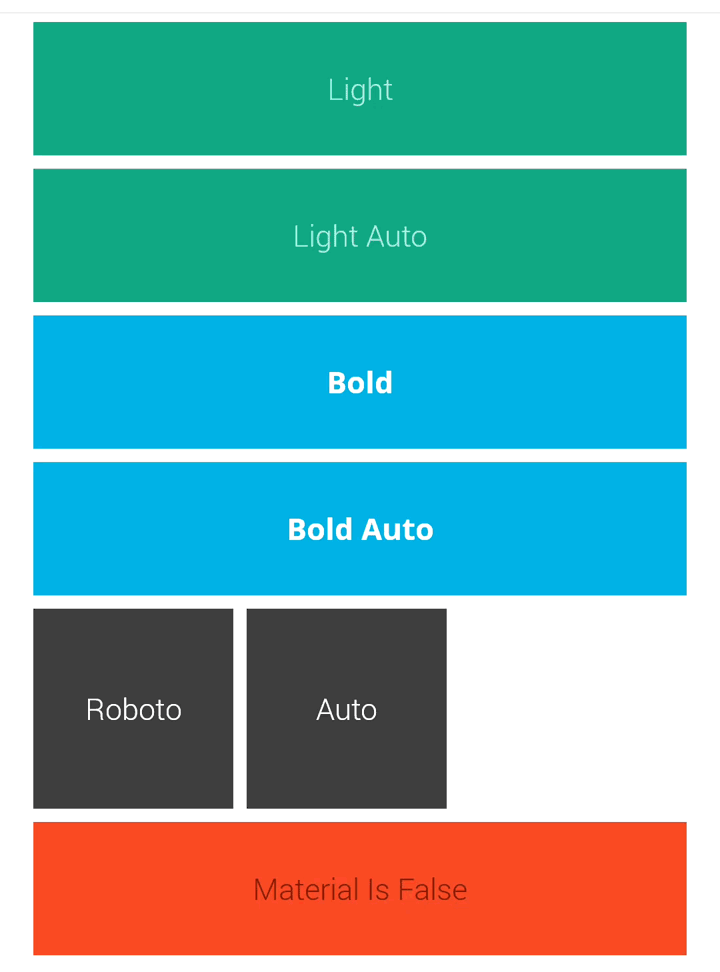
转载于:https://my.oschina.net/u/2370693/blog/467445
最后
以上就是欢呼电源最近收集整理的关于Button 不错的点击效果的全部内容,更多相关Button内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复