Dijkstra(迪杰斯特拉)算法是典型的最短路径路由算法,用于计算一个节点到其他所有节点的最短路径。主要特点是以起始点为中心向外层层扩展,直到扩展到终点为止。
Dijkstra算法采用的是贪心算法的策略,在整个算法过程中一直要维护两个表,这两个表分别表示尚未遍历的结点和已遍历的结点。大概过程如下:
- 声明两个集合,open和close,open用于存储未遍历的节点,close用来存储已遍历的节点;
- 初始阶段,将初始节点放入close,其他所有节点放入open;
- 以初始节点为中心向外一层层遍历,获取离指定节点最近的子节点放入close并从新计算路径,直至close包含所有子节点。
我在Intellij IDEA中实现了此算法,与BFS算法一样,首先我们需要构建一个图进行测试。在这里,我构建如下图:
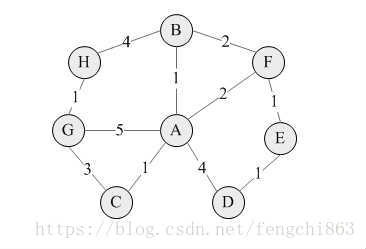
以下为构建代码,首先创建Node对象用于封装图中的vertex结点信息,它包括结点的名字和子结点,子结点就是与之相邻的所有结点。
public class Node {
private String name;
private Map<Node,Integer> child=new HashMap<>();
public Node(String name){
this.name=name;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Map<Node, Integer> getChild() {
return child;
}
public void setChild(Map<Node, Integer> child) {
this.child = child;
}
}其中自动生成了constructor、getter和setter方法,方便进行结点操作。
MapBuilder用于初始化数据源,返回图的起始节点。
public class MapBuilder {
public Node build(Set<Node> open, Set<Node> close){
Node nodeA=new Node("A");
Node nodeB=new Node("B");
Node nodeC=new Node("C");
Node nodeD=new Node("D");
Node nodeE=new Node("E");
Node nodeF=new Node("F");
Node nodeG=new Node("G");
Node nodeH=new Node("H");
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeB, 1);
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeC, 1);
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeD, 4);
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeG, 5);
nodeA.getChild().put(nodeF, 2);
nodeB.getChild().put(nodeA, 1);
nodeB.getChild().put(nodeF, 2);
nodeB.getChild().put(nodeH, 4);
nodeC.getChild().put(nodeA, 1);
nodeC.getChild().put(nodeG, 3);
nodeD.getChild().put(nodeA, 4);
nodeD.getChild().put(nodeE, 1);
nodeE.getChild().put(nodeD, 1);
nodeE.getChild().put(nodeF, 1);
nodeF.getChild().put(nodeE, 1);
nodeF.getChild().put(nodeB, 2);
nodeF.getChild().put(nodeA, 2);
nodeG.getChild().put(nodeC, 3);
nodeG.getChild().put(nodeA, 5);
nodeG.getChild().put(nodeH, 1);
nodeH.getChild().put(nodeB, 4);
nodeH.getChild().put(nodeG, 1);
open.add(nodeB);
open.add(nodeC);
open.add(nodeD);
open.add(nodeE);
open.add(nodeF);
open.add(nodeG);
open.add(nodeH);
close.add(nodeA);
return nodeA;
}
}接下来是算法部分,Dijkstra类用于计算起始结点到所有其他结点的最短路径:
public class Dijkstra {
Set<Node> open = new HashSet<Node>();
Set<Node> close = new HashSet<Node>();
Map<String, Integer> path = new HashMap<String, Integer>();//封装路径距离
Map<String, String> pathInfo = new HashMap<String, String>();//封装路径信息
public Node init() {
//初始路径,因没有A->E这条路径,所以path(E)设置为Integer.MAX_VALUE
path.put("B", 1);
pathInfo.put("B", "A->B");
path.put("C", 1);
pathInfo.put("C", "A->C");
path.put("D", 4);
pathInfo.put("D", "A->D");
path.put("E", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
pathInfo.put("E", "A");
path.put("F", 2);
pathInfo.put("F", "A->F");
path.put("G", 5);
pathInfo.put("G", "A->G");
path.put("H", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
pathInfo.put("H", "A");
//将初始节点放入close,其他节点放入open
Node start = new MapBuilder().build(open, close);
return start;
}
public void computePath(Node start) {
//取距离start节点最近的子节点,放入close
Node nearest = getShortestPath(start);
if (nearest == null) {
return;
}
close.add(nearest); //已遍历的
open.remove(nearest); //未遍历的
Map<Node, Integer> childs = nearest.getChild();
for (Node child : childs.keySet()) {
if (open.contains(child)) {//如果子节点在open中
Integer newCompute = path.get(nearest.getName()) + childs.get(child);
if (newCompute < path.get(child.getName())) {//新计算出来的距离小于之前设置的距离
path.put(child.getName(), newCompute);
pathInfo.put(child.getName(), pathInfo.get(nearest.getName()) + "->" + child.getName());
}
}
}
computePath(start);//重复执行自己,确保所有子节点被遍历
computePath(nearest);//向外一层层递归,直至所有顶点被遍历
}
public void printPathInfo() {
Set<Map.Entry<String, String>> pathInfos = pathInfo.entrySet();
for (Map.Entry<String, String> pathInfo : pathInfos) {
System.out.println(pathInfo.getKey() + ":" + pathInfo.getValue());
}
}
/**
* 获取与node最近的子节点
*/
private Node getShortestPath(Node node) {
Node res = null;
int minDis = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
Map<Node, Integer> childs = node.getChild();
// 遍历与Node相连接的所有节点,选取其中距离最短的节点
for (Node child : childs.keySet()) {
if (open.contains(child)) {
int distance = childs.get(child);
if (distance < minDis) {
minDis = distance;
res = child;
}
}
}
return res;
}
}然后我们构建了测试用例,如下:
public class DijkstraTest {
/**
*
* Method: getShortestPath(Node node)
*
*/
@Test
public void testGetShortestPath() throws Exception {
//TODO: Test goes here...
Dijkstra test=new Dijkstra();
Node start=test.init();
test.computePath(start);
test.printPathInfo();
}
} 运行结果如下:
D:A->D
E:A->F->E
F:A->F
G:A->C->G
B:A->B
C:A->C
H:A->B->H最后
以上就是正直八宝粥最近收集整理的关于Dijkstra算法求无向带权图最短路径——Java的全部内容,更多相关Dijkstra算法求无向带权图最短路径——Java内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复