此篇转载,下附原帖地址
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000018536906
目录
如何使用
区别
松散语法
SpEL
JSR303 数据校验
复杂类型封装
怎么选用?
@Value()只能给普通变量注入值,不能直接给静态变量赋值
如何使用
定义两个对象,一个学生对象,对应着一个老师对象,代码如下:
- @ConfigurationProperties
- 学生类
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") // 指定配置文件中的 student 属性与这个 bean绑定
public class Student {
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String city;
private Teacher teacher;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,Integer> scores;
//注意,为了测试必须重写 toString 和 get,set 方法
}- 老师类
public class Teacher {
private String name;
private Integer age;
private String gender;
//注意,为了测试必须重写 toString 和 get,set 方法
}- 测试类
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringbootValConproDemoApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private Student student;
@Test
public void contextLoads() {
// 这里为了方便,但工作中千万不能用 System.out
System.out.println(student.toString());
}
}- 输出结果
Student{firstName='陈', lastName='一个优秀的废人', age=24, gender='男', city='广州', teacher=Teacher{name='eses', age=24, gender='女'}, hobbys=[篮球, 羽毛球, 兵兵球], scores={java=100, Python=99, C=99}}- @Value
@Value 支持三种取值方式,分别是 字面量、${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值以及 #{SpEL}
- 学生类
@Component
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") // 指定配置文件中的 student 属性与这个 bean绑定
public class Student {
/**
* <bean class="Student">
* <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property>
* <bean/>
*/
@Value("陈") // 字面量
private String firstName;
@Value("${student.lastName}") // 从环境变量、配置文件中获取值
private String lastName;
@Value("#{12*2}") // #{SpEL}
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String city;
private Teacher teacher;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,Integer> scores;
//注意,为了测试必须重写 toString 和 get,set 方法
}- 测试结果
Student{firstName='陈', lastName='一个优秀的废人', age=24, gender='null', city='null', teacher=null, hobbys=null, scores=null}区别
| 二者区别 | @ConfigurationProperties | @Value |
|---|---|---|
| 功能 | 批量注入配置文件中的属性 | 一个个指定 |
| 松散绑定(松散语法) | 支持 | 不支持 |
| SpEL | 不支持 | 支持 |
| JSR303数据校验 | 支持 | 不支持 |
| 复杂类型封装 | 支持 | 不支持 |
从上表可以看见,@ConfigurationProperties 和 @Value 主要有 5 个不同,其中第一个功能上的不同,上面已经演示过。下面我来介绍下剩下的 4 个不同。
松散语法
松散语法的意思就是一个属性在配置文件中可以有多个属性名,举个栗子:学生类当中的 firstName 属性,在配置文件中可以叫 firstName、first-name、first_name 以及 FIRST_NAME。 而 @ConfigurationProperties 是支持这种命名的,@Value 不支持。下面以 firstName 为例,测试一下。如下代码:
- @ConfigurationProperties
学生类的 firstName 属性在 yml 文件中被定义为 first_name:
student:
first_name: 陈 # 学生类的 firstName 属性在 yml 文件中被定义为 first_name
lastName: 一个优秀的废人
age: 24
gender: 男
city: 广州
teacher: {name: eses,age: 24,gender: 女}
hobbys: [篮球,羽毛球,兵兵球]
scores: {java: 100,Python: 99,C++: 99}学生类:
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") // 指定配置文件中的 student 属性与这个 bean绑定
public class Student {
/**
* <bean class="Student">
* <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property>
* <bean/>
*/
//@Value("陈") // 字面量
private String firstName;
//@Value("${student.lastName}") // 从环境变量、配置文件中获取值
private String lastName;
//@Value("#{12*2}") // #{SpEL}
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String city;
private Teacher teacher;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,Integer> scores;
//注意,为了测试必须重写 toString 和 get,set 方法
}测试结果:
Student{firstName='陈', lastName='一个优秀的废人', age=24, gender='男', city='广州', teacher=Teacher{name='eses', age=24, gender='女'}, hobbys=[篮球, 羽毛球, 兵兵球], scores={java=100, Python=99, C=99}}- @Value
学生类:
@Component
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") // 指定配置文件中的 student 属性与这个 bean绑定
public class Student {
/**
* <bean class="Student">
* <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property>
* <bean/>
*/
//@Value("陈") // 字面量
@Value("${student.firstName}")
private String firstName;
//@Value("${student.lastName}") // 从环境变量、配置文件中获取值
private String lastName;
//@Value("#{12*2}") // #{SpEL}
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String city;
private Teacher teacher;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,Integer> scores;
//注意,为了测试必须重写 toString 和 get,set 方法
}测试结果:启动报错,找不到 bean。
从上面两个测试结果可以看出,使用 @ConfigurationProperties 注解时,yml 中的属性名为 last_name 而学生类中的属性为 lastName 但依然能取到值,而使用 @value 时,使用 lastName 确报错了。证明 @ConfigurationProperties 支持松散语法,@value 不支持。
SpEL
SpEL 使用 #{...} 作为定界符 , 所有在大括号中的字符都将被认为是 SpEL , SpEL 为 bean 的属性进行动态赋值提供了便利。
- @Value
如上述介绍 @Value 注解使用方法时,有这样一段代码:
@Value("#{12*2}") // #{SpEL}
private Integer age;证明 @Value 是支持 SpEL 表达式的。
- @ConfigurationProperties
由于 yml 中的 # 被当成注释看不到效果。所以我们新建一个 application.properties 文件。把 yml 文件内容注释,我们在 properties 文件中把 age 属性写成如下所示:
student.age=#{12*2}把学生类中的 @ConfigurationProperties 注释打开,注释 @value 注解。运行报错, age 属性匹配异常。
说明 @ConfigurationProperties 不支持 SpEL
JSR303 数据校验
- @Value
加入 @Length 校验:
@Component
@Validated
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") // 指定配置文件中的 student 属性与这个 bean绑定
public class Student {
/**
* <bean class="Student">
* <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property>
* <bean/>
*/
//@Value("陈") // 字面量
@Value("${student.first-name}")
@Length(min=5, max=20, message="用户名长度必须在5-20之间")
private String firstName;
//@Value("${student.lastName}") // 从环境变量、配置文件中获取值
private String lastName;
//@Value("#{12*2}") // #{SpEL}
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String city;
private Teacher teacher;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,Integer> scores;
}yaml:
student:
first_name: 陈测试结果:
Student{firstName='陈', lastName='null', age=null, gender='null', city='null', teacher=null, hobbys=null, scores=null}yaml 中的 firstname 长度为 1 。而检验规则规定 5-20 依然能取到属性,说明检验不生效,@Value 不支持 JSR303 数据校验
- @ConfigurationProperties
学生类:
@Component
@Validated
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") // 指定配置文件中的 student 属性与这个 bean绑定
public class Student {
/**
* <bean class="Student">
* <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property>
* <bean/>
*/
//@Value("陈") // 字面量
//@Value("${student.first-name}")
@Length(min=5, max=20, message="用户名长度必须在5-20之间")
private String firstName;
//@Value("${student.lastName}") // 从环境变量、配置文件中获取值
private String lastName;
//@Value("#{12*2}") // #{SpEL}
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String city;
private Teacher teacher;
private List<String> hobbys;
private Map<String,Integer> scores;
}测试结果:报错
[firstName],20,5]; default message [用户名长度必须在5-20之间]校验生效,支持 JSR303 数据校验。
复杂类型封装
复杂类型封装指的是,在对象以及 map (如学生类中的老师类以及 scores map)等属性中,用 @Value 取是取不到值,比如:
@Component
//@Validated
//@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "student") // 指定配置文件中的 student 属性与这个 bean绑定
public class Student {
/**
* <bean class="Student">
* <property name="lastName" value="字面量/${key}从环境变量、配置文件中获取值/#{SpEL}"></property>
* <bean/>
*/
//@Value("陈") // 字面量
//@Value("${student.first-name}")
//@Length(min=5, max=20, message="用户名长度必须在5-20之间")
private String firstName;
//@Value("${student.lastName}") // 从环境变量、配置文件中获取值
private String lastName;
//@Value("#{12*2}") // #{SpEL}
private Integer age;
private String gender;
private String city;
@Value("${student.teacher}")
private Teacher teacher;
private List<String> hobbys;
@Value("${student.scores}")
private Map<String,Integer> scores;
}这样取是报错的。而上文介绍 @ConfigurationProperties 和 @Value 的使用方法时已经证实 @ConfigurationProperties 是支持复杂类型封装的。也就是说 yaml 中直接定义 teacher 以及 scores 。 @ConfigurationProperties 依然能取到值。
怎么选用?
- 如果说,只是在某个业务逻辑中需要获取一下配置文件中的某项值,使用 @Value;比如,假设现在学生类加多一个属性叫 school 那这个属性对于该校所有学生来说都是一样的,但防止我这套系统到了别的学校就用不了了。那我们可以直接在 yml 中给定 school 属性,用 @Value 获取。当然上述只是举个粗暴的例子,实际开发时,school 属性应该是保存在数据库中的。
- 如果说,专门编写了一个 javaBean 来和配置文件进行映射,我们就直接使用 @ConfigurationProperties。
@Value()只能给普通变量注入值,不能直接给静态变量赋值
SpringBoot中使用@Value()只能给普通变量注入值,不能直接给静态变量赋值
例如,application-dev.properties 配置文件有如下配置:
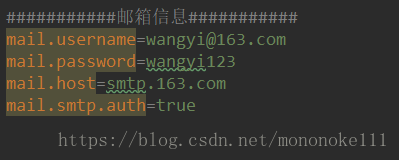
给普通变量赋值时,直接在变量声明之上添加@Value()注解即可,如下所示:
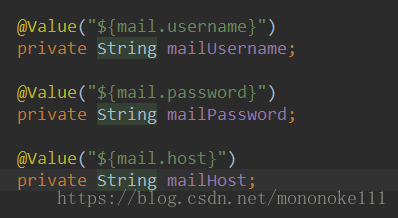
当要给静态变量注入值的时候,若是在静态变量声明之上直接添加@Value()注解是无效的,例如:
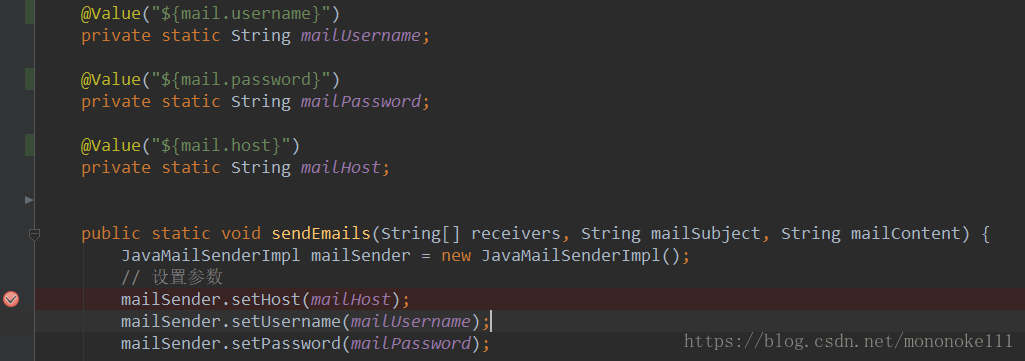
虽然没有编译和运行上的报错,经调试可知这种注解方式mailUsername、mailPassword、mailHost的值都是null,也就是说直接给静态变量读取配置文件是无效的,如下所示:
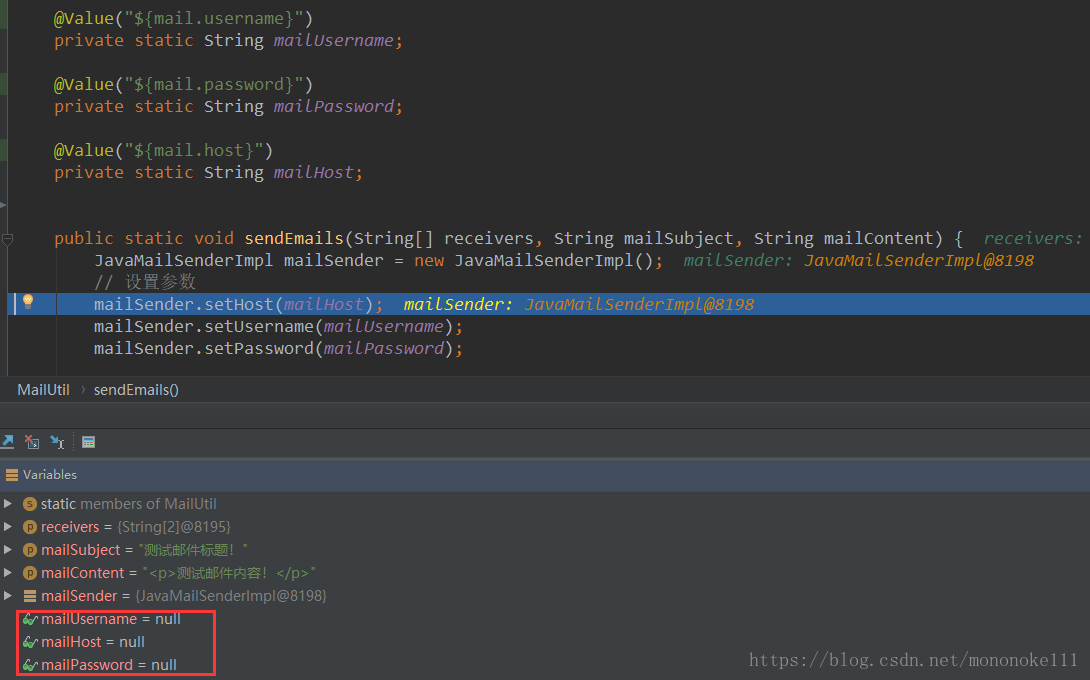
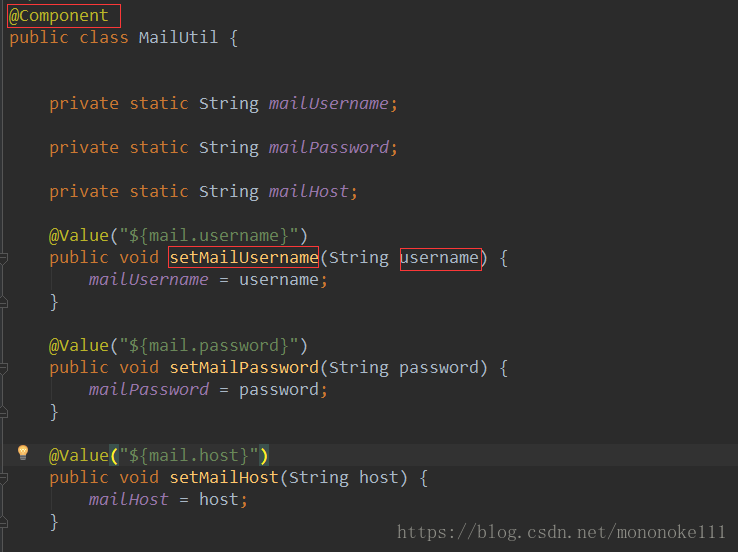
若要给静态变量赋值,可以使用set()方法,其中需要在类上加入@Component注解,方法名(例如setMailUsername)和参数名(例如username)可以任意命名,如下所示:
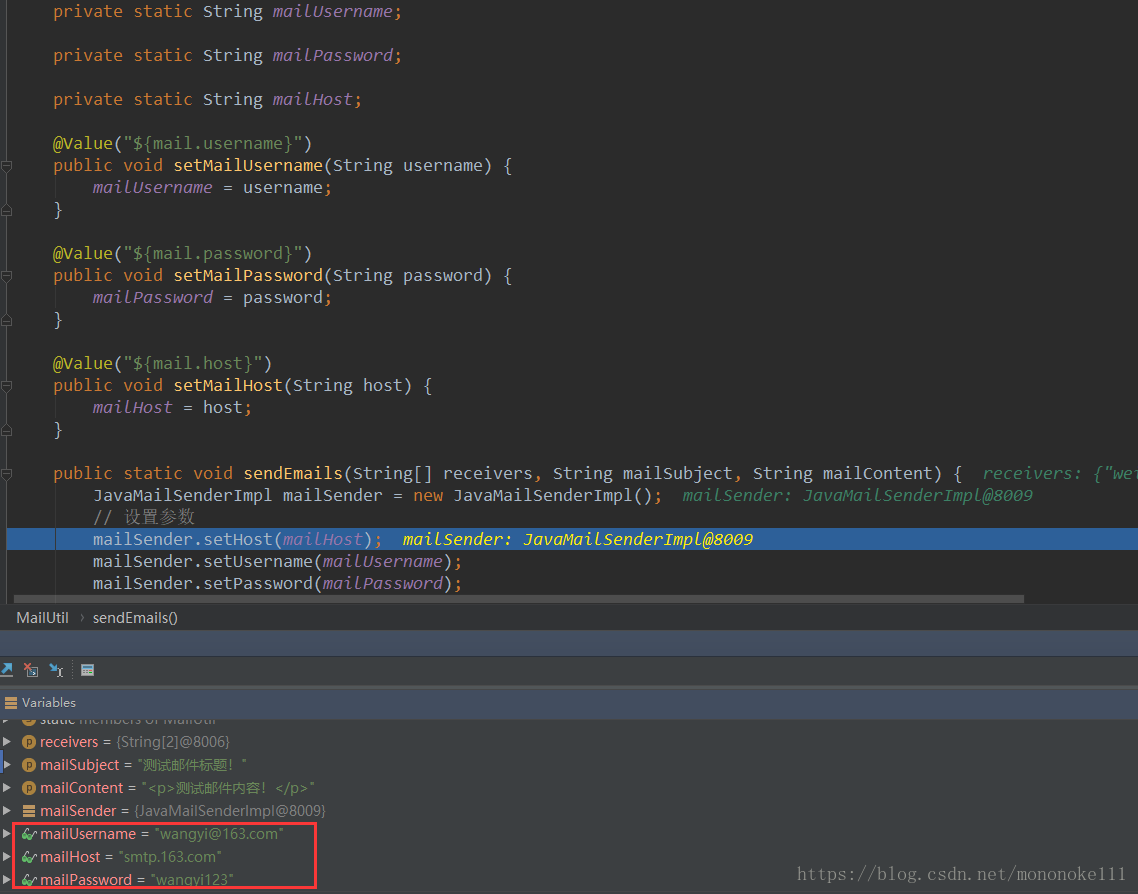
调试结果如下:
————————————————
版权声明:本文为CSDN博主「「已注销」」的原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链接及本声明。
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/mononoke111/article/details/81088472
最后
以上就是无奈保温杯最近收集整理的关于springboot @Value 和 @ConfigurationProperties@Value()只能给普通变量注入值,不能直接给静态变量赋值的全部内容,更多相关springboot内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。







![解决使用elementUI的el-date-picker报[Vue warn]: Avoid mutating a prop ...Prop being mutated: “placement“的问题](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg9.png)
发表评论 取消回复