【数据结构与算法-二叉树与图经典例题汇总】
- 典例1、路径之和-a(medium)
- 典例2、最近的公共祖先(medium)
- 典例3、二叉树转链表(medium)
- 典例4、侧面观察二叉树(medium)
- 典例5、课程安排(medium)
典例1、路径之和-a(medium)
二叉树基础
-
三种访问二叉树的机制:对于每一个子树都是按照相同的访问机制来访问的
-
二叉树定义
#include <stdio.h>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
void preorder_print(TreeNode *node,int layer){
if (!node){
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < layer; i++){
printf("-----");
}
printf("[%d]n", node->val);
preorder_print(node->left, layer + 1);
preorder_print(node->right, layer + 1);
}
int main(){
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
preorder_print(&a, 0);
return 0;
}
- 深度遍历:DFS
#include <stdio.h>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
void traversal(TreeNode *node){
if (!node){
return;
}
traversal(node->left);
traversal(node->right);
}
void traversal_print1(TreeNode *node,int layer){
if (!node){
return;
}
traversal_print1(node->left, layer + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < layer; i++){
printf("-----");
}
printf("[%d]n", node->val);
traversal_print1(node->right, layer + 1);
}
void traversal_print2(TreeNode *node,int layer){
if (!node){
return;
}
traversal_print2(node->left, layer + 1);
traversal_print2(node->right, layer + 1);
for (int i = 0; i < layer; i++){
printf("-----");
}
printf("[%d]n", node->val);
}
void traversal_print3(TreeNode *node,int layer){
if (!node){
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < layer; i++){
printf("-----");
}
printf("[%d]n", node->val);
traversal_print3(node->left, layer + 1);
traversal_print3(node->right, layer + 1);
}
int main(){
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
traversal_print1(&a, 0);
printf("n");
traversal_print2(&a, 0);
printf("n");
traversal_print3(&a, 0);
printf("n");
return 0;
}
- 广度(层次)遍历:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
void BFS_print(TreeNode* root){
std::queue<TreeNode *> Q;
Q.push(root);
while(!Q.empty()){
TreeNode *node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
printf("[%d]n", node->val);
if (node->left){
Q.push(node->left);
}
if (node->right){
Q.push(node->right);
}
}
}
int main(){
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
BFS_print(&a);
return 0;
}
-
打印顺序:
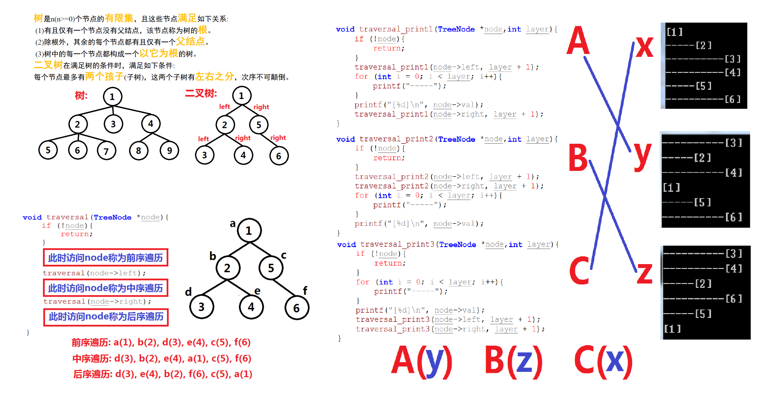
-
题目描述:
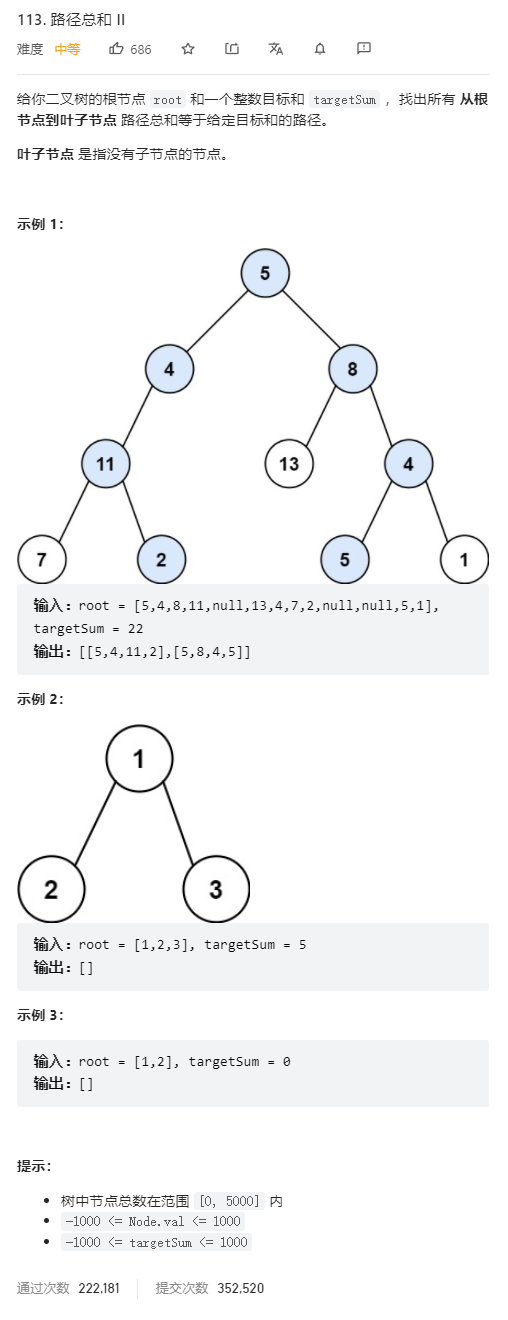
-
思路:
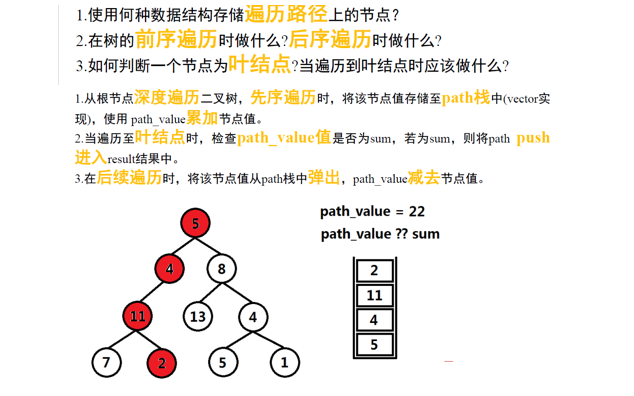
-
红色:当前正在遍历的节点
-
蓝色:已经遍历完的节点
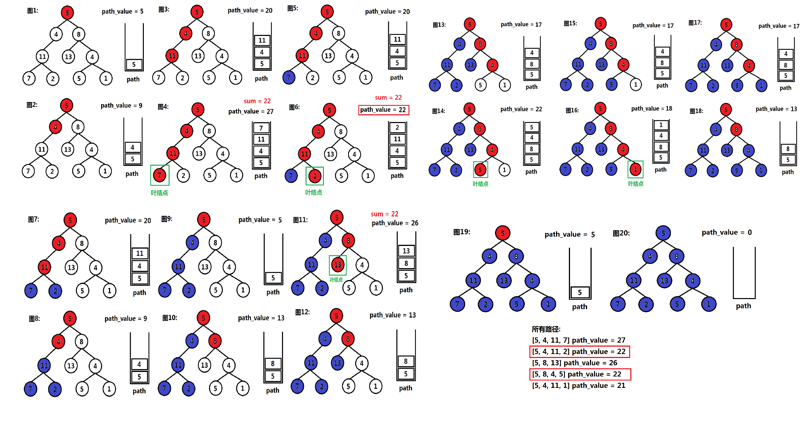
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
OJ测试代码实现:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
private:
void preorde(TreeNode* node,int targetSum, int path_resut,std::vector<int> &path,std::vector<vector<int> > &result){
if(!node){ // 如果遍历到空指针(叶节点的孩子),结束
return ;
}
path_resut += node->val;
path.push_back(node->val);
if(path_resut == targetSum && node->left==nullptr && node->right == nullptr){
result.push_back(path);
}
preorde(node->left,targetSum,path_resut,path,result);
preorde(node->right,targetSum,path_resut,path,result);
path_resut -= node->val;
path.pop_back();
}
public:
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
std::vector<int> path;
int path_resut = 0;
std::vector<std::vector<int> > result;
preorde(root,targetSum,path_resut,path,result);
return result;
}
};
- 可本地运行测试的完整代码:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<std::vector<int> > pathSum(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
std::vector<std::vector<int> > result;
std::vector<int> path;
int path_value = 0;
preorder(root, path_value, sum, path, result);
return result;
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode *node, int &path_value, int sum,
std::vector<int> &path,
std::vector<std::vector<int> > &result){
if (!node){
return;
}
path_value += node->val;
path.push_back(node->val);
if (!node->left && !node->right && path_value == sum){
result.push_back(path);
}
preorder(node->left, path_value, sum, path, result);
preorder(node->right, path_value, sum, path, result);
path_value -= node->val;
path.pop_back();
}
};
int main(){
TreeNode a(5);
TreeNode b(4);
TreeNode c(8);
TreeNode d(11);
TreeNode e(13);
TreeNode f(4);
TreeNode g(7);
TreeNode h(2);
TreeNode x(5);
TreeNode y(1);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
c.left = &e;
c.right = &f;
d.left = &g;
d.right = &h;
f.left = &x;
f.right = &y;
Solution solve;
std::vector<std::vector<int> > result = solve.pathSum(&a, 22);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
for (int j = 0; j < result[i].size(); j++){
printf("[%d]", result[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
return 0;
}
典例2、最近的公共祖先(medium)
-
题目描述:
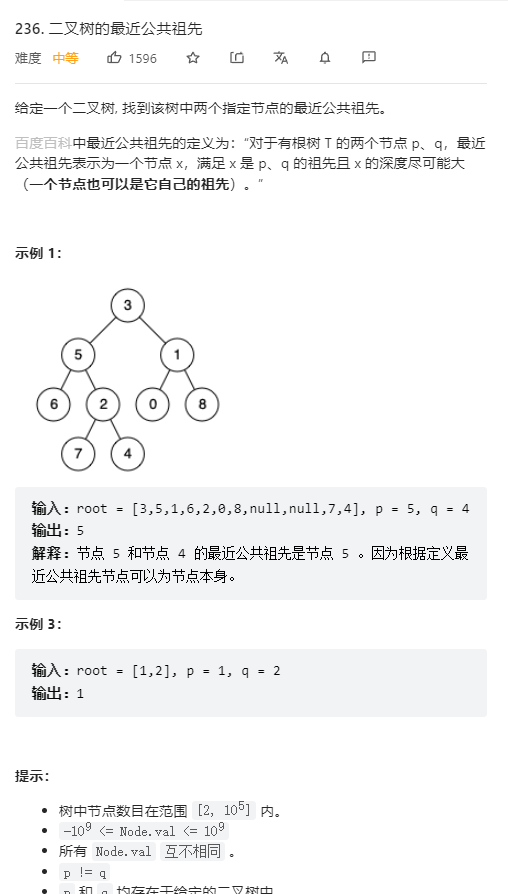
-
思路:
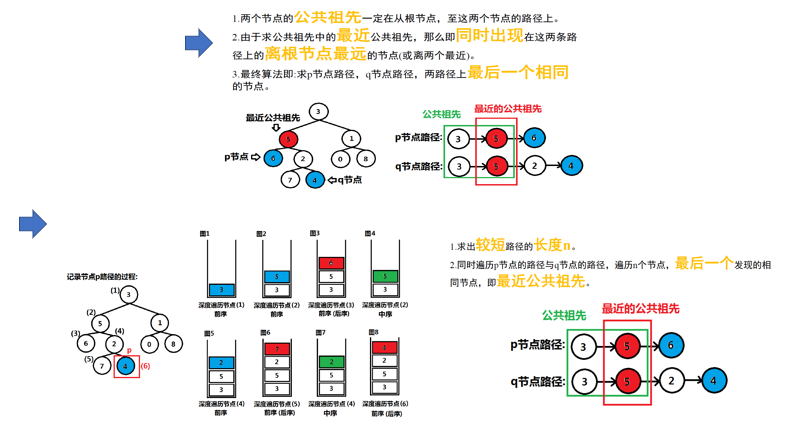
- LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
其他方法代码解析: 【剑指 Offer 68 - I & II . 二叉搜索树/二叉树的最近公共祖先】.
- 可本地运行测试的完整代码:
#include <stdio.h>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
#include <vector>
#include <set>
void preorder(TreeNode* node,
TreeNode *search,
std::vector<TreeNode*> &path,
std::vector<TreeNode*> &result,
int &finish){
if (!node || finish){
return;
}
path.push_back(node);
if (node == search){
finish = 1;
result = path;
}
preorder(node->left, search, path, result, finish);
preorder(node->right, search, path, result, finish);
path.pop_back();
}
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
std::vector<TreeNode*> path;
std::vector<TreeNode*> node_p_path;
std::vector<TreeNode*> node_q_path;
int finish = 0;
preorder(root, p, path, node_p_path, finish);
path.clear();
finish = 0;
preorder(root, q, path, node_q_path, finish);
int path_len = 0;
if (node_p_path.size() < node_q_path.size()){
path_len = node_p_path.size();
}
else{
path_len = node_q_path.size();
}
TreeNode *result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < path_len; i++){
if (node_p_path[i] == node_q_path[i]){
result = node_p_path[i];
}
}
return result;
}
};
int main(){
TreeNode a(3);
TreeNode b(5);
TreeNode c(1);
TreeNode d(6);
TreeNode e(2);
TreeNode f(0);
TreeNode x(8);
TreeNode y(7);
TreeNode z(4);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.left = &f;
c.right = &x;
e.left = &y;
e.right = &z;
Solution solve;
TreeNode *result = solve.lowestCommonAncestor(&a, &b, &f);
printf("lowestCommonAncestor = %dn", result->val);
result = solve.lowestCommonAncestor(&a, &d, &z);
printf("lowestCommonAncestor = %dn", result->val);
result = solve.lowestCommonAncestor(&a, &b, &y);
printf("lowestCommonAncestor = %dn", result->val);
return 0;
}
典例3、二叉树转链表(medium)
-
题目描述:
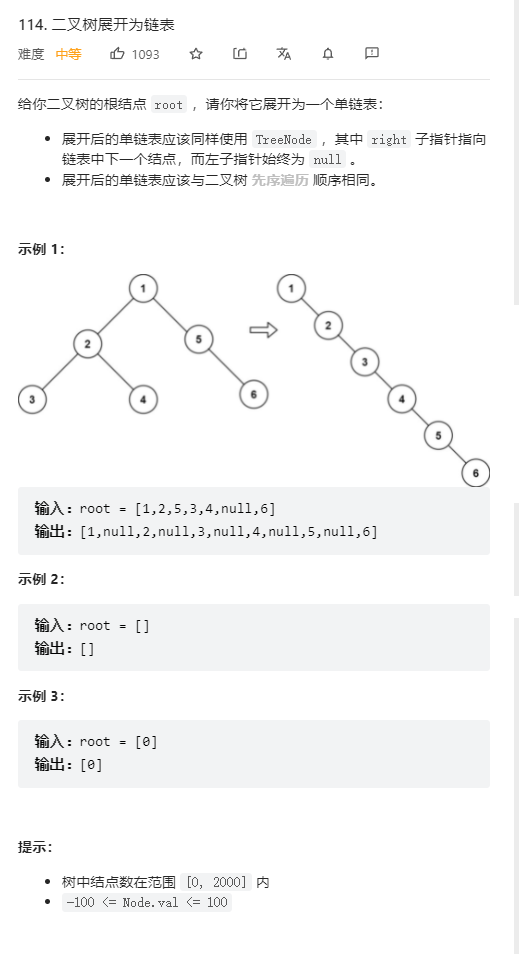
-
思路:
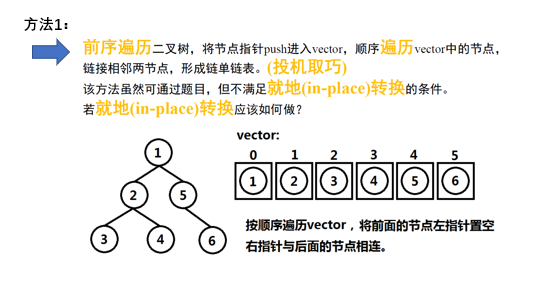
#include <stdio.h>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
#include <vector>
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode *root) {
std::vector<TreeNode *> node_vec;
preorder(root, node_vec);
for (int i = 1; i < node_vec.size(); i++){
node_vec[i-1]->left = NULL;
node_vec[i-1]->right = node_vec[i];
}
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode *node, std::vector<TreeNode *> &node_vec){
if (!node){
return;
}
node_vec.push_back(node);
preorder(node->left, node_vec);
preorder(node->right, node_vec);
}
};
int main(){
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
Solution solve;
solve.flatten(&a);
TreeNode *head = &a;
while(head){
if (head->left){
printf("ERRORn");
}
printf("[%d]", head->val);
head = head->right;
}
printf("n");
return 0;
}
方法2:
- 就地转换:不使用其他的空间;
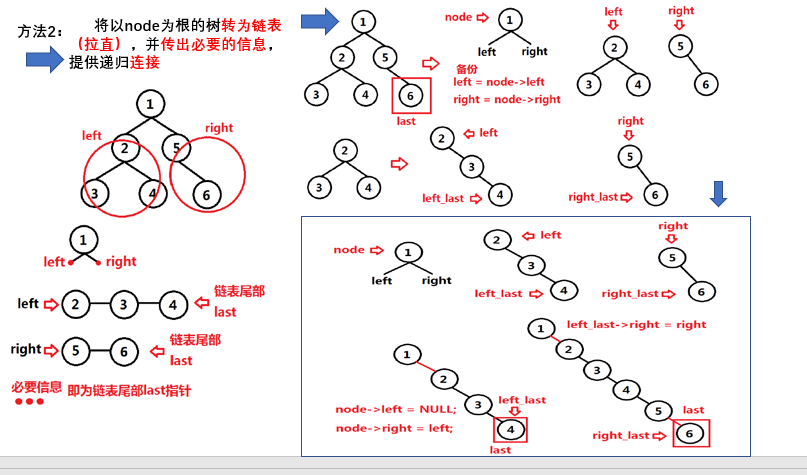
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
OJ测试代码实现:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode* root) {
TreeNode * last= nullptr;
preorde(root,last);
}
private:
void preorde(TreeNode* node,TreeNode* &last){
if (!node){
return ;
}
if(!node->left && !node->right){
last = node;
return;
}
TreeNode* left = node->left;
TreeNode* right = node->right;
TreeNode* left_last = nullptr;
TreeNode* right_last = nullptr;
if(left){
preorde(left,left_last);
node->left = nullptr; // 左节点置空
node->right = left; // 左节点 拼接到右节点上去
last = left_last ; // 更新最后节点,以便其他递归调用
}
if(right){
preorde(right,right_last);
if(left_last){// 如果有左子树的话
left_last->right = right; // 如果有左子树的话,将左子数处理好的右节点拼接到当前节点的右子树上
}
last = right_last; // 更新最后节点,以便其他递归调用
}
}
};
- 可本地运行测试的完整代码:
#include <stdio.h>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
void flatten(TreeNode *root) {
TreeNode *last = NULL;
preorder(root, last);
}
private:
void preorder(TreeNode *node, TreeNode *&last){
if (!node){
return;
}
if (!node->left && !node->right){
last = node;
return;
}
TreeNode *left = node->left;
TreeNode *right = node->right;
TreeNode *left_last = NULL;
TreeNode *right_last = NULL;
if (left){
preorder(left, left_last);
node->left = NULL;
node->right = left;
last = left_last;
}
if (right){
preorder(right, right_last);
if (left_last){
left_last->right = right;
}
last = right_last;
}
}
};
int main(){
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
Solution solve;
solve.flatten(&a);
TreeNode *head = &a;
while(head){
if (head->left){
printf("ERRORn");
}
printf("[%d]", head->val);
head = head->right;
}
printf("n");
return 0;
}
基础补充
- 广度优先搜索:BFS(层次遍历 )
- 借助队列访问节点。

典例4、侧面观察二叉树(medium)
-
题目描述:
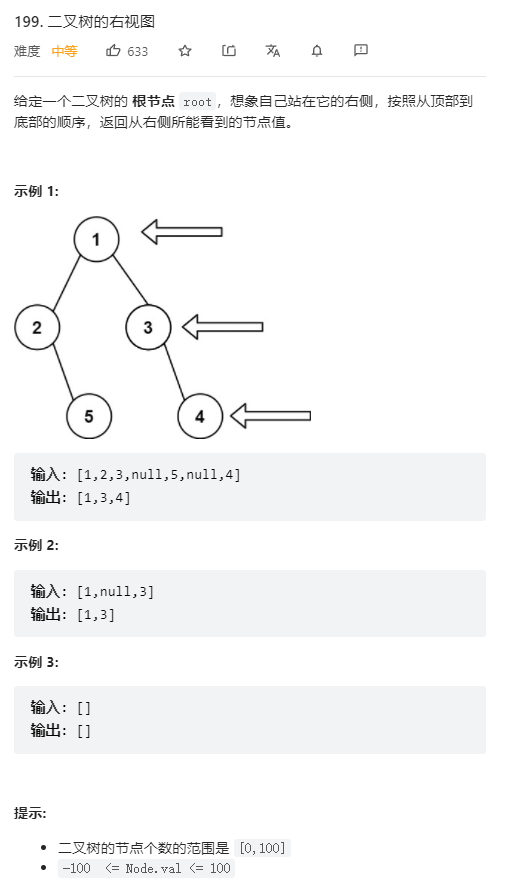
-
思路:
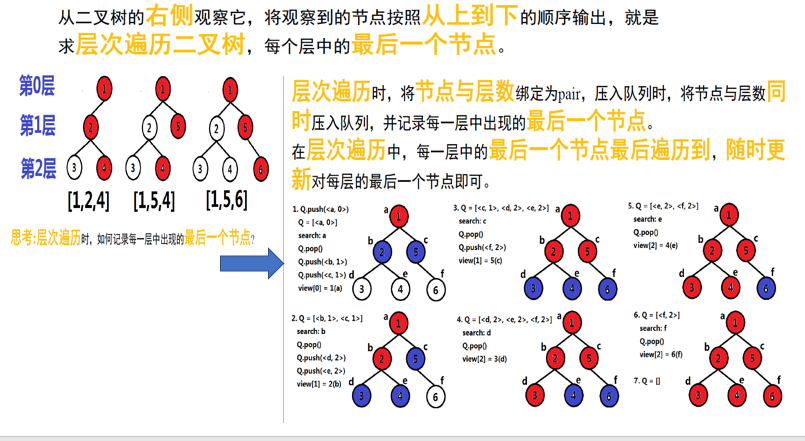
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
可本地运行测试的完整代码:
# Definition for a binary tree node.
# class TreeNode:
# def __init__(self, val=0, left=None, right=None):
# self.val = val
# self.left = left
# self.right = right
class Solution:
def rightSideView(self, root: TreeNode) -> List[int]:
if not root :return []
q = collections.deque([root])
res= [] # 存放每层的最后一个节点
q2 = collections.deque([])
while q:
res.append(q[-1].val) # 每层的最后一个节点
while q:
node = q.popleft()
if node.left: q2.append(node.left)
if node.right: q2.append(node.right)
while q2:
q.append(q2.popleft())
return res
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
struct TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode *left;
TreeNode *right;
TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
std::vector<int> rightSideView(TreeNode* root) {
std::vector<int> view;
std::queue<std::pair<TreeNode *, int> > Q;
if (root){
Q.push(std::make_pair(root, 0));
}
while(!Q.empty()){
TreeNode *node = Q.front().first;
int depth = Q.front().second;
Q.pop();
if (view.size() == depth){
view.push_back(node->val);
}
else{
view[depth] = node->val;
}
if (node->left){
Q.push(std::make_pair(node->left, depth + 1));
}
if (node->right){
Q.push(std::make_pair(node->right, depth + 1));
}
}
return view;
}
};
int main(){
TreeNode a(1);
TreeNode b(2);
TreeNode c(5);
TreeNode d(3);
TreeNode e(4);
TreeNode f(6);
a.left = &b;
a.right = &c;
b.left = &d;
b.right = &e;
c.right = &f;
Solution solve;
std::vector<int> result = solve.rightSideView(&a);
for (int i = 0; i < result.size(); i++){
printf("[%d]n", result[i]);
}
return 0;
}
典例5、课程安排(medium)
关于图的基础知识
-
概念: 顶点、边 G(V,E)
-
无向图、有向图
-
带权图(权重)、不带全图
-
使用邻接矩阵表示图:
-
行代表哪一个顶点;列代表这个顶点和哪个顶点的逻辑关系(是否相连)
-
前一个维度指向后一个维度 = 1 ,代表这两个节点向量([0][ 2] = 1 代表第0个节点和第二个节点向连,由0→2; [0][ 2] = 0 则表示不相连)
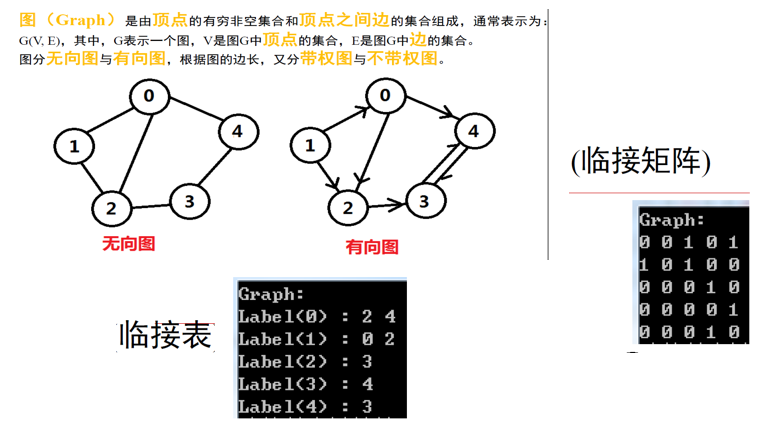
-
图的构造与邻接表
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
int main(){
const int MAX_N = 5;
GraphNode *Graph[MAX_N];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
Graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
}
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[0]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[2]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
Graph[3]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[4]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
printf("Graph:n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
printf("Label(%d) : ", i);
for (int j = 0; j < Graph[i]->neighbors.size(); j++){
printf("%d ", Graph[i]->neighbors[j]->label);
}
printf("n");
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
delete Graph[i];
}
return 0;
}
- 图的构造与邻接矩阵
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
const int MAX_N = 5;
int Graph[MAX_N][MAX_N] = {0};
Graph[0][2] = 1;
Graph[0][4] = 1;
Graph[1][0] = 1;
Graph[1][2] = 1;
Graph[2][3] = 1;
Graph[3][4] = 1;
Graph[4][3] = 1;
printf("Graph:n");
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
for (int j = 0; j < MAX_N; j++){
printf("%d ", Graph[i][j]);
}
printf("n");
}
return 0;
}
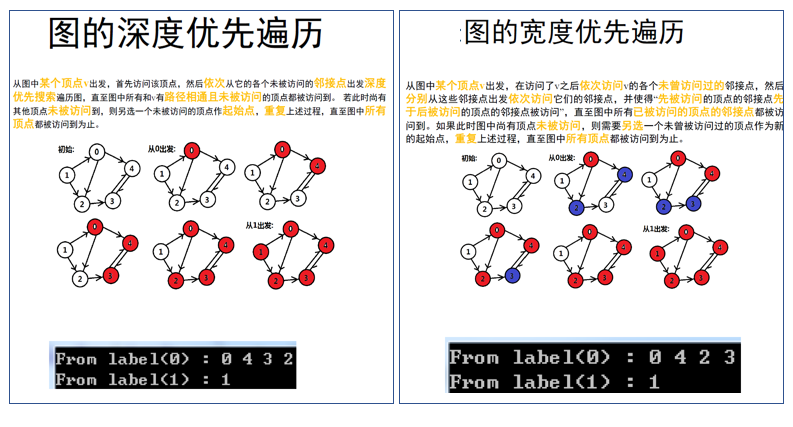
- 图的深度优先遍历
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
void DFS_graph(GraphNode *node, int visit[]){
visit[node->label] = 1;
printf("%d ", node->label);
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++){
if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
DFS_graph(node->neighbors[i], visit);
}
}
}
int main(){
const int MAX_N = 5;
GraphNode *Graph[MAX_N];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
Graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
}
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[0]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[2]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
Graph[3]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[4]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
int visit[MAX_N] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
if (visit[i] == 0){
printf("From label(%d) : ", Graph[i]->label);
DFS_graph(Graph[i], visit);
printf("n");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
delete Graph[i];
}
return 0;
}
- 图的广度优先遍历
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
void BFS_graph(GraphNode *node, int visit[]){
std::queue<GraphNode *> Q;
Q.push(node);
visit[node->label] = 1;
while(!Q.empty()){
GraphNode *node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
printf("%d ", node->label);
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++){
if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
Q.push(node->neighbors[i]);
visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] = 1;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
const int MAX_N = 5;
GraphNode *Graph[MAX_N];
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
Graph[i] = new GraphNode(i);
}
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[0]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[0]);
Graph[1]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[2]);
Graph[2]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
Graph[3]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[4]);
Graph[4]->neighbors.push_back(Graph[3]);
int visit[MAX_N] = {0};
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
if (visit[i] == 0){
printf("From label(%d) : ", Graph[i]->label);
BFS_graph(Graph[i], visit);
printf("n");
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < MAX_N; i++){
delete Graph[i];
}
return 0;
}
- 题目描述:

- 思路:
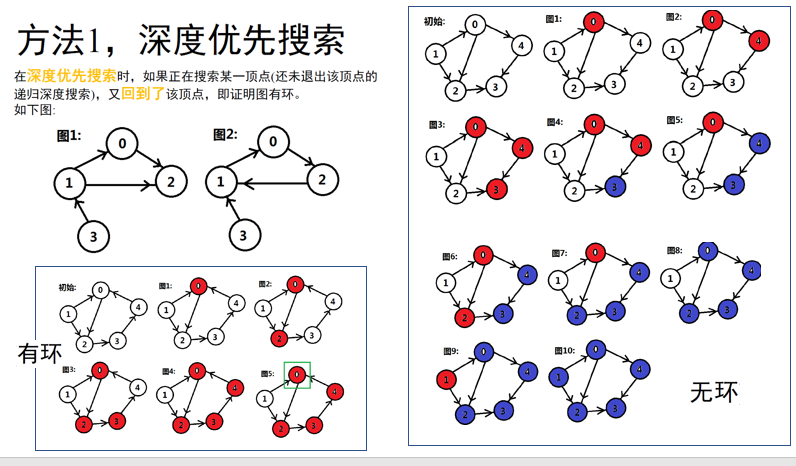
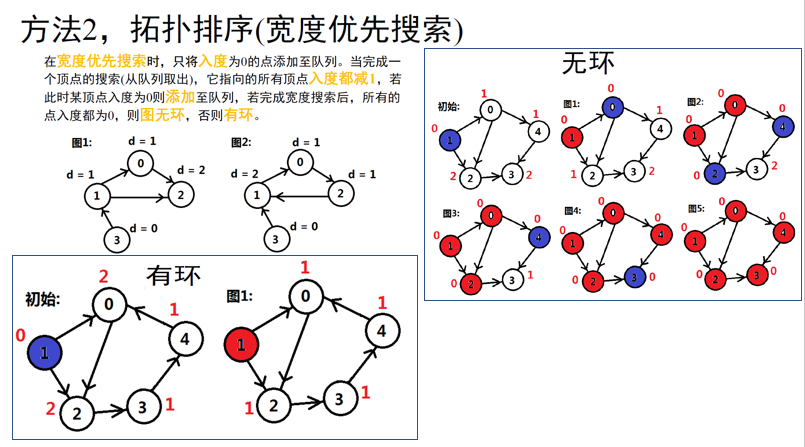
-
LeetCode提交OJ测试链接:
-
可本地运行测试的完整代码:
-
图的深度搜索解法:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
bool DFS_graph(GraphNode *node, std::vector<int> &visit){
visit[node->label] = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++){
if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == -1){
if (DFS_graph(node->neighbors[i], visit) == 0){
return false;
}
}
else if (visit[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
return false;
}
}
visit[node->label] = 1;
return true;
}
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses,
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> >& prerequisites) {
std::vector<GraphNode*> graph;
std::vector<int> visit;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
graph.push_back(new GraphNode(i));
visit.push_back(-1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++){
GraphNode *begin = graph[prerequisites[i].second];
GraphNode *end = graph[prerequisites[i].first];
begin->neighbors.push_back(end);
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++){
if (visit[i] == -1 && !DFS_graph(graph[i], visit)){
return false;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
delete graph[i];
}
return true;
}
};
int main(){
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > prerequisites;
prerequisites.push_back(std::make_pair(1, 0));
prerequisites.push_back(std::make_pair(2, 0));
prerequisites.push_back(std::make_pair(3, 1));
prerequisites.push_back(std::make_pair(3, 2));
Solution solve;
printf("%dn", solve.canFinish(4, prerequisites));
return 0;
}
- 图的广度搜索解法:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
struct GraphNode{
int label;
std::vector<GraphNode *> neighbors;
GraphNode(int x) : label(x) {};
};
class Solution {
public:
bool canFinish(int numCourses,
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> >& prerequisites) {
std::vector<GraphNode*> graph;
std::vector<int> degree;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
degree.push_back(0);
graph.push_back(new GraphNode(i));
}
for (int i = 0; i < prerequisites.size(); i++){
GraphNode *begin = graph[prerequisites[i].second];
GraphNode *end = graph[prerequisites[i].first];
begin->neighbors.push_back(end);
degree[prerequisites[i].first]++;
}
std::queue<GraphNode *> Q;
for (int i = 0; i < numCourses; i++){
if (degree[i] == 0){
Q.push(graph[i]);
}
}
while(!Q.empty()){
GraphNode *node = Q.front();
Q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < node->neighbors.size(); i++){
degree[node->neighbors[i]->label]--;
if (degree[node->neighbors[i]->label] == 0){
Q.push(node->neighbors[i]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < graph.size(); i++){
delete graph[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i < degree.size(); i++){
if (degree[i]){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
};
int main(){
std::vector<std::pair<int, int> > prerequisites;
prerequisites.push_back(std::make_pair(1, 0));
prerequisites.push_back(std::make_pair(2, 0));
prerequisites.push_back(std::make_pair(3, 1));
prerequisites.push_back(std::make_pair(3, 2));
Solution solve;
printf("%dn", solve.canFinish(4, prerequisites));
return 0;
}
最后
以上就是不安唇膏最近收集整理的关于【数据结构与算法-二叉树与图经典例题汇总】的全部内容,更多相关【数据结构与算法-二叉树与图经典例题汇总】内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复