TorchScript是Pytorch模型(继承自nn.Module)的中间表示,保存后的torchscript模型可以在像C++这种高性能的环境中运行
TorchScript是一种从PyTorch代码创建可序列化和可优化模型的方法。任何TorchScript程序都可以从Python进程中保存,并加载到没有Python依赖的进程中。
简单来说,在pytorch的灵活的动态图特性下,torchscript提供了依然能够获取模型结构(模型定义)的工具。
TorchScript能将动态图转为静态图。
torchscript常和torch.jit合起来用
例① Tracing
Modulestorch.jit.trace做的事是把模型和example输入传进去,然后它会调用模型,然后记录下模型run的时候所进行的操作。并且会创建一个torch.jit.ScriptModule 实例
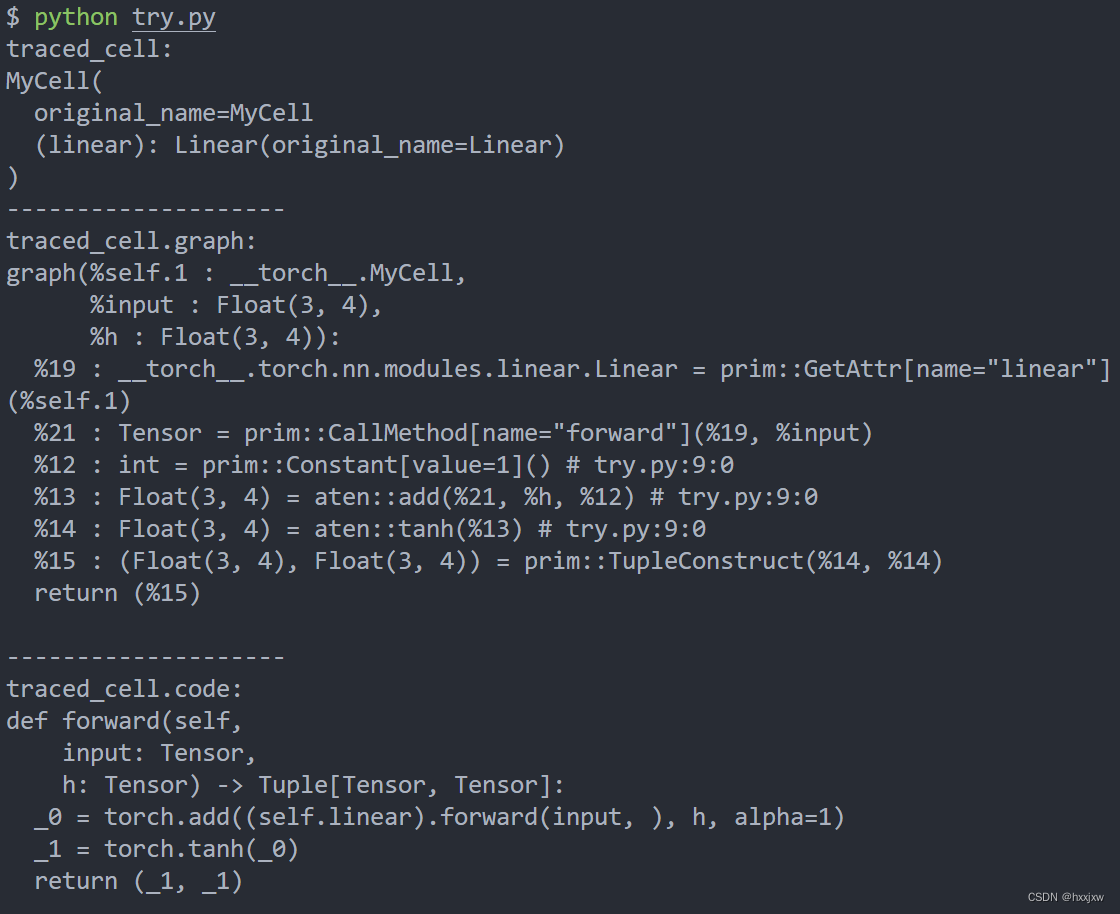
torchscript记录模型是通过中间表示的形式的,在这里就是一种图的形式print(traced_cell.graph)即可以输出中间形式
然后,这是一种非常low-level的表示,graph中的多数信息对于我们来说是没有用的,我们可以用print(traced_cell.code)来输出python语法形式的code
import torch class MyCell(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(MyCell, self).__init__() self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 4) def forward(self, x, h): new_h = torch.tanh(self.linear(x) + h) return new_h, new_h my_cell = MyCell() x, h = torch.rand(3, 4), torch.rand(3, 4) traced_cell = torch.jit.trace(my_cell, (x, h)) print('traced_cell: ') print(traced_cell) traced_cell(x, h) print('-'*20) print('traced_cell.graph: ') print(traced_cell.graph) print('-'*20) print('traced_cell.code: ') print(traced_cell.code)
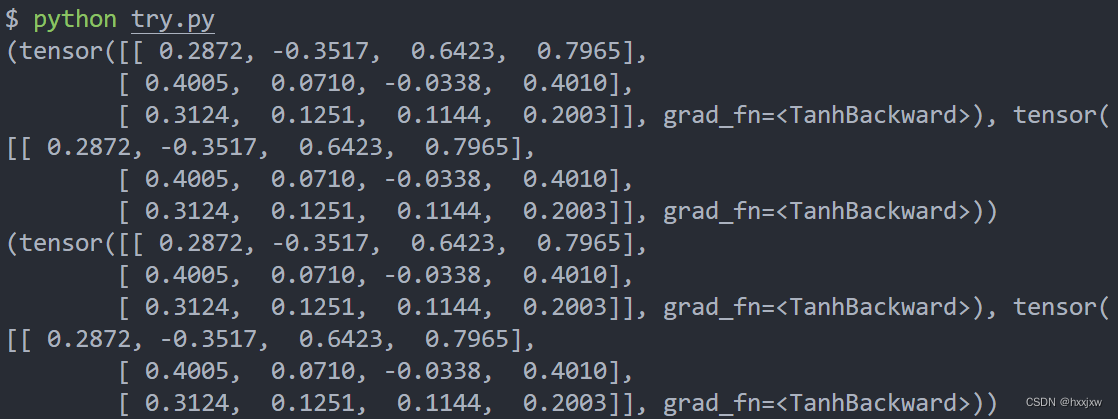
torchscript转化后的model和原model输出的结果是一样的
import torch class MyCell(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(MyCell, self).__init__() self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 4) def forward(self, x, h): new_h = torch.tanh(self.linear(x) + h) return new_h, new_h my_cell = MyCell() x, h = torch.rand(3, 4), torch.rand(3, 4) traced_cell = torch.jit.trace(my_cell, (x, h)) print(my_cell(x,h)) print(traced_cell(x,h))
例② torch.jit.script
前面我们说了,torch.jit.trace做的事是把模型和example输入传进去,然后它会调用模型,然后记录下模型run的时候所进行的操作
那么让我们有decision branch的时候呢
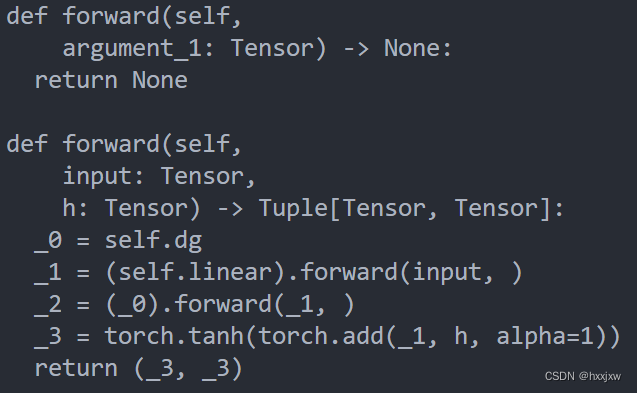
import torch class MyDecisionGate(torch.nn.Module): def forward(self, x): if x.sum() > 0: return x else: return -x class MyCell(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, dg): super(MyCell, self).__init__() self.dg = dg self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 4) def forward(self, x, h): new_h = torch.tanh(self.dg(self.linear(x)) + h) return new_h, new_h my_cell = MyCell(MyDecisionGate()) x, h = torch.rand(3, 4), torch.rand(3, 4) traced_cell = torch.jit.trace(my_cell, (x, h)) print(traced_cell.dg.code) print(traced_cell.code)
可以看到,当输出.code的时候, if-else branch不见了,torch.jit.trace记录的只是当前代码走的路径,control-flow被摸除了。比如同一个代码,这次走if分支,下次走else分支,那么torch.jit.trace记录的就会不同
在这种情况下,我们可以用torch.jit.script
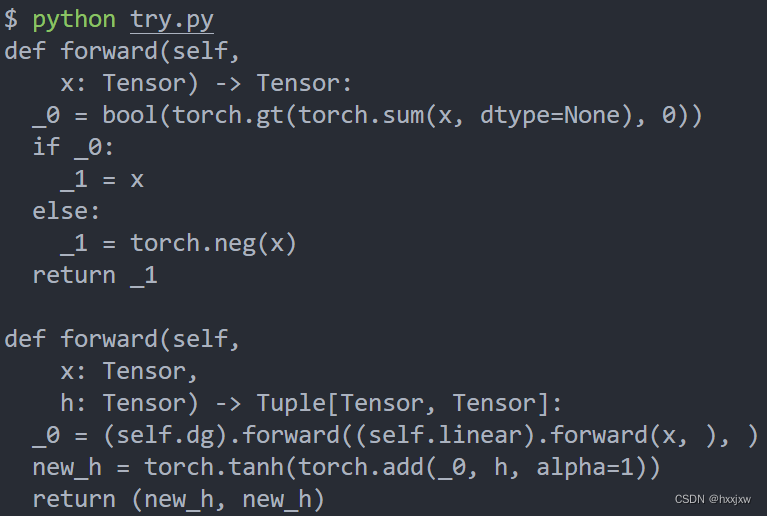
import torch class MyDecisionGate(torch.nn.Module): def forward(self, x): if x.sum() > 0: return x else: return -x class MyCell(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, dg): super(MyCell, self).__init__() self.dg = dg self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 4) def forward(self, x, h): new_h = torch.tanh(self.dg(self.linear(x)) + h) return new_h, new_h scripted_gate = torch.jit.script(MyDecisionGate()) my_cell = MyCell(scripted_gate) scripted_cell = torch.jit.script(my_cell) print(scripted_gate.code) print(scripted_cell.code)
可以看到,我们已经可以capture到control flow了
forward方法会被默认编译,forward中被调用的方法也会按照被调用的顺序被编译
如果想要编译一个forward以外且未被forward调用的方法,可以添加
@torch.jit.export.如果想要方法不被编译,可使用@torch.jit.ignore 或 @torch.jit.unused
如
# Same behavior as pre-PyTorch 1.2 @torch.jit.script def some_fn(): return 2 # Marks a function as ignored, if nothing # ever calls it then this has no effect @torch.jit.ignore def some_fn2(): return 2 # As with ignore, if nothing calls it then it has no effect. # If it is called in script it is replaced with an exception. @torch.jit.unused def some_fn3(): import pdb; pdb.set_trace() return 4 # Doesn't do anything, this function is already # the main entry point @torch.jit.export def some_fn4(): return 2例③ Scripting 和 Tracing的混用
从上面可以看到,script似乎比trace更强大,但是某些情况下我们还是需要使用trace,例如一个模型结构有很多decision branch但是是基于constant value的
scripting和tracing是可以混用的,可以在一个traced module中调用script,也可以在一个scripted module中调用trace
scripted module中调用trace
import torch class MyDecisionGate(torch.nn.Module): def forward(self, x): if x.sum() > 0: return x else: return -x class MyCell(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, dg): super(MyCell, self).__init__() self.dg = dg self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 4) def forward(self, x, h): new_h = torch.tanh(self.dg(self.linear(x)) + h) return new_h, new_h class MyRNNLoop(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(MyRNNLoop, self).__init__() self.cell = torch.jit.trace(MyCell(scripted_gate), (x, h)) def forward(self, xs): h, y = torch.zeros(3, 4), torch.zeros(3, 4) for i in range(xs.size(0)): y, h = self.cell(xs[i], h) return y, h x, h = torch.rand(3, 4), torch.rand(3, 4) scripted_gate = torch.jit.script(MyDecisionGate()) rnn_loop = torch.jit.script(MyRNNLoop()) print(rnn_loop.code)traced module中调用script
import torch class MyDecisionGate(torch.nn.Module): def forward(self, x): if x.sum() > 0: return x else: return -x class MyCell(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, dg): super(MyCell, self).__init__() self.dg = dg self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 4) def forward(self, x, h): new_h = torch.tanh(self.dg(self.linear(x)) + h) return new_h, new_h class MyRNNLoop(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(MyRNNLoop, self).__init__() self.cell = torch.jit.trace(MyCell(scripted_gate), (x, h)) def forward(self, xs): h, y = torch.zeros(3, 4), torch.zeros(3, 4) for i in range(xs.size(0)): y, h = self.cell(xs[i], h) return y, h class WrapRNN(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(WrapRNN, self).__init__() self.loop = torch.jit.script(MyRNNLoop()) def forward(self, xs): y, h = self.loop(xs) return torch.relu(y) x, h = torch.rand(3, 4), torch.rand(3, 4) scripted_gate = torch.jit.script(MyDecisionGate()) traced = torch.jit.trace(WrapRNN(), (torch.rand(10, 3, 4))) print(traced.code)加载和保存torchscript model
#rnn_loop.save('rnn_loop.pth') traced.save('wrapped_rnn.pt') loaded = torch.jit.load('wrapped_rnn.pt') print(loaded) print(loaded.code)import torch class MyDecisionGate(torch.nn.Module): def forward(self, x): if x.sum() > 0: return x else: return -x class MyCell(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self, dg): super(MyCell, self).__init__() self.dg = dg self.linear = torch.nn.Linear(4, 4) def forward(self, x, h): new_h = torch.tanh(self.dg(self.linear(x)) + h) return new_h, new_h class MyRNNLoop(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(MyRNNLoop, self).__init__() self.cell = torch.jit.trace(MyCell(scripted_gate), (x, h)) def forward(self, xs): h, y = torch.zeros(3, 4), torch.zeros(3, 4) for i in range(xs.size(0)): y, h = self.cell(xs[i], h) return y, h class WrapRNN(torch.nn.Module): def __init__(self): super(WrapRNN, self).__init__() self.loop = torch.jit.script(MyRNNLoop()) def forward(self, xs): y, h = self.loop(xs) return torch.relu(y) x, h = torch.rand(3, 4), torch.rand(3, 4) scripted_gate = torch.jit.script(MyDecisionGate()) traced = torch.jit.trace(WrapRNN(), (torch.rand(10, 3, 4))) traced.save('wrapped_rnn.pth') loaded = torch.jit.load('wrapped_rnn.pth') print(loaded) print(loaded.code)
踩坑
在C++平台上部署PyTorch模型流程+踩坑实录 (qq.com)
最后
以上就是舒服微笑最近收集整理的关于TorchScript (将动态图转为静态图)(模型部署)(jit)(torch.jit.trace)(torch.jit.script)的全部内容,更多相关TorchScript内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复