上文已讲述了回溯法以及01背包问题的原理,本文讲述如何顺序执行解决01背包问题以及通过模板模式重构软件。
一、顺序执行流程图
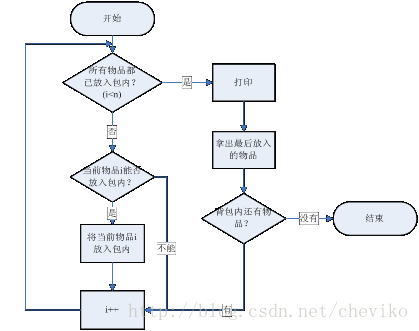
图1无剪枝函数的01背包问题顺序执行算法流程图
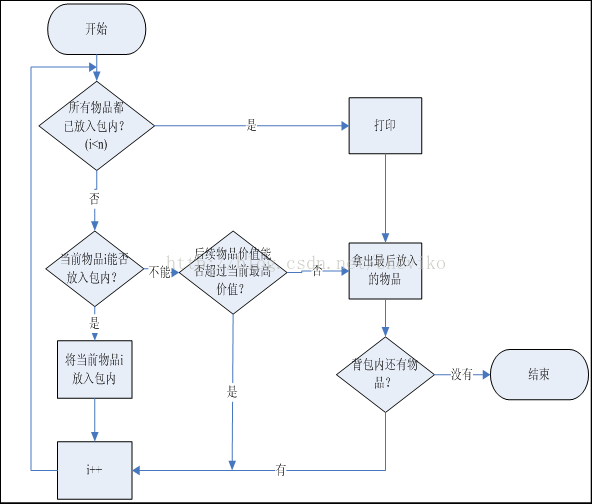
图2 有剪枝函数的01背包问题顺序执行算法流程图
无剪枝函数是通用的深度遍历算法,为了减少搜索深度可通过剪枝函数处理完全不可能的分枝。与递归方案的区别主要表现在i>=n后需要“回溯”,即用后进先出的方式将物品逐个拿出。
二、执行代码
递归与顺序执行方法仅仅是实现方法Backtracking(int i)不同,其余的完全一致,因此可将具体实现延迟至子类中。模板方法使得自雷可以改变一个算法的结构即可重定义该算法的某些特定步骤,因此采用模板模式。类图结构如图3所示:
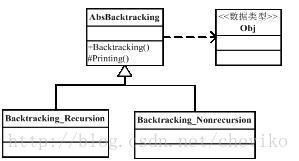
图3 回溯法模板模式类图
代码1 测试代码
public static void Main (string[] args)
{
Obj[] objs = new Obj[4];
objs[0] = new Obj() { Weight = 7, Price = 42 };
objs[1] = new Obj() { Weight = 3, Price = 12 };
objs[2] = new Obj() { Weight = 4, Price = 40 };
objs[3] = new Obj() { Weight = 5, Price = 25 };
AbsBacktracking r = new Backtracking_Nonrecursion();
r.W = 10;
r.objs = objs;
Console.WriteLine("Nonrecursion Model:");
r.Backtracking(0);
Console.WriteLine("Recursion Model:");
r = new Backtracking_Recursion();
r.W = 10;
r.objs = objs;
r.Backtracking(0);
Console.Read();
}代码2 抽象类 AbsBacktracking
public abstract class AbsBacktracking
{
#region field
protected int m_currentWeight = 0;
protected int m_currentPrice = 0;
#endregion
#region property
/// <summary>
/// 背包容量
/// </summary>
/// <value>默认20</value>
public int W
{
get;
set;
}
public int n
{
get
{
return objs == null ? 0 : objs.Length;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 物品,包括重量/价值和数量
/// </summary>
/// <value>The objects.</value>
public Obj[] objs
{
get;
set;
}
#endregion
public abstract void Backtracking(int i);
protected void Printing()
{
Console.Write("<");
for (int i = 0; i < objs.Length; i++)
{
Console.Write(objs[i].Selected ? "1 " : "0 ");
}
Console.WriteLine(">, price: " + m_currentPrice.ToString()
+ "t weight: " + m_currentWeight.ToString());
}
}代码3 类Backtracking_Nonrecursion
public class Backtracking_Nonrecursion:AbsBacktracking
{
public override void Backtracking(int i)
{
while (true)
{
if (i < n)
{
if (m_currentWeight + objs[i].Weight <= W)
{
//将第i个物品放入包中
m_currentWeight += objs[i].Weight;
m_currentPrice += objs[i].Price;
objs[i].Selected = true;
}
}
else
{
//打印路径
Printing();
i--;
while (i >= 0 && !objs[i].Selected)
{
i--;
}
if (i < 0)
{
return;
}
else
{
//将i从包内拿出
m_currentWeight -= objs[i].Weight;
m_currentPrice -= objs[i].Price;
objs[i].Selected = false;
}
}
i++;
}
}
}
代码4 代码片段Backtracking_Recursion
public class Backtracking_Recursion :AbsBacktracking
{
public override void Backtracking (int i)
{
if (i >= n ) {
Printing();
return;
}
if (objs[i].Weight + m_currentWeight <= W) {
m_currentWeight += objs [i].Weight;
m_currentPrice += objs [i].Price;
objs [i].Selected = true;
Backtracking (i + 1);
m_currentPrice -= objs [i].Price;
m_currentWeight -= objs [i].Weight;
}
objs [i].Selected = false;
Backtracking (i + 1);
}
}代码5 Obj代码片段
public class Obj
{
/// <summary>
/// 物品重量
/// </summary>
public int Weight
{
get;
set;
}
/// <summary>
/// 物品价值
/// </summary>
public int Price
{
get;
set;
}
/// <summary>
/// 该物品是否放入包内
/// </summary>
internal bool Selected
{
get;
set;
}
}三、运行结果:
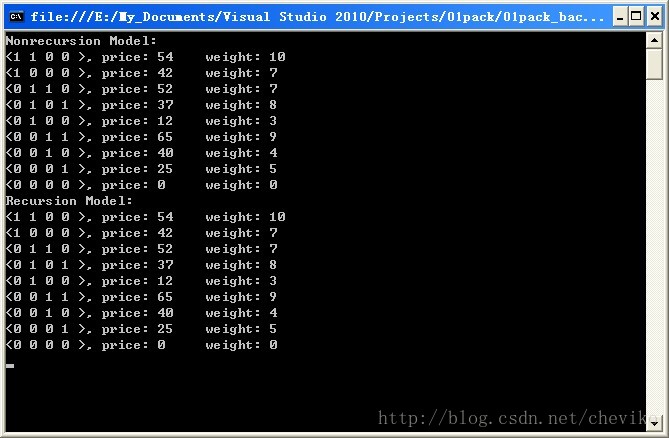
注:上述实现中没有添加剪枝函数功能,也没有添加判断最优路径功能,读者可继续优化。
下载源代码
最后
以上就是含糊花瓣最近收集整理的关于回溯法-01背包问题之二:顺序执行模式的全部内容,更多相关回溯法-01背包问题之二内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复