CompletableFuture 分别实现两个接口 Future与 CompletionStage。
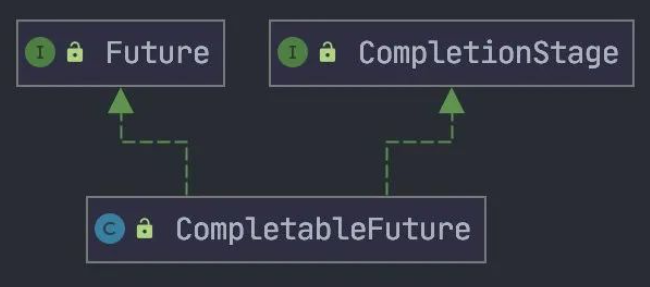
Future 接口大家都比较熟悉,这里主要讲讲 CompletionStage。
CompletableFuture 大部分方法来自CompletionStage 接口,正是因为这个接口,CompletableFuture才有如此强大功能。
想要理解 CompletionStage 接口,我们需要先了解任务的时序关系的。我们可以将任务时序关系分为以下几种:
-
串行执行关系
-
并行执行关系
-
AND 汇聚关系
-
OR 汇聚关系
1.串行执行关系
任务串行执行,下一个任务必须等待上一个任务完成才可以继续执行。
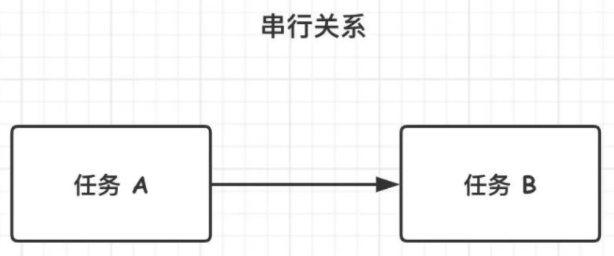
CompletionStage 有四组接口可以描述串行这种关系,分别为:
// 同步
CompletableFuture<U> thenApply(Function<? super T, ? extends u> fn)
CompletableFuture<Void> thenAccept(Consumer<? super T> action)
CompletableFuture<Void> thenRun(Runnable action)
// 这个比较特殊,类似于Stream.flatmap
CompletableFuture<U> thenCompose(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn)
// 异步
CompletionStage<U> thenApplyAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends u> fn)
CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(Consumer<? super T> action)
CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(Runnable action)
// 这个比较特殊,类似于Stream.flatmap
CompletionStage<U> thenComposeAsync(Function<? super T, ? extends CompletionStage<U>> fn)
thenApply 方法需要传入核心参数为 Function<T,R>类型。这个类核心方法为:
R apply(T t)所以这个接口将会把上一个任务返回结果当做入参,执行结束将会返回结果。
thenAccept 方法需要传入参数对象为 Consumer<T>类型,这个类核心方法为:
void accept(T t)返回值 void 可以看出,这个方法不支持返回结果,但是需要将上一个任务执行结果当做参数传入。
thenRun 方法需要传入参数对象为 Runnable 类型,这个类大家应该都比较熟悉,核心方法既不支持传入参数,也不会返回执行结果。
thenCompose 方法作用与 thenApply 一样,只不过 thenCompose 需要返回新的 CompletionStage。这么理解比较抽象,可以集合代码一起理解。
CompletableFuture<String> cf =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello,楼下小哥");
cf.thenApply(String::toLowerCase);
// 需要重新创建一个CompletionStage
cf.thenCompose(s -> CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(s::toLowerCase));方法中带有 Async ,代表可以异步执行,这个系列还有重载方法,可以传入自定义的线程池,上图未展示,读者只可以自行查看 API。
最后我们通过代码展示 thenApply 使用方式:
CompletableFuture<String> cf
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> "hello,楼下小哥")// 1
.thenApply(s -> s + "@程序通事") // 2
.thenApply(String::toUpperCase); // 3
System.out.println(cf.join());
// 输出结果 HELLO,楼下小哥@程序通事这段代码比较简单,首先我们开启一个异步任务,接着串行执行后续两个任务。任务 2 需要等待任务1 执行完成,任务 3 需要等待任务 2。
上面方法,大家需要记住了 Function<T,R>,Consumer<T>,Runnable 三者区别,根据场景选择使用。 |
2.AND 汇聚关系
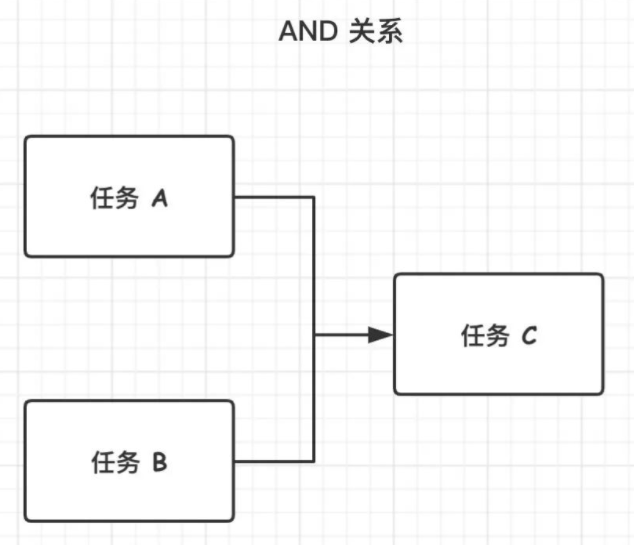
如上所示,只有任务 A 与任务 B 都完成之后,任务 C 才会开始执行。
CompletionStage 有以下接口描述这种关系。
// 同步
CompletableFuture<V> thenCombine(CompletionStage<U> other, BiFunction<T,U,V> fn)
CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBoth(CompletionStage<U> other, BiConsumer<T,U> action)
CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBoth(CompletionStage<U> other, Runnable action)
// 异步
CompletableFuture<V> thenCombineAsync(CompletionStage<U> other, BiFunction<T,U,V> fn)
CompletableFuture<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(CompletionStage<U> other, BiConsumer<T,U> action)
CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterBothAsync(CompletionStage<U> other, Runnable action)
// 多组任务
static CompletableFuture<Void> allOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)thenCombine 方法核心参数 BiFunction ,作用与 Function一样,只不过 BiFunction 可以接受两个参数,而 Function 只能接受一个参数。
thenAcceptBoth 方法核心参数BiConsumer 作用也与 Consumer一样,不过其需要接受两个参数。
runAfterBoth 方法核心参数最简单,上面已经介绍过,不再介绍。
这三组方法只能完成两个任务 AND 汇聚关系,如果需要完成多个任务汇聚关系,需要使用 CompletableFuture#allOf,不过这里需要注意,这个方法是不支持返回任务结果。
AND 汇聚关系相关示例代码,开头已经使用过了,这里再粘贴一下,方便大家理解:
// 任务1.订购航班
CompletableFuture<String> orderAirplane = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询航班");
sleep(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("订购航班");
return "航班信息";
});
// 任务2.订购酒店
CompletableFuture<String> orderHotel = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println("查询酒店");
sleep(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
System.out.println("订购酒店");
return "酒店信息";
});
// 任务3.任务1和任务2都完成,才能去订购租车服务
CompletableFuture<String> hireCar = orderHotel.thenCombine(orderAirplane, (airplane, hotel) -> {
System.out.println("根据航班和酒店订购租车服务");
sleep(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return "租车信息";
});
// 等待任务3执行结果
System.out.println(hireCar.join());
// 执行结果
查询航班
查询酒店
订购航班
订购酒店
根据航班和酒店订购租车服务
租车信息3.OR 汇聚关系
有 AND 汇聚关系,当然也存在 OR 汇聚关系。OR 汇聚关系代表只要多个任务中任一任务完成,就可以接着接着执行下一任务。
CompletionStage 有以下接口描述这种关系:
// 同步
CompletableFuture<V> applyToEither(CompletionStage<U> other, Function<T,U> fn)
CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEither(CompletionStage<U> other, Consumer<T> action)
CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEither(CompletionStage<U> other, Runnable action)
// 异步
CompletableFuture<V> applyToEitherAsync(CompletionStage<U> other, Function<T,U> fn)
CompletableFuture<Void> acceptEitherAsync(CompletionStage<U> other, Consumer<T> action)
CompletableFuture<Void> runAfterEitherAsync(CompletionStage<U> other, Runnable action)
// 多组任务
static CompletableFuture<Void> anyOf(CompletableFuture<?>... cfs)前面三组接口方法传参与 AND 汇聚关系一致,这里也不再详细解释了。
当然 OR 汇聚关系可以使用 CompletableFuture#anyOf 执行多个任务。
下面示例代码展示如何使用 applyToEither 完成 OR 关系。
CompletableFuture<String> cf
= CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
sleep(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return "hello,楼下小哥";
});// 1
CompletableFuture<String> cf2 = cf.supplyAsync(() -> {
sleep(3, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
return "hello,程序通事";
});
// 执行 OR 关系
CompletableFuture<String> cf3 = cf2.applyToEither(cf, s -> s);
// 输出结果,由于 cf2 只休眠 3 秒,优先执行完毕
System.out.println(cf2.join());
// 结果:hello,程序通事
4.异常处理
CompletableFuture 方法执行过程若产生异常,当调用 get,join获取任务结果才会抛出异常。
CompletableFuture<Integer> cf =
CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> (66/0))
.thenApply(r -> r*10);
System.out.println(cf.join());
// java.util.concurrent.CompletionException:java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero上面代码我们显示使用 try..catch 处理上面的异常。不过这种方式不太优雅,CompletionStage 提供几个方法,可以优雅处理异常。
// 同步
CompletableFuture<T> exceptionally(Function<Throwable, ? extends T> fn)
CompletableFuture<T> whenComplete(BiConsumer<T, ? super Throwable> action)
CompletableFuture<T> handle(BiFunction<T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn)
// 异步
CompletableFuture<T> whenCompleteAsync(BiConsumer<T, ? super Throwable> action)
CompletableFuture<T> handleAsync(BiFunction<T, Throwable, ? extends U> fn)exceptionally 使用方式类似于 try..catch 中 catch代码块中异常处理。
whenComplete 与 handle 方法就类似于 try..catch..finanlly 中 finally 代码块。无论是否发生异常,都将会执行的。这两个方法区别在于 handle 支持返回结果。
下面示例代码展示 handle 用法:
CompletableFuture<Integer>f0 = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> (7 / 0))
.thenApply(r -> r * 10)
.handle((integer, throwable) -> {
// 如果异常存在,打印异常,并且返回默认值
if (throwable != null) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
return 0;
} else {
// 如果
return integer;
}
});
System.out.println(f0.join());
/**
*java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero
* .....
*
* 0
*/最后
以上就是单身钢铁侠最近收集整理的关于CompletableFuture详解~CompletionStage的全部内容,更多相关CompletableFuture详解~CompletionStage内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复