关于如何用Docker搭建Elasticsearch集群环境可以参考前一篇:Elasticsearch实践(一)用Docker搭建Elasticsearch集群。本文主要介绍,如果在Springboot体系中集成Elasticsearch服务。本文基于:Elasticsearch版本是2.2.4,Springboot版本是1.5.3.RELEASE,spring-data-elasticsearch:2.1.3.RELEASE。
Elasticsearch官方API
Elasticsearch提供了多种api。可以直接使用官方提供的Java API进行使用。ElasticSearc Java API。如果是使用Spring框架的项目,还可以用spring-data-elasticsearch的api。基于spring可以使用Annotation,索引文档不需要任何xml式的配置。而且使用上非常简便。其存储、查询接口继承了JpaRepository,所以对于引入JPA的项目来说,上手非常快。
Elasticsearch也提供了http协议的API,资源API风格是restful的,所以也都比较好记忆。在有需要的场景时查官网是最快的。
Springboot项目中使用spring-data-elasticsearch框架集成
Springboot项目集成elasticsearch,可以使用spring-data-elasticsearch。官方链接:
spring-data-elasticsearch Doc 熟悉JPA以及使用过Spring-data-common项目的开发者,应该很快会上手spring-data-elasticsearch。首先要做的就是在gradle项目中,引入‘org.springframework.data:spring-data-elasticsearch:2.1.3.RELEASE’以及‘org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch:your_springboot_version’ 。在我们对于索引数据的crud操作api中,主要用的是ElasticsearchRepository 接口,其继承与spring-data的基础repository包的接口CrudRepository。先看一下接口的主要方法:
@NoRepositoryBean
public interface CrudRepository<T, ID extends Serializable> extends Repository<T, ID> {
/**
* Saves a given entity. Use the returned instance for further operations as the save operation might have changed the
* entity instance completely.
*
* @param entity
* @return the saved entity
*/
<S extends T> S save(S entity);
/**
* Saves all given entities.
*
* @param entities
* @return the saved entities
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given entity is {@literal null}.
*/
<S extends T> Iterable<S> save(Iterable<S> entities);
/**
* Retrieves an entity by its id.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @return the entity with the given id or {@literal null} if none found
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code id} is {@literal null}
*/
T findOne(ID id);
/**
* Returns whether an entity with the given id exists.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @return true if an entity with the given id exists, {@literal false} otherwise
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if {@code id} is {@literal null}
*/
boolean exists(ID id);
/**
* Returns all instances of the type.
*
* @return all entities
*/
Iterable<T> findAll();
/**
* Returns all instances of the type with the given IDs.
*
* @param ids
* @return
*/
Iterable<T> findAll(Iterable<ID> ids);
/**
* Returns the number of entities available.
*
* @return the number of entities
*/
long count();
/**
* Deletes the entity with the given id.
*
* @param id must not be {@literal null}.
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given {@code id} is {@literal null}
*/
void delete(ID id);
/**
* Deletes a given entity.
*
* @param entity
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given entity is {@literal null}.
*/
void delete(T entity);
/**
* Deletes the given entities.
*
* @param entities
* @throws IllegalArgumentException in case the given {@link Iterable} is {@literal null}.
*/
void delete(Iterable<? extends T> entities);
/**
* Deletes all entities managed by the repository.
*/
void deleteAll();
...
}
其对于Elasticsearch的文档(@Document)的数据的操作就类似于JPA中对于数据库表(@Entity)的接口。可以用findByXX的方式进行查询,也可以自定义@Query()方式进行查询。在开发的过程中,对于一些特殊的查询场景,可以查询spring-data-elasticsearch源码中的示例,基本包含了各种场景的API,项目git:spring-data-elasticsearch Git
使用spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch做启动时搜索服务的配置
使用Springboot,可以在启动时对很多服务Bean进行注入。一下是通过Autowire方式,使用spring-boot-starter-data-elasticsearch:2.1.3.RELEASE来处理基于Springboot的微服务启动时连接Elasticsearch集群,以及注入应用代码需要使用的 ElasticsearchTemplate。Configuration类如下:
import org.apache.commons.lang3.StringUtils;
import org.elasticsearch.client.transport.TransportClient;
import org.elasticsearch.common.settings.Settings;
import org.elasticsearch.common.transport.InetSocketTransportAddress;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.core.ElasticsearchTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.elasticsearch.repository.config.EnableElasticsearchRepositories;
import java.net.InetAddress;
/**
* 使用的是es 2.4.4 版本,因为springboot 1.5.x,以及目前版本最多支持到es 2.x。
* <p>
* Created by lijingyao on 2017/5/17 16:32.
*/
@Configuration
@EnableElasticsearchRepositories(basePackages = "com.puregold.ms")
public class SearchConfig {
// 假设使用三个node,(一主两备)的配置。在实际的生产环境,需在properties文件中替换成实际ip(内网或者外网ip)
@Value("${elasticsearch.host1}")
private String esHost;// master node
@Value("${elasticsearch.host2:}")
private String esHost2;//replica node
@Value("${elasticsearch.host3:}")
private String esHost3;//replica node
@Value("${elasticsearch.port}")
private int esPort;
@Value("${elasticsearch.clustername}")
private String esClusterName;
@Bean
public TransportClient transportClient() throws Exception {
Settings settings = Settings.settingsBuilder()
.put("cluster.name", esClusterName)
.build();
TransportClient transportClient = TransportClient.builder()
.settings(settings)
.build()
.addTransportAddress(new InetSocketTransportAddress(InetAddress.getByName(esHost), esPort));
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(esHost2)) {
transportClient.addTransportAddress(new InetSocketTransportAddress(InetAddress.getByName(esHost2), esPort));
}
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(esHost3)) {
transportClient.addTransportAddress(new InetSocketTransportAddress(InetAddress.getByName(esHost3), esPort));
}
return transportClient;
}
@Bean
public ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate() throws Exception {
return new ElasticsearchTemplate(transportClient());
}
}
使用spring-data-elasticsearch基于注解的示例API
创建索引和文档,同JPA的 @Entity,@Table,可以通过在搜索的文档实体类添加@Document注解的方式,在启动Springboot应用时会直接创建以及更新Elasticsearch的index以及document。
下面创建一个示例。示例中包含两个Document,一个是OrderDocument,一个是DetailOrderDocument。示例中OrderDocument和DetailOrderDocument是parent-child关联,可以参考官方对于p-c的描述:indexing-parent-child。Elasticsearch支持多种对于文档模型的关联。在建立parent child关系的时候需要注意:child 需要根据parant的id进行路由,parantid 和child的parantid 必须是string。否则回在启动时报错:
nested exception is java.lang.IllegalArgumentException: Parent ID property should be String OrderDocument
@Document(indexName = OrderDocument.INDEX, type = OrderDocument.ORDER_TYPE, refreshInterval = "-1")
public class OrderDocument {
public static final String INDEX = "orders-test";
public static final String ORDER_TYPE = "order-document";
public static final String DETAIL_TYPE = "order-detail-document";
@Id
private String id;
// 订单备注,不需要分词,可以搜索
@Field(type = FieldType.String, index = FieldIndex.not_analyzed)
private String note;
// 订单名称,可以通过ik 分词器进行分词
@Field(type = FieldType.String, searchAnalyzer = "ik", analyzer = "ik")
private String name;
// 订单价格
@Field(type = FieldType.Long)
private Long price;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getNote() {
return note;
}
public void setNote(String note) {
this.note = note;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Long getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Long price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
DetailOrderDocument
@Document(indexName = OrderDocument.INDEX, type = OrderDocument.DETAIL_TYPE, shards = 10, replicas = 2, refreshInterval = "-1")
public class DetailOrderDocument {
@Id
private String id;
// 指定主订单关联的父子关系
@Field(type = FieldType.String, store = true)
@Parent(type = OrderDocument.ORDER_TYPE)
private String parentId;
// 子订单价格
@Field(type = FieldType.Long)
private Long price;
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getParentId() {
return parentId;
}
public void setParentId(String parentId) {
this.parentId = parentId;
}
public Long getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(Long price) {
this.price = price;
}
}
以上就在 “orders-test” 索引中创建了两个Document。@Id注解对应着Elasticsearch的id。可以系统自动生成,也可以创建文档数据时指定固定的id,但是一定要保证唯一性。
启动好之后可以通过curl xget来查询索引的结构。结果如下:
{
"orders-test" : {
"aliases" : { },
"mappings" : {
"order-detail-document" : {
"_parent" : {
"type" : "order-document" },
"_routing" : {
"required" : true },
"properties" : {
"parentId" : { "type" : "string", "store" : true },
"price" : { "type" : "long" } }
},
"order-document" : {
"properties" : {
"name" : { "type" : "string", "analyzer" : "ik" },
"note" : { "type" : "string", "index" : "not_analyzed" },
"price" : { "type" : "long" } }
}
},
"settings" : {
"index" : {
"refresh_interval" : "-1",
"number_of_shards" : "10",
"creation_date" : "1511403448676",
"store" : {
"type" : "fs" },
"number_of_replicas" : "2",
"uuid" : "sHA5s7kEQA2AWCAA8-aBlQ",
"version" : {
"created" : "2040499" }
}
},
"warmers" : { }
}
}
另,刚才代码中,通过设置@Document的参数 number_of_shards,number_of_replicas。可以看到创建文档的settings参数:”number_of_shards” : “10”, “number_of_replicas” : “2”。如果不指定参数,则默认分别是 number_of_shards=5,number_of_replicas=1。其他默认参数可以查看public @interface Document源码。
有特殊字符的自生成的id
用findOne 时会报错,可以用findById 来代替,用query terms精确查找是可以的
{
"error" : {
"root_cause" : [ {
"type" : "routing_missing_exception",
"reason" : "routing is required for [XX]/[YY]/[yourid]",
"index" : "forests"
} ],
"type" : "routing_missing_exception",
"reason" : "routing is required for [XX]/[YY]/[yourid]",
"index" : "forests"
},
"status" : 400
}Repositories&ElasticsearchTemplate
文档创建好之后,对于文档数据的索引可以继承spring-data-elasticsearch的ElasticsearchRepository。使用CurdRepository接口规范来完成基础的查询,存储,更新操作。如下简单举例了两个查询语句。
public interface DetailOrderDocumentRepository extends ElasticsearchRepository<DetailOrderDocument, String> {
List<DetailOrderDocument> findByParentId(String parentId, Sort sort);
DetailOrderDocument findById(String id);
}
如果是比较复杂的查询场景,可以在Repository接口写@Query语句。也可以使用ElasticsearchTemplate来写更灵活的定制化查询:
@Component
public class OrderManager {
@Autowired
private ElasticsearchTemplate elasticsearchTemplate;
public Page<OrderDocument> queryPagedOrders(Integer pageNo, Integer pageSize, String name, Long minPrice, Long maxPrice) {
// 默认,价格升序(为了支持丰富的排序场景,建议将所有可能的排序规则放到统一的enum中
Pageable pageable = new PageRequest(pageNo, pageSize, new Sort(new Sort.Order(Sort.Direction.ASC, "price")));
NativeSearchQueryBuilder nbq = new NativeSearchQueryBuilder().withIndices(OrderDocument.INDEX).withTypes(OrderDocument
.ORDER_TYPE).withSearchType(SearchType.DEFAULT).withPageable(pageable);
BoolQueryBuilder bqb = boolQuery();
// 匹配订单name
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(name)) {
bqb.must(termQuery("name", name));
}
// 查询价格区间 minPrice<=price<=maxPrice
if (minPrice != null && minPrice >= 0) {
bqb.filter(rangeQuery("price").gte(minPrice));
}
if (maxPrice != null && maxPrice >= 0) {
bqb.filter(rangeQuery("price").lte(maxPrice));
}
Page<OrderDocument> page = elasticsearchTemplate.queryForPage(nbq.withQuery(bqb).build(), OrderDocument.class);
return page;
}
}
其他注意事项
- 如果需要删除parent child映射的索引
一般的索引都可以直接使用:
curl -XDELETE 'http://yourip:9200/orders-test/?pretty'但parant-child 关系mapping的时候,删除之后,如果想重建索引,在启动springboot的时候会出现异常:
can’t add a _parent field that points to an already existing type, that isn’t already a parent 解决方案是在@Document 属性中设置 createIndex = false(默认是true) ,只在parent document上设置就可以了.这样就可以自由删除index,启动时重建索引。
- 更新文档的分词
官方对于更新映射的说法:mapping-intro
也就是Elasticsearch不支持直接更新mapping字段的索引方式(不能把一个analyzed字段设置成not_analyzed)。 可以支持添加新的映射字段并且制定分词方式(如 ik),或者只能删除index,重建索引 。
如我们示例代码的:
@Field(type = FieldType.String, searchAnalyzer = "ik", analyzer = "ik")
private String name;一旦索引创建完成,无法再变更name字段为not_analyzed。所以在一开始设计索引文档时需要谨慎判断。
- 分页,数据查询多的场景
对于数据量很大的文档的索引查询,会出现以下报错:
Failed to execute phase [query], all shards failed; shardFailures {[X-XXXXX][YYYY][0]: RemoteTransportException[[your-node][yourip:9300][indices:data/read/search[phase/query]]]; nested:
QueryPhaseExecutionException[Result window is too large, from + size must be less than or equal to: [10000] but was [99020].
See the scroll api for a more efficient way to request large data sets. This limit can be set by changing the [index.max_result_window] index level parameter.]; }{[X-XXXXX][YYYY][1]: RemoteTransportException[[可以通过以下命令修改索引index_name。这个是index级别的设置,但是不建议更改设置,会增加ES node的内存负担。
curl -XPUT "http://your_cluster:9200/index_name/_settings" -d '{ "index" : { "max_result_window" : 500000 } }' 虽然可以解决索引数据量大的问题,但是接口的性能会有问题:基本上平均返回时间会+200-300ms。推荐用scroll api:
Elasticsearch在处理大结果集时可以使用scan和scroll。在Spring Data Elasticsearch中,可以向下面那样使用ElasticsearchTemplate来使用scan和scroll处理大结果集。可以参考:关于scroll 。
search api返回一个单一的结果“页”,而 scroll API 可以被用来检索大量的结果(甚至所有的结果),就像在传统数据库中使用的游标 cursor。
使用示例如下:
String scrollId = elasticsearchTemplate.scan(nbq.withQuery(bqb).build(), 1000, false); Page<OrderDocument> page = elasticsearchTemplate.scroll(scrollId, 2000L, OrderDocument.class);- 查看节点所有配置信息
http://your_cluster:9200/_nodes?pretty
结果中还可以看到所有可用插件列表。可以用来检验分词插件等是否安装成功。
查看mapping信息:
http://your_cluster:9200/index_name/_mapping/document_name?pretty
- 删除child文档索引值,并且添加其他的索引值:
可以查看官方文档Indexing parent and child。通过curl删除,查询时都需要指定parentId,因为前面已经介绍过了,child文档是通过parentId进行路由的.如下需要添加routing。
curl -XDELETE 'http://your_cluster:9200/orders-test/order-detail-document/_query?routing=parent_order_id&pretty' -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d'
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{ "term" :
{ "id" : "detail_order_id" }
}
]
}
}
}
'查询时也一样:
http://your_cluster:9200/orders-test/order-detail-document/_search?&_routing= parent_order_id&q=id:detail_order_id&pretty同理,新增的时候也需要指定routing。
相关文档
Elasticsearch相关的文档比较少,实施过程中遇到一些问题基本都是要边对照官方文档和源码来解决的。对于Elasticsearch或者其他搜索框架有问题的希望能一起探讨。公司目前在招聘高级Java工程师,架构师,我们有技术,有激情,有美女,有美食。有兴趣的同学欢迎投递,或者直接联系作者沟通。Java高级开发工程师-招聘
ElasticSearc-V5.4 Java API
Java client api
数据建模
映射-索引类型
First Step with Spring Boot and Elasticsearch
spring-data-elasticsearch Doc
spring-data-elasticsearch Git
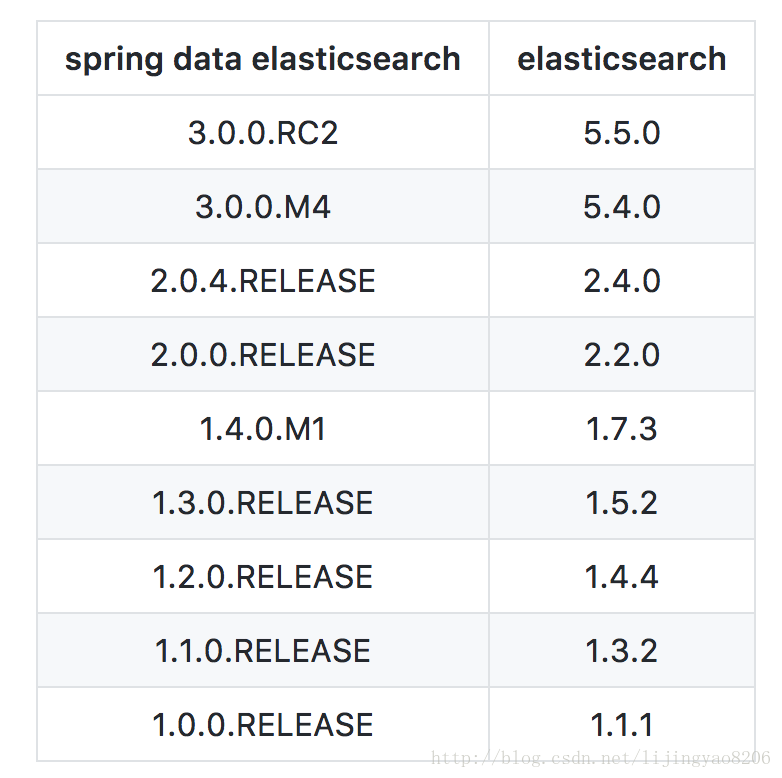
更新
最新的SpringDataElasticsearch 可以支持到了5.x版本。目前还是rc版,在Realease版本出来之后,服务会进行一次升级,届时会更新一个升级文章。目前对应版本信息如下:
最后
以上就是老实悟空最近收集整理的关于Elasticsearch实践(二)在Springboot微服务中集成搜索服务的全部内容,更多相关Elasticsearch实践(二)在Springboot微服务中集成搜索服务内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复