接上一篇博客,继续解决完全背包问题。
问题描述:给定n种物品和一个背包。物品i的重量是wi,其价值为vi,背包的容量为C。应该如何选择装入背包中的物品,使得装入背包中物品的总价值最大?每种物品有无限个。
利用上一篇博客的子功能,我们可以获得所有的使背包饱和(即无法再装入任何一个物品)的方案,求取所有方案的背包价值,找出最大价值及其对应的拿取方案即可。
上代码:
//给定n种物品和一个背包。物品i的重量是wi,其价值为vi,背包的容量为C。应该如何选择装入背包中的物品,使得装入背包中物品的总价值最大?每种物品有无限个
//利用完全背包填满问题的递归函数,遍历得到所有使背包饱和的结果,求取每个方案的价值,查找最大值并输出最佳拿取方案
#include "pch.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <math.h>
using namespace std;
//打印拿取方案
void PrintVector(vector<int> take_or_not)
{
cout << "【最佳拿取方案】" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < take_or_not.size(); i++)
{
cout << "拿取" << "第" << i << "个物品:" << take_or_not[i] << " 个" << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
//给出拿取情况向量与重量列表向量,求解当前背包重量,也可以用于求解价值
int CalculateWeight(vector<int> taken_items, vector<int> weights)
{
int weight = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < taken_items.size(); i++)
weight = weight + taken_items[i] * weights[i];
return weight;
}
//判断剩余空间能否放下从i开始的某个物品,一个都放不了则返回False
bool TakeMore(vector<int> weights, int left_capacity, int i)
{
for (; i < weights.size(); i++)
{
if (weights[i] <= left_capacity)
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*递归解决该问题*/
//给出背包(剩余)容量,物品重量列表,拿取方案列表,要拿取的物品位置i
//主函数调用时先初始化take_or_not与i为0
//该问题中,solutions用于存储所有使背包饱和的拿取方案
void Recursion(int capacity, vector<int> weights, vector<int>& take_or_not, int i, vector<vector<int>>& solutions)
{
int left_capacity = capacity - CalculateWeight(take_or_not, weights);
//如果已经到最后一个物品,则直接用最后一个物品装满背包,进行操作,并返回
if (i == (take_or_not.size() - 1))
{
take_or_not[i] = left_capacity / weights[i];
//更新left_capacity
left_capacity = capacity - CalculateWeight(take_or_not, weights);
if (take_or_not[i] >= 0)
{
//判断当前拿取方案是否饱和,如果每个物品都放不下了再进行操作
if (!TakeMore(weights, left_capacity, 0))
{
//operation,存储当前拿取方案
solutions.push_back(take_or_not);
}
}
//返回前将最后一个物品清空
take_or_not[i] = 0;
return;
}
//定义flag,用于判断是否执行了for循环
bool flag = false;
//第i个物品数量从0开始递增,直到装满背包为止,每加1就对i+1进行递归
for (int o = 0; weights[i] <= left_capacity; o++)
{
take_or_not[i] = o;
//更新left_capacity
left_capacity = capacity - CalculateWeight(take_or_not, weights);
Recursion(capacity, weights, take_or_not, i + 1, solutions);
flag = true;
}
//如果当前i不是最后一个物品,且未执行for循环,则继续递归
if (i != take_or_not.size() - 1 && !flag)
Recursion(capacity, weights, take_or_not, i + 1, solutions);
//当前物品遍历结束后,该物品数量清零并返回
take_or_not[i] = 0;
return;
}
//在solution中查找并输出背包价值最大值及最佳拿取方案
void Backpack(vector<vector<int>> solutions, vector<int> values)
{
//定义最大价值,初始化为0
int max_value = 0;
//第一次遍历,求得最大值,并输出
for (auto solution : solutions)
{
int current_value = CalculateWeight(solution, values);
max_value = max_value > current_value ? max_value : current_value;
}
cout << "【背包最大价值】" << endl << max_value << endl;
//第二次遍历,求得最佳拿取方案,并输出
for (auto solution : solutions)
{
int current_value = CalculateWeight(solution, values);
if (current_value == max_value)
PrintVector(solution);
}
}
int main()
{
//初始化
int capacity;
vector<int> weights;
vector<int> values;
int number;
cout << "输入背包容量及物品件数:" << endl;
cin >> capacity >> number;
cout << "输入这" << number << "个物品的重量" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++)
{
int weight;
cin >> weight;
weights.push_back(weight);
}
cout << "输入这" << number << "个物品的价值" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < number; i++)
{
int value;
cin >> value;
values.push_back(value);
}
//定义拿取方案,用于递归
vector<int> take_or_not(number, 0);
//定义递归操作符
int i = 0;
//定义solutions,用于存储所有使背包饱和的拿取方案
vector<vector<int>> solutions;
//递归获取所有solution
Recursion(capacity, weights, take_or_not, i, solutions);
//在solution中查找并输出背包价值最大值及最佳拿取方案
Backpack(solutions, values);
return 0;
}
/*
输入:
10 3
2 5 8
1 4 7
*/
示例运行结果:
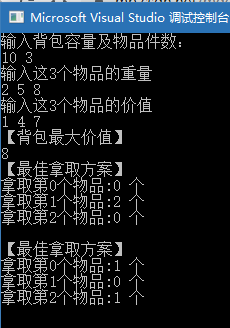
最后
以上就是沉静宝马最近收集整理的关于【c++回顾】3.1经典算法问题-完全背包问题2--背包价值最大问题的全部内容,更多相关【c++回顾】3内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。
![[区间DP] 凸边形三角剖分(子问题的表达)](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg7.png)




![[动态规划]装满背包的方法(数量不限)](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg12.png)


发表评论 取消回复