(给ImportNew加星标,提高Java技能)
编译:ImportNew/唐尤华
dzone.com/articles/http2-server-push-via-http-client-api

还记得 HttpUrlConnection 吗?JDK 11已经重新了设计这个 API,改为 HTTP Client API
对 HttpUrlConnection 你还有印象吗?JDK 11为 HttpUrlConnection 重新设计了 HTTP Client API。HTTP Client API 使用简单,支持 HTTP/2(默认)和 HTTP/1.1。为了向后兼容,当服务器不支持 HTTP/2时,HTTP Client API 会自动从 HTTP/2 降到 HTTP1.1。
此外,HTTP Client API 支持同步和异步编程模型,并依靠 stream 传输数据(reactive stream)。它还支持 WebSocket 协议,用于实时 Web 应用程序,降低客户端与服务器间通信开销。
除了多路复用(Multiplexing),HTTP/2 另一个强大的功能是服务器推送。传统方法(HTTP/1.1)中,主要通过浏览器发起请求 HTML 页面,解析接收的标记(Markup)并标识引用的资源(例如JS、CSS、图像等)。
为了获取资源,浏览器会继续发送资源请求(每个资源一个请求)。相反,HTTP/2 会发送 HTML 页面和引用的资源,不需要浏览器主动请求。因此,浏览器请求 HTML 页面后,就能收到页面以及显示所需的所有其他信息。HTTP Client API 通过 PushPromiseHandler 接口支持 HTTP/2 功能。
接口实现必须作为 send() 或 sendAsync() 方法的第三个参数填入。PushPromiseHandler 依赖下面三项协同:
客户端发起的 send request(initiatingRequest)
合成 push request(pushPromiseRequest)
acceptor 函数,必须成功调用该函数才能接受 push promise(acceptor)
调用特定 acceptor 函数接受 push promise。acceptor 函数必须传入一个 BodyHandler(不能为 null)用来处理 Promise 的 request body。acceptor 函数会返回一个 CompletableFuture 实例,完成 promise response。
基于以上信息,看一下 PushPromiseHandler 实现:
private static final List>
asyncPushRequests = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>();
...private static HttpResponse.PushPromiseHandler pushPromiseHandler() {return (HttpRequest initiatingRequest,
HttpRequest pushPromiseRequest,
Function ,
CompletableFuture>> acceptor) -> {
CompletableFuture pushcf =
acceptor.apply(HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString())
.thenApply(HttpResponse::body)
.thenAccept((b) -> System.out.println("nPushed resource body:n " + b));
asyncPushRequests.add(pushcf);
System.out.println("nJust got promise push number: " +
asyncPushRequests.size());
System.out.println("nInitial push request: " +
initiatingRequest.uri());
System.out.println("Initial push headers: " +
initiatingRequest.headers());
System.out.println("Promise push request: " +
pushPromiseRequest.uri());
System.out.println("Promise push headers: " +
pushPromiseRequest.headers());
};
}现在,触发一个 request 把 PushPromiseHandler 传给 sendAsync():
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://http2.golang.org/serverpush"))
.build();
client.sendAsync(request,
HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString(), pushPromiseHandler())
.thenApply(HttpResponse::body)
.thenAccept((b) -> System.out.println("nMain resource:n" + b))
.join();
asyncPushRequests.forEach(CompletableFuture::join);
System.out.println("nFetched a total of " +
asyncPushRequests.size() + " push requests");完整源代码可在 GitHub 上找到。
github.com/PacktPublishing/Java-Coding-Problems/tree/master/Chapter13/P268_ServerPush
如果要把所有 push promise 及 response 汇总到指定的 map 中,可以使用 PushPromiseHandler.of() 方法,如下所示:
private static final ConcurrentMap CompletableFuture>> promisesMap
= new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private static final Function HttpResponse.BodyHandler> promiseHandler
= (HttpRequest req) -> HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString();public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://http2.golang.org/serverpush"))
.build();
client.sendAsync(request,
HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofString(), pushPromiseHandler())
.thenApply(HttpResponse::body)
.thenAccept((b) -> System.out.println("nMain resource:n" + b))
.join();
System.out.println("nPush promises map size: " +
promisesMap.size() + "n");
promisesMap.entrySet().forEach((entry) -> {
System.out.println("Request = " + entry.getKey() +", nResponse = " + entry.getValue().join().body());
});
}private static HttpResponse.PushPromiseHandler pushPromiseHandler() {return HttpResponse.PushPromiseHandler.of(promiseHandler, promisesMap);
}完整源代码可在 GitHub 上找到。
github.com/PacktPublishing/Java-Coding-Problems/tree/master/Chapter13/P268_ServerPushToMap
前面两个解决方案中 BodyHandler 都用到了 String 类型的 ofString()。如果服务器还需要推送二进制数据(比如图像),就不是很适用。因此,如果要处理二进制数据,则需要用 ofByteArray() 切换到byte[] 类型的 BodyHandler。也可以用 ofFile() 把 push 资源保存到磁盘,下面的解决方案是之前方案的改进版:
private static final ConcurrentMap CompletableFuture>>
promisesMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();private static final Function HttpResponse.BodyHandler> promiseHandler
= (HttpRequest req) -> HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofFile(
Paths.get(req.uri().getPath()).getFileName());public static void main(String[] args)
throws IOException, InterruptedException {
HttpClient client = HttpClient.newHttpClient();
HttpRequest request = HttpRequest.newBuilder()
.uri(URI.create("https://http2.golang.org/serverpush"))
.build();
client.sendAsync(request, HttpResponse.BodyHandlers.ofFile(
Path.of("index.html")), pushPromiseHandler())
.thenApply(HttpResponse::body)
.thenAccept((b) -> System.out.println("nMain resource:n" + b))
.join();
System.out.println("nPush promises map size: " +
promisesMap.size() + "n");
promisesMap.entrySet().forEach((entry) -> {
System.out.println("Request = " + entry.getKey() +", nResponse = " + entry.getValue().join().body());
});
}private static HttpResponse.PushPromiseHandler pushPromiseHandler() {return HttpResponse.PushPromiseHandler.of(promiseHandler, promisesMap);
}上面的代码把 push 资源保存到应用程序 classpath 中,正如下面截屏看到的:
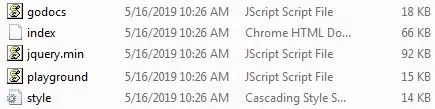
完整源代码可在 GitHub 上找到。
github.com/PacktPublishing/Java-Coding-Problems/tree/master/Chapter13/P268_ServerPushToDisk
推荐阅读
(点击标题可跳转阅读)
不要在 Docker 镜像中使用 Fat Jar
使用 Gateling 进行性能测试
用 JShell 快速实现代码原型
看完本文有收获?请转发分享给更多人
关注「ImportNew」,提升Java技能

好文章,我在看❤️
最后
以上就是冷傲大神最近收集整理的关于c语言实现http服务器_使用 Java 11 HTTP Client API 实现 HTTP/2 服务器推送的全部内容,更多相关c语言实现http服务器_使用内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复