kibana的基本介绍
Kibana是一个开源的分析和可视化平台,设计用于和Elasticsearch一起工作。
你用Kibana来搜索,查看,并和存储在Elasticsearch索引中的数据进行交互。
你可以轻松地执行高级数据分析,并且以各种图标、表格和地图的形式可视化数据。
Kibana使得理解大量数据变得很容易。它简单的、基于浏览器的界面使你能够快速创建和共享动态仪表板,实时显示Elasticsearch查询的变化。
接着使用我们的es用户在node01服务器上面来实现我们的kibana的安装部署
一 Kibana安装
第一步:下载资源上传服务器并解压
node01服务器使用es用户执行以下命令来下载安装包并解压
cd /home/es
在线下载
wget https://artifacts.elastic.co/downloads/kibana/kibana-6.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz
tar -zxf kibana-6.7.0-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /export/servers/es/
第二步:修改配置文件
node01服务器使用es用户执行以下命令来修改配置文件
cd /export/servers/es/kibana-6.7.0-linux-x86_64/config/
vi kibana.yml
配置内容如下:
server.host: "node01"
elasticsearch.hosts: ["http://node01:9200"]
第三步:启动服务
node01服务器使用es用户执行以下命令启动kibana服务
cd /export/servers/es/kibana-6.7.0-linux-x86_64
nohup bin/kibana >/dev/null 2>&1 &
如何停止kibana进程:停止kibana服务进程
查看进程号
ps -ef | grep node
然后使用kill -9杀死进程即可
第四步:浏览器访问
浏览器地址访问kibana服务
http://node01:5601
二 使用kibana管理索引
curl是利用URL语法在命令行方式下工作的开源文件传输工具,使用curl可以简单实现常见的get/post请求。简单的认为是可以在命令行下面访问url的一个工具。在centos的默认库里面是有curl工具的,如果没有请yum安装即可。
curl
-X 指定http的请求方法 有HEAD GET POST PUT DELETE
-d 指定要传输的数据
-H 指定http请求头信息
2.1、使用 Xput创建索引
1、创建索引
在我们的kibana的dev tools当中执行以下语句
curl -XPUT http://node01:9200/blog01/?pretty
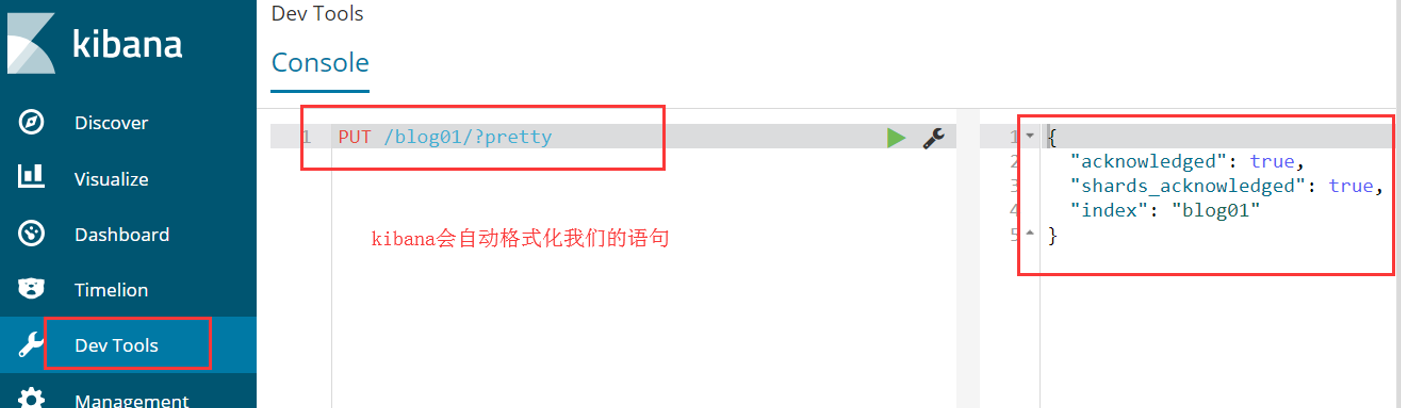
2、插入文档
前面的命令使用 PUT 动词将一个文档添加到 /article(文档类型),并为该文档分配 ID 为1。URL 路径显示为index/doctype/ID(索引/文档类型/ID)。
curl -XPUT http://node01:9200/blog01/article/1?pretty -d '{"id": "1", "title": "这是个测试,哈哈哈"}'
可能出现问题:
问题:Content-Type header [application/x-www-form-urlencoded] is not supported
解决:
curl -XPUT http://node01:9200/blog01/article/1?pretty -d '{"id": "1", "title": "这是个测试,哈哈哈"}' -H "Content-Type: application/json"
原因:
此原因时由于ES增加了安全机制, 进行严格的内容类型检查,严格检查内容类型也可以作为防止跨站点请求伪造攻击的一层保护。
官网解释:http.content_type.required
3、查询文档
curl -XGET http://node01:9200/blog01/article/1?pretty
可能出现的问题:
Content-Type header [application/x-www-form-urlencoded] is not supported
解决:
curl -XPUT http://node01:9200/blog01/article/1?pretty -d '{"id": "1", "title": "What is lucene"}' -H "Content-Type: application/json"
curl -XGET http://node01:9200/blog01/article/1?pretty -H "Content-Type: application/json"
4、更新文档
curl -XPUT http://node01:9200/blog01/article/1?pretty -d '{"id": "1", "title": " 这个是更新后的结果显示哈!"}'
可能的问题:
Content-Type header [application/x-www-form-urlencoded] is not supported
解决:
curl -XPUT http://node01:9200/blog01/article/1?pretty -d '{"id": "1", "title": " What is elasticsearch"}' -H "Content-Type: application/json"
5、搜索文档
curl -XGET "http://node01:9200/blog01/article/_search?q=title:结果"
注意:搜索时,如果title是中文,就会出现异常:
{
"statusCode": 500,
"error": "Internal Server Error",
"message": "An internal server error occurred"
}
可能出现问题:
Content-Type header [application/x-www-form-urlencoded] is not supported
解决:
curl -XGET "http://node01:9200/blog01/article/_search?q=title:'elasticsearch'&pretty" -H "Content-Type: application/json"
6、删除文档
curl -XDELETE "http://node01:9200/blog01/article/1?pretty"
7、删除索引
curl -XDELETE http://node01:9200/blog01?pretty
2.2、返回值说明
1、Hits
返回结果中最重要的部分是 hits ,它包含 total 字段来表示匹配到的文档总数,并且一个 hits 数组包含所查询结果的前十个文档。
在 hits 数组中每个结果包含文档的 _index 、 _type 、 _id ,加上 _source 字段。这意味着我们可以直接从返回的搜索结果中使用整个文档。这不像其他的搜索引擎,仅仅返回文档的ID,需要你单独去获取文档。
每个结果还有一个 _score ,它衡量了文档与查询的匹配程度。默认情况下,首先返回最相关的文档结果,就是说,返回的文档是按照 _score 降序排列的。在这个例子中,我们没有指定任何查询,故所有的文档具有相同的相关性,因此对所有的结果而言 1 是中性的 _score 。
max_score 值是与查询所匹配文档的 _score 的最大值。
2、took
took 值告诉我们执行整个搜索请求耗费了多少毫秒
3、Shard
_shards 部分 告诉我们在查询中参与分片的总数,以及这些分片成功了多少个失败了多少个。正常情况下我们不希望分片失败,但是分片失败是可能发生的。
如果我们遭遇到一种灾难级别的故障,在这个故障中丢失了相同分片的原始数据和副本,那么对这个分片将没有可用副本来对搜索请求作出响应。假若这样,Elasticsearch 将报告这个分片是失败的,但是会继续返回剩余分片的结果。
4、timeout
timed_out 值告诉我们查询是否超时。默认情况下,搜索请求不会超时。 如果低响应时间比完成结果更重要,你可以指定 timeout 为 10 或者 10ms(10毫秒),或者 1s(1秒):
GET /_search?timeout=10ms
在请求超时之前,Elasticsearch 将会返回已经成功从每个分片获取的结果。
2.3、花式查询
在kibana提供的界面上进行操作。
POST /school/student/_bulk
{ "index": { "_id": 1 }}
{ "name" : "liubei", "age" : 20 , "sex": "boy", "birth": "1996-01-02" , "about": "i like diaocan he girl" }
{ "index": { "_id": 2 }}
{ "name" : "guanyu", "age" : 21 , "sex": "boy", "birth": "1995-01-02" , "about": "i like diaocan" }
{ "index": { "_id": 3 }}
{ "name" : "zhangfei", "age" : 18 , "sex": "boy", "birth": "1998-01-02" , "about": "i like travel" }
{ "index": { "_id": 4 }}
{ "name" : "diaocan", "age" : 20 , "sex": "girl", "birth": "1996-01-02" , "about": "i like travel and sport" }
{ "index": { "_id": 5 }}
{ "name" : "panjinlian", "age" : 25 , "sex": "girl", "birth": "1991-01-02" , "about": "i like travel and wusong" }
{ "index": { "_id": 6 }}
{ "name" : "caocao", "age" : 30 , "sex": "boy", "birth": "1988-01-02" , "about": "i like xiaoqiao" }
{ "index": { "_id": 7 }}
{ "name" : "zhaoyun", "age" : 31 , "sex": "boy", "birth": "1997-01-02" , "about": "i like travel and music" }
{ "index": { "_id": 8 }}
{ "name" : "xiaoqiao", "age" : 18 , "sex": "girl", "birth": "1998-01-02" , "about": "i like caocao" }
{ "index": { "_id": 9 }}
{ "name" : "daqiao", "age" : 20 , "sex": "girl", "birth": "1996-01-02" , "about": "i like travel and history" }
1、使用match_all做查询
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
}
}
问题:通过match_all匹配后,会把所有的数据检索出来,但是往往真正的业务需求并非要找全部的数据,而是检索出自己想要的;并且对于es集群来说,直接检索全部的数据,很容易造成GC现象。所以,我们要学会如何进行高效的检索数据
2、通过关键字段进行查询
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"match": {"about": "travel"}
}
}
如果此时想查询喜欢旅游的,并且不能是男孩的,怎么办?
【这种方式是错误的,因为一个match下,不能出现多个字段值[match] query doesn’t support multiple fields】,需要使用复合查询
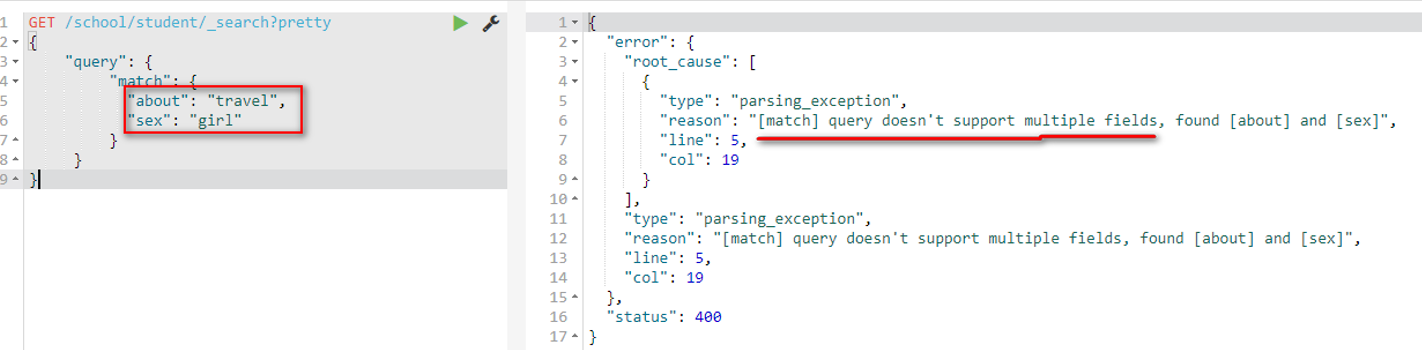
3、bool的复合查询
当出现多个查询语句组合的时候,可以用bool来包含。bool合并聚包含:must,must_not或者should, should表示or的意思
例子:查询非男性中喜欢旅行的人
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match": {"about": "travel"}},
"must_not": {"match": {"sex": "boy"}}
}
}
}
4、bool的复合查询中的should
should表示可有可无的(如果should匹配到了就展示,否则就不展示)
例子:
查询喜欢旅行的,如果有男性的则显示,否则不显示
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "match": {"about": "travel"}},
"should": {"match": {"sex": "boy"}}
}
}
}
5、term匹配
使用term进行精确匹配(比如数字,日期,布尔值或 not_analyzed的字符串(未经分析的文本数据类型))
语法
{ “term”: { “age”: 20 }}
{ “term”: { “date”: “2018-04-01” }}
{ “term”: { “sex”: “boy” }}
{ “term”: { “about”: “trivel” }}
例子:
查询喜欢旅行的
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "term": {"about": "travel"}},
"should": {"term": {"sex": "boy"}}
}}
}
6、使用terms匹配多个值
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": { "terms": {"about": ["travel","history"]}}
}
}
}
term主要是用于精确的过滤比如说:”我爱你”
在match下面匹配可以为包含:我、爱、你、我爱等等的解析器
在term语法下面就精准匹配到:”我爱你”
7、Range过滤
Range过滤允许我们按照指定的范围查找一些数据:操作范围:gt::大于,gae::大于等于,lt::小于,lte::小于等于
例子:
查找出大于20岁,小于等于25岁的学生
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"range": {
"age": {"gt":20,"lte":25}
}
}
}
8、exists和 missing过滤
exists和missing过滤可以找到文档中是否包含某个字段或者是没有某个字段
例子:
查找字段中包含age的文档
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"exists": {
"field": "age"
}
}
}
9、bool的多条件过滤
用bool也可以像之前match一样来过滤多行条件:
must :: 多个查询条件的完全匹配,相当于 and 。
must_not :: 多个查询条件的相反匹配,相当于 not 。
should :: 至少有一个查询条件匹配, 相当于 or
例子:
过滤出about字段包含travel并且年龄大于20岁小于30岁的同学
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"term": {
"about": {
"value": "travel"
}
}},{"range": {
"age": {
"gte": 20,
"lte": 30
}
}}
]
}
}
}
10、查询与过滤条件合并
通常复杂的查询语句,我们也要配合过滤语句来实现缓存,用filter语句就可以来实现
例子:
查询出喜欢旅行的,并且年龄是20岁的文档
GET /school/student/_search?pretty
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": {"match": {"about": "travel"}},
"filter": [{"term":{"age": 20}}]
}
}
}
2.4、索引映射(mappings)管理
1、为什么要映射
elasticsearch中的文档等价于java中的对象,那么在java对象中有字段(比如string、int、long等),同理在elasticsearch索引中的具体字段也是有类型的。
PUT /document/article/1
{
"title" : "elasticsearchshi是是什么",
"author" : "zhangsan",
"titleScore" : 60
}
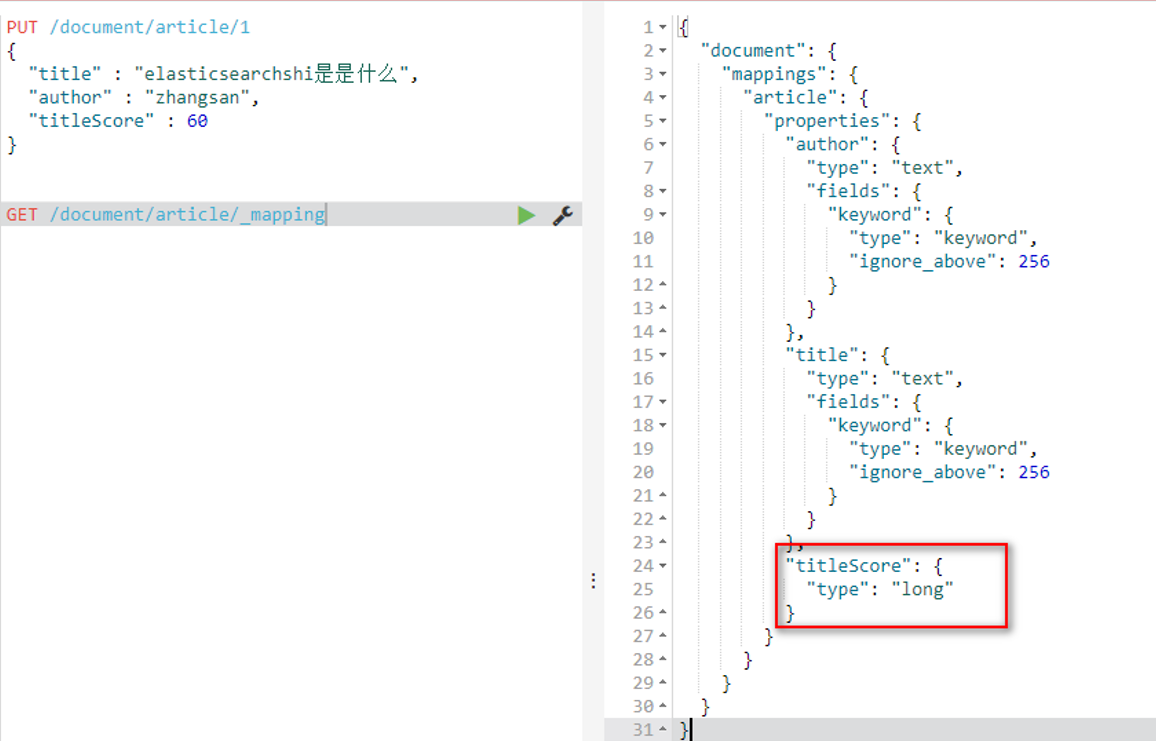
这种操作并没有指定字段类型,那么elasticsearch会自动根据数据类型的格式识别字段的类型;查看索引字段类型:
GET /document/article/_mapping
可以发现titleScore的类型是long。
然后在插入一条数据:
PUT /document/article/2
{
"title" : "elasticsearchshi是是什么",
"author" : "zhangsan",
"titleScore" : 66.666
}
查询数据:
GET /document/article/2
我们会发现es能存入,并没有报错(注意),这其实是一个问题,因为如果后期elaticsearch对接java的时候,我们会写一个类对数据做封装,比如:
class Article{
private String title;
private String author;
private String titleScore //《什么类型合适》?如果使用long类型,那么后面肯定会有数据格式转换的异常 doublelong
}
所以,我们如果能提前知道字段类型,那么最好使用mapping的映射管理,提前指定字段的类型,防止后续的程序问题;
DELETE document
PUT document
{
"mappings": {
"article" : {
"properties":
{
"title" : {"type": "text"} ,
"author" : {"type": "text"} ,
"titleScore" : {"type": "double"}
}
}
}
}
get document/article/_mapping
2、基本命令
DELETE school
PUT school
{
"mappings": {
"logs" : {
"properties": {"messages" : {"type": "text"}}
}
}
}
添加索引:school,文档类型类logs,索引字段为message ,字段的类型为text
GET /school/_mapping/logs
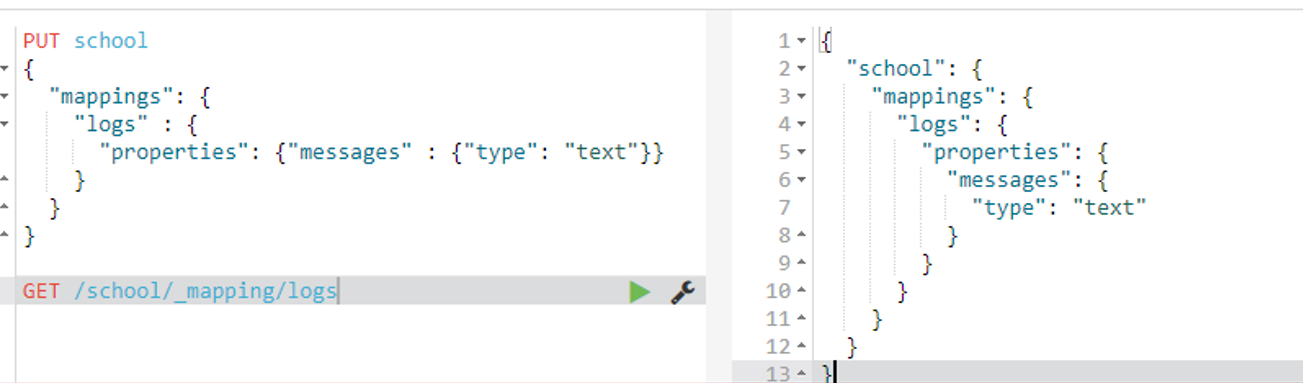
继续添加字段
POST /school/_mapping/logs
{
"properties": {"number" : {"type": "text"}}
}
GET /school/_mapping/logs
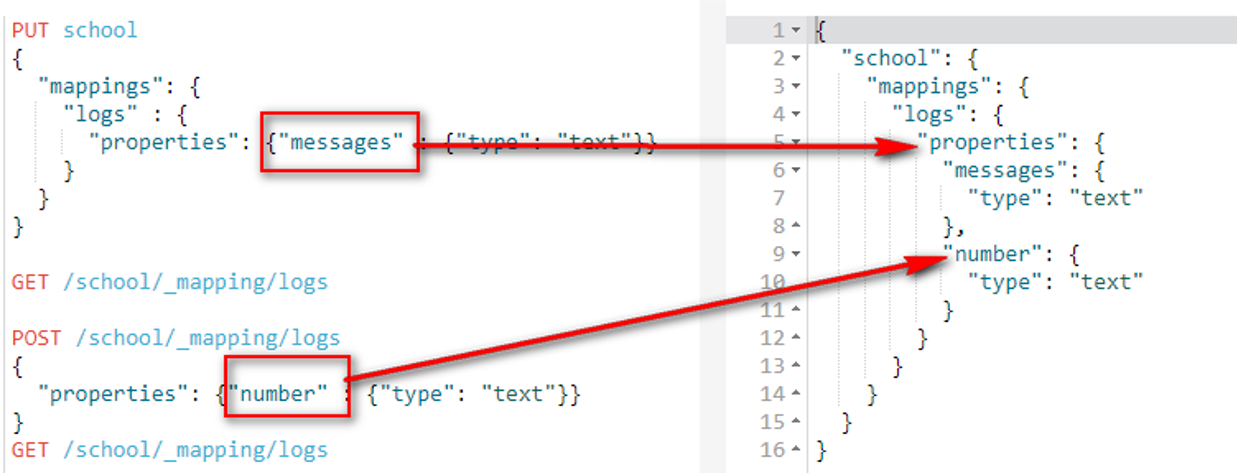
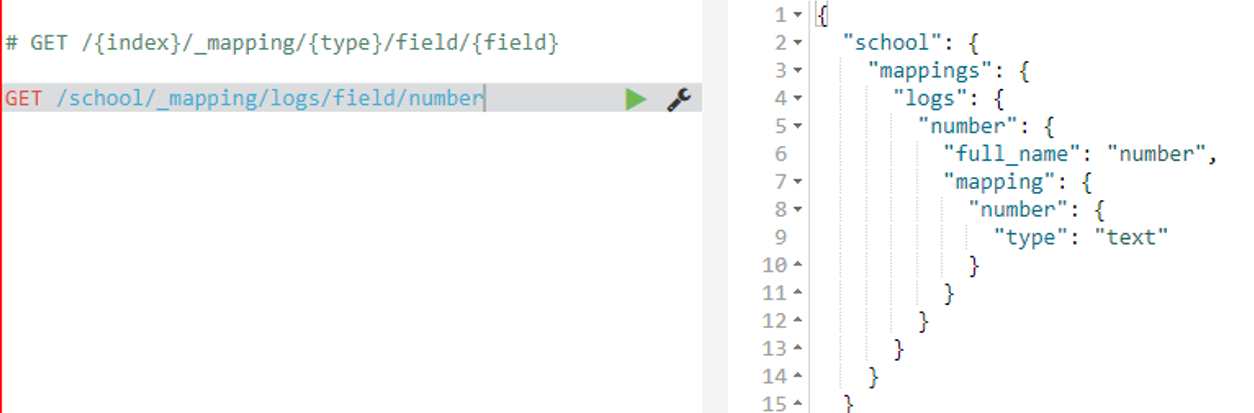
3、获取映射字段
语法:
GET /{index}/_mapping/{type}/field/{field}
GET /school/_mapping/logs/field/number
2.5、索引库配置管理(settings)
1、 索引库配置
所谓的settings就是用来修改索引分片和副本数的;
比如有的重要索引,副本数很少甚至没有副本,那么我们可以通过setting来添加副本数
DELETE document
PUT document
{
"mappings": {
"article" : {
"properties":
{
"title" : {"type": "text"} ,
"author" : {"type": "text"} ,
"titleScore" : {"type": "double"}
}
}
}
}
GET /document/_settings
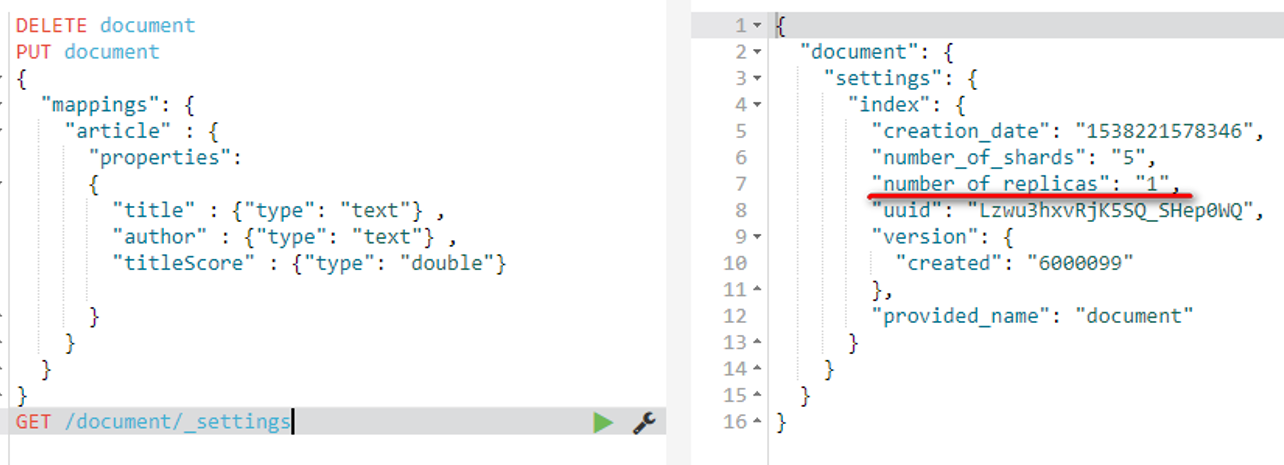
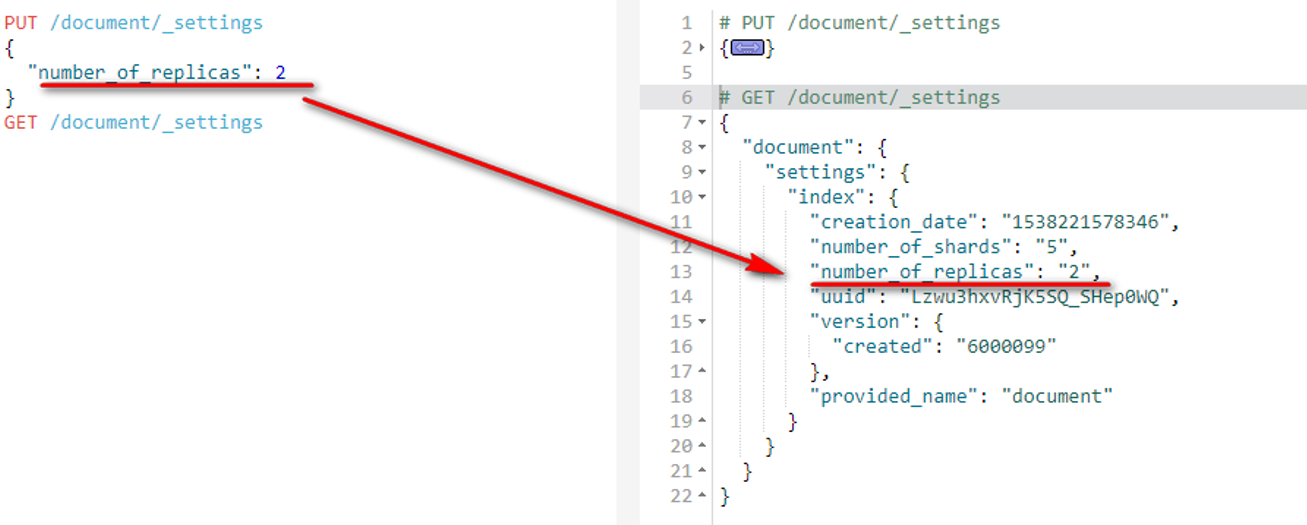
可以看到当前的副本数是1,那么为了提高容错性,我们可以把副本数改成2:
PUT /document/_settings
{
"number_of_replicas": 2
}
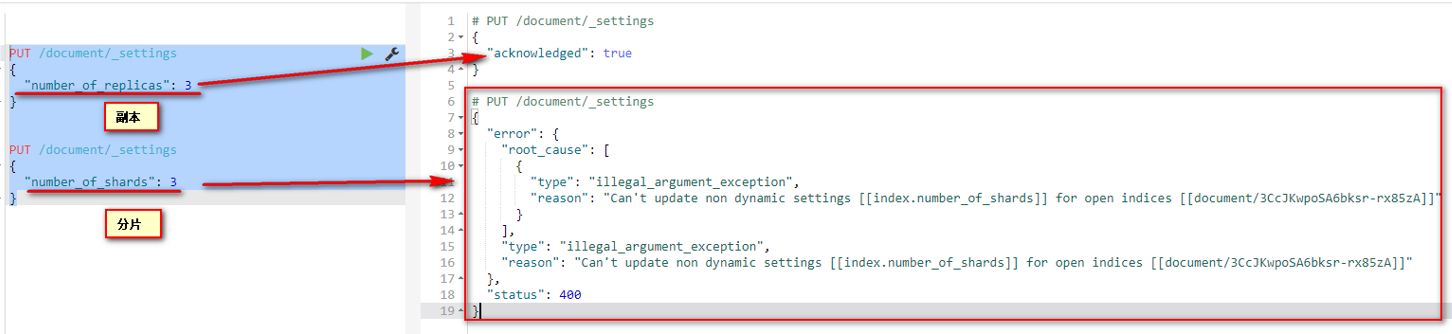
副本可以改,分片不能改
PUT /document/_settings
{
"number_of_shards": 3
}
2、 零停机重新索引数据
实际生产,对于文档的操作,偶尔会遇到这种问题:
某一个字段的类型不符合后期的业务了,但是当前的索引已经创建了,我们知道es在字段的mapping建立后就不可再次修改mapping的值。
1、新建索引库articles1,并添加数据
DELETE articles1
PUT articles1
{
"settings":{
"number_of_shards":3,
"number_of_replicas":1
},
"mappings":{
"article":{
"dynamic":"strict",
"properties":{
"id":{"type": "text", "store": true},
"title":{"type": "text","store": true},
"readCounts":{"type": "integer","store": true},
"times": {"type": "text", "index": false}
}
}
}
}
PUT articles1/article/1
{
"id" : "1",
"title" : "世界1",
"readCounts" : 2 ,
"times" : "2018-05-01"
}
get articles1/article/1
2、 新建索引库articles2
DELETE articles2
PUT articles2
{
"settings":{
"number_of_shards":5,
"number_of_replicas":1
},
"mappings":{
"article":{
"dynamic":"strict",
"properties":{
"id":{"type": "text", "store": true},
"title":{"type": "text","store": true},
"readCounts":{"type": "integer","store": true},
"times": {"type": "date", "index": false}
}
}
}
}
GET articles2/article/1
3、拷贝数据并验证
POST _reindex
{
"source": {
"index": "articles1"
},
"dest": {
"index": "articles2"
}
}
GET articles2/article/1
最后
以上就是狂野吐司最近收集整理的关于Kibana安装及基本操作(附资源)kibana的基本介绍一 Kibana安装二 使用kibana管理索引的全部内容,更多相关Kibana安装及基本操作(附资源)kibana的基本介绍一内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复