muduo库线程池实现
muduo库实现了一个线程池的功能,能够设定固定线程池的大小以及任务队列的大小;测试程序的主线程用于将任务添加到任务队列中,由线程池中的工作线程消费,其中用到了线程的mutex锁以及条件变量对线程进行同步;
线程池实现利用了bind和function的基于对象的变成方法,如果对这些不熟的话,可以先看博主之前记录的文章:C++基于对象编程与function,bind用法.
thread线程的封装
实现了Thread类,类中定义了包括线程的线程名,线程Id,以及线程创建和等待等常用函数,具体实现代码如图;
// thread.h
#ifndef THREAD_POOL_THREAD_H
#define THREAD_POOL_THREAD_H
#include <string>
#include <utility>
#include <functional>
#include <pthread.h>
namespace thread_pool {
class Thread {
public:
typedef std::function<void()> ThreadFunc;
Thread(const int &id, std::string name, ThreadFunc func)
: id_(id),
threadName_(std::move(name)),
func_(std::move(func)),
start_(false),
join_(false) {
}
~Thread() {
if (start_ && !join_)
pthread_detach(threadId_);
}
std::string getThreadName() const {
return threadName_;
}
int getThreadId() const {
return id_;
}
void start() {
assert(!start_);
start_ = true;
pthread_create(&threadId_, nullptr, threadFunc, this);
}
static void *threadFunc(void *arg) {
auto thread = static_cast<Thread *>(arg);
thread->func_();
return nullptr;
}
int join() {
assert(start_);
assert(!join_);
join_ = true;
return pthread_join(threadId_, nullptr);
}
private:
pthread_t threadId_;
int id_;
std::string threadName_;
ThreadFunc func_;
bool start_;
bool join_;
};
}
线程同步方法的封装
muduo线程池线程之间的同步主要通过pthread_mutex_t和pthread_cond_t实现,分别类为mutex和condition。
mutex方法类似于C++ 11线程中lock_guard,实现了MutexLockGuard,RAII的方法进行加锁和解锁,这种实现需要注意考虑加锁解锁范围的考虑,设置锁范围较大容易引起效率问题。在thread_pool.c中也有体现,通过"{}"局部加解锁方式,减小加锁范围。
条件变量是要与锁结合使用的,因此condition.h方法基于mutex.h封装的类MutexLock实现;
// mutex.h
#ifndef THREAD_POOL_MUTEX_H
#define THREAD_POOL_MUTEX_H
#include <pthread.h>
#include <iostream>
// 简单封装pthread_mutex_t,用起来更加便捷
class MutexLock {
public:
MutexLock() {
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex_, nullptr);
}
~MutexLock() {
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex_);
}
void lock() {
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex_);
}
void unlock() {
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex_);
}
pthread_mutex_t *getPthreadMutex() {
return &mutex_;
}
private:
pthread_mutex_t mutex_;
};
// RAII的方法,只需调用MutexLockGuard,无需关注lock(),unlock(),由构造函数与析构函数完成
class MutexLockGuard {
public:
explicit MutexLockGuard(MutexLock &mutex)
: mutex_(mutex) {
mutex_.lock();
}
~MutexLockGuard() {
mutex_.unlock();
}
private:
//这个地方一定要传引用,是必须;
MutexLock &mutex_;
};
#endif //THREAD_POOL_MUTEX_H
// condition.h
#ifndef THREAD_POOL_CONDITION_H
#define THREAD_POOL_CONDITION_H
#include <pthread.h>
#include "mutex.h"
class Condition {
public:
Condition(MutexLock &mutex)
: mutex_(mutex) {
pthread_cond_init(&cond_, nullptr);
}
~Condition() {
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond_);
}
void notify() {
pthread_cond_signal(&cond_);
}
void notifyAll() {
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond_);
}
void wait() {
pthread_cond_wait(&cond_, mutex_.getPthreadMutex());
}
private:
//需要采用&,保持线程池中mutex的一致性
MutexLock &mutex_;
pthread_cond_t cond_{};
};
线程池的实现
线程池中线程的管理,使用vector实现,用unique_ptr指向Thread,智能指针的使用,防止内存泄漏的出现;
任务队列采用deque实现,任务添加到队列的尾端,从队列的头部取出任务执行;
采用两个条件变量,notFull_, notEmpty_在消息队列满和空时,让进行进入等待状态;
具体的实现在代码中进行注释讲解;
// thread_pool.h
#ifndef THREAD_POOL_THREAD_POOL_H
#define THREAD_POOL_THREAD_POOL_H
#include "thread.h"
#include "condition.h"
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#include <deque>
#include <memory>
namespace thread_pool {
class ThreadPool {
public:
typedef std::function<void()> Task;
ThreadPool(std::string name = std::string("thread_pool"));
~ThreadPool();
void setMaxSize(size_t num) {
maxQueueSize_ = num;
}
size_t queueSize() const;
bool isRunning() {
return running_;
}
bool isFull() {
return maxQueueSize_ <= queue_.size();
}
void start(int numThreads);
void stop();
void run(Task task);
Task take();
private:
void runInThread();
MutexLock mutex_;
// 线程池非满条件变量
Condition notFull_;
// 线程池非空条件变量
Condition notEmpty_;
std::string name_;
// 任务队列的最大大小
size_t maxQueueSize_;
// 标志线程池是否正在运行
bool running_;
// vector管理线程
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<thread_pool::Thread>> threads_;
// 任务队列
std::deque<Task> queue_;
};
}
#endif //THREAD_POOL_THREAD_POOL_H
#include "thread_pool.h"
#include <utility>
// C++ 11采用move方法,98就用const std::string& name
thread_pool::ThreadPool::ThreadPool(std::string name)
: name_(std::move(name)),
maxQueueSize_(0),
running_(false),
mutex_(),
notFull_(mutex_),
notEmpty_(mutex_) {
}
thread_pool::ThreadPool::~ThreadPool() {
if (running_)
stop();
}
void thread_pool::ThreadPool::start(int numThreads) {
assert(!running_);
running_ = true;
for (int i = 0; i < numThreads; ++i) {
std::string name = "thread_" + std::to_string(i);
// emplace_back()初始化线程最大的好处就是避免了初始化线程的一次拷贝过程
threads_.emplace_back(new thread_pool::Thread(i, name, std::bind(&ThreadPool::runInThread, this)));
threads_[i]->start();
}
}
void thread_pool::ThreadPool::stop() {
assert(running_);
{
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
// 根据take函数的实现,running_ = false必须在notfyAll之前,否则会导致线程一直阻塞;
running_ = false;
// 结束时,调用notEmpty_.notifyAll(),通知所有工作线程不要阻塞在not_empty_.wait()上
notEmpty_.notifyAll();
}
// 结束join所有工作线程
for (auto &thr :threads_)
thr->join();
}
size_t thread_pool::ThreadPool::queueSize() const {
return maxQueueSize_;
}
void thread_pool::ThreadPool::run(thread_pool::ThreadPool::Task task) {
// 若线程池的工作线程个数为0,线程池不起作用,由主线程执行任务;
if (threads_.empty())
task();
else {
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
// 若非空则往队列中添加任务,通知一个线程跳出notEmpty_.wait()的等待,执行任务
while (isFull())
notFull_.wait();
queue_.push_back(std::move(task));
notEmpty_.notify();
}
}
thread_pool::ThreadPool::Task thread_pool::ThreadPool::take() {
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
// 若队列为空,则一直阻塞在not_Empty_.wait()
while (queue_.empty() && running_)
notEmpty_.wait();
Task task;
if (!queue_.empty()) {
// 取任务消费完,通知主线程任务队列非空
task = queue_.front();
queue_.pop_front();
if (maxQueueSize_ > 0)
notFull_.notify();
}
return task;
}
void thread_pool::ThreadPool::runInThread() {
// 线程的任务执行函数,以running_为标志,持续运行,当stop()后,跳出循环
while (running_) {
Task task(take());
if (task)
task();
}
}
线程池代码单元测试
测试的代码在main.c函数中实现,测试的函数为简单的打印标号,测试函数实现如下:
// main.c
#include <iostream>
#include "thread.h"
#include "thread_pool.h"
#include <memory>
#include <vector>
#include <unistd.h>
void printString(const std::string &str) {
std::cout << str << std::endl;
usleep(100 * 100);
}
void test(int maxSize) {
thread_pool::ThreadPool pool;
pool.setMaxSize(maxSize);
pool.start(5);
for (int i = 0; i < 100; ++i) {
std::string buf = "task" + std::to_string(i);
pool.run(std::bind(printString, buf));
}
pool.stop();
std::cout << "Done" << std::endl;
}
int main() {
test(50);
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
设置的线程池的任务队列大小为50,线程池中线程的数为5,共100个任务添加到任务队列中,由线程池消费;
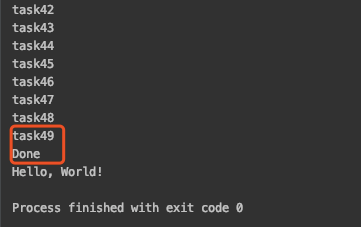
运行后发现一个问题,这样实现的线程池,总有若干任务在线程池终止时无法被消费掉,考虑的情况如下(若有不对,欢迎补充):部分线程在获取到task()任务,但并未执行,此时主线程调用线程池的stop()函数,发送notEmpty_.notifyAll()信号,但是此时线程并没有阻塞在wait()上,就导致信号通知失效,并没有消费掉残留在任务队列中的任务,这种情况在任务队列越大,线程数量越少时,越明显。
图为100个任务时的执行情况:
改进的调用方案:
测试程序采用了一个countDownLatch.h,利用这个类实现将线程池任务队列中的任务全部执行完毕,这里挺巧妙的,先看代码;
// countDownLatch.h
#ifndef THREAD_POOL_COUNTDOWNLATCH_H
#define THREAD_POOL_COUNTDOWNLATCH_H
#include "mutex.h"
#include "condition.h"
class CountDownLatch {
public:
CountDownLatch(int count)
: mutex_(),
condition_(mutex_),
count_(count) {
}
~CountDownLatch() {}
void wait() {
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
if (count_ > 0)
condition_.wait();
}
void countDown() {
MutexLockGuard lock(mutex_);
--count_;
if (count_)
condition_.notifyAll();
}
private:
Condition condition_;
MutexLock mutex_;
int count_;
};
#endif //THREAD_POOL_COUNTDOWNLATCH_H
测试程序中,利用主线程往countDownLatch中添加count_为1,将countDownLatch任务添加到线程池任务队列的最后一个,主线程阻塞在countDownLatch.wait()函数中;
//main.cpp
CountDownLatch latch(1);
pool.run(std::bind(&CountDownLatch::countDown, &latch));
latch.wait();
pool.stop();
线程池中线程只有消费完最后一个线程的时候,主线程才能进入stop()状态,保证任务队列中消息全部消费完毕,现在测试程序的执行全部正确了。
最后
以上就是健忘银耳汤最近收集整理的关于muduo网络库线程池的实现muduo库线程池实现的全部内容,更多相关muduo网络库线程池内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复