好久没有用C了,呵呵,差不多有2年了,哎,当时努力学C的时候还是因为考研的呢,考上之后就再没有用了。现在重新拿起,感觉不一样。
来个简单的,实现严蔚敏版数据结构中ADT规定的基本操作:
首先一个定义常量的头文件:define.h
#define
TRUE 1
#define FALSE 0
#define ERROR -1
typedef int Status;
#define FALSE 0
#define ERROR -1
typedef int Status;
基本操作放在头文件中名为:sqlist.h
 代码
代码
/*
author:sandals
date:2010-05-02
description:线性表顺序存储结构的头文件,实现了线性表的基本操作
*/
// ------顺序存储结构---------
#define LIST_INIT_SIZE 100 // SqList的初始分配大小
#define LIST_INCREMENT 10 // SqList的增量分配大小
typedef struct {
ElemType * elem;
int length;
int listsize;
} SqList;
Status InitList_Sq(SqList * L){
// 构造空的线性表
L -> elem = (ElemType * )malloc(LIST_INIT_SIZE * sizeof (ElemType));
if ( ! L -> elem) return ERROR;
L -> length = 0 ;
L -> listsize = LIST_INIT_SIZE;
return TRUE;
} // InitList_Sq
void DestoryList_Sq(SqList * L){
// 销毁已存在的线性表
if (L -> elem) free(L -> elem);
L -> length = 0 ;
} // DestoryList_Sq
void ClearList_Sq(SqList * L){
// 清空线性表
L -> length = 0 ;
} // ClearList_Sq
Status ListEmpty_Sq(SqList L){
// 线性表为空返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE
if ( ! L.elem) return ERROR;
if (L.length != 0 ) return TRUE;
return FALSE;
} // ListEmpty_Sq
Status ListLength_Sq(SqList L){
// 返回线性表的长度
if ( ! L.elem) return ERROR;
return L.length;
} // ListLength_Sq
Status GetElem_Sq(SqList L, int i,ElemType * e){
// 用e返回L的第i个元素值
if (i > L.length || i < 1 ) return ERROR;
* e = L.elem[i - 1 ];
return TRUE;
} // GetElem_Sq
int LocateElem_Sq(SqList L,ElemType e, int ( * cmp)(ElemType el,ElemType e)){
// 返回L中第一个与e满足cmp函数的数据元素位序,若不存在则返回0
int i = 0 ;
for (i = 0 ;i < L.length;i ++ ){
if (cmp(L.elem[i],e))
return i;
}
return 0 ;
} // LocateElem_Sq
Status PriorElem_Sq(SqList L,ElemType cur_e,ElemType * e){
// 若cur_e为L中的元素,则返回其前驱
int loc = 0 ;
int compareEqual(ElemType a,ElemType b);
loc = LocateElem_Sq(L,cur_e,compareEqual);
if (loc > 0 ) {
* e = L.elem[loc - 1 ];
return TRUE;
}
else
return FALSE;
} // PriorElem_Sq
Status NextElem_Sq(SqList L,ElemType cur_e,ElemType * e){
// 若cur_e为L中的元素,返回其后继
int loc;
int compareEqual(ElemType a,ElemType b);
loc = LocateElem_Sq(L,cur_e,compareEqual);
if (loc < L.length - 1 ){
* e = L.elem[loc + 1 ];
return TRUE;
}
else
return FALSE;
}
Status ListInsert_Sq(SqList * L, int i,ElemType e){
// 在L的每i个元素之前插入e
int j = 0 ;
if ((i > L -> length && L -> length != 0 ) || i < 1 ) return ERROR; // 位置不合法
if (L -> length >= L -> listsize)
{
L -> elem = (ElemType * )realloc(L -> elem,(LIST_INIT_SIZE + LIST_INCREMENT) * sizeof (ElemType));
if ( ! L -> elem) return ERROR; // 分配失败
L -> listsize += LIST_INCREMENT;
}
for (j = L -> length;j >= i;j -- ){
L -> elem[j] = L -> elem[j - 1 ];
}
L -> elem[j] = e;
L -> length ++ ;
return TRUE;
} // ListInsert_Sq
Status ListDelete_Sq(SqList * L, int i,ElemType * e){
// 删除L中第i元素,并用e返回
int j = 0 ;
if (L -> length == 0 || i < 1 || i > L -> length) return ERROR;
* e = L -> elem[i - 1 ];
for (j = i - 1 ;j < L -> length - 1 ;j ++ )
L -> elem[j] = L -> elem[j + 1 ];
L -> length -- ;
return TRUE;
} // ListDelete_Sq
void ListTraverse_Sq(SqList L, void ( * visit)(ElemType e)){
// 遍历L
int i;
for (i = 0 ;i < L.length;i ++ )
visit(L.elem[i]);
} // ListTraverse_Sq
int compareEqual(ElemType a,ElemType b){
// 比较元素,相等返回1
if (a == b) return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
void visit(ElemType e){
// 输出e
printf( " %d " ,e);
}
author:sandals
date:2010-05-02
description:线性表顺序存储结构的头文件,实现了线性表的基本操作
*/
// ------顺序存储结构---------
#define LIST_INIT_SIZE 100 // SqList的初始分配大小
#define LIST_INCREMENT 10 // SqList的增量分配大小
typedef struct {
ElemType * elem;
int length;
int listsize;
} SqList;
Status InitList_Sq(SqList * L){
// 构造空的线性表
L -> elem = (ElemType * )malloc(LIST_INIT_SIZE * sizeof (ElemType));
if ( ! L -> elem) return ERROR;
L -> length = 0 ;
L -> listsize = LIST_INIT_SIZE;
return TRUE;
} // InitList_Sq
void DestoryList_Sq(SqList * L){
// 销毁已存在的线性表
if (L -> elem) free(L -> elem);
L -> length = 0 ;
} // DestoryList_Sq
void ClearList_Sq(SqList * L){
// 清空线性表
L -> length = 0 ;
} // ClearList_Sq
Status ListEmpty_Sq(SqList L){
// 线性表为空返回TRUE,否则返回FALSE
if ( ! L.elem) return ERROR;
if (L.length != 0 ) return TRUE;
return FALSE;
} // ListEmpty_Sq
Status ListLength_Sq(SqList L){
// 返回线性表的长度
if ( ! L.elem) return ERROR;
return L.length;
} // ListLength_Sq
Status GetElem_Sq(SqList L, int i,ElemType * e){
// 用e返回L的第i个元素值
if (i > L.length || i < 1 ) return ERROR;
* e = L.elem[i - 1 ];
return TRUE;
} // GetElem_Sq
int LocateElem_Sq(SqList L,ElemType e, int ( * cmp)(ElemType el,ElemType e)){
// 返回L中第一个与e满足cmp函数的数据元素位序,若不存在则返回0
int i = 0 ;
for (i = 0 ;i < L.length;i ++ ){
if (cmp(L.elem[i],e))
return i;
}
return 0 ;
} // LocateElem_Sq
Status PriorElem_Sq(SqList L,ElemType cur_e,ElemType * e){
// 若cur_e为L中的元素,则返回其前驱
int loc = 0 ;
int compareEqual(ElemType a,ElemType b);
loc = LocateElem_Sq(L,cur_e,compareEqual);
if (loc > 0 ) {
* e = L.elem[loc - 1 ];
return TRUE;
}
else
return FALSE;
} // PriorElem_Sq
Status NextElem_Sq(SqList L,ElemType cur_e,ElemType * e){
// 若cur_e为L中的元素,返回其后继
int loc;
int compareEqual(ElemType a,ElemType b);
loc = LocateElem_Sq(L,cur_e,compareEqual);
if (loc < L.length - 1 ){
* e = L.elem[loc + 1 ];
return TRUE;
}
else
return FALSE;
}
Status ListInsert_Sq(SqList * L, int i,ElemType e){
// 在L的每i个元素之前插入e
int j = 0 ;
if ((i > L -> length && L -> length != 0 ) || i < 1 ) return ERROR; // 位置不合法
if (L -> length >= L -> listsize)
{
L -> elem = (ElemType * )realloc(L -> elem,(LIST_INIT_SIZE + LIST_INCREMENT) * sizeof (ElemType));
if ( ! L -> elem) return ERROR; // 分配失败
L -> listsize += LIST_INCREMENT;
}
for (j = L -> length;j >= i;j -- ){
L -> elem[j] = L -> elem[j - 1 ];
}
L -> elem[j] = e;
L -> length ++ ;
return TRUE;
} // ListInsert_Sq
Status ListDelete_Sq(SqList * L, int i,ElemType * e){
// 删除L中第i元素,并用e返回
int j = 0 ;
if (L -> length == 0 || i < 1 || i > L -> length) return ERROR;
* e = L -> elem[i - 1 ];
for (j = i - 1 ;j < L -> length - 1 ;j ++ )
L -> elem[j] = L -> elem[j + 1 ];
L -> length -- ;
return TRUE;
} // ListDelete_Sq
void ListTraverse_Sq(SqList L, void ( * visit)(ElemType e)){
// 遍历L
int i;
for (i = 0 ;i < L.length;i ++ )
visit(L.elem[i]);
} // ListTraverse_Sq
int compareEqual(ElemType a,ElemType b){
// 比较元素,相等返回1
if (a == b) return TRUE;
else
return FALSE;
}
void visit(ElemType e){
// 输出e
printf( " %d " ,e);
}
测试用的文件:sqlistTest.c

 代码
代码
#include
<
stdio.h
>
#include < stdlib.h >
typedef int ElemType;
#include " define.h "
#include " sqlist.h "
void main(){
SqList L;
ElemType e;
InitList_Sq( & L);
ListInsert_Sq( & L, 1 , 1 );
ListInsert_Sq( & L, 1 , 2 );
ListInsert_Sq( & L, 1 , 3 );
ListInsert_Sq( & L, 1 , 4 );
ListTraverse_Sq(L,visit);
printf( " n " );
if (PriorElem_Sq(L, 2 , & e))
// ListDelete_Sq(&L,1,&e);
printf( " e=%dn " ,e);
// ListTraverse_Sq(L,visit);
printf( " n " );
}
#include < stdlib.h >
typedef int ElemType;
#include " define.h "
#include " sqlist.h "
void main(){
SqList L;
ElemType e;
InitList_Sq( & L);
ListInsert_Sq( & L, 1 , 1 );
ListInsert_Sq( & L, 1 , 2 );
ListInsert_Sq( & L, 1 , 3 );
ListInsert_Sq( & L, 1 , 4 );
ListTraverse_Sq(L,visit);
printf( " n " );
if (PriorElem_Sq(L, 2 , & e))
// ListDelete_Sq(&L,1,&e);
printf( " e=%dn " ,e);
// ListTraverse_Sq(L,visit);
printf( " n " );
}
测试的结果:
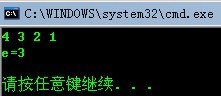
转载于:https://www.cnblogs.com/sandals/archive/2010/05/02/SqList.html
最后
以上就是魁梧毛豆最近收集整理的关于线性表顺序存储的基本操作方法(C语言)的全部内容,更多相关线性表顺序存储内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复