先上效果
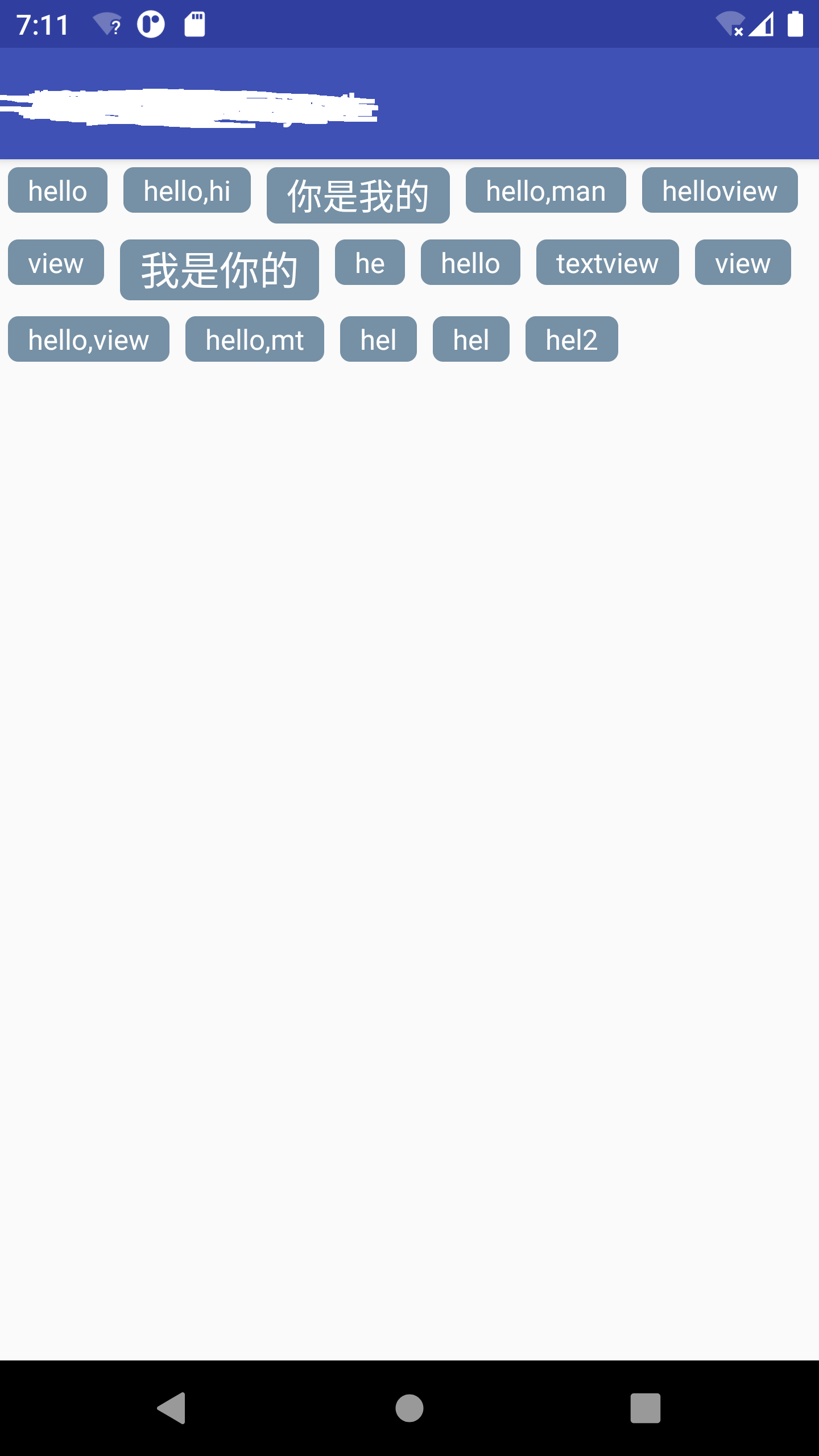
具体实现请参考如下:
import android.content.Context;
import android.os.Build;
import android.support.annotation.RequiresApi;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class WaterfallFlowLayout3 extends ViewGroup {
// 存储每一行的View
private List<List<View>> mEachLineView = new ArrayList<>();
// 每一行的宽度,以每行最高View的宽度为每行的宽度
private List<Integer> mEachLineHeight = new ArrayList<>();
public WaterfallFlowLayout3(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public WaterfallFlowLayout3(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
public WaterfallFlowLayout3(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
}
@RequiresApi(api = Build.VERSION_CODES.LOLLIPOP)
public WaterfallFlowLayout3(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr, int defStyleRes) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr, defStyleRes);
}
@Override
public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) {
return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean b, int i, int i1, int i2, int i3) {
// onLayout其实就是获取左、上、右、下四个值,然后设置此4个值
int left;
int top;
int right;
int bottom;
// 当前行的左和上位置
int curLeft = 0;
int curTop = 0;
// 一行一行的遍历
for (int index = 0; index < mEachLineView.size(); index++) {
List<View> listView = mEachLineView.get(index);
if (listView == null || listView.isEmpty()) {
continue;
}
// 遍历一行的每一个View
for (View view : listView) {
if (view == null) {
continue;
}
// 获取间距布局参数
MarginLayoutParams marginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) view.getLayoutParams();
if (marginLayoutParams == null) {
continue;
}
// 获取当前View的四个点的坐标值
left = curLeft + marginLayoutParams.leftMargin;
top = curTop + marginLayoutParams.topMargin;
right = left + view.getMeasuredWidth();
bottom = top + view.getMeasuredHeight();
// 最终就是调用这个方法进行摆放
view.layout(left, top, right, bottom);
// 将当前的左坐标位置往后移动,用于下一个view的计算
curLeft += view.getMeasuredWidth() + marginLayoutParams.leftMargin + marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
}
// 新的一行要从左边开始
curLeft = 0;
// 换行要将顶部的坐标往下移动
curTop += mEachLineHeight.get(index);
}
mEachLineHeight.clear();
mEachLineView.clear();
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
mEachLineView.clear();
mEachLineHeight.clear();
// 1.获取父容器的参数
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
// 2.onMeasure的目的也就是获取本View的宽和高的值,此处先定义变量
int measureWidth = 0;
int measureHeight = 0;
// 3.根据父容器的模式来获设置本View的宽和高,也就是2中的数值
// 3.1 宽和高都是match_parent
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY && heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
// 如果都是match_parent那就不需要计算,直接设置为父容器的宽和高
measureWidth = widthSize;
measureHeight = heightSize;
} else {
// 用来统计当前行的宽和高
int curLineWidth = 0;
int curLineMaxHeight = 0;
// 当前子view的宽度和高度
int curChildWidth = 0;
int curChildHeight = 0;
// 每行摆放的子view的集合
List<View> curLineViews = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取该容器中所有的子View进行遍历计算
int childCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < childCount; i++) {
View childView = getChildAt(i);
if (childView == null) {
continue;
}
// 首先测量子View
measureChild(childView, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
// 获取子view的宽高
MarginLayoutParams marginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) childView.getLayoutParams();
// 计算当前子view的宽和高
curChildWidth = marginLayoutParams.leftMargin + childView.getMeasuredWidth() + marginLayoutParams.rightMargin;
curChildHeight = marginLayoutParams.topMargin + childView.getMeasuredHeight() + marginLayoutParams.bottomMargin;
// 判断如果当前行的宽度和已经大于父容器的宽度,那么就需要换行
if (curChildWidth + curLineWidth > widthSize) {
// 需要换行,先将换行前最后一行参数(也就是当前行)
// 总的View的宽度和高度赋值后(这也是我们测量获取的两个目标值),然后保存当前行的信息
measureWidth = Math.max(measureWidth, curLineWidth);
measureHeight += curLineMaxHeight;
mEachLineView.add(curLineViews);
mEachLineHeight.add(curLineMaxHeight);
// 创建新的一行
curLineViews = new ArrayList<>();
// 将当前的子view放到新一行的开头
curLineViews.add(childView);
// 新的一行目前只摆放了一个view所以当前行的宽度和高度都是当前子view的宽和高
curLineWidth = curChildWidth;
curLineMaxHeight = curChildHeight;
} else {
// 不需要换行
curLineViews.add(childView);
curLineWidth += curChildWidth;
curLineMaxHeight = Math.max(curLineMaxHeight, curChildHeight);
}
// 最后一个处在最后一行上,因最后一行因为不需要换行,所以最后一行的view数列没有被添加到数列中,此处需要单独处理
if (i == childCount - 1) {
// 最后一行同样也要参与到想要获取的目标值之中
measureWidth = Math.max(measureWidth, curLineWidth);
measureHeight += curLineMaxHeight;
mEachLineView.add(curLineViews);
mEachLineHeight.add(curChildHeight);
}
}
}
// 最终目的就是在此处设置已经计算好的本容器的宽和高
setMeasuredDimension(measureWidth, measureHeight);
}
}
最后
以上就是炙热犀牛最近收集整理的关于Android 自定义流式布局的全部内容,更多相关Android内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复