问题描述:
最近在训练说话人识别模型x-vector时,在网络结构中,将frame-level特征进行 statistics pooling前给TDNN输出的特征添加随机噪声以提高模型的性能,但踩了个坑导致训练效率非常低,用nvidia-smi命令查看GPU的效率,时而100%时而0%,这其中肯定有问题。通过排查发现不是数据加载的问题,而是模型定义的问题。下面详细分析。
模型定义的代码如下:
class xvecTDNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, numSpks, p_dropout):
...
def forward(self, x, eps):
# Note: x must be (batch_size, feat_dim, chunk_len)
x = self.dropout_tdnn1(self.bn_tdnn1(F.relu(self.tdnn1(x))))
x = self.dropout_tdnn2(self.bn_tdnn2(F.relu(self.tdnn2(x))))
x = self.dropout_tdnn3(self.bn_tdnn3(F.relu(self.tdnn3(x))))
x = self.dropout_tdnn4(self.bn_tdnn4(F.relu(self.tdnn4(x))))
x = self.dropout_tdnn5(self.bn_tdnn5(F.relu(self.tdnn5(x))))
if self.training:
x = x + torch.randn(x.size()).to(self.device)*eps
stats = torch.cat((x.mean(dim=2), x.std(dim=2)), dim=1)
x = self.dropout_fc1(self.bn_fc1(F.relu(self.fc1(stats))))
x = self.dropout_fc2(self.bn_fc2(F.relu(self.fc2(x))))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
原因分析:
导致训练效率低下的主要原因是添加噪声的那行代码:
x = x + torch.randn(x.size()).to(self.device)*eps
可以发现这行代码是先利用CPU生成一个与x的shape一样的矩阵,然后再传送到GPU。由于CPU处理速度数据的速度远比GPU慢,并且CPU和GPU之间的数据传输需要时间,所以这一步的实现严重影响了模型训练的速度。利用time()函数打印每一步的时间发现,这一行代码执行的时间居然要2秒多!而整个模型跑前向后向加起来总共也就0.02秒,拖慢了一百多倍!不可忍!
解决办法:
查阅PyTorch文档后发现,torch.randn(shape, out)可以直接在GPU中生成随机数,只要shape是tensor.cuda.Tensor类型即可。这样,就不需要在 CPU 中生成大矩阵再传给GPU,而直接在GPU中生成就行,这样就节省了大量的时间了。因此,下面的代码就可以进行这种操作了。
if self.training:
shape=x.size()
noise = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(shape) if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.FloatTensor(shape)
torch.randn(shape, out=noise)
x += noise*eps
因此,将模型的代码替换如下,即可实现既能添加噪声又能高效训练:
class xvecTDNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, numSpks, p_dropout):
...
def forward(self, x, eps):
# Note: x must be (batch_size, feat_dim, chunk_len)
x = self.dropout_tdnn1(self.bn_tdnn1(F.relu(self.tdnn1(x))))
x = self.dropout_tdnn2(self.bn_tdnn2(F.relu(self.tdnn2(x))))
x = self.dropout_tdnn3(self.bn_tdnn3(F.relu(self.tdnn3(x))))
x = self.dropout_tdnn4(self.bn_tdnn4(F.relu(self.tdnn4(x))))
x = self.dropout_tdnn5(self.bn_tdnn5(F.relu(self.tdnn5(x))))
if self.training:
shape=x.size()
noise = torch.cuda.FloatTensor(shape) if torch.cuda.is_available() else torch.FloatTensor(shape)
torch.randn(shape, out=noise)
x += noise*eps
stats = torch.cat((x.mean(dim=2), x.std(dim=2)), dim=1)
x = self.dropout_fc1(self.bn_fc1(F.relu(self.fc1(stats))))
x = self.dropout_fc2(self.bn_fc2(F.relu(self.fc2(x))))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x
修改代码后,用nvidia-smi查看GPU使用情况,会发现GPU的利用率一直在100%
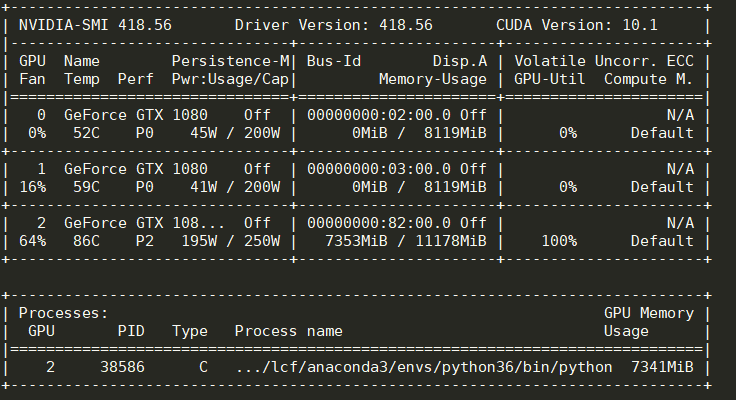
最后
以上就是紧张导师最近收集整理的关于pytorch训练时给隐层网络特征图添加随机噪声导致训练效率低的解决办法的全部内容,更多相关pytorch训练时给隐层网络特征图添加随机噪声导致训练效率低内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。





![深度学习训练中噪声减小吗_深度学习中的噪声-梯度噪声[1]](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg6.png)


发表评论 取消回复