目录
1. 一层神经网络
2. 自己实现的二层神经网络
3. 基于TensorFlow的二层神经网络
4. 多层神经网络
5. 在多层神经网络中加入反向传播
1. 一层神经网络
搭建了一个最基本的一层神经网络,需要预先定义好权重和偏置,使用sigmod()函数作为激活函数。
import numpy as np
# 激活函数的定义
# 非线性转化方程(non-linear transformation function), sigmoid函数(S 曲线)用来作为activation function
def sigmoid(x):
# Our activation function: f(x) = 1 / (1 + e^(-x))
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
class Neuron:
def __init__(self, weights, bias):
self.weights = weights
self.bias = bias
# 正向传播
def feedforward(self, inputs):
# Weight inputs, add bias, then use the activation function
total = np.dot(self.weights, inputs) + self.bias
return sigmoid(total)
weights = np.array([0, 1]) # w1 = 0, w2 = 1
bias = 1 # b = 4
n = Neuron(weights, bias)
x = np.array([2, 3]) # x1 = 2, x2 = 3
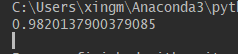
print(n.feedforward(x))正向传播的输出
2. 自己实现的二层神经网络
采用面向对象编程方式,需要自己实现训练函数fit
神经网络模块
# 模块名:NeuralNetwork.py
import numpy as np
# 双曲函数
def tanh(x):
return np.tanh(x)
# 双曲函数的导数,在更新权重的时候需要用到
def tanh_deriv(x):
return 1.0 - np.tanh(x) * np.tanh(x)
# 逻辑函数(常用于0-1标准化)
def logistic(x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
# 逻辑函数的导数
def logistic_derivative(x):
return logistic(x) * (1 - logistic(x))
# 面向对象编程
class NeuralNetwork:
# 构造函数
# layers:每层有几个神经元(一个list)
# 使用的标准化函数
def __init__(self, layers, activation='tanh'):
"""
:param layers: A list containing the number of units in each layer.
Should be at least two values
:param activation: The activation function to be used. Can be
"logistic" or "tanh"
"""
if activation == 'logistic':
self.activation = logistic
self.activation_deriv = logistic_derivative
elif activation == 'tanh':
self.activation = tanh
self.activation_deriv = tanh_deriv
# 空list,用于存放权重
self.weights = []
# 从第一从到最后一个隐藏层
for i in range(1, len(layers) - 1):
self.weights.append((2 * np.random.random((layers[i - 1] + 1, layers[i] + 1)) - 1) * 0.25) #生成i-1层到i层之间的权重
self.weights.append((2 * np.random.random((layers[i] + 1, layers[i + 1])) - 1) * 0.25) #生成i层到i+1层之间的权重
# 训练
# X:训练集
# class label 标记
# Learning rate: 学习率
# epochs: 更新权重和偏置的时候,采用抽样的方式进行更新
def fit(self, X, y, learning_rate=0.2, epochs=10000):
X = np.atleast_2d(X) #至少是二维的矩阵
temp = np.ones([X.shape[0], X.shape[1] + 1]) #初始化原始矩阵
temp[:, 0:-1] = X # adding the bias unit to the input layer 将偏置向量添加到输入层
X = temp
y = np.array(y) #转换成array
for k in range(epochs):
i = np.random.randint(X.shape[0])
a = [X[i]]
# 正向更新
for l in range(len(self.weights)): # going forward network, for each layer
# Computer the node value for each layer (O_i) using activation function
a.append(self.activation(np.dot(a[l], self.weights[l])))
# 计算顶层的误差
error = y[i] - a[-1] # Computer the error at the top layer
# For output layer, Err calculation (delta is updated error)
deltas = [ error * self.activation_deriv(a[-1])]
# 反向更新BP
# Staring backprobagation
for l in range(len(a) - 2, 0, -1): # we need to begin at the second to last layer
# Compute the updated error (i,e, deltas) for each node going from top layer to input layer
deltas.append(deltas[-1].dot(self.weights[l].T) * self.activation_deriv(a[l]))
deltas.reverse() # 因为是反向,所以需要颠倒
for i in range(len(self.weights)):
layer = np.atleast_2d(a[i])
delta = np.atleast_2d(deltas[i])
self.weights[i] += learning_rate * layer.T.dot(delta)
def predict(self, x):
x = np.array(x)
temp = np.ones(x.shape[0] + 1)
temp[0:-1] = x
a = temp
for l in range(0, len(self.weights)):
a = self.activation(np.dot(a, self.weights[l]))
return a测试模块
import NeuralNetwork
import numpy as np
nn = NeuralNetwork.NeuralNetwork([2, 2, 1], 'tanh')
X = np.array([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]])
y = np.array([0, 1, 1, 0])
nn.fit(X, y) #训练神经网络模型
for i in [[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]:
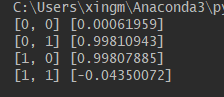
print(i, nn.predict(i))测试结果
3. 基于TensorFlow的二层神经网络
搭建一个基于TensorFlow的二层神经网络,输入层、隐藏层和输出层的节点个数分别为1、10和1。训练数据个数300,训练次数1000,激活函数选用ReLU。因为引入了TensorFlow,训练的过程可以不必自己实现。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
# 创建一个神经网络层
def add_layer(input, in_size, out_size, activation_function = None):
"""
:param input:
神经网络层的输入
:param in_zize:
输入数据的大小
:param out_size:
输出数据的大小
:param activation_function:
神经网络激活函数,默认没有
"""
# 定义神经网络的初始化权重
Weights = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal([in_size, out_size]))
# 定义神经网络的偏置
biases = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([1, out_size]) + 0.1)
# 计算w*x+b
W_mul_x_plus_b = tf.matmul(input, Weights) + biases
# 根据是否有激活函数进行处理
if activation_function is None:
output = W_mul_x_plus_b
else:
output = activation_function(W_mul_x_plus_b)
return output
# 创建一个具有输入层、隐藏层、输出层的三层神经网络,神经元个数分别为1,10,1
# 创建只有一个特征的输入数据,数据数目为300,输入层
x_data = np.linspace(-1, 1, 300)[:, np.newaxis]
# 创建数据中的噪声
noise = np.random.normal(0, 0.05, x_data.shape)
# 创建输入数据对应的输出
y_data = np.square(x_data) + 1 + noise
# 定义输入数据,None是样本数目,表示多少输入数据都行,1是输入数据的特征数目
xs = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
# 定义输出数据,与xs同理
ys = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, [None, 1])
# 定义一个隐藏层
hidden_layer = add_layer(xs, 1, 10, activation_function = tf.nn.relu)
# 定义输出层
prediction = add_layer(hidden_layer, 10, 1, activation_function = None)
# 求解神经网络参数
# 定义损失函数
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.reduce_sum(tf.square(ys - prediction), reduction_indices = [1]))
# 定义训练过程
train_step = tf.train.GradientDescentOptimizer(0.1).minimize(loss)
# 变量初始化
init = tf.global_variables_initializer()
# 定义Session
sess = tf.Session()
# 执行初始化工作
sess.run(init)
# 进行训练
for i in range(1000):
# 执行训练,并传入数据
sess.run(train_step, feed_dict = {xs: x_data, ys: y_data})
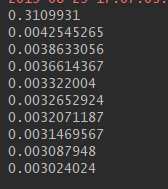
if i % 100 == 0:
print(sess.run(loss, feed_dict = {xs: x_data, ys: y_data}))
# 关闭Session
sess.close()
每训练100次打印一次loss的值,可以看出,随着训练次数的增多,loss越来越小,优化的余地也越来越少
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/Quincuntial/article/details/70148801
4. 多层神经网络
构建一个四层的神经网络(三层隐含层),思路基本一致,将初始话权值,计算损失值,调制权值的过程重复的多做几次就好了(也可以用循环)。
import numpy as np
class NeuralNetwork():
def __init__(self, input):
# random控制1以内的随机数作为初始权重
np.random.seed(50)
# 输入层3个神经元作为第一层
# 第二层定义4个神经元
layer2 = 4
# 第三层定义5个神经元
layer3 = 5
# 第三层定义5个神经元
layer4 = 4
# 随机初始化各层权重
self.synaptic_weights1 = 2 * np.random.random((input, layer2)) - 1
self.synaptic_weights2 = 2 * np.random.random((layer2, layer3)) - 1
self.synaptic_weights3 = 2 * np.random.random((layer3, layer4)) - 1
self.synaptic_weights4 = 2 * np.random.random((layer4, 1)) - 1
def __sigmoid(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def __sigmoid_derivative(self, x):
return x * (1 - x)
def train(self, training_set_inputs, training_set_outputs, number_of_training_iterations):
for iteration in range(number_of_training_iterations):
# 正向传播过程,即神经网络“思考”的过程
activation_values2 = self.__sigmoid(np.dot(training_set_inputs, self.synaptic_weights1))
activation_values3 = self.__sigmoid(np.dot(activation_values2, self.synaptic_weights2))
activation_values4 = self.__sigmoid(np.dot(activation_values3, self.synaptic_weights3))
output = self.__sigmoid(np.dot(activation_values4, self.synaptic_weights4))
# 计算各层损失值
delta5 = (training_set_outputs - output) * self.__sigmoid_derivative(output)
delta4 = np.dot(self.synaptic_weights4, delta5.T) * (self.__sigmoid_derivative(activation_values4).T)
delta3 = np.dot(self.synaptic_weights3, delta4.T) * (self.__sigmoid_derivative(activation_values3).T)
delta2 = np.dot(self.synaptic_weights2, delta3) * (self.__sigmoid_derivative(activation_values2).T)
# 计算需要调制的值
adjustment4 = np.dot(activation_values4.T, delta5)
adjustment3 = np.dot(activation_values3.T, delta4)
adjustment2 = np.dot(activation_values2.T, delta3.T)
adjustment1 = np.dot(training_set_inputs.T, delta2.T)
# 调制权值
self.synaptic_weights1 += adjustment1
self.synaptic_weights2 += adjustment2
self.synaptic_weights3 += adjustment3
self.synaptic_weights4 += adjustment4
def think(self, inputs):
activation_values2 = self.__sigmoid(np.dot(inputs, self.synaptic_weights1))
activation_values3 = self.__sigmoid(np.dot(activation_values2, self.synaptic_weights2))
activation_values4 = self.__sigmoid(np.dot(activation_values3, self.synaptic_weights3))
output = self.__sigmoid(np.dot(activation_values4, self.synaptic_weights4))
return output
if __name__ == "__main__":
neural_network = NeuralNetwork(3) #三个输入,分别是像素的b、g、r分量
print("Random starting synaptic weights (layer 1): ")
print(neural_network.synaptic_weights1)
print("nRandom starting synaptic weights (layer 2): ")
print(neural_network.synaptic_weights2)
print("nRandom starting synaptic weights (layer 3): ")
print(neural_network.synaptic_weights3)
print("nRandom starting synaptic weights (layer 4): ")
print(neural_network.synaptic_weights4)
# 训练集不变
training_set_inputs = np.array([[0, 0, 1], [1, 1, 1], [1, 0, 1], [0, 1, 1]])
training_set_outputs = np.array([[0, 1, 1, 0]]).T
# training_set_inputs = np.array([[123/255, 123/255, 54/255], [255/255, 12/255, 205/255], [1/255, 234/255, 255/255], [0/255, 1/255, 1/255]])
# training_set_outputs = np.array([[110/255, 165/255, 210/255, 13/255]]).T
neural_network.train(training_set_inputs, training_set_outputs, 10000)
print("nNew synaptic weights (layer 1) after training: ")
print(neural_network.synaptic_weights1)
print("nNew synaptic weights (layer 2) after training: ")
print(neural_network.synaptic_weights2)
print("nNew synaptic weights (layer 3) after training: ")
print(neural_network.synaptic_weights3)
print("nNew synaptic weights (layer 4) after training: ")
print(neural_network.synaptic_weights4)
# 新样本测试
# print("nConsidering new situation [255/255, 12/255, 205/255] -> 95?: ")
# print(255 * neural_network.think(np.array([255/255, 12/255, 205/255])))
print("nConsidering new situation [1, 0, 0] -> ?: ")
print(neural_network.think(np.array([0, 1, 1])))
print("Considering new situation [1, 1, 1] -> ?: ")
print(neural_network.think(np.array([1, 1, 1])))
print("Considering new situation [0, 0, 1] -> ?: ")
print(neural_network.think(np.array([0, 0, 1])))5. 在多层神经网络中加入反向传播
-
优化方法 : 梯度下降法
-
Layers : n fully-connected layers
-
损失函数 : 平方和误差
import numpy as np
np.seterr(over='ignore')
class NeuralNetwork():
def __init__(self):
np.random.seed(1) # Seed the random number generator
self.weights = {} # Create dict to hold weights
self.num_layers = 1 # Set initial number of layer to one (input layer)
self.adjustments = {} # Create dict to hold adjustements
def add_layer(self, shape):
# Create weights with shape specified + biases
self.weights[self.num_layers] = np.vstack((2 * np.random.random(shape) - 1, 2 * np.random.random((1, shape[1])) - 1))
# Initialize the adjustements for these weights to zero
self.adjustments[self.num_layers] = np.zeros(shape)
self.num_layers += 1
def __sigmoid(self, x):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-x))
def __sigmoid_derivative(self, x):
return x * (1 - x)
def predict(self, data):
# Pass data through pretrained network
for layer in range(1, self.num_layers+1):
data = np.dot(data, self.weights[layer-1][:, :-1]) + self.weights[layer-1][:, -1] # + self.biases[layer]
data = self.__sigmoid(data)
return data
def __forward_propagate(self, data):
# Progapagate through network and hold values for use in back-propagation
activation_values = {}
activation_values[1] = data
for layer in range(2, self.num_layers+1):
data = np.dot(data.T, self.weights[layer-1][:-1, :]) + self.weights[layer-1][-1, :].T # + self.biases[layer]
data = self.__sigmoid(data).T
activation_values[layer] = data
return activation_values
def simple_error(self, outputs, targets):
return targets - outputs
def sum_squared_error(self, outputs, targets):
return 0.5 * np.mean(np.sum(np.power(outputs - targets, 2), axis=1))
def __back_propagate(self, output, target):
deltas = {}
# Delta of output Layer
deltas[self.num_layers] = output[self.num_layers] - target
# Delta of hidden Layers
for layer in reversed(range(2, self.num_layers)): # All layers except input/output
a_val = output[layer]
weights = self.weights[layer][:-1, :]
prev_deltas = deltas[layer+1]
deltas[layer] = np.multiply(np.dot(weights, prev_deltas), self.__sigmoid_derivative(a_val))
# Caclculate total adjustements based on deltas
for layer in range(1, self.num_layers):
self.adjustments[layer] += np.dot(deltas[layer+1], output[layer].T).T
def __gradient_descente(self, batch_size, learning_rate):
# Calculate partial derivative and take a step in that direction
for layer in range(1, self.num_layers):
partial_d = (1/batch_size) * self.adjustments[layer]
self.weights[layer][:-1, :] += learning_rate * -partial_d
self.weights[layer][-1, :] += learning_rate*1e-3 * -partial_d[-1, :]
def train(self, inputs, targets, num_epochs, learning_rate=1, stop_accuracy=1e-5):
error = []
for iteration in range(num_epochs):
for i in range(len(inputs)):
x = inputs[i]
y = targets[i]
# Pass the training set through our neural network
output = self.__forward_propagate(x)
# Calculate the error
loss = self.sum_squared_error(output[self.num_layers], y)
error.append(loss)
# Calculate Adjustements
self.__back_propagate(output, y)
self.__gradient_descente(i, learning_rate)
# Check if accuarcy criterion is satisfied
if np.mean(error[-(i+1):]) < stop_accuracy and iteration > 0:
break
return(np.asarray(error), iteration+1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
# ----------- XOR Function -----------------
# Create instance of a neural network
nn = NeuralNetwork()
# Add Layers (Input layer is created by default)
nn.add_layer((2, 9))
nn.add_layer((9, 1))
# XOR function
training_data = np.asarray([[0, 0], [0, 1], [1, 0], [1, 1]]).reshape(4, 2, 1)
training_labels = np.asarray([[0], [1], [1], [0]])
error, iteration = nn.train(training_data, training_labels, 5000)
print('Error = ', np.mean(error[-4:]))
print('Epoches needed to train = ', iteration)
# nn.predict(testing_data)
最后
以上就是开朗橘子最近收集整理的关于[Machine Learning] 搭建神经网络(一层、二层和多层)的全部内容,更多相关[Machine内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。




![[Machine Learning] 搭建神经网络(一层、二层和多层)](https://www.shuijiaxian.com/files_image/reation/bcimg4.png)



发表评论 取消回复