仅作为记录,大佬请跳过。
文章目录
- 参考
- 实例一完整代码
- 实例二完整代码
参考
感谢大佬博主文章
实例1传送门
实例2传送门
实例一完整代码
简介:输入了这个正弦曲线,输出一个移位的正弦曲线
代码:
import torch
from torch import nn
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.figure(figsize=(8, 5))
# how many time steps/data pts are in one batch of data
seq_length = 20
# generate evenly spaced data pts
time_steps = np.linspace(0, np.pi, seq_length + 1)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
data.resize((seq_length + 1, 1)) # size becomes (seq_length+1, 1), adds an input_size dimension
x = data[:-1] # all but the last piece of data
y = data[1:] # all but the first
# # display the data
# plt.plot(time_steps[1:], x, 'r.', label='input, x') # x
# plt.plot(time_steps[1:], y, 'b.', label='target, y') # y
#
# plt.legend(loc='best')
# plt.show()
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, output_size, hidden_dim, n_layers):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
# define an RNN with specified parameters
# batch_first means that the first dim of the input and output will be the batch_size
self.rnn = nn.RNN(input_size, hidden_dim, n_layers, batch_first=True)
# last, fully-connected layer
self.fc = nn.Linear(hidden_dim, output_size)
def forward(self, x, hidden):
# x (batch_size, seq_length, input_size)
# hidden (n_layers, batch_size, hidden_dim)
# r_out (batch_size, time_step, hidden_size)
batch_size = x.size(0)
# get RNN outputs
r_out, hidden = self.rnn(x, hidden)
# shape output to be (batch_size*seq_length, hidden_dim)
r_out = r_out.view(-1, self.hidden_dim)
# get final output
output = self.fc(r_out)
return output, hidden
# **********************#
# 检查输入和输出维度
# **********************#
# test that dimensions are as expected
test_rnn = RNN(input_size=1, output_size=1, hidden_dim=10, n_layers=2)
# generate evenly spaced, test data pts
time_steps = np.linspace(0, np.pi, seq_length)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
data.resize((seq_length, 1))
test_input = torch.Tensor(data).unsqueeze(0) # give it a batch_size of 1 as first dimension
print('Input size: ', test_input.size())
# test out rnn sizes
test_out, test_h = test_rnn(test_input, None)
print('Output size: ', test_out.size())
print('Hidden state size: ', test_h.size())
# **********************#
# 训练网络
# **********************#
# decide on hyperparameters
input_size=1
output_size=1
hidden_dim=32
n_layers=1
# instantiate an RNN
rnn = RNN(input_size, output_size, hidden_dim, n_layers)
print(rnn)
# **********************#
# 损失函数和优化器
# **********************#
# MSE loss and Adam optimizer with a learning rate of 0.01
criterion = nn.MSELoss()
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(rnn.parameters(), lr=0.01)
# **********************#
# 定义训练函数
# **********************#
# train the RNN
def train(rnn, n_steps, print_every):
# initialize the hidden state
hidden = None
loss_value=[]
for batch_i, step in enumerate(range(n_steps)):
# defining the training data
time_steps = np.linspace(step * np.pi, (step + 1) * np.pi, seq_length + 1)
data = np.sin(time_steps)
data.resize((seq_length + 1, 1)) # input_size=1
x = data[:-1]
y = data[1:]
# convert data into Tensors
x_tensor = torch.Tensor(x).unsqueeze(0) # unsqueeze gives a 1, batch_size dimension
y_tensor = torch.Tensor(y)
# outputs from the rnn
prediction, hidden = rnn(x_tensor, hidden)
## Representing Memory ##
# make a new variable for hidden and detach the hidden state from its history
# this way, we don't backpropagate through the entire history
hidden = hidden.data
# calculate the loss
loss = criterion(prediction, y_tensor)
# zero gradients
optimizer.zero_grad()
# perform backprop and update weights
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
# display loss and predictions
if batch_i % print_every == 0:
print('Loss: ', loss.item())
plt.plot(time_steps[1:], x, 'r.') # input
plt.plot(time_steps[1:], prediction.data.numpy().flatten(), 'b.') # predictions
loss_value.append(loss.item())
plt.show()
return rnn,loss_value
# train the rnn and monitor results
n_steps = 75
print_every = 15
trained_rnn,rnn_loss_value = train(rnn, n_steps, print_every)
plt.plot(rnn_loss_value)
plt.show()
效果:
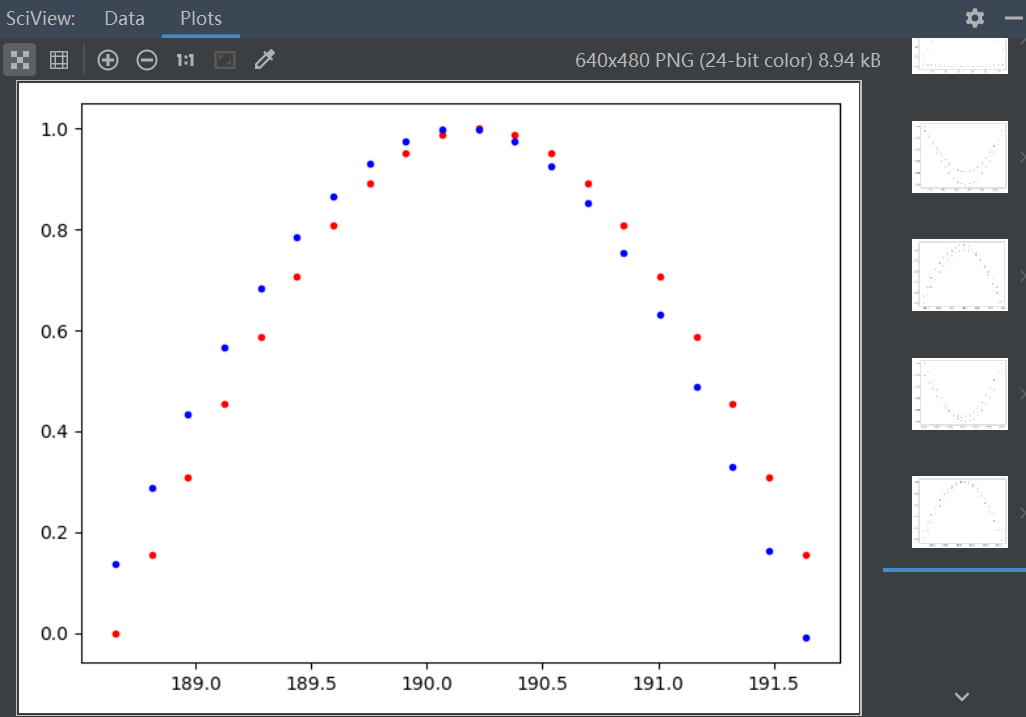
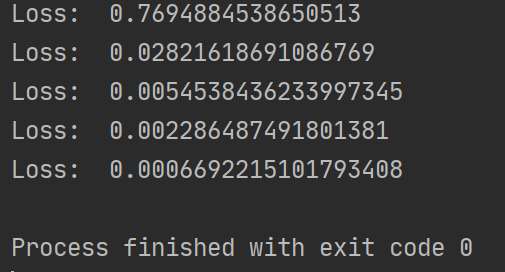
注:
实例二完整代码
简介:输入一个姓名,网络判断该名字是什么国家语言
需要用到数据,下载网址是在文首实例2传送门里的:

from __future__ import unicode_literals, print_function, division
from io import open
import glob
import os
'''
1.准备数据
'''
# ****************************#
# 查找数据txt文件的相对路径
# ****************************#
def findFiles(path): return glob.glob(path)
# print(findFiles('data/names/*.txt'))
import unicodedata
import string
all_letters = string.ascii_letters + " .,;'"
n_letters = len(all_letters)
# ****************************#
# 数据变成ASCII
# ****************************#
# 将Unicode字符串转换为纯ASCII, 感谢https://stackoverflow.com/a/518232/2809427
def unicodeToAscii(s):
return ''.join(
c for c in unicodedata.normalize('NFD', s)
if unicodedata.category(c) != 'Mn'
and c in all_letters
)
# print(unicodeToAscii('Ślusàrski'))
# 构建category_lines字典,每种语言的名字列表
category_lines = {} # 装.txt文件夹里的每行,且都属于这个语言类-用字典
all_categories = [] # 装.txt文件夹的名字
# 读取文件并分成几行
def readLines(filename):
lines = open(filename, encoding='utf-8').read().strip().split('n')
return [unicodeToAscii(line) for line in lines]
for filename in findFiles('data/names/*.txt'):
category = os.path.splitext(os.path.basename(filename))[0] # 将文件名和扩展名分开 https://blog.csdn.net/ztf312/article/details/83039392
all_categories.append(category)
lines = readLines(filename)
category_lines[category] = lines # 一个字典对应一个list类型
n_categories = len(all_categories)
# print(category_lines['Italian'][:5])
# ****************************#
# 单词转变为张量
# ****************************#
import torch
# 从all_letters中查找字母索引,例如 "a" = 0
def letterToIndex(letter):
return all_letters.find(letter)
# 仅用于演示,将字母转换为<1 x n_letters> 张量
def letterToTensor(letter):
tensor = torch.zeros(1, n_letters)
tensor[0][letterToIndex(letter)] = 1
return tensor
# 将一行转换为<line_length x 1 x n_letters>,
# 或一个0ne-hot字母向量的数组
def lineToTensor(line):
tensor = torch.zeros(len(line), 1, n_letters)
for li, letter in enumerate(line):
tensor[li][0][letterToIndex(letter)] = 1
return tensor
# print(letterToTensor('J'))
# print(lineToTensor('Jones').size())
'''
2.构造神经网络
'''
# ****************************#
# 构建rnn
# ****************************#
import torch.nn as nn
class RNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size):
super(RNN, self).__init__()
self.hidden_size = hidden_size
self.i2h = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, hidden_size)
self.i2o = nn.Linear(input_size + hidden_size, output_size)
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1) # 好像是类似sigmoid的激活函数
def forward(self, input, hidden):
combined = torch.cat((input, hidden), 1) # torch.cat是将两个张量(tensor)拼接在一起 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_39709535/article/details/80803003
hidden = self.i2h(combined)
output = self.i2o(combined)
output = self.softmax(output)
return output, hidden
def initHidden(self):
return torch.zeros(1, self.hidden_size)
n_hidden = 128
rnn = RNN(n_letters, n_hidden, n_categories) # rnn输入个数:所有英文字母字符的个数;输出:18种类别
# ****************************#
# 字母例子——输出值和隐层值
# ****************************#
input = letterToTensor('A') # 要预测的A,在所有字母字符的全零序列中(input),将A所在的位置置一
hidden =torch.zeros(1, n_hidden)
output, next_hidden = rnn(input, hidden)
# print(output)
# ****************************#
# 单词例子——输出值和隐层值
# ****************************#
input = lineToTensor('Albert')
hidden = torch.zeros(1, n_hidden)
output, next_hidden = rnn(input[0], hidden) # input[0],是单词‘Albert’中的字母'A'
# print(output)
'''
2.2 训练
'''
# ****************************#
# 使用 Tensor.topk函数得到最大值在结果中的位置索引
# ****************************#
def categoryFromOutput(output):
top_n, top_i = output.topk(1)
category_i = top_i[0].item()
return all_categories[category_i], category_i
# print(categoryFromOutput(output))
# ****************************#
# 一种快速获取训练示例(得到一个名字及其所属的语言类别)的方法
# ****************************#
import random
def randomChoice(l):
return l[random.randint(0, len(l) - 1)]
def randomTrainingExample():
category = randomChoice(all_categories)
line = randomChoice(category_lines[category])
category_tensor = torch.tensor([all_categories.index(category)], dtype=torch.long) # 所选择的语言在所有语言类数组中的索引
line_tensor = lineToTensor(line)
return category, line, category_tensor, line_tensor
# for i in range(10):
# category, line, category_tensor, line_tensor = randomTrainingExample()
# print('category =', category, '/ line =', line)
# ****************************#
# 训练神经网络
# ****************************#
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
learning_rate = 0.005 # If you set this too high, it might explode. If too low, it might not learn
def train(category_tensor, line_tensor):
hidden = rnn.initHidden()
rnn.zero_grad()
for i in range(line_tensor.size()[0]):
output, hidden = rnn(line_tensor[i], hidden) # 【将‘Albert’字母,依次一个一个地是那个如神经网络;每次都输出一个输出值和隐层值;当最后一个字母输入完后,得到最终的out值;将最终的output值(tensor序列:在本类所在的位置数值最大)与target类别比较,得到loss,迭代训练】————采取随机抽取的方式进行训练
loss = criterion(output, category_tensor)
loss.backward()
# 将参数的梯度添加到其值中,乘以学习速率
for p in rnn.parameters():
p.data.add_(-learning_rate, p.grad.data)
return output, loss.item()
import time
import math
n_iters = 100000
print_every = 5000
plot_every = 1000
# 跟踪绘图的损失
current_loss = 0
all_losses = []
def timeSince(since):
now = time.time()
s = now - since
m = math.floor(s / 60)
s -= m * 60
return '%dm %ds' % (m, s)
start = time.time()
for iter in range(1, n_iters + 1):
category, line, category_tensor, line_tensor = randomTrainingExample()
output, loss = train(category_tensor, line_tensor)
current_loss += loss
# 打印迭代的编号,损失,名字和猜测
if iter % print_every == 0:
guess, guess_i = categoryFromOutput(output) # print_every次数后,用于预测一个值
correct = '✓' if guess == category else '✗ (%s)' % category
print('%d %d%% (%s) %.4f %s / %s %s' % (iter, iter / n_iters * 100, timeSince(start), loss, line, guess, correct))
# 将当前损失平均值添加到损失列表中
if iter % plot_every == 0:
all_losses.append(current_loss / plot_every) # plot_every次数后,得到这一段时间的平均loss,用于画loss曲线
current_loss = 0
'''
2.3、绘画出结果
'''
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib.ticker as ticker
plt.figure()
plt.plot(all_losses)
plt.show()
效果:
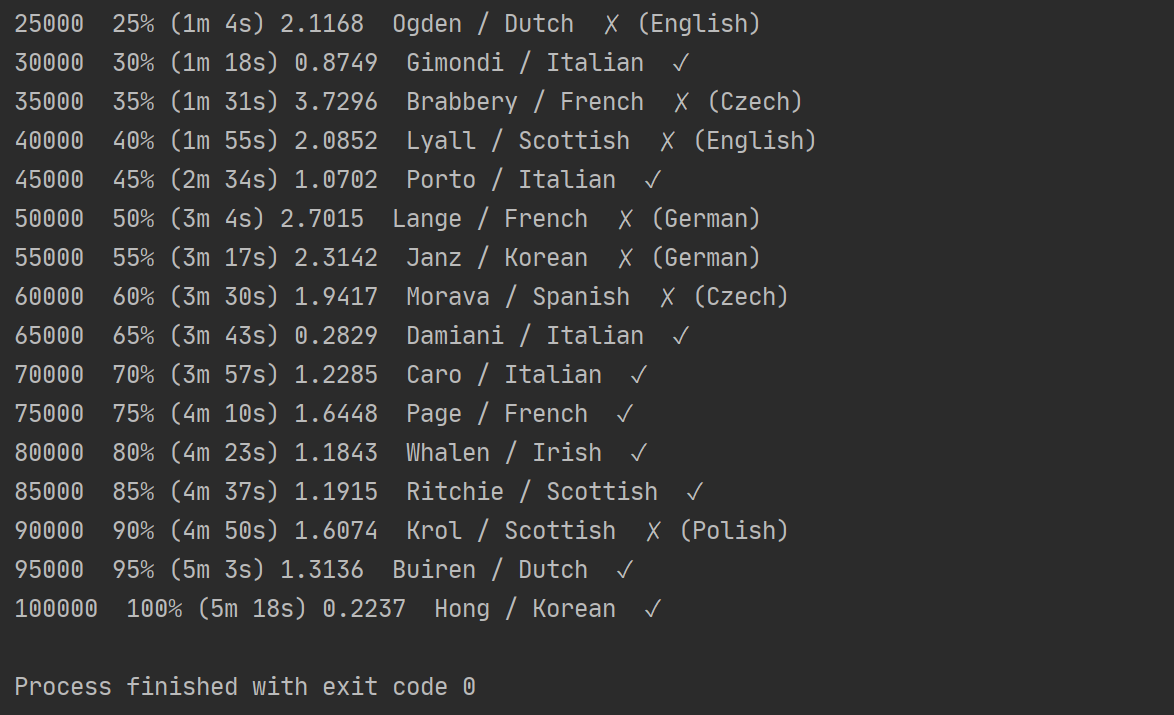
最后
以上就是故意汉堡最近收集整理的关于两个rnn实例,可直接运行参考实例一完整代码实例二完整代码的全部内容,更多相关两个rnn实例内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复