const数据成员的初始化方式:
- 使用类内值(C++11支持)
class Human {
public:
Human();
~ Human();
private:
const int Age =18;
};
- 使用构造函数的初始化列表
Human::Human():Age(18) {
......
}
(如果同时使用这两种方式,以初始化列表中的值为最终初始化结果)
注意: 不能在构造函数或其他成员函数内,对const成员赋值!
如果一个成员函数内部,不会修改任何数据成员,就把它定义为const成员函数。
const成员函数内,不能修改任何数据成员!
C++的成员函数设置建议:
如果一个对象的成员函数,不会修改任何数据成员,那么就强烈:
把这个成员函数,定义为const成员函数!
易错点:
非const引用, 不能对const变量进行引用。
注意: const引用, 可以对非const变量进行引用。如下图。
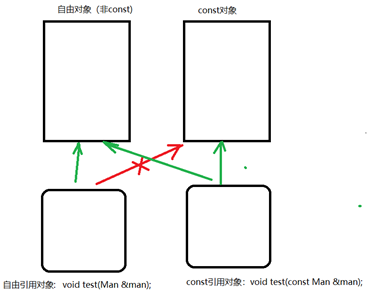
示例代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
class Man {
public:
Man() {}
void play() const {
cout << "I am playing ...." << std::endl;
}
};
void play(const Man &man) {
man.play();
}
void asment(Man &man) {
man.play();
}
int main(void) {
const Man man;
play(man); //const引用对象引用const对象
// asment(man); //自由引用对象,引用const对象,错误
Man man1;
play(man1); //const引用对象引用非const对象
asment(man1); //自由引用对象,引用非const对象
}
最后
以上就是沉静玉米最近收集整理的关于C++ const使用注意事项的全部内容,更多相关C++内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。
本图文内容来源于网友提供,作为学习参考使用,或来自网络收集整理,版权属于原作者所有。








发表评论 取消回复