SimpleDB lab1 Ex1 ~ Ex4
2020-10-17
1 环境配置
- 运行开发环境:JDK-1.8
- 开发工具:IDEA
配置步骤
- 依赖包配置:
打开File->project structure->library,添加SimpleDB->lib中的jar包到项目中。 - 指定JDK
打开File->project structure->project, 设置JDK为下载好的JDK-1.8, 并将language Level设置为8. - 设置输出目录
依然是在project structure->project中,找到project compiler output, 设置为 simpleDB/out (自定义即可) - 设置 source root, test root
在目录中,右键 SimpleDB->src->java 文件夹,选择 mark dir as source root
邮件SimpleDB->test 文件夹,选择mark dir as test root
并取消其他默认设置的test root 或者source root等。
测试
点击build,成功生成即可。
其他
之后完成练习之后,可以直接去对应的test.java文件中,点击Debug进行调试等,无需配置ant环境、
2 ex1 tuple tupleDesc
| filed1(int 11) | filed2(int 11) | filed2(string 4) | tupleDesc |
|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 11 | test | tuple |
大致关系如上表所示。
tuple中包含字段的实际值(Field),tupleDesc则描述其字段名、字段类型等属性(TdItems)。所以实现思路还是很清晰的。
代码
Tuple.java
public class Tuple implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
// 根据构造函数
private TupleDesc td;
// RecordID
private RecordId recordId;
private List<Field> fields;
/**
* Create a new tuple with the specified schema (type).
*
* @param td
* the schema of this tuple. It must be a valid TupleDesc
* instance with at least one field.
*/
public Tuple(TupleDesc td) {
// some code goes here
this.td = td;
this.fields = new ArrayList<>();
}
/**
* @return The TupleDesc representing the schema of this tuple.
* 元组描述代表元组的结构
*/
public TupleDesc getTupleDesc() {
// some code goes here
return this.td;
}
/**
* @return The RecordId representing the location of this tuple on disk. May
* be null.
* RecordID代表元组在磁盘上的位置,可以为空
*/
public RecordId getRecordId() {
// some code goes here
return this.recordId;
}
/**
* Set the RecordId information for this tuple.
*
* @param rid
* the new RecordId for this tuple.
*/
public void setRecordId(RecordId rid) {
// some code goes here
this.recordId = rid;
}
/**
* Change the value of the ith field of this tuple.
*
* @param i
* index of the field to change. It must be a valid index.
* @param f
* new value for the field.
*/
public void setField(int i, Field f) {
// some code goes here
if(i >= this.fields.size())
this.fields.add(f);
else
this.fields.set(i, f);
}
/**
* @return the value of the ith field, or null if it has not been set.
*
* @param i
* field index to return. Must be a valid index.
*/
public Field getField(int i) {
// some code goes here
if(this.fields.size() <= i)
return null;
return this.fields.get(i);
}
/**
* Returns the contents of this Tuple as a string. Note that to pass the
* system tests, the format needs to be as follows:
*
* column1tcolumn2tcolumn3t...tcolumnN
* // 输出tuple的内容,中间用空格分隔开
* where t is any whitespace (except a newline)
*/
public String toString() {
// some code goes here
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
for (Field field : this.fields) {
res.append(field.toString());
res.append(" ");
}
String ret = res.toString();
if(fields.size() != 0)
ret = ret.substring(0, res.length() - 1);
return ret;
}
/**
* @return
* An iterator which iterates over all the fields of this tuple
* */
public Iterator<Field> fields()
{
// some code goes here
return fields.iterator();
}
/**
* reset the TupleDesc of this tuple (only affecting the TupleDesc)
* */
public void resetTupleDesc(TupleDesc td)
{
// some code goes here
this.td = td;
}
}
TupleDesc.java
public class TupleDesc implements Serializable {
/**
* A help class to facilitate organizing the information of each field
* */
public static class TDItem implements Serializable {
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* The type of the field
* */
public final Type fieldType;
/**
* The name of the field
* */
public final String fieldName;
public TDItem(Type t, String n) {
this.fieldName = n;
this.fieldType = t;
}
public String toString() {
return fieldName + "(" + fieldType + ")";
}
}
private List<TDItem> tdItemList = new ArrayList<>();
// 做了一个map 保存字段名和位置信息 O(1)查询
private HashMap<String, Integer> name2IndexMap = new HashMap<>();
/**
* @return
* An iterator which iterates over all the field TDItems
* that are included in this TupleDesc
* */
public Iterator<TDItem> iterator() {
// some code goes here
return this.tdItemList.iterator();
}
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* Create a new TupleDesc with typeAr.length fields with fields of the
* specified types, with associated named fields.
*
* 创建一组新的元组属性描述,参数为字段类型,字段名称,其中字段名称是非空的,字段类型必须至少有一个
*
* @param typeAr
* array specifying the number of and types of fields in this
* TupleDesc. It must contain at least one entry.
* @param fieldAr
* array specifying the names of the fields. Note that names may
* be null.
*/
public TupleDesc(Type[] typeAr, String[] fieldAr) {
// some code goes here
for (int i = 0; i < typeAr.length; i++) {
TDItem tdItem = new TDItem(typeAr[i], fieldAr[i]);
this.tdItemList.add(tdItem);
name2IndexMap.put(fieldAr[i], i);
}
}
/**
* Constructor. Create a new tuple desc with typeAr.length fields with
* fields of the specified types, with anonymous (unnamed) fields.
*
* @param typeAr
* array specifying the number of and types of fields in this
* TupleDesc. It must contain at least one entry.
*/
public TupleDesc(Type[] typeAr) {
// some code goes here
for (Type type : typeAr) {
TDItem tdItem = new TDItem(type, "");
this.tdItemList.add(tdItem);
}
}
/**
* @return the number of fields in this TupleDesc
*/
public int numFields() {
// some code goes here
return tdItemList.size();
}
/**
* Gets the (possibly null) field name of the ith field of this TupleDesc.
*
* @param i
* index of the field name to return. It must be a valid index.
* @return the name of the ith field
* @throws NoSuchElementException
* if i is not a valid field reference.
*/
public String getFieldName(int i) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
return tdItemList.get(i).fieldName;
}
/**
* Gets the type of the ith field of this TupleDesc.
*
* @param i
* The index of the field to get the type of. It must be a valid
* index.
* @return the type of the ith field
* @throws NoSuchElementException
* if i is not a valid field reference.
*/
public Type getFieldType(int i) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
return tdItemList.get(i).fieldType;
}
/**
* Find the index of the field with a given name.
*
* @param name
* name of the field.
* @return the index of the field that is first to have the given name.
* @throws NoSuchElementException
* if no field with a matching name is found.
*/
public int fieldNameToIndex(String name) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
if(this.name2IndexMap.get(name) == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException("没有名为: %s 的字段");
return this.name2IndexMap.get(name);
}
/**
* @return The size (in bytes) of tuples corresponding to this TupleDesc.
* Note that tuples from a given TupleDesc are of a fixed size.
* 给定TupleDesc的元组,size是固定的
* 因为类型只有定长 string 和 int
* 加起来就行了0.0
*/
public int getSize() {
// some code goes here
int size = 0;
for (TDItem tdItem : tdItemList) {
size += tdItem.fieldType.getLen();
}
return size;
}
/**
* Merge two TupleDescs into one, with td1.numFields + td2.numFields fields,
* with the first td1.numFields coming from td1 and the remaining from td2.
*
* @param td1
* The TupleDesc with the first fields of the new TupleDesc
* @param td2
* The TupleDesc with the last fields of the TupleDesc
* @return the new TupleDesc
*/
public static TupleDesc merge(TupleDesc td1, TupleDesc td2) {
// some code goes here
int numFields = td1.numFields() + td2.numFields();
Type[] typeAr = new Type[numFields];
String[] fieldAr = new String[numFields];
int index = 0;
for (TDItem tdItem : td1.tdItemList) {
typeAr[index] = tdItem.fieldType;
fieldAr[index] = tdItem.fieldName;
index++;
}
for (TDItem tdItem : td2.tdItemList) {
typeAr[index] = tdItem.fieldType;
fieldAr[index] = tdItem.fieldName;
index++;
}
return new TupleDesc(typeAr, fieldAr);
}
/**
* Compares the specified object with this TupleDesc for equality. Two
* TupleDescs are considered equal if they have the same number of items
* and if the i-th type in this TupleDesc is equal to the i-th type in o
* for every i.
*
* @param o
* the Object to be compared for equality with this TupleDesc.
* @return true if the object is equal to this TupleDesc.
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
// some code goes here
if(o == null)
return false;
if(!o.getClass().equals(TupleDesc.class))
return false;
TupleDesc tupleDesc = (TupleDesc) o;
if(tupleDesc.numFields() != this.numFields())
return false;
for (int i = 0; i < this.tdItemList.size(); i++) {
if(!tupleDesc.tdItemList.get(i).toString()
.equals(tdItemList.get(i).toString()))
return false;
}
return true;
}
public int hashCode() {
// If you want to use TupleDesc as keys for HashMap, implement this so
// that equal objects have equals hashCode() results
int res = 17;
return (res * 37 + tdItemList.hashCode() ) * 37 + name2IndexMap.hashCode();
}
/**
* Returns a String describing this descriptor. It should be of the form
* "fieldType[0](fieldName[0]), ..., fieldType[M](fieldName[M])", although
* the exact format does not matter.
*
* @return String describing this descriptor.
*/
public String toString() {
// some code goes here
if(this.tdItemList.size() == 0)
return "";
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
for (TDItem tdItem : this.tdItemList) {
stringBuilder.append(tdItem.toString());
stringBuilder.append(",");
}
String ret = stringBuilder.toString();
return ret.substring(0, ret.length() - 1);
}
}
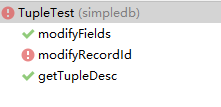
modifyRecord之后实现,本次练习不需要。
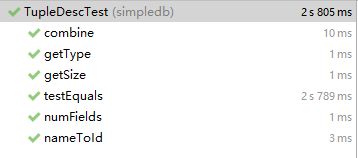
ps. 不知道后续会不会有啥坑,暂时先用List,有问题再更新。
3 Ex2 Catalog
2020-10-18
目标明确,要实现上图中的东西。
package simpledb;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* The Catalog keeps track of all available tables in the database and their
* associated schemas.
* For now, this is a stub catalog that must be populated with tables by a
* user program before it can be used -- eventually, this should be converted
* to a catalog that reads a catalog table from disk.
* Catalog 目录
* 实际上类似数据库管理工具中,show tables命令
* 主要存储了数据库的table信息
* contains a list of tables and the schema of those tables
* @Threadsafe 需要保证线程安全
*/
public class Catalog {
private static class Table{
String tableName;
String pkeyField;
DbFile dbFile;
public Table(String tableName, String pkeyField, DbFile dbFile){
this.tableName =tableName;
this.dbFile = dbFile;
this.pkeyField = pkeyField;
}
}
private List<Table> tables = new ArrayList<>();
/**
* Constructor.
* Creates a new, empty catalog.
*/
public Catalog() {
// some code goes here
}
/**
* Add a new table to the catalog.
* This table's contents are stored in the specified DbFile.
* @param file the contents of the table to add; file.getId() is the identfier of
* this file/tupledesc param for the calls getTupleDesc and getFile
* @param name the name of the table -- may be an empty string. May not be null. If a name
* conflict exists, use the last table to be added as the table for a given name.
* @param pkeyField the name of the primary key field
*/
public void addTable(DbFile file, String name, String pkeyField) {
// some code goes here
for (Table table : tables) {
if(table.tableName.equals(name) || table.dbFile.getId() == file.getId()){
this.tables.set(tables.indexOf(table), new Table(name, pkeyField, file));
}
}
this.tables.add(new Table(name, pkeyField, file));
}
public void addTable(DbFile file, String name) {
addTable(file, name, "");
}
/**
* Add a new table to the catalog.
* This table has tuples formatted using the specified TupleDesc and its
* contents are stored in the specified DbFile.
* @param file the contents of the table to add; file.getId() is the identfier of
* this file/tupledesc param for the calls getTupleDesc and getFile
*/
public void addTable(DbFile file) {
addTable(file, (UUID.randomUUID()).toString());
}
/**
* Return the id of the table with a specified name,
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the table doesn't exist
*/
public int getTableId(String name) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
for (Table table : tables) {
if(table.tableName.equals(name)){
return table.dbFile.getId();
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到名为: %s的表", name));
}
/**
* Returns the tuple descriptor (schema) of the specified table
* @param tableid The id of the table, as specified by the DbFile.getId()
* function passed to addTable
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the table doesn't exist
*/
public TupleDesc getTupleDesc(int tableid) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
for(Table table : tables) {
if(table.dbFile.getId() == tableid) {
return table.dbFile.getTupleDesc();
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到tableID为:%d的表", tableid));
}
/**
* Returns the DbFile that can be used to read the contents of the
* specified table.
* @param tableid The id of the table, as specified by the DbFile.getId()
* function passed to addTable
*/
public DbFile getDatabaseFile(int tableid) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
for(Table table : tables) {
if(table.dbFile.getId() == tableid) {
return table.dbFile;
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到tableID为:%d的表", tableid));
}
public String getPrimaryKey(int tableid) {
// some code goes here
for(Table table : tables) {
if(table.dbFile.getId() == tableid) {
return table.pkeyField;
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到tableID为:%d的表", tableid));
}
public Iterator<Integer> tableIdIterator() {
// some code goes here
Iterator<Integer> it = new Iterator<Integer>() {
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return tables.iterator().hasNext();
}
@Override
public Integer next() {
return tables.iterator().next().dbFile.getId();
}
};
return it;
}
public String getTableName(int id) {
// some code goes here
for(Table table : tables) {
if(table.dbFile.getId() == id) {
return table.tableName;
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到id为:%d的表", id));
}
/** Delete all tables from the catalog */
public void clear() {
// some code goes here
this.tables.clear();
}
/**
* Reads the schema from a file and creates the appropriate tables in the database.
* @param catalogFile
*/
public void loadSchema(String catalogFile) {
String line = "";
String baseFolder=new File(new File(catalogFile).getAbsolutePath()).getParent();
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(catalogFile)));
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
//assume line is of the format name (field type, field type, ...)
String name = line.substring(0, line.indexOf("(")).trim();
//System.out.println("TABLE NAME: " + name);
String fields = line.substring(line.indexOf("(") + 1, line.indexOf(")")).trim();
String[] els = fields.split(",");
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<Type> types = new ArrayList<Type>();
String primaryKey = "";
for (String e : els) {
String[] els2 = e.trim().split(" ");
names.add(els2[0].trim());
if (els2[1].trim().toLowerCase().equals("int"))
types.add(Type.INT_TYPE);
else if (els2[1].trim().toLowerCase().equals("string"))
types.add(Type.STRING_TYPE);
else {
System.out.println("Unknown type " + els2[1]);
System.exit(0);
}
if (els2.length == 3) {
if (els2[2].trim().equals("pk"))
primaryKey = els2[0].trim();
else {
System.out.println("Unknown annotation " + els2[2]);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
Type[] typeAr = types.toArray(new Type[0]);
String[] namesAr = names.toArray(new String[0]);
TupleDesc t = new TupleDesc(typeAr, namesAr);
HeapFile tabHf = new HeapFile(new File(baseFolder+"/"+name + ".dat"), t);
addTable(tabHf,name,primaryKey);
System.out.println("Added table : " + name + " with schema " + t);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(0);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println ("Invalid catalog entry : " + line);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
通过了测试,但是目前实现方式有点蠢,而且没注意到线程安全,后续再改
2020/10/19
有两个小问题,首先是线程安全问题。java提供了一些线程安全的数据结构。如HashTable,ConcurrentHashMap,CopyOnWriteArrayList,CopyOnWriteArraySet,ConcurrentLinkedQueue,Vector,StringBuffer等。
本次选取ConcurrentHashMap, 他是HashMap的线程安全版。相对于HashTable, 再多线程环境下,效率要更高一些。因为HashTable实现线程安全使用了synchronized修饰方法的方式,从而当一个线程访问HashTable的同步方法时,其他线程也访问同步方法就会出现阻塞状态。
另外,考虑到函数中有许多根据ID查询表信息的操作,使用List需要遍历,相较HashMap,效率显然要更低一些。
做此考虑之后,重构代码如下所示:
package simpledb;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap;
/**
* The Catalog keeps track of all available tables in the database and their
* associated schemas.
* For now, this is a stub catalog that must be populated with tables by a
* user program before it can be used -- eventually, this should be converted
* to a catalog that reads a catalog table from disk.
* Catalog 目录
* 实际上类似数据库管理工具中,show tables命令
* 主要存储了数据库的table信息
* contains a list of tables and the schema of those tables
* @Threadsafe 需要保证线程安全
*/
public class Catalog {
private static class Table{
String tableName;
String pkeyField;
DbFile dbFile;
Table(String tableName, String pkeyField, DbFile dbFile){
this.tableName =tableName;
this.dbFile = dbFile;
this.pkeyField = pkeyField;
}
}
private ConcurrentHashMap<Integer, Table> tables;
/**
* Constructor.
* Creates a new, empty catalog.
*/
public Catalog() {
// some code goes here
this.tables = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
}
/**
* Add a new table to the catalog.
* This table's contents are stored in the specified DbFile.
* @param file the contents of the table to add; file.getId() is the identfier of
* this file/tupledesc param for the calls getTupleDesc and getFile
* @param name the name of the table -- may be an empty string. May not be null. If a name
* conflict exists, use the last table to be added as the table for a given name.
* @param pkeyField the name of the primary key field
*/
public void addTable(DbFile file, String name, String pkeyField) {
// some code goes here
Set<Integer> keySet = tables.keySet();
for (Integer key : keySet) {
// 如果表已经存在于目录中,则将前一个替换
if(tables.get(key).tableName.equals(name)){
this.tables.remove(key);
break;
}
}
Table t = new Table(name, pkeyField, file);
this.tables.put(file.getId(), t);
}
public void addTable(DbFile file, String name) {
addTable(file, name, "");
}
/**
* Add a new table to the catalog.
* This table has tuples formatted using the specified TupleDesc and its
* contents are stored in the specified DbFile.
* @param file the contents of the table to add; file.getId() is the identfier of
* this file/tupledesc param for the calls getTupleDesc and getFile
*/
public void addTable(DbFile file) {
addTable(file, (UUID.randomUUID()).toString());
}
/**
* Return the id of the table with a specified name,
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the table doesn't exist
*/
public int getTableId(String name) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
Set<Integer> keys = tables.keySet();
for (Integer key : keys) {
if(tables.get(key).tableName.equals(name)){
return key;
}
}
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到名为: %s的表", name));
}
/**
* Returns the tuple descriptor (schema) of the specified table
* @param tableid The id of the table, as specified by the DbFile.getId()
* function passed to addTable
* @throws NoSuchElementException if the table doesn't exist
*/
public TupleDesc getTupleDesc(int tableid) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
if(!tables.containsKey(tableid))
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到tableID为:%d的表", tableid));
return tables.get(tableid).dbFile.getTupleDesc();
}
/**
* Returns the DbFile that can be used to read the contents of the
* specified table.
* @param tableid The id of the table, as specified by the DbFile.getId()
* function passed to addTable
*/
public DbFile getDatabaseFile(int tableid) throws NoSuchElementException {
// some code goes here
if(!tables.containsKey(tableid))
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到tableID为:%d的表", tableid));
return tables.get(tableid).dbFile;
}
public String getPrimaryKey(int tableid) {
// some code goes here
if(!tables.containsKey(tableid))
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到tableID为:%d的表", tableid));
return tables.get(tableid).pkeyField;
}
public Iterator<Integer> tableIdIterator() {
// some code goes here
return tables.keySet().iterator();
}
public String getTableName(int id) {
// some code goes here
if(!tables.containsKey(id))
throw new NoSuchElementException(String.format("没有找到id为:%d的表", id));
return tables.get(id).tableName;
}
/** Delete all tables from the catalog */
public void clear() {
// some code goes here
this.tables.clear();
}
/**
* Reads the schema from a file and creates the appropriate tables in the database.
* @param catalogFile
*/
public void loadSchema(String catalogFile) {
String line = "";
String baseFolder=new File(new File(catalogFile).getAbsolutePath()).getParent();
try {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(new File(catalogFile)));
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
//assume line is of the format name (field type, field type, ...)
String name = line.substring(0, line.indexOf("(")).trim();
//System.out.println("TABLE NAME: " + name);
String fields = line.substring(line.indexOf("(") + 1, line.indexOf(")")).trim();
String[] els = fields.split(",");
ArrayList<String> names = new ArrayList<String>();
ArrayList<Type> types = new ArrayList<Type>();
String primaryKey = "";
for (String e : els) {
String[] els2 = e.trim().split(" ");
names.add(els2[0].trim());
if (els2[1].trim().toLowerCase().equals("int"))
types.add(Type.INT_TYPE);
else if (els2[1].trim().toLowerCase().equals("string"))
types.add(Type.STRING_TYPE);
else {
System.out.println("Unknown type " + els2[1]);
System.exit(0);
}
if (els2.length == 3) {
if (els2[2].trim().equals("pk"))
primaryKey = els2[0].trim();
else {
System.out.println("Unknown annotation " + els2[2]);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
Type[] typeAr = types.toArray(new Type[0]);
String[] namesAr = names.toArray(new String[0]);
TupleDesc t = new TupleDesc(typeAr, namesAr);
HeapFile tabHf = new HeapFile(new File(baseFolder+"/"+name + ".dat"), t);
addTable(tabHf,name,primaryKey);
System.out.println("Added table : " + name + " with schema " + t);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.exit(0);
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
System.out.println ("Invalid catalog entry : " + line);
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
顺利通过测试:
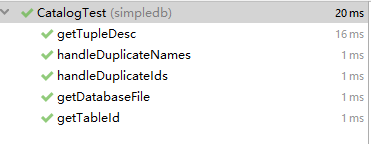
4 EX3 Buffer Pool
2020/10/23
缓冲池,存储最近访问的页。
用来加快访问速度。读磁盘速度较慢,所以将部分页缓存至内存。一个缓冲池中,最多拥有numPages的页,在lab1中,超过该限制,则抛出异常,之后会实现过期淘汰策略。
lab1
只需要完成getPage()函数,并且不需要完成锁、事务、淘汰机制等。在seqscan的时候会涉及到该函数。根据要求,每次查找一个页
- 如果查到则返回
- 如果没有查到,但是有空间,则插入缓冲池,并返回
- 如果没有查到,且缓冲池没有空间,则直接抛出异常 (后续实现淘汰策略)
public class BufferPool {
/** Bytes per page, including header. */
private static final int DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE = 4096;
private static int pageSize = DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE;
// 注意到线程安全问题,仍选用ConcurrentHashMap
private ConcurrentHashMap<PageId, Page> pages;
/** Default number of pages passed to the constructor. This is used by
other classes. BufferPool should use the numPages argument to the
constructor instead. */
public static final int DEFAULT_PAGES = 50;
private final int maxPages;
/**
* Creates a BufferPool that caches up to numPages pages.
*
* @param numPages maximum number of pages in this buffer pool.
*/
public BufferPool(int numPages) {
// some code goes here
pages = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
maxPages = numPages;
}
public static int getPageSize() {
return pageSize;
}
// THIS FUNCTION SHOULD ONLY BE USED FOR TESTING!!
public static void setPageSize(int pageSize) {
BufferPool.pageSize = pageSize;
}
// THIS FUNCTION SHOULD ONLY BE USED FOR TESTING!!
public static void resetPageSize() {
BufferPool.pageSize = DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE;
}
/**
* Retrieve the specified page with the associated permissions.
* Will acquire a lock and may block if that lock is held by another
* transaction.
* <p>
* @param tid the ID of the transaction requesting the page
* @param pid the ID of the requested page
* @param perm the requested permissions on the page
*/
public Page getPage(TransactionId tid, PageId pid, Permissions perm)
throws TransactionAbortedException, DbException {
// some code goes here
if(!pages.containsKey(pid))
return pages.get(pid);
if(pages.size() >= maxPages)
throw new DbException("lab1--缓冲池空间不足");
Page page = Database.getCatalog().getDatabaseFile(pid.getTableId()).readPage(pid);
pages.put(pid, page);
return page;
}
}
5 EX4 HeapFile Access Method
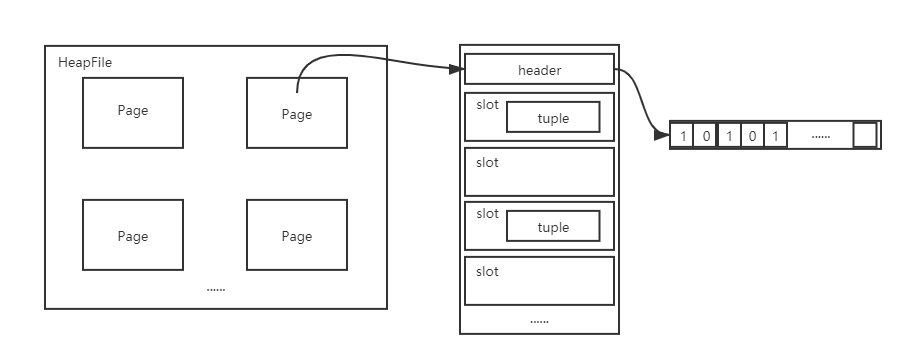
如图所示,每个HeapFile中存储多个Page, 每个Page由header + slots组成。其中,header是一个二进制的数,其每一位代表了对应的slot中是否存在一个tuple。
因此,每个page最多存储的tuple也很容易计算了:floor(PageSize * 8 / (TupleSize * 8 + 1))
该部分代码如下:
// HeapPage.java
package simpledb;
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
/**
* Each instance of HeapPage stores data for one page of HeapFiles and
* implements the Page interface that is used by BufferPool.
*
* @see HeapFile
* @see BufferPool
*
*/
public class HeapPage implements Page {
final HeapPageId pid;
final TupleDesc td;
final byte header[];
final Tuple tuples[];
final int numSlots;
byte[] oldData;
private final Byte oldDataLock=new Byte((byte)0);
/**
* Create a HeapPage from a set of bytes of data read from disk.
* The format of a HeapPage is a set of header bytes indicating
* the slots of the page that are in use, some number of tuple slots.
* Specifically, the number of tuples is equal to: <p>
* floor((BufferPool.getPageSize()*8) / (tuple size * 8 + 1))
* <p> where tuple size is the size of tuples in this
* database table, which can be determined via {@link Catalog#getTupleDesc}.
* The number of 8-bit header words is equal to:
* <p>
* ceiling(no. tuple slots / 8)
* <p>
* @see Database#getCatalog
* @see Catalog#getTupleDesc
* @see BufferPool#getPageSize()
*/
public HeapPage(HeapPageId id, byte[] data) throws IOException {
this.pid = id;
this.td = Database.getCatalog().getTupleDesc(id.getTableId());
this.numSlots = getNumTuples();
DataInputStream dis = new DataInputStream(new ByteArrayInputStream(data));
// allocate and read the header slots of this page
header = new byte[getHeaderSize()];
for (int i=0; i<header.length; i++)
header[i] = dis.readByte();
tuples = new Tuple[numSlots];
try{
// allocate and read the actual records of this page
for (int i=0; i<tuples.length; i++)
tuples[i] = readNextTuple(dis,i);
}catch(NoSuchElementException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
dis.close();
setBeforeImage();
}
/** Retrieve the number of tuples on this page.
@return the number of tuples on this page
*/
private int getNumTuples() {
// some code goes here
int tupleSize = Database.getCatalog().getTupleDesc(pid.getTableId()).getSize();
int pageSize = Database.getBufferPool().getPageSize();
return (int) Math.floor((pageSize * 8)/(tupleSize * 8 +1));
}
/**
* Computes the number of bytes in the header of a page in a HeapFile with each tuple occupying tupleSize bytes
* @return the number of bytes in the header of a page in a HeapFile with each tuple occupying tupleSize bytes
*/
private int getHeaderSize() {
// some code goes here
return (int) Math.ceil(getNumTuples()/8.0);
}
/** Return a view of this page before it was modified
-- used by recovery */
public HeapPage getBeforeImage(){
try {
byte[] oldDataRef = null;
synchronized(oldDataLock)
{
oldDataRef = oldData;
}
return new HeapPage(pid,oldDataRef);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
//should never happen -- we parsed it OK before!
System.exit(1);
}
return null;
}
public void setBeforeImage() {
synchronized(oldDataLock)
{
oldData = getPageData().clone();
}
}
/**
* @return the PageId associated with this page.
*/
public HeapPageId getId() {
// some code goes here
return this.pid;
}
/**
* Suck up tuples from the source file.
*/
private Tuple readNextTuple(DataInputStream dis, int slotId) throws NoSuchElementException {
// if associated bit is not set, read forward to the next tuple, and
// return null.
if (!isSlotUsed(slotId)) {
for (int i=0; i<td.getSize(); i++) {
try {
dis.readByte();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new NoSuchElementException("error reading empty tuple");
}
}
return null;
}
// read fields in the tuple
Tuple t = new Tuple(td);
RecordId rid = new RecordId(pid, slotId);
t.setRecordId(rid);
try {
for (int j=0; j<td.numFields(); j++) {
Field f = td.getFieldType(j).parse(dis);
t.setField(j, f);
}
} catch (java.text.ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
throw new NoSuchElementException("parsing error!");
}
return t;
}
/**
* Generates a byte array representing the contents of this page.
* Used to serialize this page to disk.
* <p>
* The invariant here is that it should be possible to pass the byte
* array generated by getPageData to the HeapPage constructor and
* have it produce an identical HeapPage object.
*
* @see #HeapPage
* @return A byte array correspond to the bytes of this page.
*/
public byte[] getPageData() {
int len = BufferPool.getPageSize();
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(len);
DataOutputStream dos = new DataOutputStream(baos);
// create the header of the page
for (int i=0; i<header.length; i++) {
try {
dos.writeByte(header[i]);
} catch (IOException e) {
// this really shouldn't happen
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// create the tuples
for (int i=0; i<tuples.length; i++) {
// empty slot
if (!isSlotUsed(i)) {
for (int j=0; j<td.getSize(); j++) {
try {
dos.writeByte(0);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
continue;
}
// non-empty slot
for (int j=0; j<td.numFields(); j++) {
Field f = tuples[i].getField(j);
try {
f.serialize(dos);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
// padding
int zerolen = BufferPool.getPageSize() - (header.length + td.getSize() * tuples.length); //- numSlots * td.getSize();
byte[] zeroes = new byte[zerolen];
try {
dos.write(zeroes, 0, zerolen);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
dos.flush();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return baos.toByteArray();
}
/**
* Static method to generate a byte array corresponding to an empty
* HeapPage.
* Used to add new, empty pages to the file. Passing the results of
* this method to the HeapPage constructor will create a HeapPage with
* no valid tuples in it.
*
* @return The returned ByteArray.
*/
public static byte[] createEmptyPageData() {
int len = BufferPool.getPageSize();
return new byte[len]; //all 0
}
/**
* Delete the specified tuple from the page; the corresponding header bit should be updated to reflect
* that it is no longer stored on any page.
* @throws DbException if this tuple is not on this page, or tuple slot is
* already empty.
* @param t The tuple to delete
*/
public void deleteTuple(Tuple t) throws DbException {
// some code goes here
// not necessary for lab1
}
/**
* Adds the specified tuple to the page; the tuple should be updated to reflect
* that it is now stored on this page.
* @throws DbException if the page is full (no empty slots) or tupledesc
* is mismatch.
* @param t The tuple to add.
*/
public void insertTuple(Tuple t) throws DbException {
// some code goes here
// not necessary for lab1
}
/**
* Marks this page as dirty/not dirty and record that transaction
* that did the dirtying
*/
public void markDirty(boolean dirty, TransactionId tid) {
// some code goes here
// not necessary for lab1
}
/**
* Returns the tid of the transaction that last dirtied this page, or null if the page is not dirty
*/
public TransactionId isDirty() {
// some code goes here
// Not necessary for lab1
return null;
}
/**
* Returns the number of empty slots on this page.
*/
public int getNumEmptySlots() {
// some code goes here
int n = getNumTuples();
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0;i < n; i++){
if(!isSlotUsed(i))
res++;
}
return res;
}
/**
* Returns true if associated slot on this page is filled.
*/
public boolean isSlotUsed(int i) {
// some code goes here
int c = i % 8;
int s = i / 8;
return ((header[s] >> c ) & 1) == 1;
}
/**
* Abstraction to fill or clear a slot on this page.
*/
private void markSlotUsed(int i, boolean value) {
// some code goes here
// not necessary for lab1
}
/**
* @return an iterator over all tuples on this page (calling remove on this iterator throws an UnsupportedOperationException)
* (note that this iterator shouldn't return tuples in empty slots!)
*/
public Iterator<Tuple> iterator() {
// some code goes here
List<Tuple> tupleList = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i = 0; i < getNumTuples(); i++) {
if(isSlotUsed(i)){
tupleList.add(tuples[i]);
}
}
return tupleList.iterator();
}
}
// HeapPageId.java
package simpledb;
import simpledb.utils.CompHashCode;
/** Unique identifier for HeapPage objects. */
public class HeapPageId implements PageId {
private int tableId;
private int pgNo;
/**
* Constructor. Create a page id structure for a specific page of a
* specific table.
*
* @param tableId The table that is being referenced
* @param pgNo The page number in that table.
*/
public HeapPageId(int tableId, int pgNo) {
// some code goes here
this.tableId = tableId;
this.pgNo = pgNo;
}
/** @return the table associated with this PageId */
public int getTableId() {
// some code goes here
return tableId;
}
/**
* @return the page number in the table getTableId() associated with
* this PageId
*/
public int getPageNumber() {
// some code goes here
return pgNo;
}
/**
* @return a hash code for this page, represented by the concatenation of
* the table number and the page number (needed if a PageId is used as a
* key in a hash table in the BufferPool, for example.)
* @see BufferPool
*/
public int hashCode() {
// some code goes here
return CompHashCode.compute(HeapPageId.class, this);
}
/**
* Compares one PageId to another.
*
* @param o The object to compare against (must be a PageId)
* @return true if the objects are equal (e.g., page numbers and table
* ids are the same)
*/
public boolean equals(Object o) {
// some code goes here
if( o == null) {
return false;
}
if(o.getClass() != HeapPageId.class)
return false;
HeapPageId heapPageId = (HeapPageId) o;
return (heapPageId.pgNo == this.pgNo && heapPageId.tableId == this.tableId);
}
/**
* Return a representation of this object as an array of
* integers, for writing to disk. Size of returned array must contain
* number of integers that corresponds to number of args to one of the
* constructors.
*/
public int[] serialize() {
int data[] = new int[2];
data[0] = getTableId();
data[1] = getPageNumber();
return data;
}
}
// RecordID.java
package simpledb;
import simpledb.utils.CompHashCode;
import java.io.Serializable;
/**
* A RecordId is a reference to a specific tuple on a specific page of a
* specific table.
*/
public class RecordId implements Serializable {
private PageId pid;
private int tupleno;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L;
/**
* Creates a new RecordId referring to the specified PageId and tuple
* number.
*
* @param pid
* the pageid of the page on which the tuple resides
* @param tupleno
* the tuple number within the page.
*/
public RecordId(PageId pid, int tupleno) {
// some code goes here
this.pid = pid;
this.tupleno = tupleno;
}
/**
* @return the tuple number this RecordId references.
*/
public int getTupleNumber() {
// some code goes here
return this.tupleno;
}
/**
* @return the page id this RecordId references.
*/
public PageId getPageId() {
// some code goes here
return this.pid;
}
/**
* Two RecordId objects are considered equal if they represent the same
* tuple.
*
* @return True if this and o represent the same tuple
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
// some code goes here
if(o == null) return false;
if(o.getClass() != RecordId.class) return false;
RecordId rid = (RecordId) o;
return rid.pid.equals(this.pid) && rid.tupleno == this.tupleno;
}
/**
* You should implement the hashCode() so that two equal RecordId instances
* (with respect to equals()) have the same hashCode().
*
* @return An int that is the same for equal RecordId objects.
*/
@Override
public int hashCode() {
// some code goes here
return CompHashCode.compute(RecordId.class, this);
}
}
另外,由于计算hashCode的方法大同小异,故统一成了一个工具类,代码如下:
package simpledb.utils;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
public class CompHashCode {
public static int compute(Class<?> aClass, Object o) {
Field[] fields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
int res = 17;
for (Field field : fields) {
if(field.getType() == int.class
|| field.getType() == byte.class
|| field.getType() == char.class
|| field.getType() == short.class) {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
res = res * 37 + (int)(field.get(o));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
else if(field.getType() == double.class) {
long tmp = 0;
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
tmp = Double.doubleToLongBits(field.getDouble(o));
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int c = (int)(tmp ^ (tmp >>> 32));
res = res * 37 + c;
}
else if(field.getType() == boolean.class) {
int c = 0;
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
c = field.getBoolean(o) ? 1:0;
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
res = res * 37 + c;
} else {
try {
field.setAccessible(true);
res = res * 37 + field.get(o).hashCode();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
运行结果:
- TupleTest
- RecordIdTest
- HeapPageIdTest
- HeapPageReadTest
最后
以上就是朴素硬币最近收集整理的关于SimpleDB开发环境搭建及Lab1_Exercise 1-4SimpleDB lab1 Ex1 ~ Ex4的全部内容,更多相关SimpleDB开发环境搭建及Lab1_Exercise内容请搜索靠谱客的其他文章。








发表评论 取消回复